unit 3 anatomy - spinal cord and spinal nerves
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
spinal cord segments / conus medullaris
end of spinal cord, L1 and L2
cauda equina (horses tail)
bundle of nerve roots, L2-S5
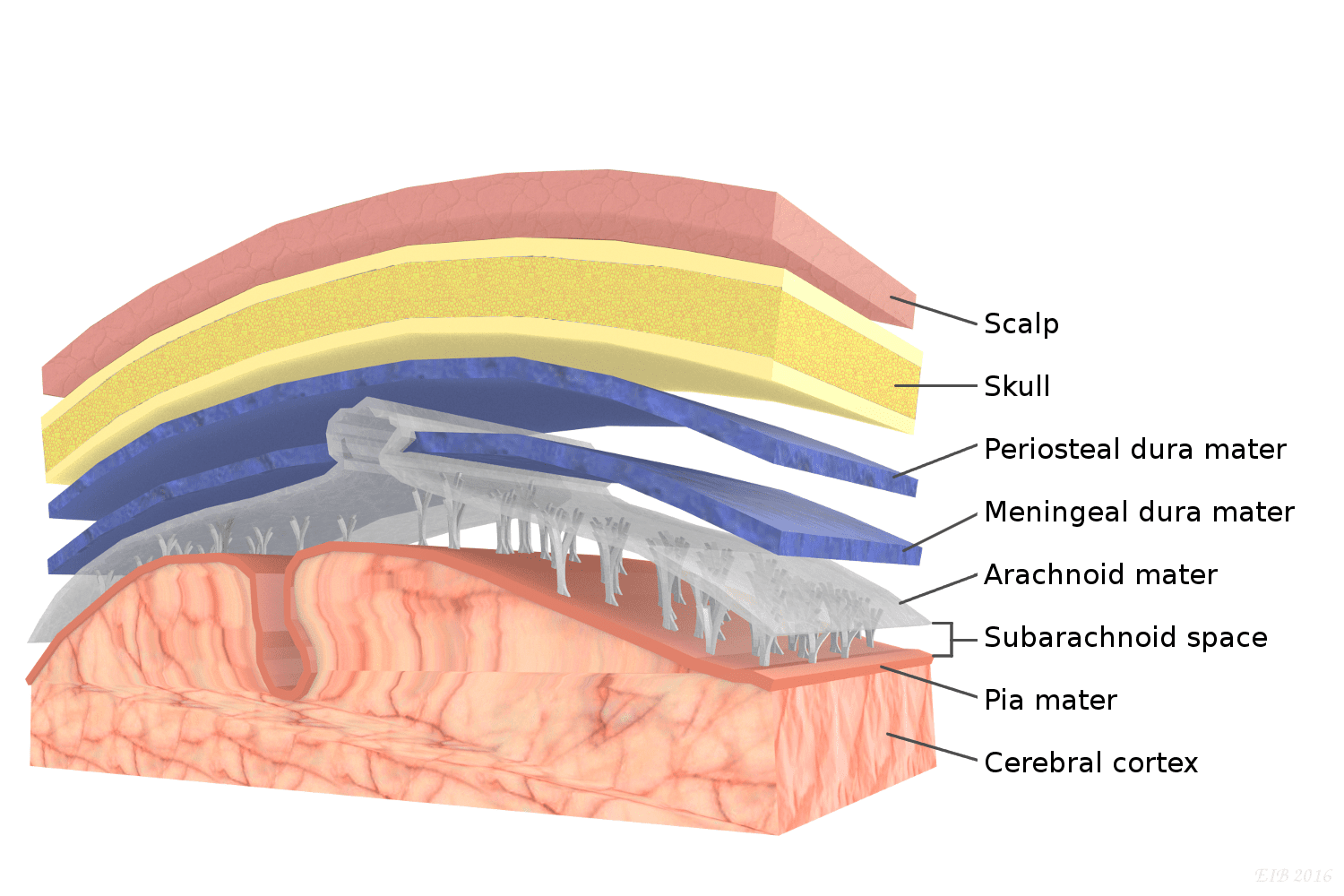
pia mater
delicate transparent membrane composed of 1-2 layers of squamous to cuboidal cells and delicate collagenous and elastic fibers
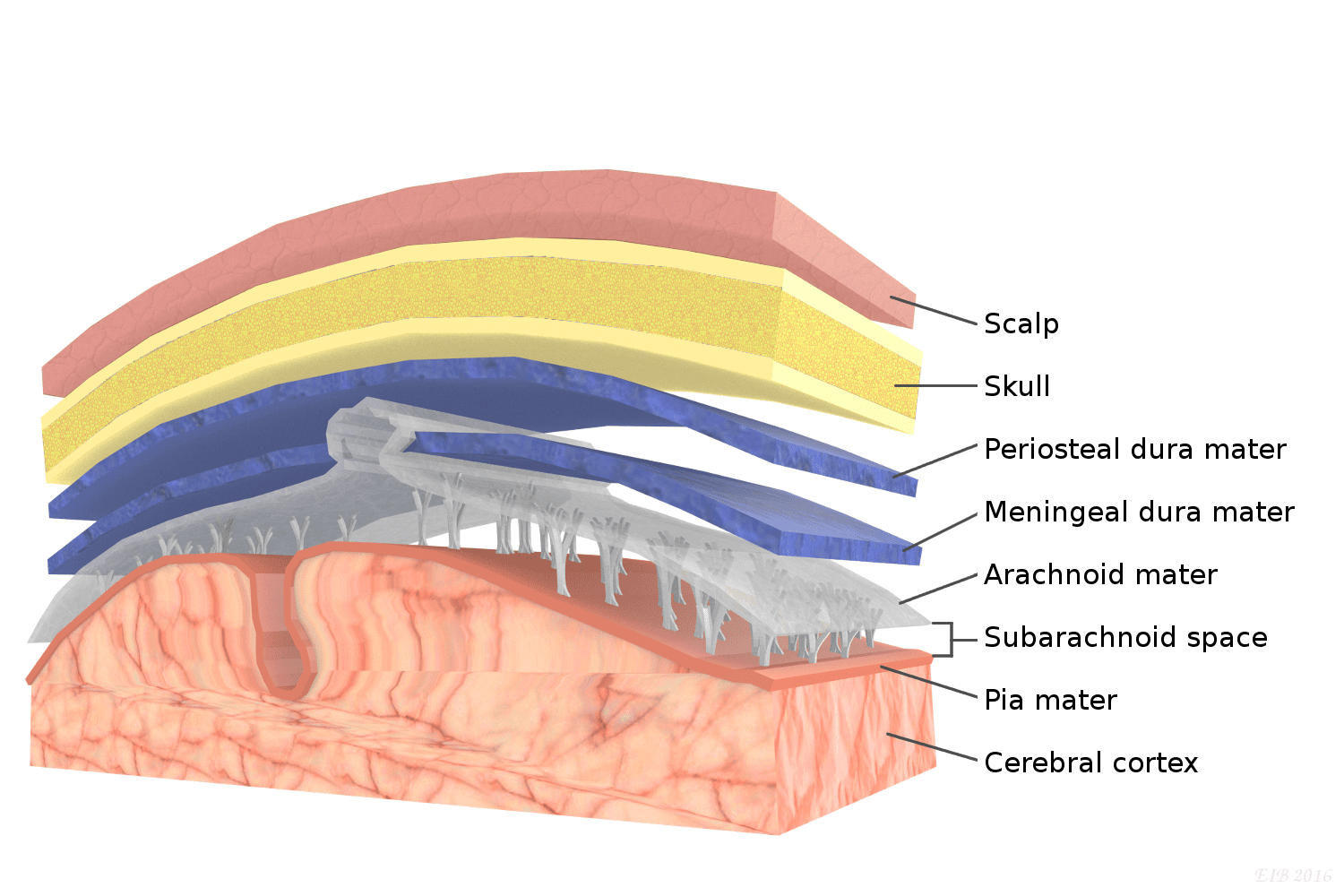
arachnoid mater
consists of arachnoid membrane, 5-6 layers of squamous cuboidal cells, loose array or collagenous and elastic fibers
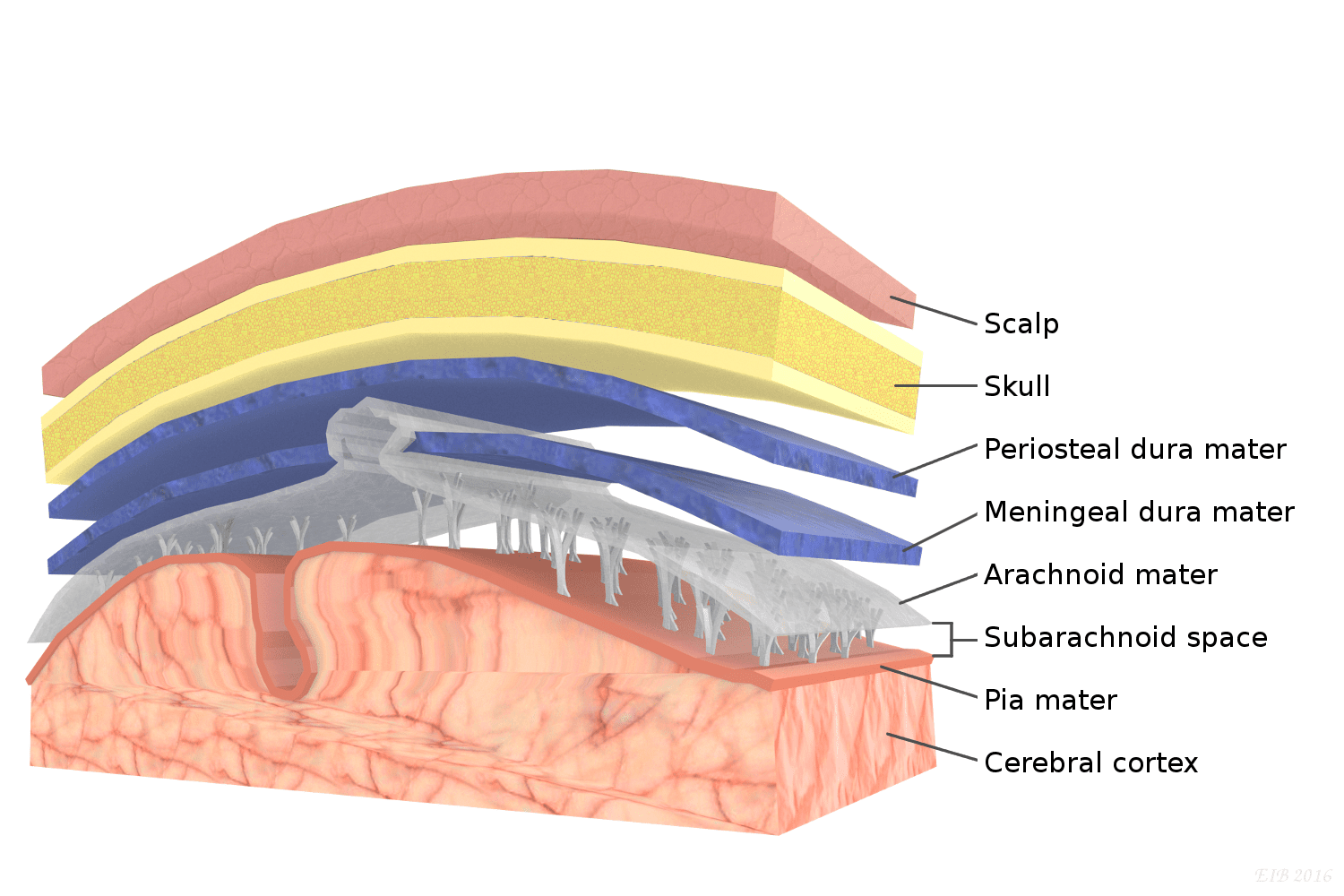
dura mater
thickest, most superficial layer, forms a loose-fitting sleeve (dural sheath), touch collagenous
lumbar puncture
a medical procedure that involves inserting a needle into the spinal canal to extract cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
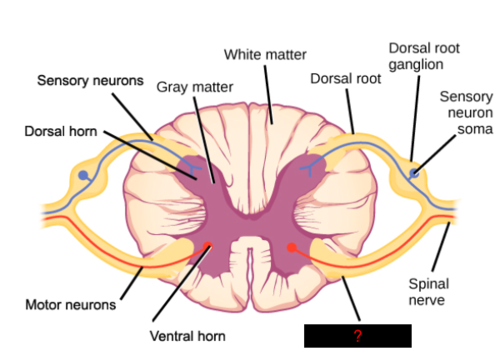
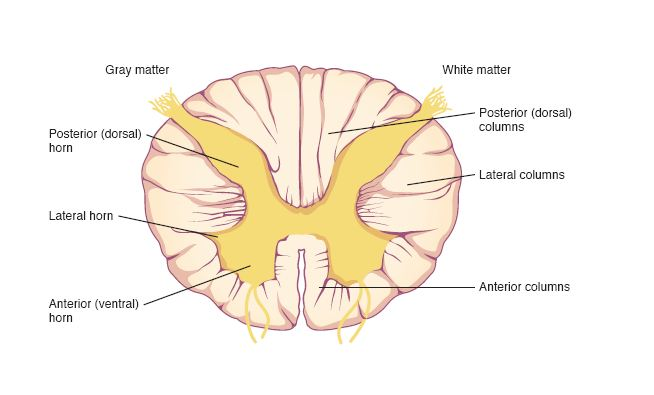
gray matter
contains cell bodies, dendrites, and proximal parts of the axons of neurons, site of synaptic contact between neurons and site of synaptic integration in the CNS
white matter
contains myelinated axons, carry signals from one part of CNS to another
dorsal (posterior) horns
the site where complex interconnections occur between excitatory and inhibitory interneurons and the descending inhibitory tracts from the brain
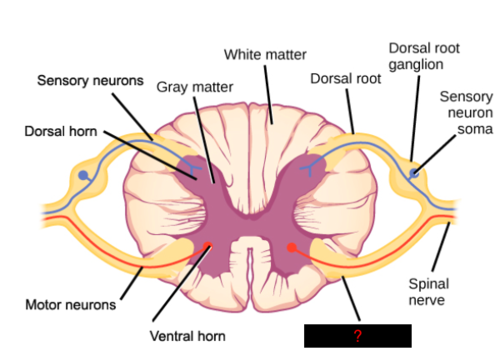
ventral (anterior) horns
a part of the spinal cord that contains motor neurons that control skeletal muscles
columns
dorsal, lateral, and ventral columns
sections of white matter that contain tracts carryinginfo up and down
ascending spinal tracts
pathways in the spinal cord that transmit sensory information to the brain, carry up
dorsal column
a sensory pathway located in the white matter of the spinal cord
spinothalamic tract
bundle of nerve fibers that ascend the spinal cord and brainstem and carry signals to the thalamus for light touch, tickle, itch, heat, cold, pain, and pressure
descending spinal tracts
conduct motor impulses down the cord
corticospinal tract
bundle of nerve fibers that descend through the brainstem and spinal cord and carry motor signals from the cerebral cortex to the neurons that innervate the skeletal muscles of the limbs
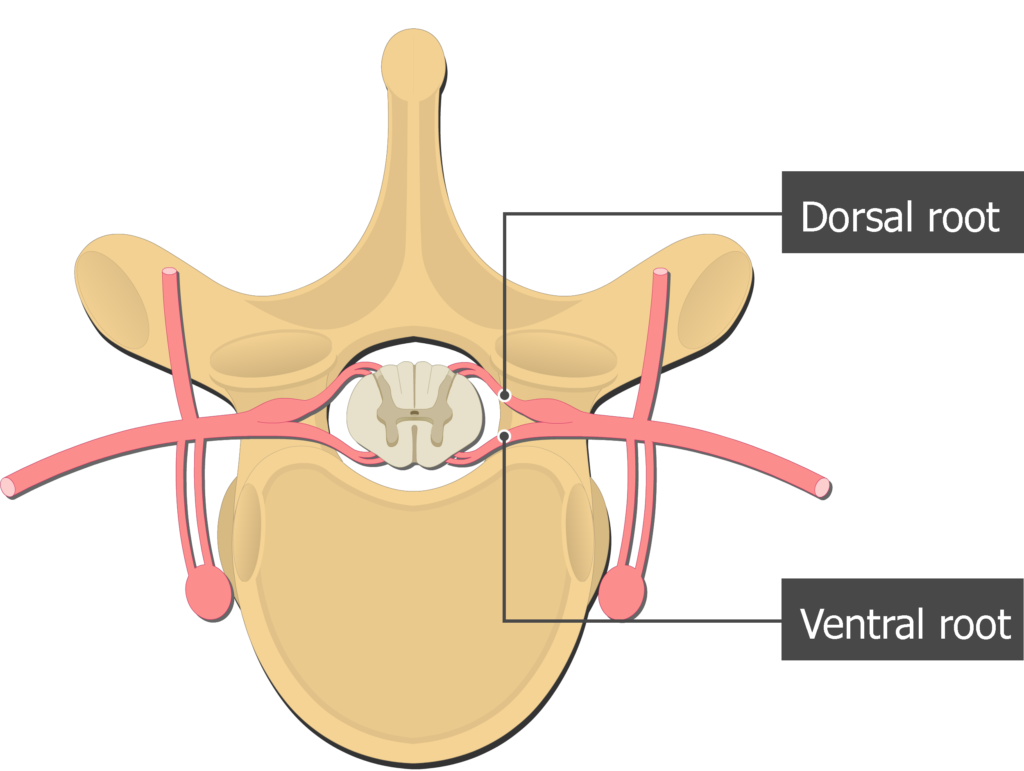
dorsal roots
carries sensory (afferent) nerve fibers
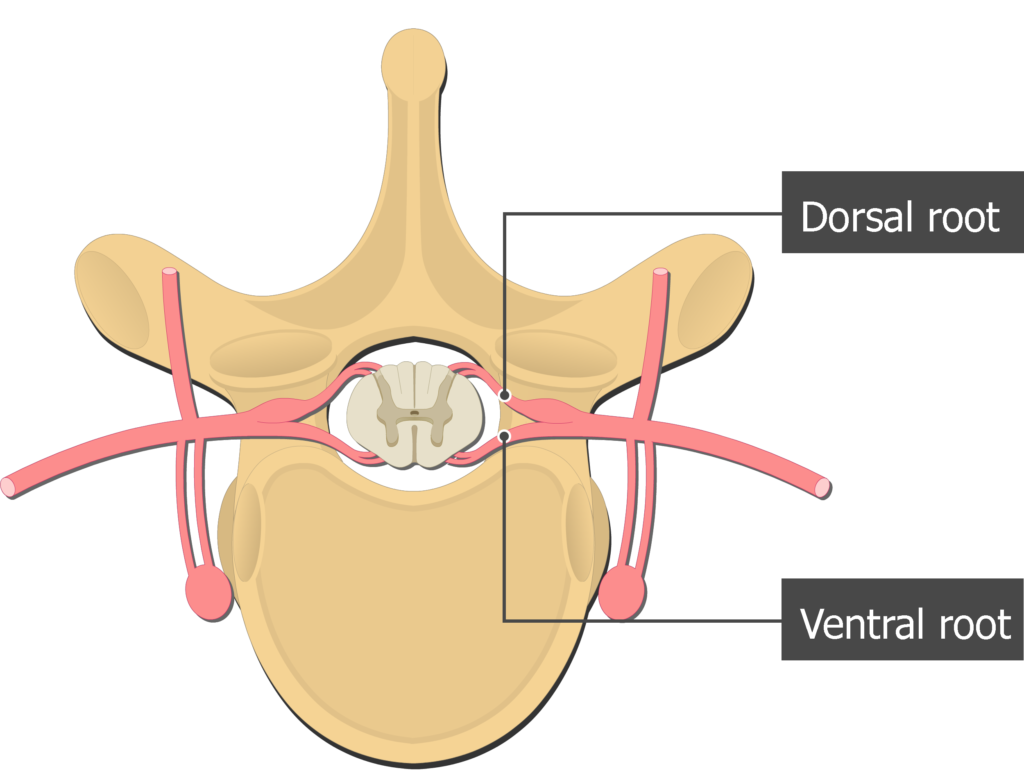
ventral roots
contains the large cell bodies of the somatic motor (efferent) neurons
dorsal root ganglion
near the spinal cord, contains the cell bodies of afferent neurons
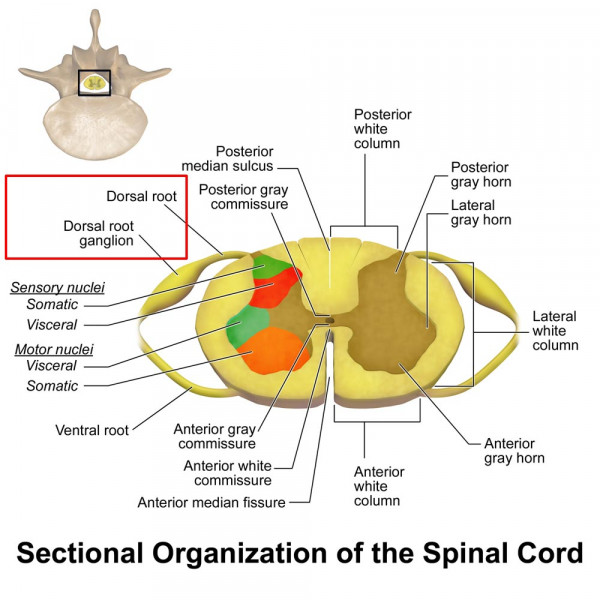
mixed spinal nerve exit IVF
where spinal cords exit the vertebral canal
dorsal ramus
a branch of a spinal nerve that exits the spinal cord through the intervertebral foramen
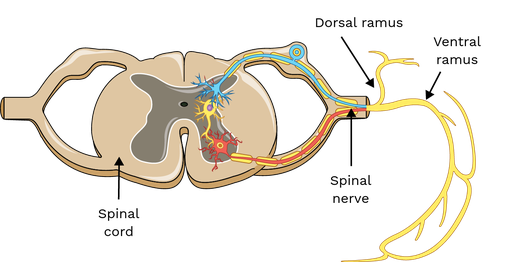
ventral ramus
anterior branches of the spinal nerves
cervical spinal nerves
a set of eight pairs of nerves that originate from the cervical region of the spinal cord, and C1 to C8
exits above corresponding vetebrae
thoracic spinal nerves
a set of 12 pairs of nerves that originate from the thoracic region of the spinal cord
exits below corresponding vertebrae
lumbar spinal nerves
a set of nerves that originate from the lumbar region of the spinal cord, L1 to L5
exists below corresponding vetebrae
sacral spinal nerves
part of the sacral plexus, which is located in the lower back and helps control movement in the lower body
exits below corresponding vetebrae
cervical plexus
neck nerve network (C1–C4) that supplies motor and sensory signals, including the phrenic nerve for breathing.
phrenic nerve
travel down each side of mediastinum, innervate diaphragm, and play role in breathing
brachial plexus
formed predominantly by the anterior rami of nerves C5 to T1. passes over the first rib into the axilla and innervates the upper limb and some muscles of the neck/shoulder. subdivisions are roots, trunks, divisions, and cords. 5 major nerves: musculacutaneous, axillary, radial, median, ulnar
median nerve
provides motor functions to the forearm, wrist, and hand
lumbar plexus
L1–L4 nerve network supplying motor and sensory signals to the lower abdomen, thigh, and part of the leg.
femoral nerve
a large nerve in the thigh that controls the muscles and sensation in the lower limbs
sacral plexus
L4–S4 nerve network supplying motor and sensory signals to the pelvis, buttocks, legs, and feet.
sciatic nerve
tibial nerve and common fibular nerve, common focus on pain/injury, passes through the greater sciatic notch of the hip bone, extends through thigh, and extends back of the knee
reflex arc
A reflex arc is a fast, automatic response where a stimulus activates a sensory (afferent) neuron, which passes the signal to an interneuron in the spinal cord. The interneuron then activates a motor (efferent) neuron, causing the effector (muscle or gland) to respond.
What covers the spinal nerve
epineurium
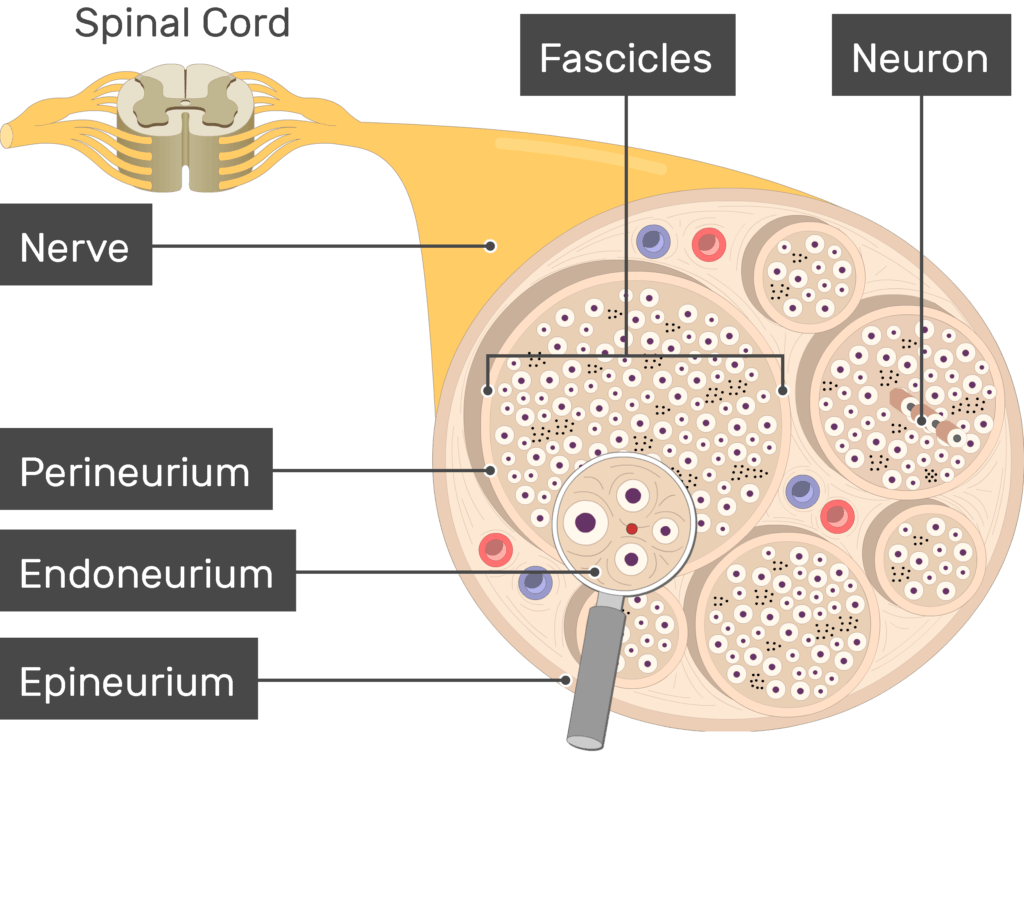
what covers the fascicle
perineurium
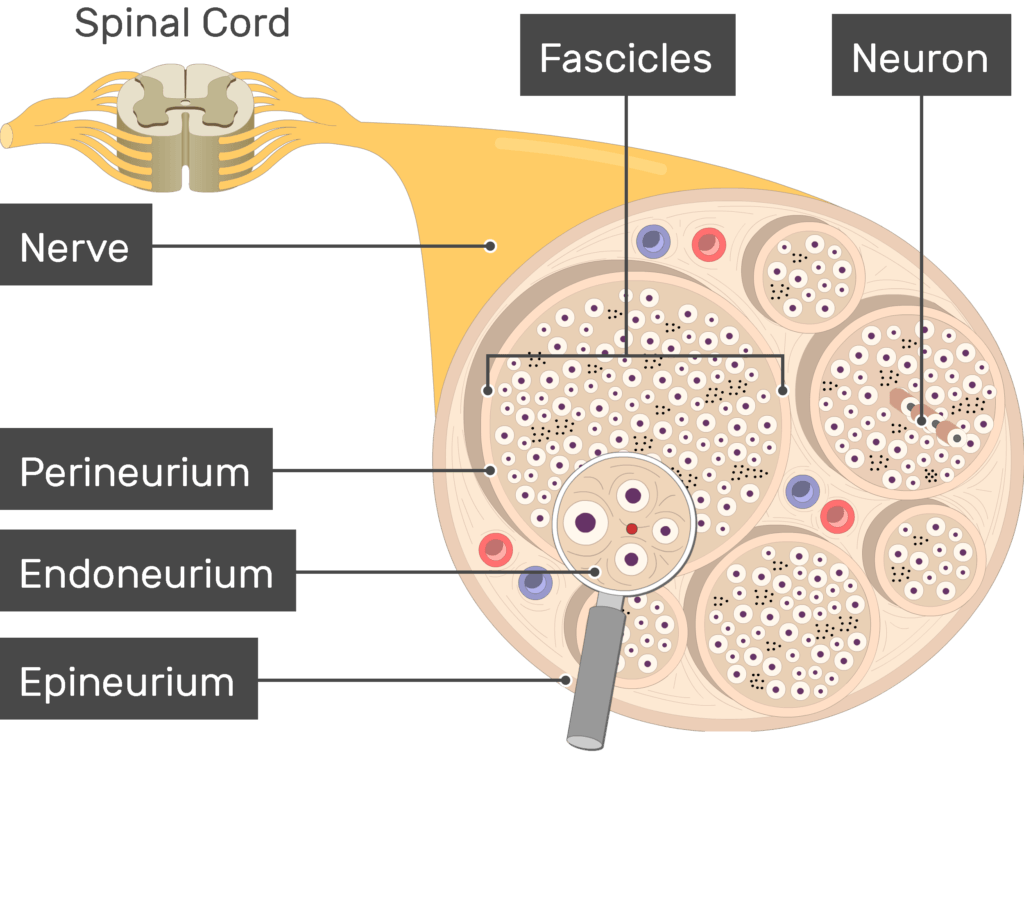
What covers the individual neuron
endoneurium
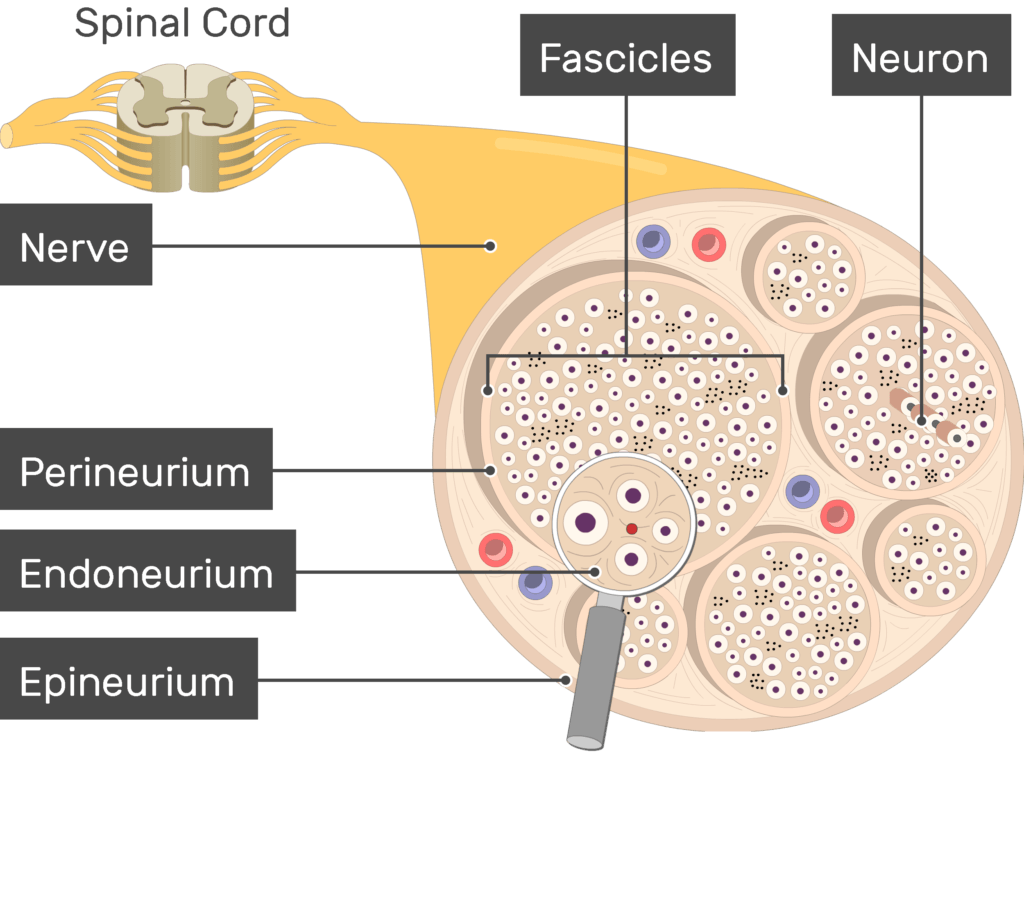
mixed nerve
when dorsal and ventral roots join at the IVF carrying both motor and sensory signals
Innervate
to connect a nerve to a body part so it can send or receive signals.