Energy and Forms of Energy, Energy Transformation
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
potential energy
stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object
the energy that an object has because of the position, shape, or condition of the object

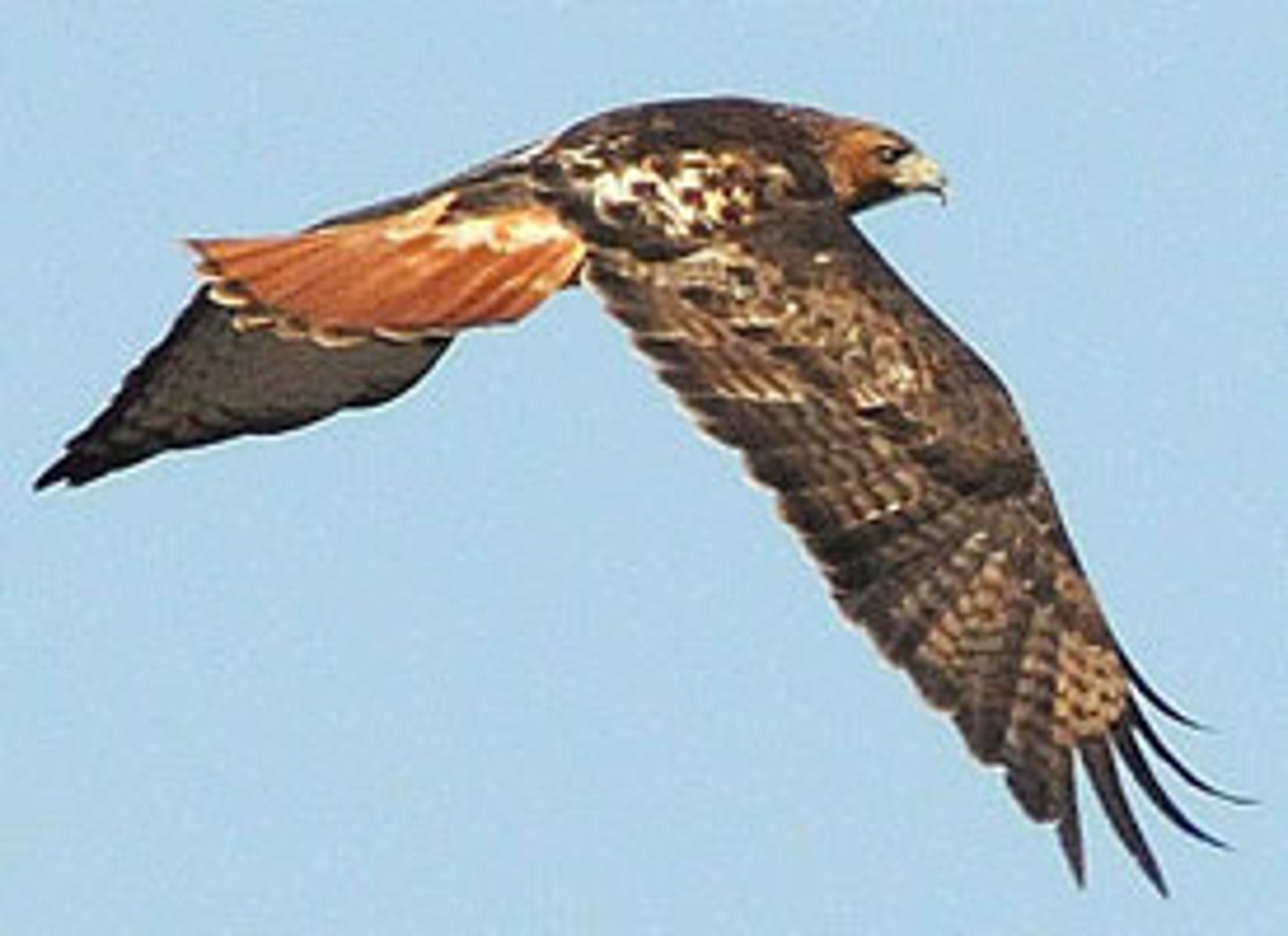
kinetic energy
the energy of motion

work
the transfer of energy that occurs when a force is applied over a distance

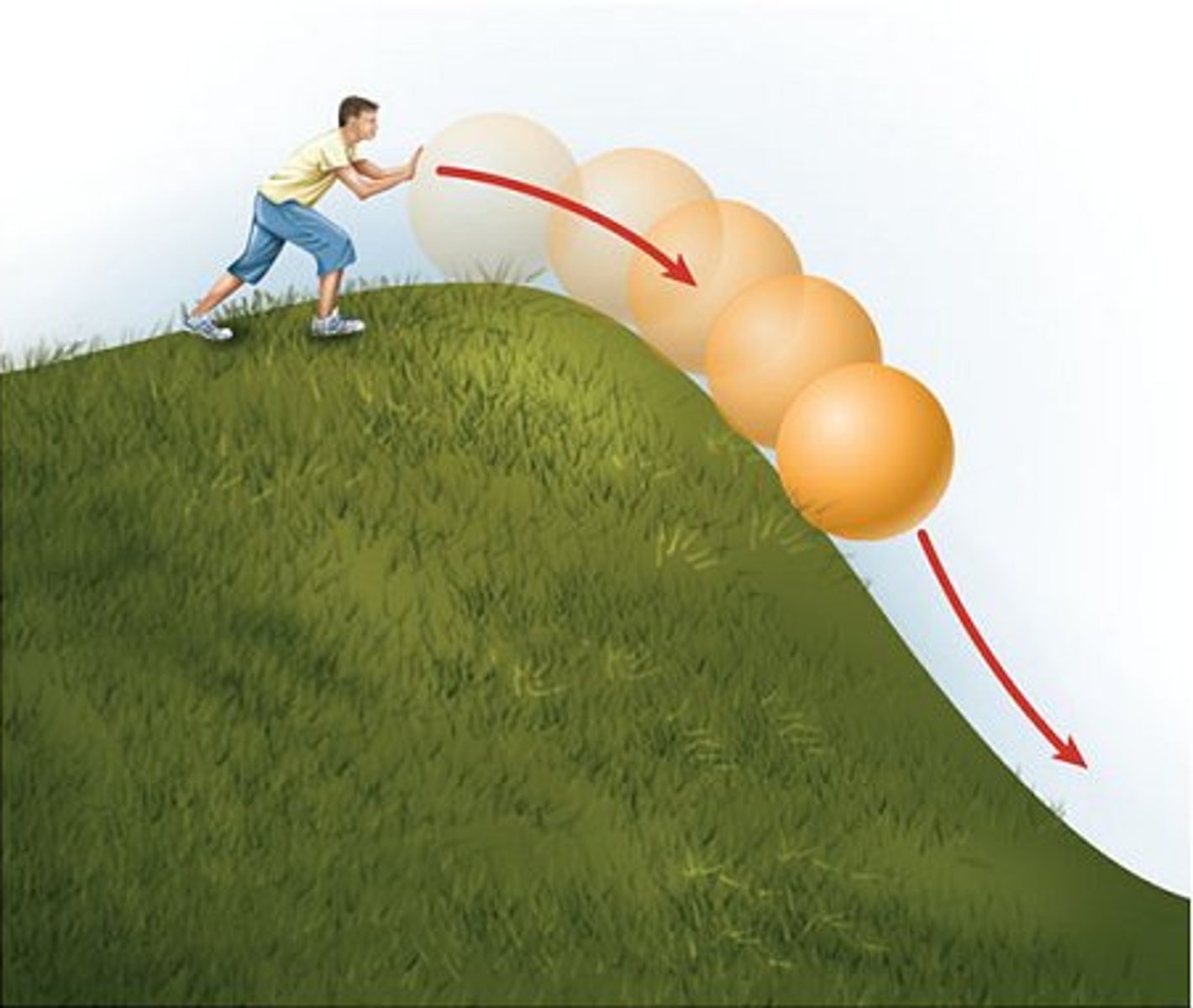
elastic potential energy
the energy of stretched or compressed objects
gravitational potential energy
Potential energy that depends on the height of an object

mechanical energy
The energy associated with the motion and position of everyday objects. Formula is potential energy + kinetic energy.
thermal energy
The total energy of motion in the particles of a substance

electrical energy
Energy caused by the movement of electrons.
The energy of electric charges

chemical energy
Potential energy stored in chemical bonds

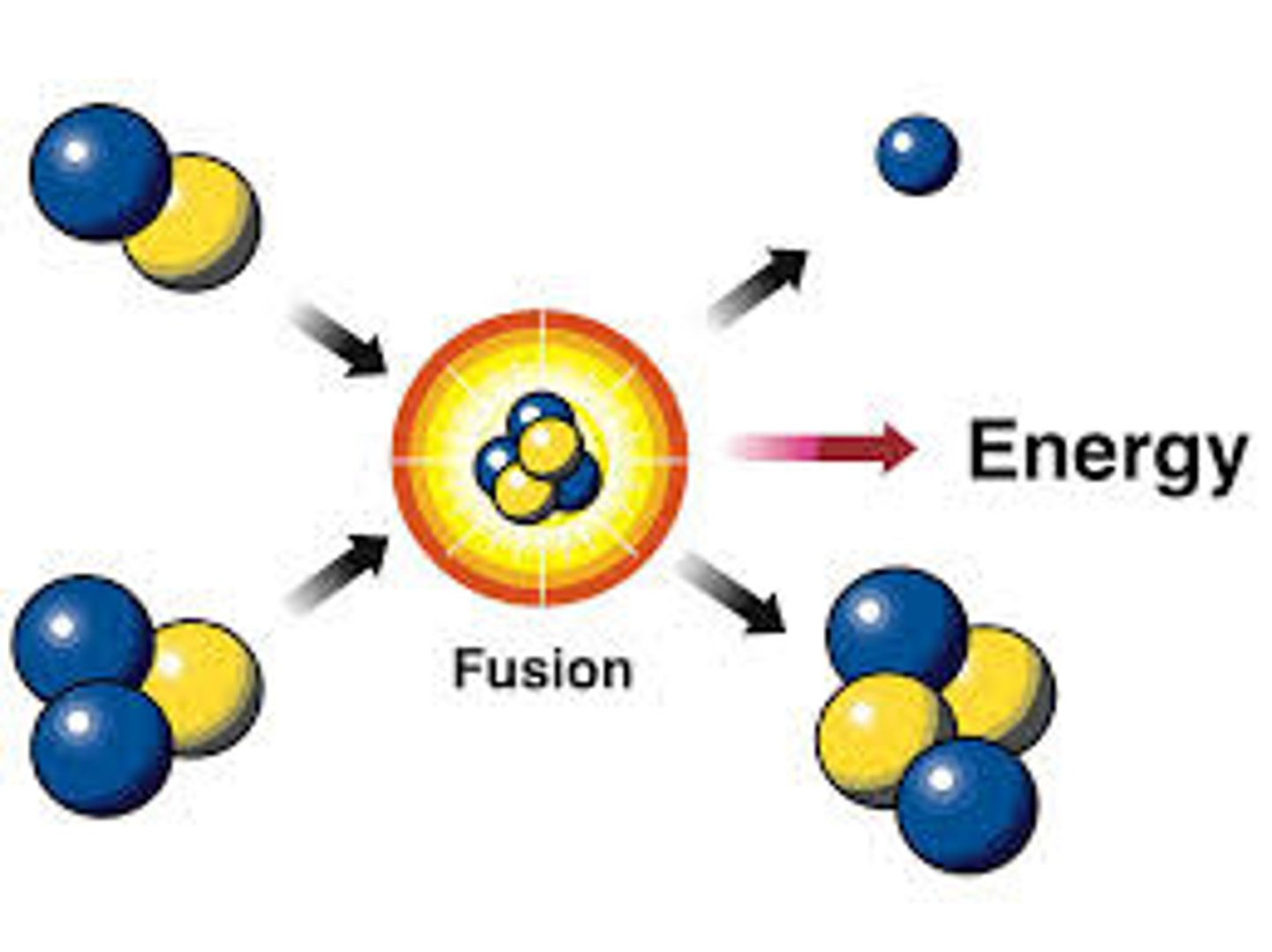
nuclear energy
Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom
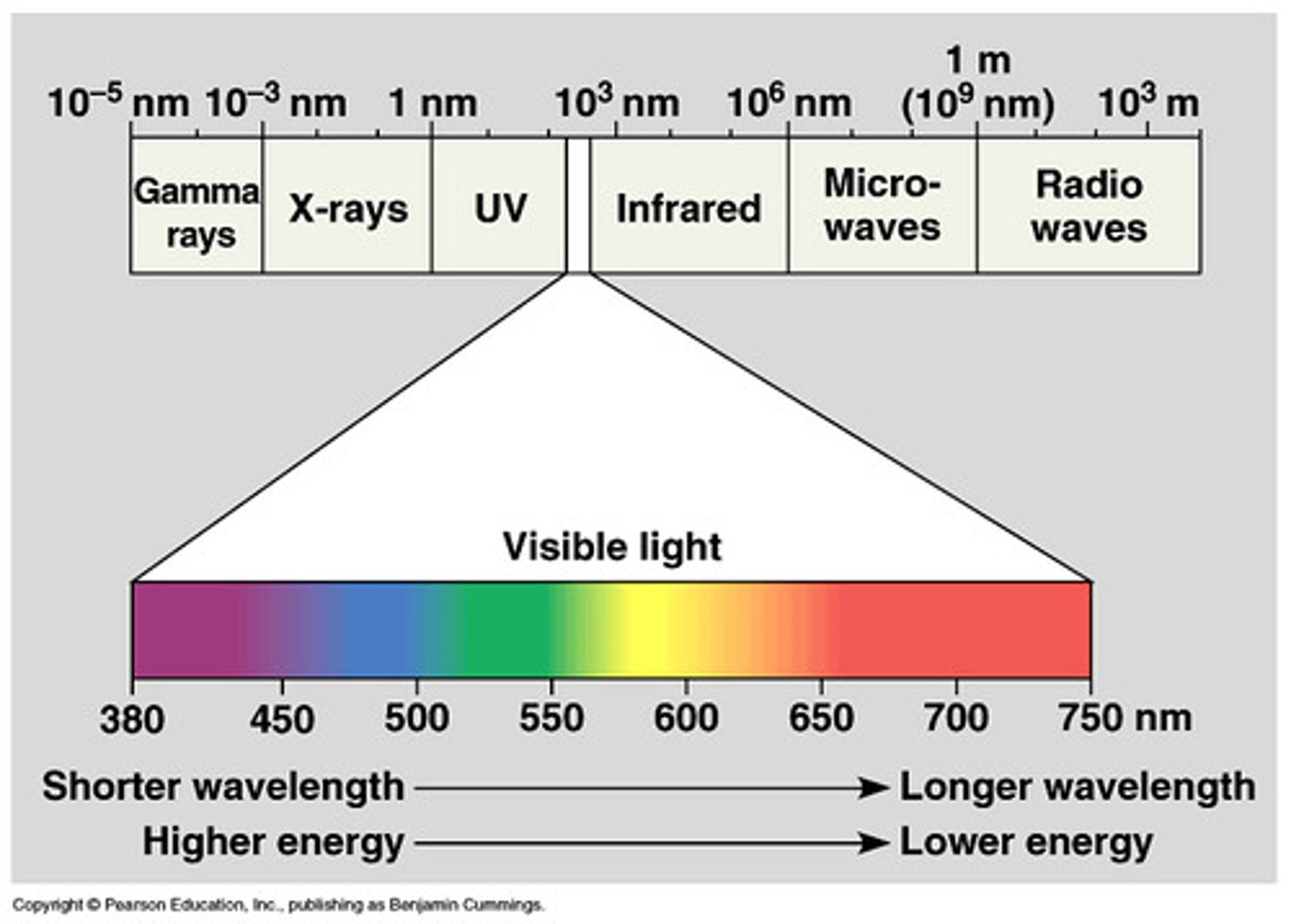
electromagnetic energy
A form of energy that travels through space as waves.
The energy of light and other forms of radiation.
sound energy
Energy caused by an object's vibrations.
Energy of vibrations carried by air, water, or other matter.

example of mechanical energy
A football thrown by a quarterback, riding a bicycle, or kicking a soccer ball.
example of thermal energy
ice cream melting on a hot day, hot springs, campfire, or cup of hot tea.

example of electrical energy
a shock from a metal doorknob, lightning, batteries in use, or static
example of chemical energy
energy stored in a match, gasoline, foods you eat, or cells in your body.
example of nuclear energy
nuclear fusion in sun, nuclear power plants use fission
examples of electromagnetic
The sunlight, microwaves, and x-rays.
examples of sound energy
clapping, snapping fingers, singing, or anyone's voice.
energy
the ability to do work or cause change
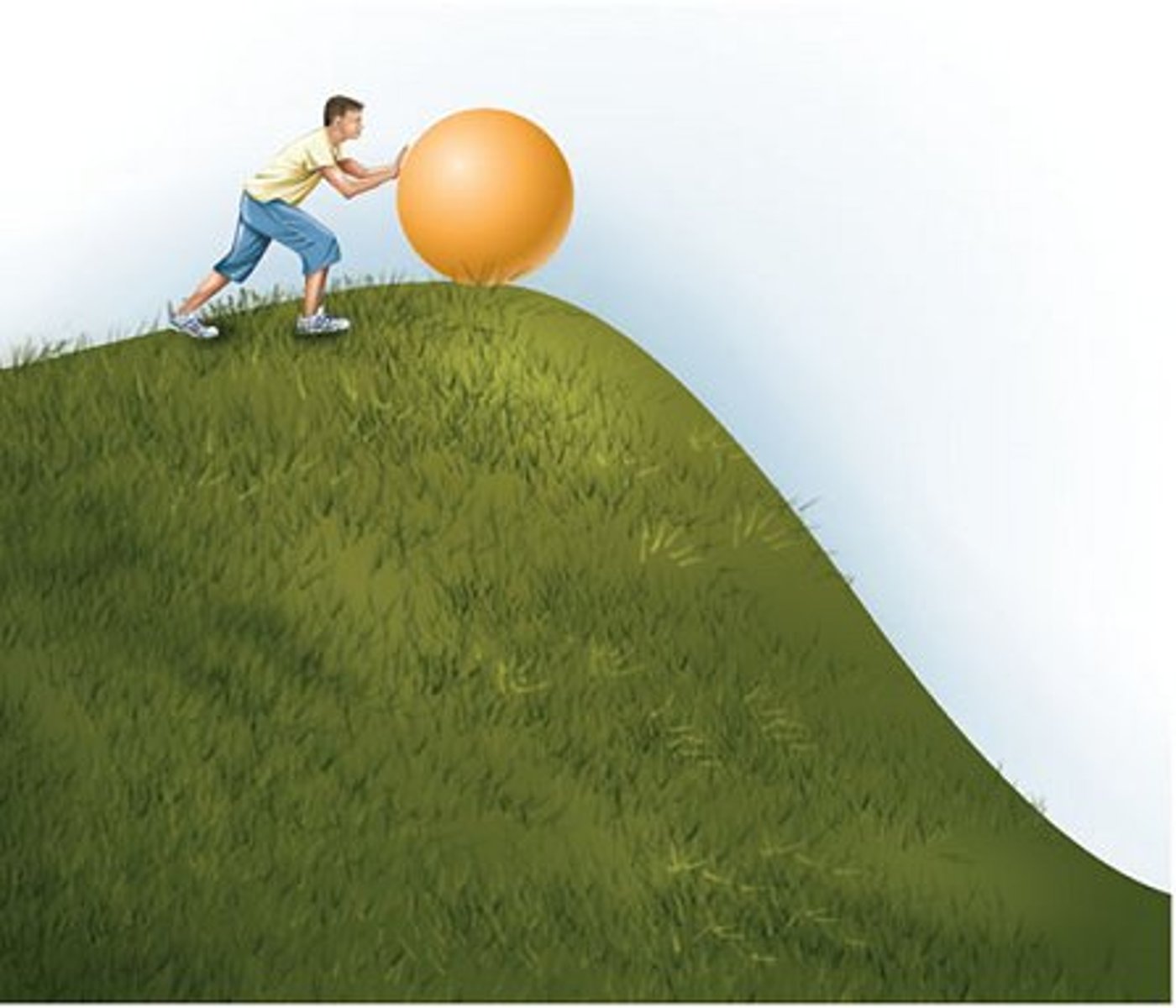

When you stretch a rubber band, you give it
elastic potential energy
According to the _____________________________________________________, energy can not be destroyed or created.
law of conservation of energy
energy transformation (steam iron)
electric energy to thermal energy
energy transformation (sun to plants)
electromagnetic energy to chemical energy
Joules
SI unit for energy
energy transformation (wood burning)
chemical energy to thermal & radiant energy
two types of potential energy
gravitational and elastic
Most common energy transformations is between
kinetic and potential energy
forms of energy
electric, mechanical, nuclear, thermal, electromagnetic, sound, and chemical
energy transformation (sun to plants to animal eating plants and running)
electromagnetic to chemical to mechanical
energy transformation
a change from one form of energy to another
matter
anything that has mass and takes up space (volume)
In waterfalls such as Niagra Falls,
potential energy is transformed to kinetic energy.
When potential energy increases,
kinetic energy decreases.
When kinetic energy increases,
potential energy decreases.
solar to light and heat energy
mechanical to sound
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy can't be created or destroyed, only changed
Energy transformation
A change from one form of energy to another
Heat energy
thermal energy
energy
Ability to do work
energy transfer
The passing or movement of one form of energy to another
potential energy

kinetic energy

light and heat
two forms of energy a light bulb releases

chemical to sound

mechanical to electrical

electrical to mechanical
chemical to thermal

mechanical to mechanical

solar to electrical
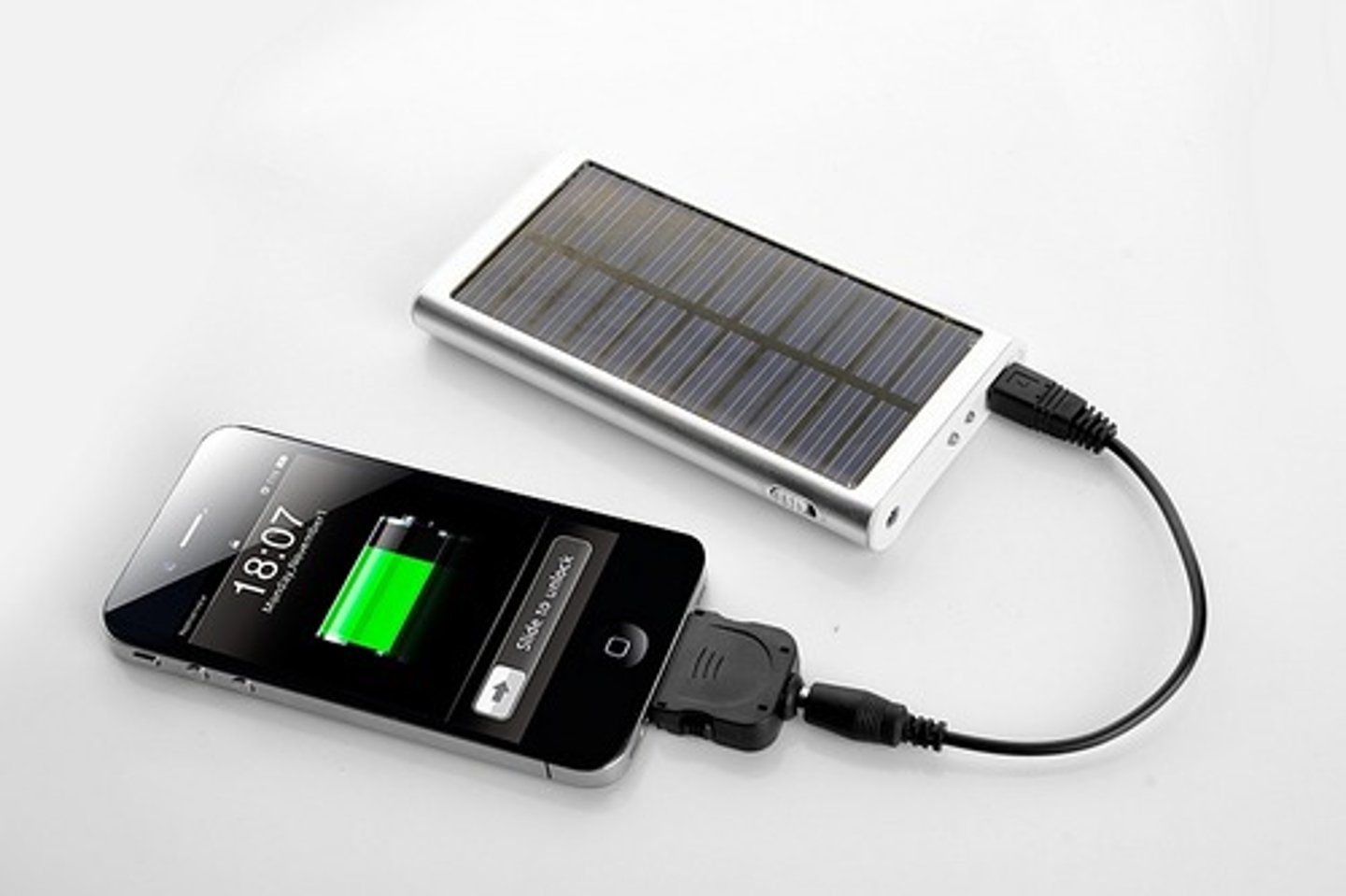

solar to chemical
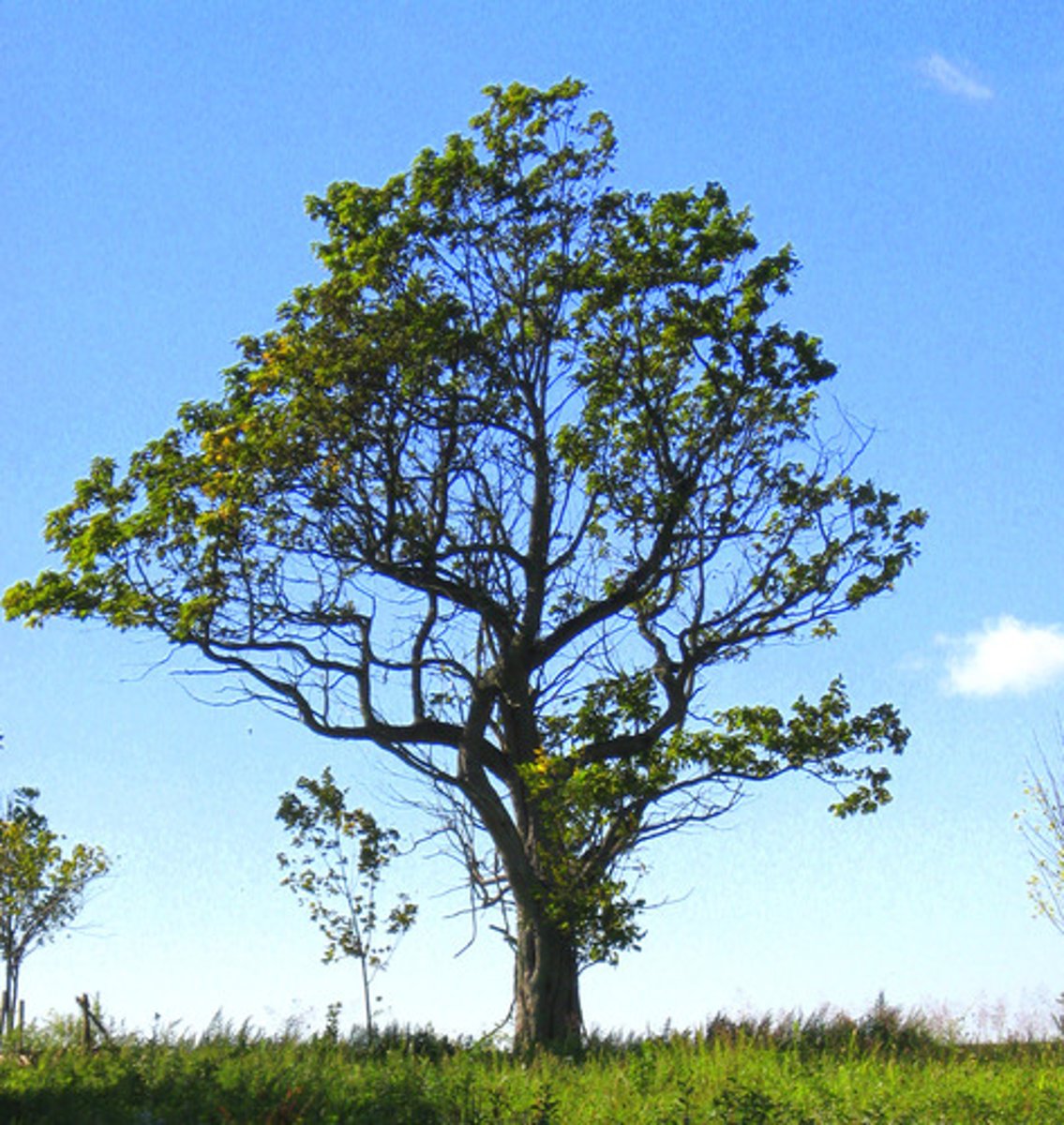

chemical to mechanical
chemical to electrical to light
battery powered laptop
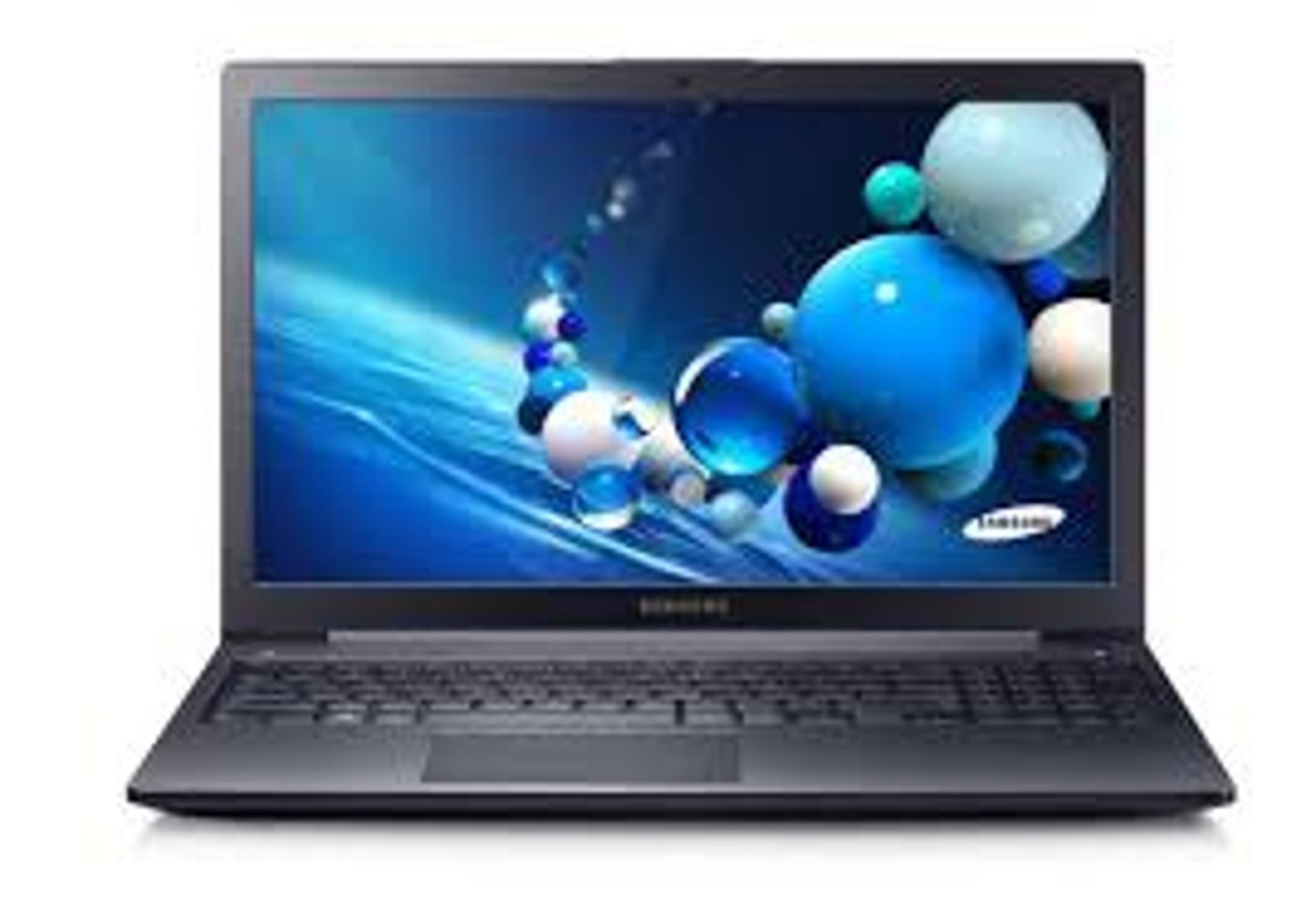

electrical to heat
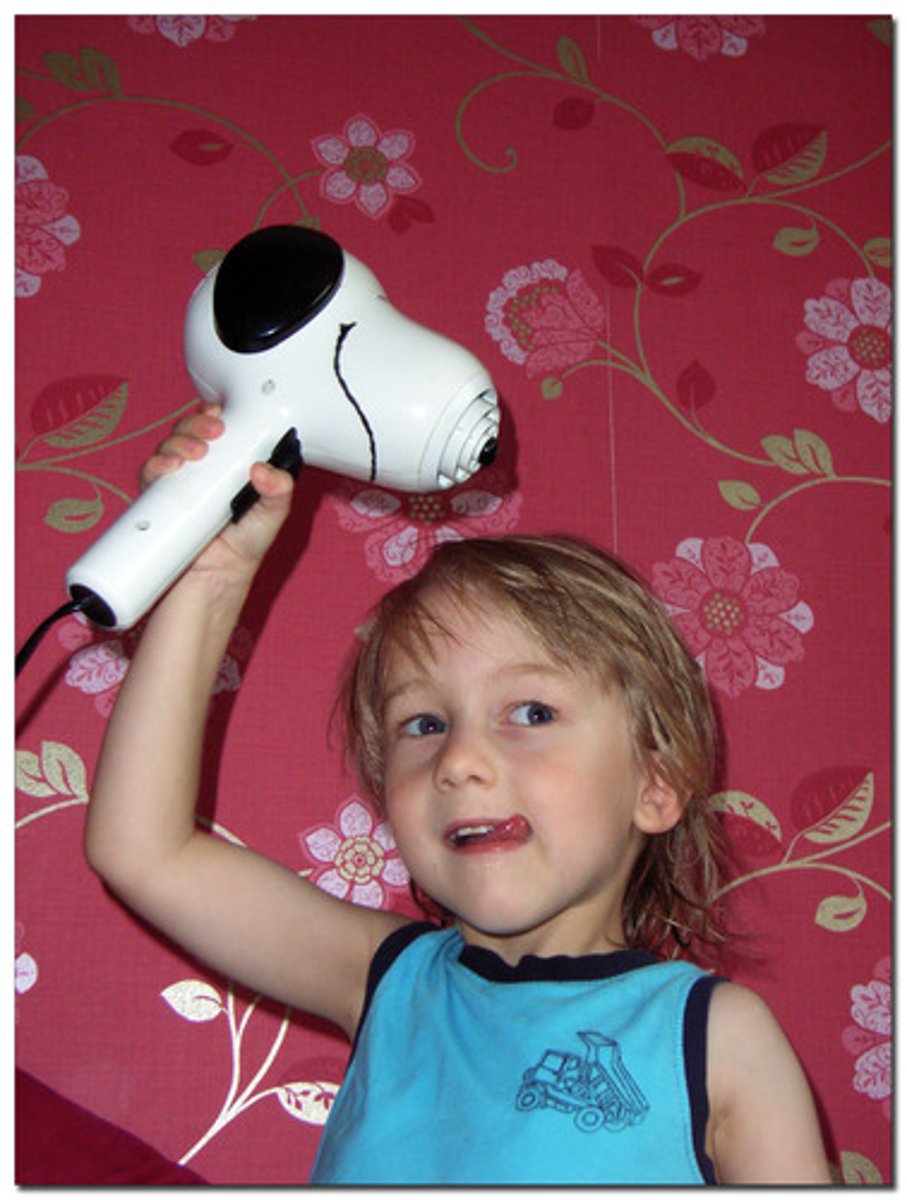

chemical to mechanical to chemical
cow eating grass and producing milk
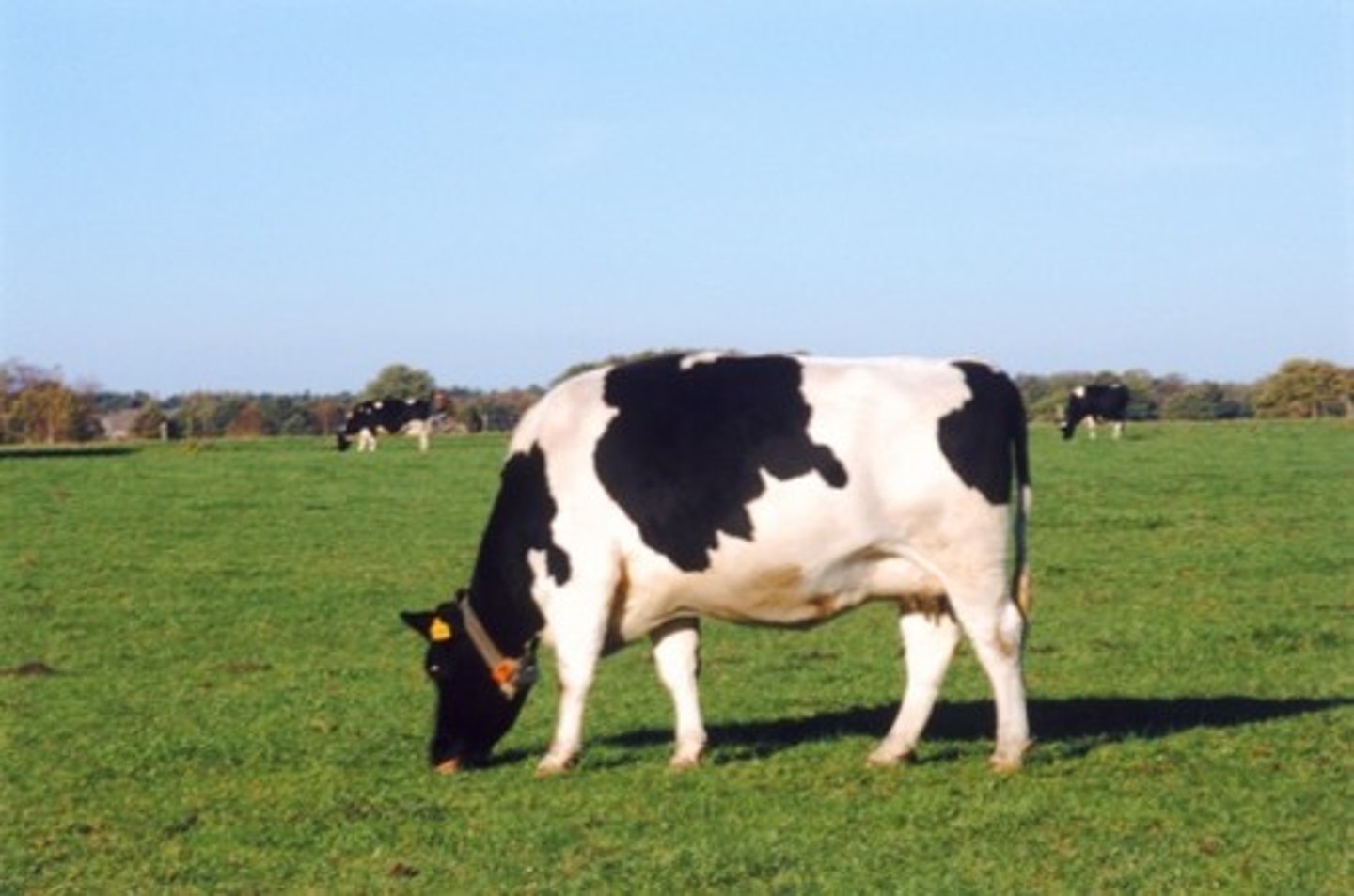

electrical to thermal
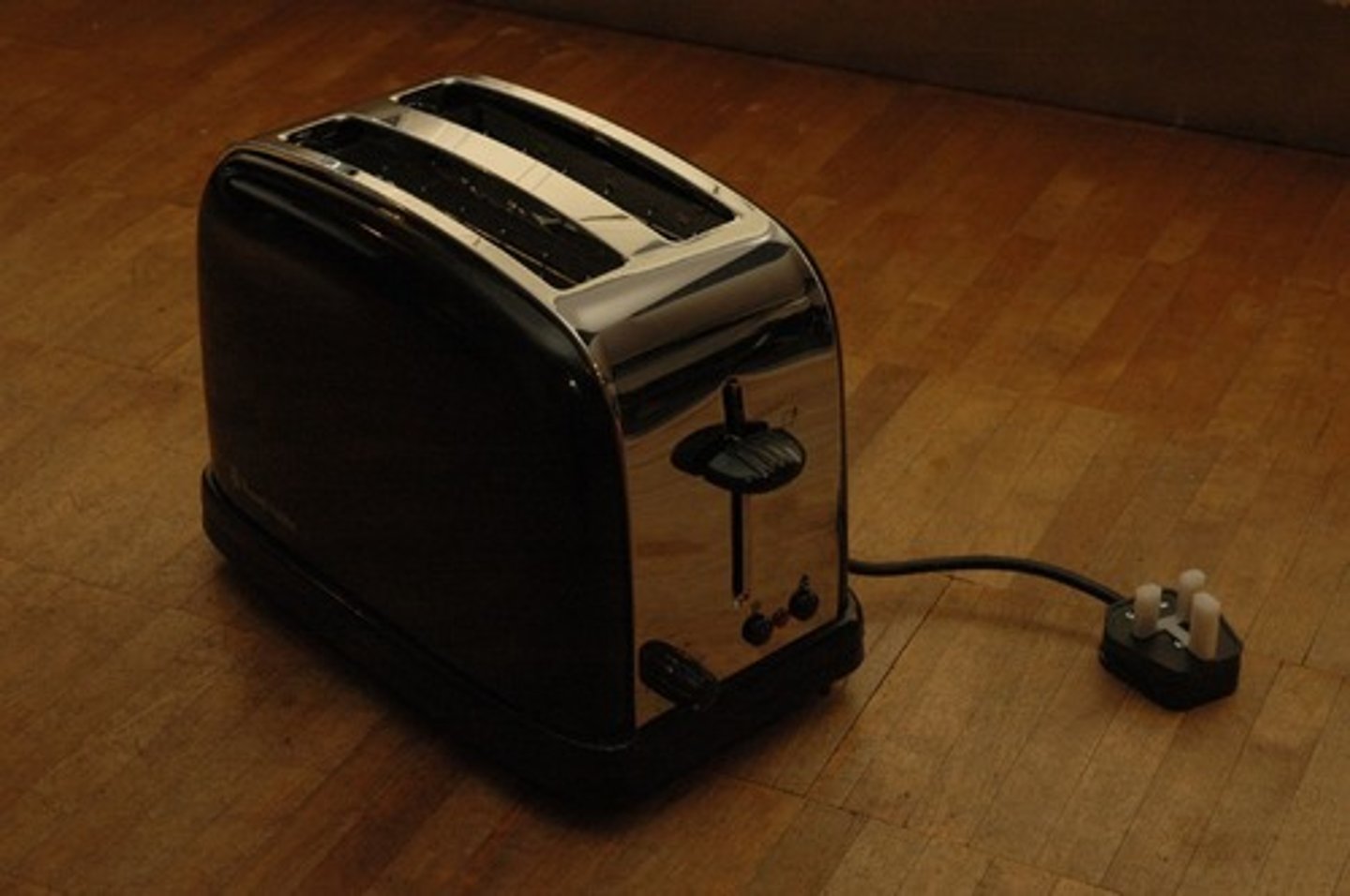

electrical to light to thermal

electrical to thermal
plugging hot plate
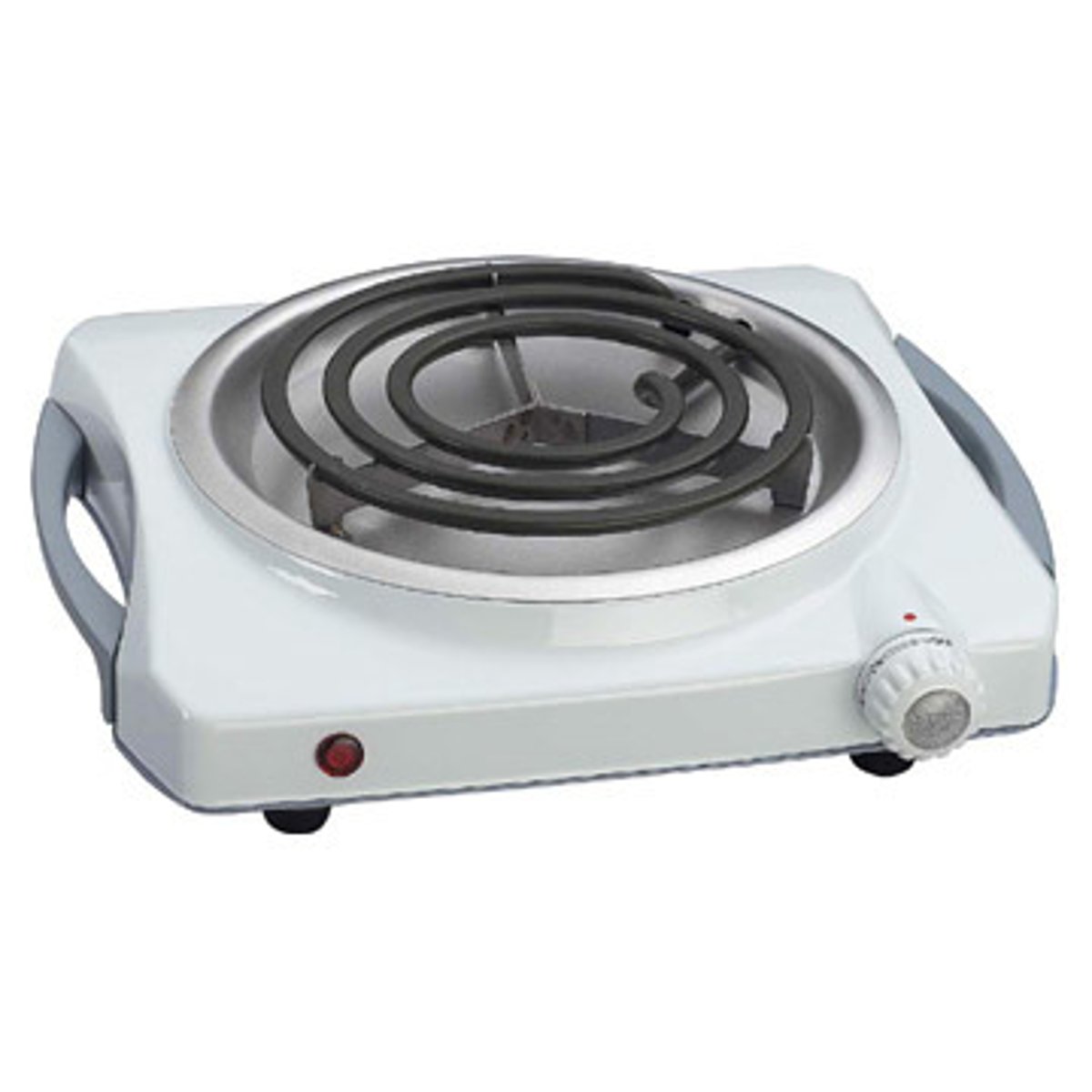

chemical to mechanical
hawk eats mouse and uses energy to fly
