6-7 Amino Acids and translation
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Fibrous proteins
insoluble and provide structure
cytoskeleton
coatings (seeds)
ie silk
Globular
enzymes (catalysts)
transport protein (haemoglobin)
hormones (insulin)
defense (antibodies)
toxins (snake venom)
Receptor (rhodopsin)
Amino acid: general structure
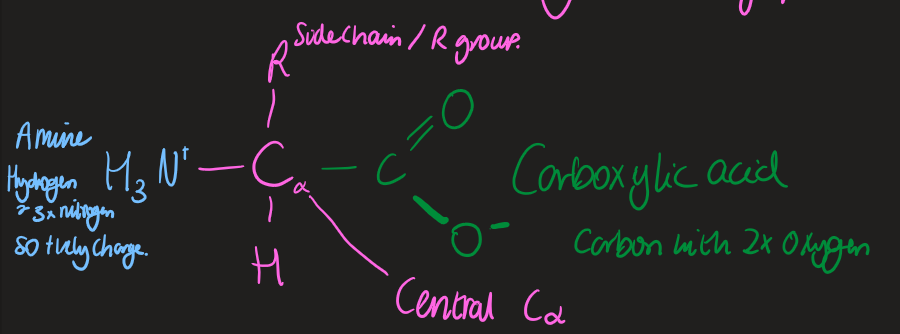
Zwitterionic
posesses both positive and negative charges
Chiral
amino acid property- only L amino acids exist in biology (glycine is not chiral)
Amino acid properties
Zwitterionic
Chiral
range of sidechain / R groups
Aliphatic
No charge on sidechain
increasing in hydrophobicity with sidechain size
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine
Imino acid
only amino acid with a secondary amine group present. all others primary amines
sidechain from 5 membered ring- looping from the c alpha to the nitrogen
confers diff properties on the polypeptide chain
proline
Polar
sidechains contains hydroxyl groups
H-bond acceptors/ donors
hydrophbic in nature
Serine, Threonine
Basic
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
Which amino acid has a pKa of 10
lysine
which amino acid has a pKa of 12
Arginine
which amino acid has a pKa of 6.5
Histidine
Acidic and amide derivatives
change o- (carboxyl group) to H2N
Aspartate, Aspargenine, Glutamate, Glutamine
Formation of a peptide bond:
Carboxylic acid reacts with amine
how do you estimate molecular mass of a protein
take number of amino acids and multiply by 110
how do you describe an amino acid
start at N- terminus (Amide) and then end at C terminus (hydroxyl group)
Tautomers
same molecule but can exist in 2 states
properties of a peptide bond
planar structure
partial double bond characteristic
exist as tautomers
Protein backbone conformation
each Ca carbon has 2x peptide planes connected to it
orientation of these is defined by phi and psi
what determines backbone conformation
phi and psi
what is glutamic acid used as
excitatory neurotransmitter
whats glycine used for
inhibitory neurotransmitter
amino acids not from the standard 20 amino acids
Hydroxyproline: hydroxylation of of proline in collagen
Gamma amino butyric acid: signaling molecule in the brain
Natural antibiotics e.g. texiobactin a new class of antibiotics to treat drug resistant bacteria
D- amino acid, methylated phenylalanine and alpha amino acid enduracididine
Prokaryotic
70S
subunit (small and large)
Large (50S)
34 proteins
3rRNAs
Small (30S)
21 proteins
1rRNA
Eukaryotic
80S
2 Sununits:
large (60S)
49 proteins
3 rRNAs
small (40S)
33 proteins
1rRNA
Svedberg coefficient
rate at which a particle sediments in a centrifuge
Binding sites on tRNA
A site (amino acid)
P site (peptide)
E site (exit)
Phe
UUC UUU
Leu
UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, CUG
Ile
AUU, AUC, AUA
Met
AUG
Val
GUU, GUC, GUA, GUG
ser
UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG
Pro
CCU, CCC, CCA CCG
Thr
ACU, ACC, ACA, ACG
Ala
GCU, GCC, GCA, GCG
Tyr
UAU, UAC
Stop
UAA, UAG, UGA
His
CAU, CAC
Gln
CAA, CAG
Asn
AAU, AAC
Lys
AAA, AAG
Asp
GAU, GAC
Glu
GAA, GAG
Cys
UGU, UGC
Trp
UGG
Arg
CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG
Ser
AGU, AGC
Arg
AGA, AGG
Gly
GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG
where does protein synthesis occur
cytoplasm/ surface of the ER
Inhibitor and mode of action
tetracycline: block binding of aminoacyl- tRNA to the A- site
Streptomycin: Blocks the transition from the initiation of translation to enlongations
Chloramphenicol: prevents the peptidyl transferases reaction
Erythromycin: Block the tunnel where the nascent peptide emerges preventing protein synthesis