Chemistry: Isotopes, Periodic table and Bonding, Simple and Giant molecular structures
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the relative atomic mass?
The weighted average mass of the isotopes of an element, relative to the mass of 1/12th of a 12 carbon atom.
What is an isotope?
different atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
How do you calculate the relative atomic mass
(% of isotope 1 x isotope 1 mass number) + (% of isotope 2 x isotope 2 mass number)
/ 100
On the periodic table, what do each of the groups mean?
Their outer shell has that number of electrons
What is group 1 and their reactions?
Alkali Metals and they react vigorously with water to form hydrogen and hydroxides with similar formulae.
What is group 2 and their reactions?
Alkaline metals and they form chlorides with similar formulae.
What is group 7 and their reactions?
Halogens and they react with hydrogen to compounds with similar formulae.
What is group 0 and their reactions?
Noble gases and they are almost completely unreactive. Helium and neon do not react with anything. They all have full shells.
What are some properties of metals?
-conduct electricity (delocalised electrons free to move)
-forms basic oxides (reacts with acids to form salts)
-lustrous-shiny
-ductile-able to be drawn into wire
-malleable-can be hammered into a sheet
-form ionic compounds
-form positive ions
What are some properties of non-metals?
- not a conductor of electricity (no free moving electrons exp graphite and silicon)
- forms acidic oxides (reacts with bases/alkaline to form salts)
- not shiny
- low melting point
- brittle
- form ionic and covalent compounds
- form negative ions
What is the definition of Ionic Bonding?
Strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
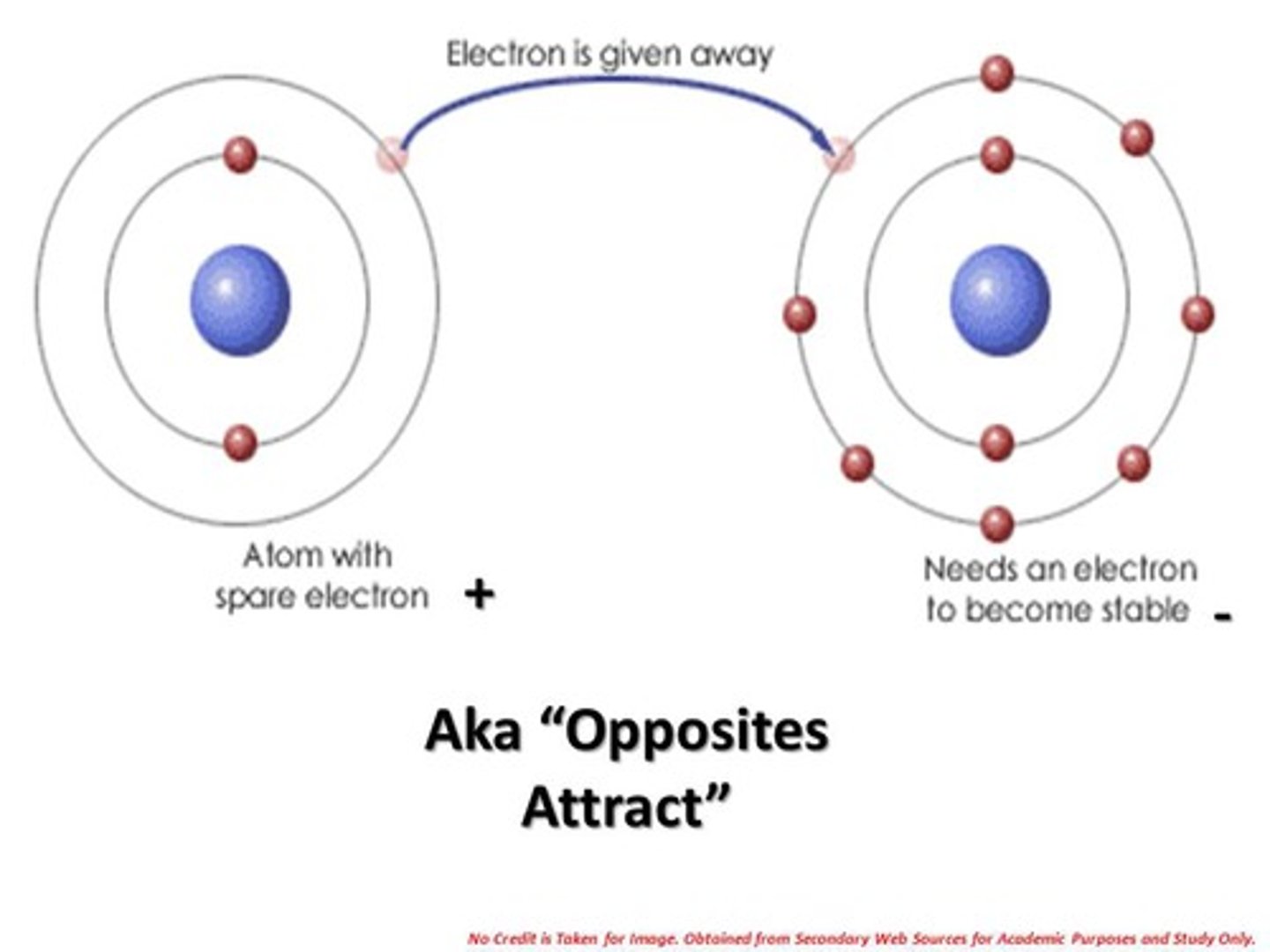
What happens to the metal and the non-metal atoms in ionic bonding?
Metals give electrons (+) meaning they are cations.
Non-metals want electrons (-) meaning they are anions.

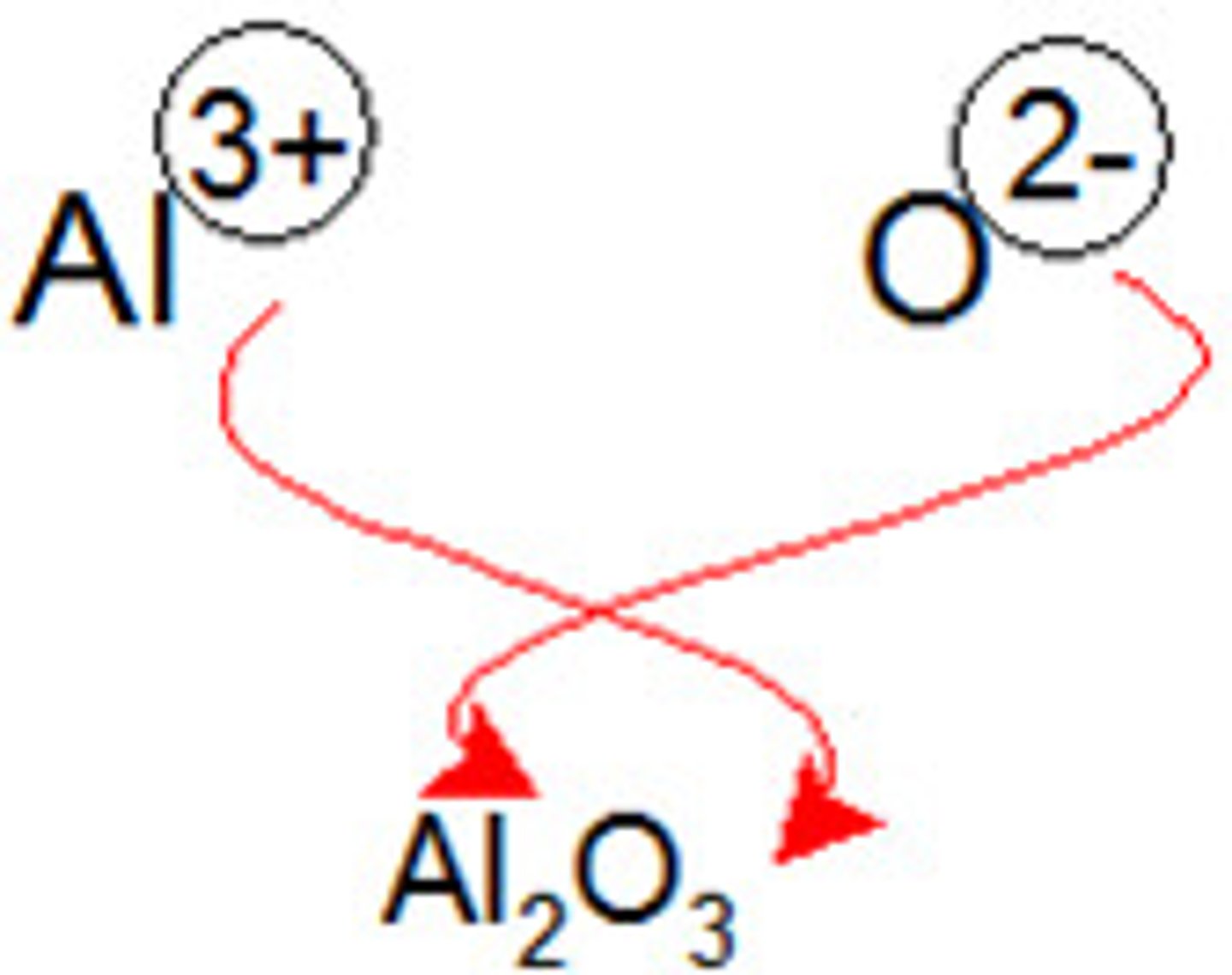
Which method is used in ionic bonding for formulas?
Criss Cross applesauce method.
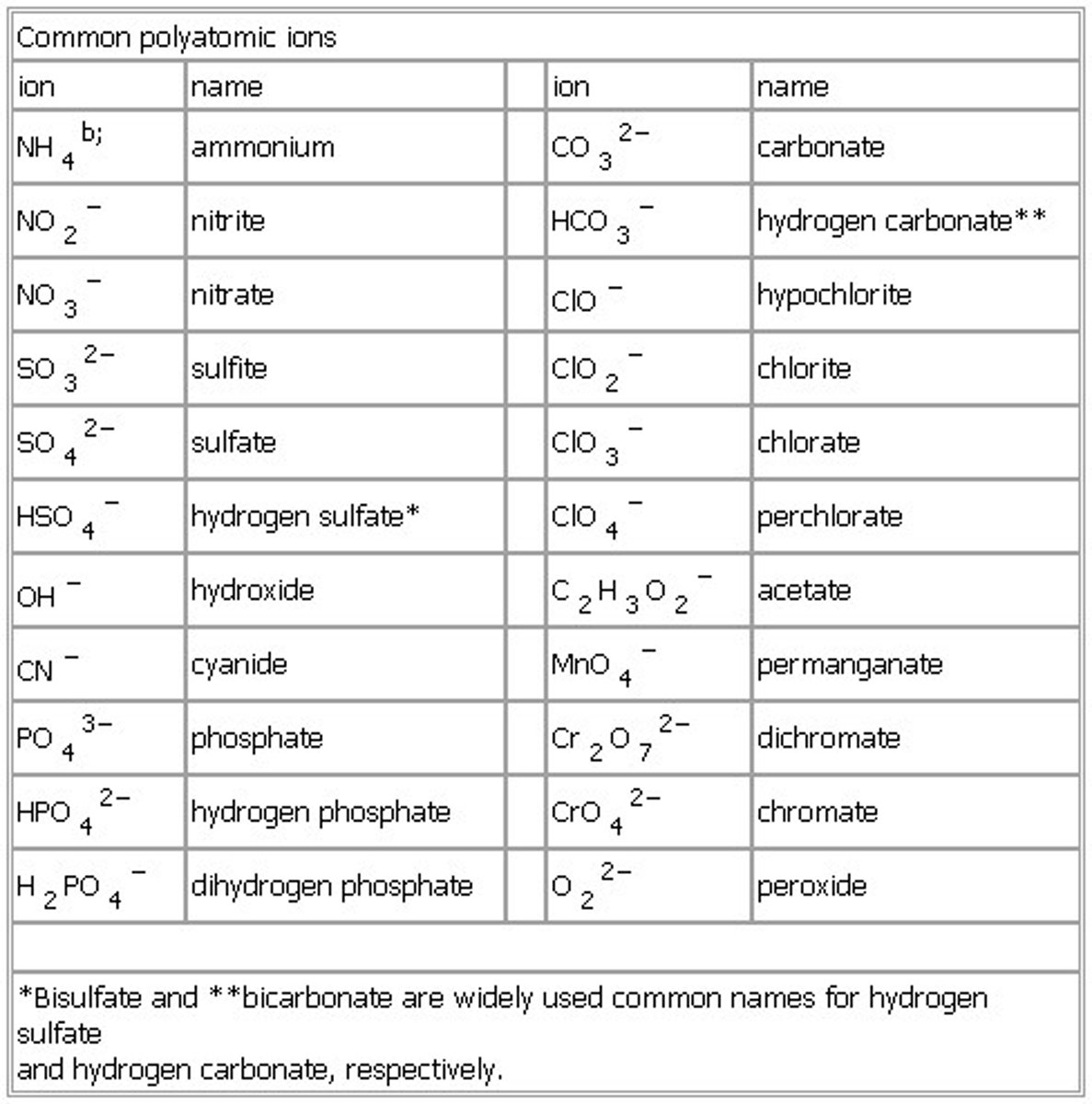
What are the polyatomic Ions?
Hydroxide, OH-
Nitrate, NO3-
Carbonate, CO32-,
Sulfate, SO42-
Ammonium, NH4+
What is an ionic lattice?
a repeating pattern of positive and negative ions
What are some properties of ions
-Usually soluble in water
-High melting point
-hight boiling point
-brittle
conducts electricity when molten (melted) or aqueous (dissolved in water)
- Does NOT conduct electricity when solid.
Why do giant ionic structures have high melting points?
Because of the strong electrostatic forces. between them, it takes a great deal of energy to separate the positive and negative ions in a crystal lattice
What is Covalent bonding?
The strong electrostatic attraction between the nuclei of the atoms making up the bond and the shared pair of electrons.
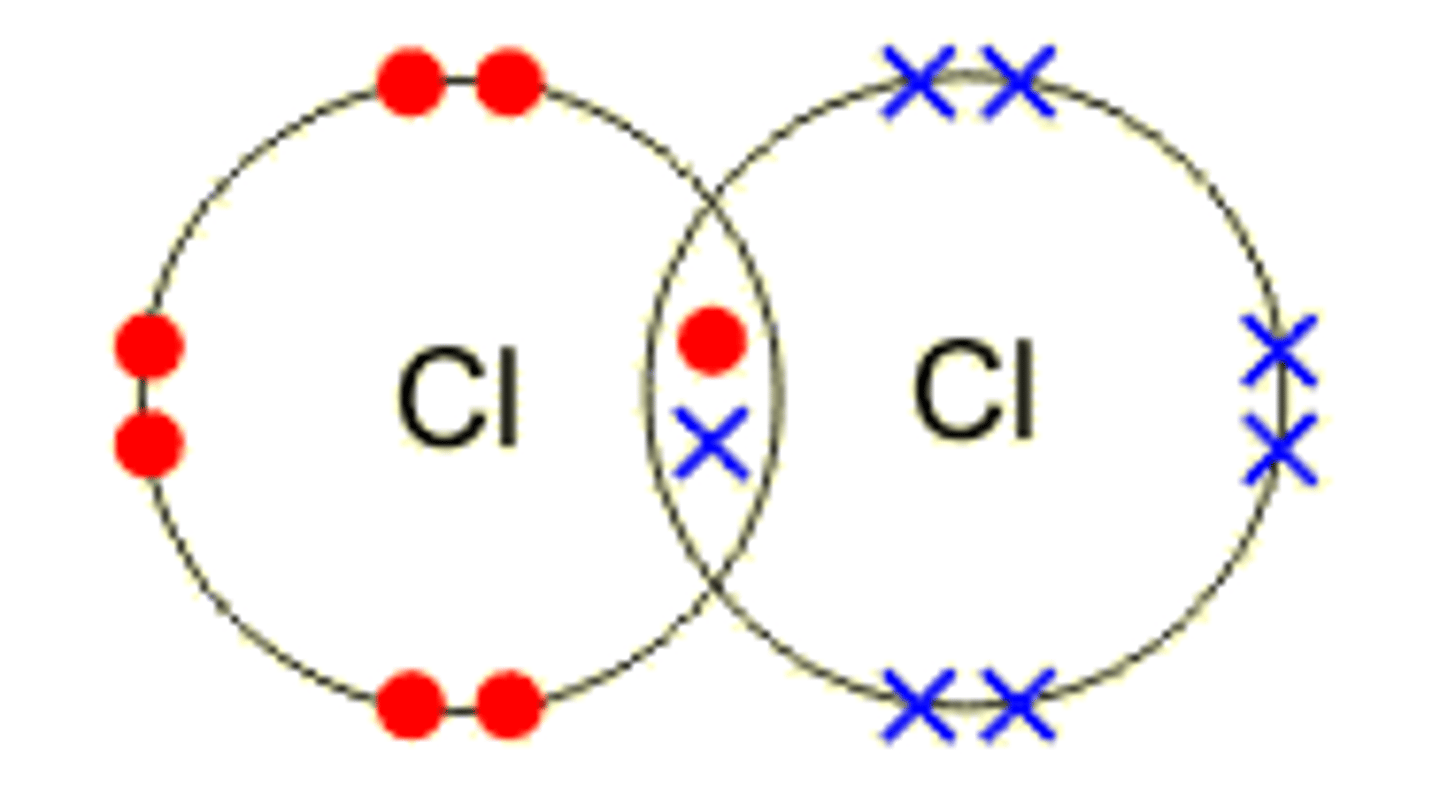
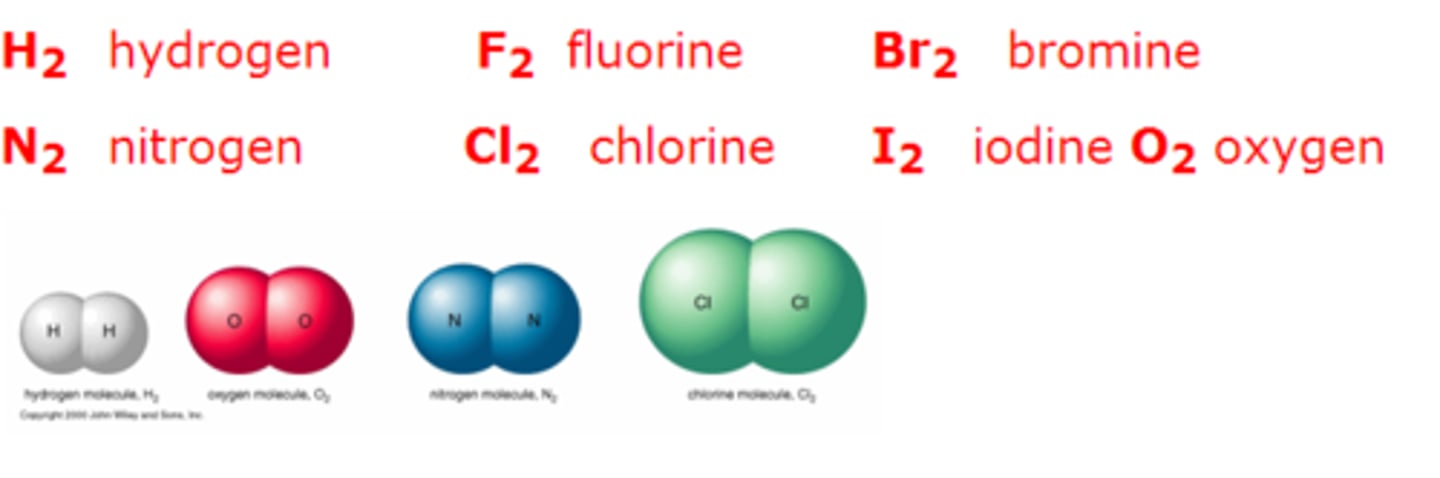
What are diatomic molecules?
any chemical compound that is made up of only two atoms eg. H2, N2, O2, etc
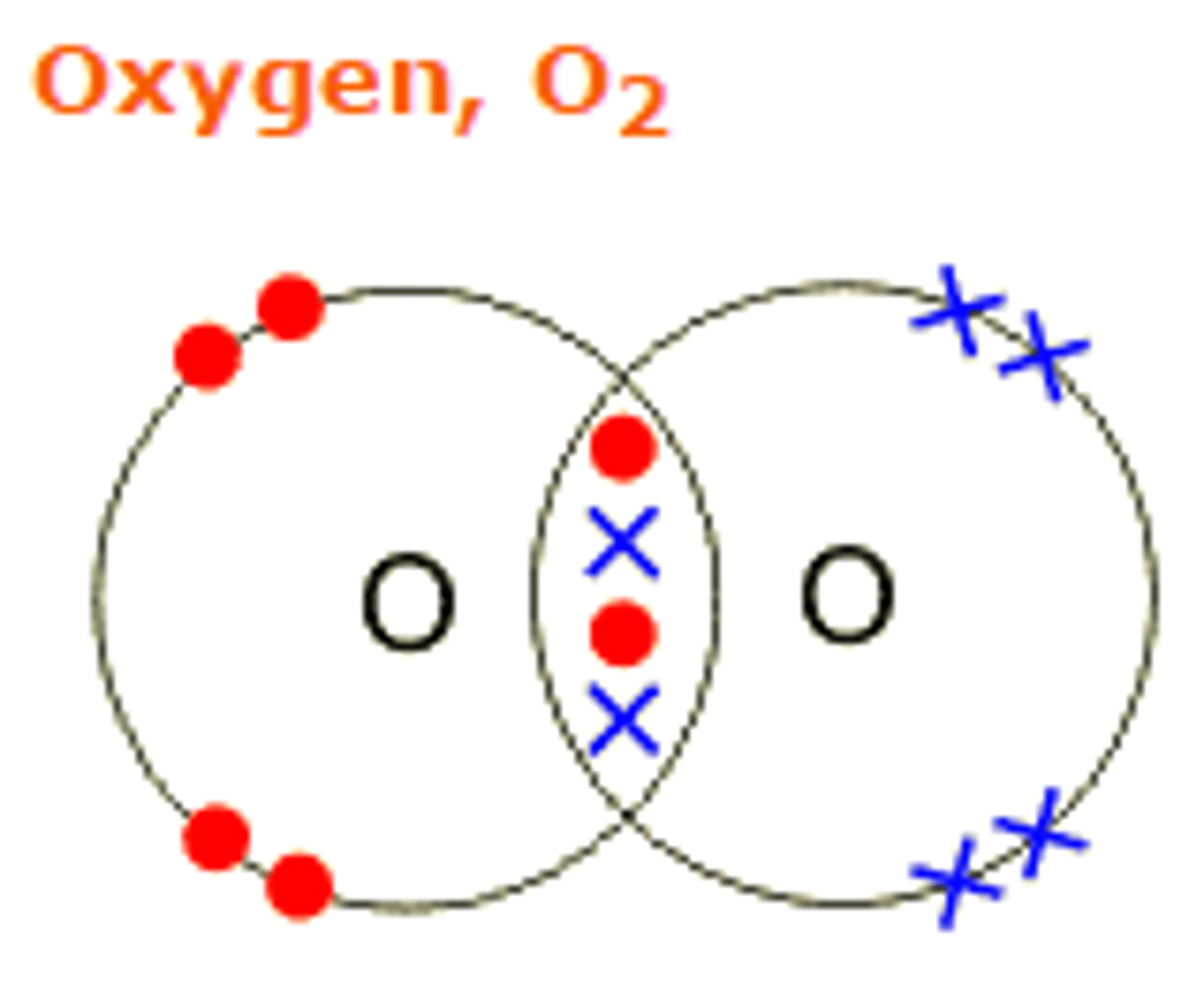
What does covalent bonding do?
when the bond forms, energy is released, making things more stable. The more energy released the more stable to system.
What are simple molecular structures?
Molecules have fixed numbers of atoms covalently bonded and the forces between molecules are intermolecular forces.
Describe simple molecular structures intermolecular forces
Weaker than covalent bonds.
When we boil water, the covalent bonds aren't broken
they are substances of molecules with intermolecular forces of attraction.
Tend to have low boiling/melting points
What are giant covalent structures?
Giant covalent structures the atoms are joined up by covalent bonds over huge (but variable) numbers of atoms
Why do giant covalent structures have higher melting and boiling points than simple molecular structures?
Melting giant covalent bonds require a break in actual bonds, not like with simple molecules which is only breaking intermolecular forces.
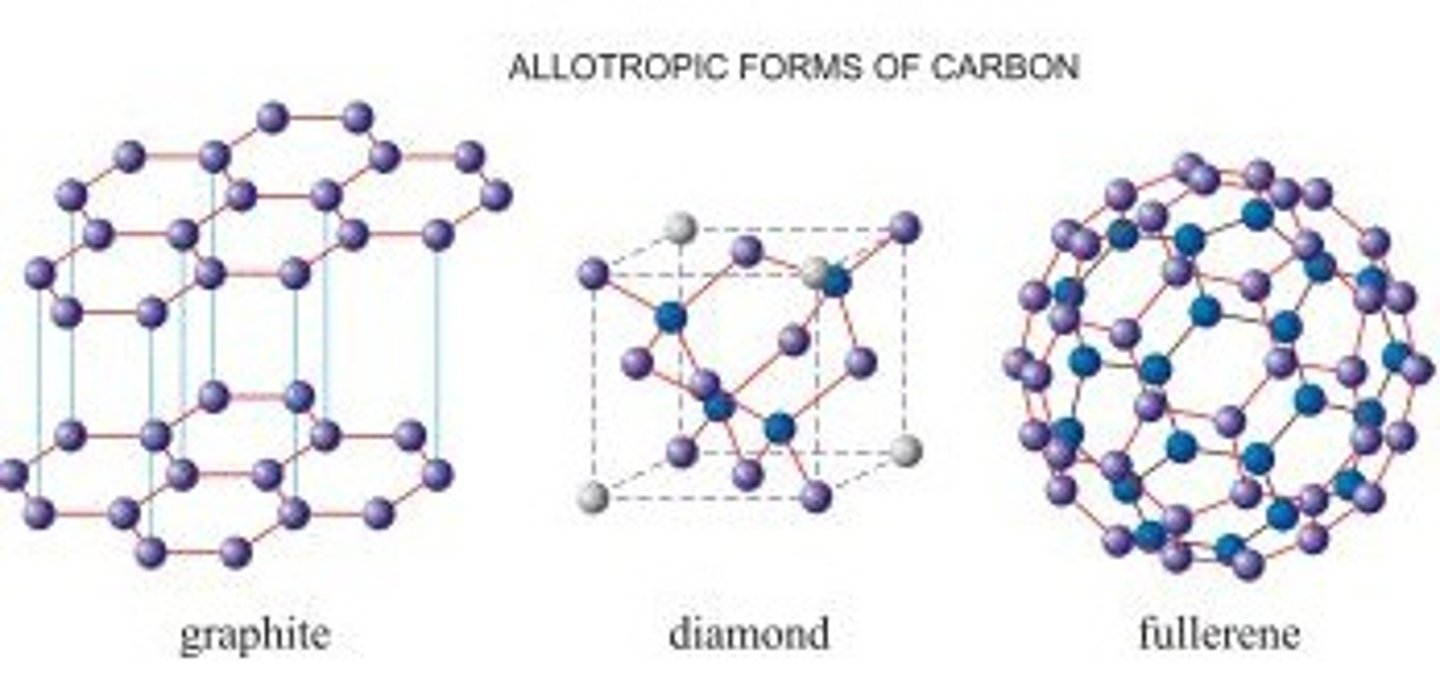
What are allotropes?
Different forms of the same element, e.g. diamond, graphite and C60 fullerene are 3 allotropes of carbon.
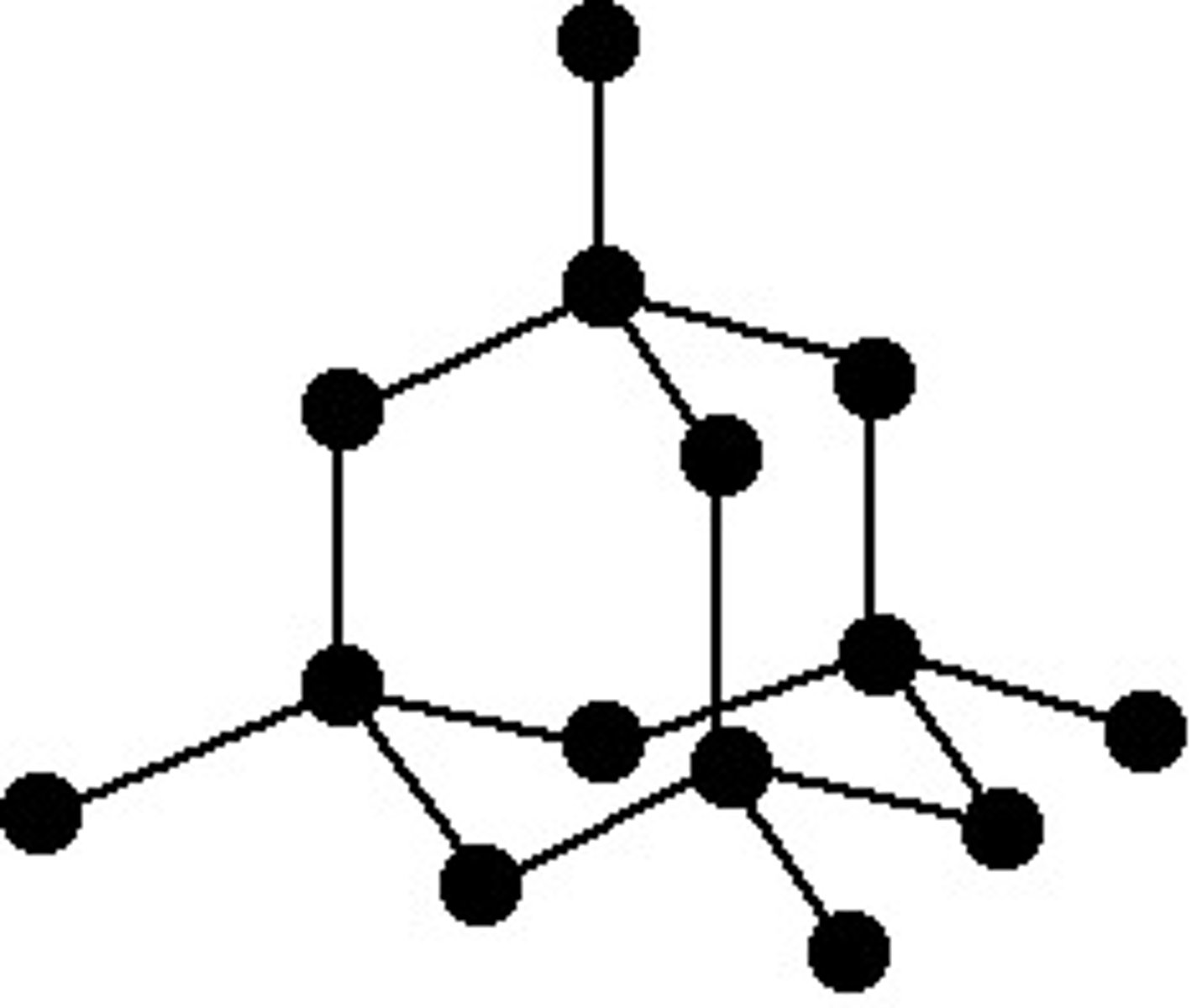
What is the structure of diamond?
Each carbon atom has 4 electrons in outer shell, forming 4 covalent bonds.
Each carbon is bonded to 4 other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
What are the properties of diamond?
Giant covalent structure
not a molecule
number of atoms is variable depending on size of crystal.
high melting and boiling points
strong C-C bonds
Hard
Doesn't conduct electricity
Conducts heat
What is the structure of graphite?
Layered structure
What are the properties of graphite?
Soft material (weak attraction between layers)
Used in pencils (with clay) to make harder. Graphite layers are left behind
Pure graphite is a lubricant
High melting and boiling points
conducts electricity (each atom has 5 bonds, leaving one delocalised electron to move through layers)
What is the structure of fullerene C60?
In solid or liquids there are C60 molecules with weak intermolecular forces.
has a simle molecular structure which effects it's properties.
What are the properties of fullerene C60?
lower melting and boiling points
not hard like diamond
does not conduct electricity (can only move delocalised electron through one molecule)