Variables Affecting Conformity
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is the Asch effect?
the idea that individuals will usually conform to the majority
Asch’s first name?
Solomon
When did Asch investigate coformity?
1956
Asch 1956: Aim of experiment?
to see if a lone participant would conform to a group
Asch 1956: sample?
123 male US undergraduates
Asch 1956 - procedure: what were participants shown?
shown a standard vertical line, and 3 comparison lines of different lengths
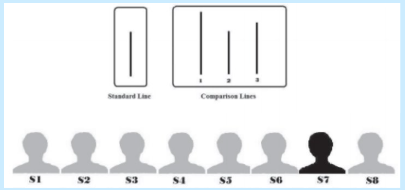
Asch 1956 - procedure: what were participants then asked to say?
which of the comparison lines were the same as the standard line
Asch 1956 - procedure: what did the group tested each time consist of?
each time a group of participants, with only one real participant and the rest being confederates, were tested
Asch 1956 - procedure: in how many trials were the confederates instructed to give the wrong answer?
in 12 out of 18 trials
Asch 1956 - procedure: what did the Asch want to see?
if the participant agreed with the group
Asch 1956 - findings: what percentage of the time did the participant agree with the incorrect response given by the group?
33% of the time
Asch 1956 - findings: what fraction of participants never conformed to the group?
one quarter
Asch 1956 - findings: what proportion of participants conformed all 12 times?
1 in 20 participants
Asch 1956 - findings: what proportion of participants conformed on 6 or more trials?
half
Asch 1956: what was the control group?
participants answering without a group of confederates
Asch 1956: what percentage of the time did participants in the control group make mistakes?
only made mistakes 1% of the time
Asch 1956: when Asch interviewed his participants later, what did he find out was the reason for their conformity?
they changed their public behaviour, giving incorrect answers, to avoid disapproval from others - continued to privately trust their own perceptions
Asch 1956: therefore, what type of conformity were Asch’s participants showing?
compliance
Asch’s variations?
factors that could male the participants’ conformity rate increase or decrease
The 3 Asch’s variations?
size of the majority, unanimity of the majority and the difficulty of the task
Asch variations - size of majority: what effect did the majority being 1 or 2 people on conformity?
little effect
Asch variations - size of majority: what rate of conformity did the majority being 3 people cause?
31.8%
Asch variations - size of majority: what impact do amounts over 3 people acting as the majority have?
minimal impacts (suggesting 3 is the magic majority number)
Asch variations - unanimity of the majority: what happened to incorrect answers given by the participant when they were given a supporter?
incorrect answers dropped from 33% to just 5.5%
Asch variations: what effect did Asch find increasing the difficulty of the task had?
increased conformity
Asch variations: what type of conformity are participants showing when the difficulty of the task is increased?
internalisation
What investigation looked into conformity when increasing the difficulty of a task?
Lucas et al (2006)
What did Lucas et al (2006) find?
that, if the difficulty of the task was increased, self-efficacy came in to play
What is self-efficacy?
how confident an individual is in their ability
What does the participant having high self-efficacy lead to?
them being more independent - and not conforming
What does the participant having low self-efficacy lead to?
them being less independent - and conforming
What study investigated the gender differences in conformity?
Eagly and Carli (1981)
Eagly and Carli (1981): what gender did they find conformed more?
women
Positive - P: Where was Asch’s research carried out?
in a lab setting
Positive - Ex: therefore, what could Asch control and ensure?
it meant Asch could control the conditions and ensure it was a standardised procedure
Positive - Ev: an example of something Asch controlled in his experiment - where did the participants sit?
Asch controlled where the non-confederate participant sat - placing them second to last ever time
Positive - L: What benefit is there to Asch’s research being scientific?
his research is scientific and therefore reliable and easy to replicate
Negative - P: What may have participants guessed?
that the confederates were not real participants
Negative - Ex: what would have been difficult for confederates during the experiment?
to act consistently convincingly when giving the wrong answer - which could’ve led to participants realising they were confederates
Negative - Ev 1: What study supported this claim?
Mori and Arai (2010)
Negative - Ev 2: Mori and Arai (2010) - what did give each participant?
glasses with special polarising filters - three wore identical glasses and a fourth wore a pair with a different filter - causing them to see the stimuli differently
Negative - Ev 3: Mori and Arai (2010) - what was the rate of conformity found?
lower average rate of conformity
Negative - L: why does Mori and Arai (2010) reduce the validity of Asch’s research?
as participants could’ve been showing demand characteristics
Negative - P: what is low in the Asch experiment?
it has low generalisability
Generalisability?
extent that research findings from a study sample can be applied to the wider population, different settings, or other times, essentially linking to external validity
Negative - Ev 1: who repeated Asch’s study in the UK?
Perrin and Spencer (1980)
Negative - Ev 2: what was the rate of conformity found by Perrin and Spencer (1980)?
only one conforming response out of 396 trials
Negative - Ex 1: where and when was Asch’s study carried out?
in the 1950s in the US
Negative - Ex 2: Why was conformity more important in 1950s America?
because, in 1956, Americans were arguably more scared to go against the majority as the US was going through a strong anti-communist period
Negative - L: therefore, despite Asch’s experiment explaining conformity in the 1950s, what may it not be applicable to?
today’s society
Negative - P: what kind of bias may Asch’s research have?
cultural bias
Negative - Ev 1: who looked at a range of Asch-type studies from various cultures?
Smith et al. (2006)
Negative - Ev 2: what was the average rate of conformity found in Smith et al. (2006)?
31.2%
Negative - Ev 3: what did Smith et al. (2006) find large differences in conformity rates between?
different countries
Negative - Ev 4: conformity rate average in individualist cultures (Europe, US)?
around 25%
Negative - Ev 5: conformity rate average in collectivist cultures (Africa, Asia, South America)?
around 37%
Negative - Ex: what did Markus and Katayama (1991) suggest the reason for higher conformity in collectivist cultures was?
because it’s viewed more favourably - a form of ‘social glue’ that binds communities together
Negative - L: Therefore, what can’t Asch’s findings be applied to?
can’t be applied outside of western culture
Negative - P: what else could there be explaining the conformity?
extraneous variables
Negative - Ev: what research did Perrin and Spencer (1980) carry out that provided them with similar levels of conformity as in Asch’s experiment?
they used a variation of their research in which youths on probation were the participants, and probation officers were confederates
Negative - Ex 1: what does this research argue isn’t the sole explanation of the difference of conformity?
the fact Asch’s research was carried out a long time ago
Negative - Ex 2: What does this research suggest could be the reason for conforming?
the perceived costs of not conforming (i.e. the fear of being thought as a communist)
Negative - L: therefore, what does this show may not be the only reason for conformity?
that an overwhelming majority influence may not be the only reason for conformity
Negative - P: what size is the conformity Asch’s research actually shows?
a small amount of conformity
Negative - Ev 1: What fraction of the critical trials did participants conform to the majority group’s answers in?
only in one third of the critical trials - two thirds of the time participants didn’t conform
Negative - Ex: therefore what can it be argued that this study actually shows?
that we have a tendency to show independent behaviour when faced with an overwhelming majority believing differently - Asch himself thought this
Negative - L: therefore, what may it be inappropriate to conclude?
that Asch’s research sows we show conformity, as the majority of participants did not comply
Negative - P: what wasn’t explored/researched with conformity?
larger majority group sizes
Negative - Ev 1: What did Bond (2005) conclude about research on conformity?
that it only uses a limited range of majority sizes
Negative - Ev 2: what majority did Asch conclude was sufficient?
3
Negative - Ev 3 - what majority size did most research after Asch’s use?
majority of 3 - no studies used a majority larger than 9 (most between 2-4)
Negative - Ex: what does this mean we know very little about?
the effect of larger majority sizes on conformity
Negative - L: therefore, what can’t Asch’s research be applied to?
larger groups - such as crowds