CHAPTER 5 ( Measuring National Income and Output
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Macroeconomics
Is the study of the relationships between aggregate economic variables, and the choices made by policy makers to influence those variables
What is the most important measure of output in the economy?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
What do Measures of Output include?
Nominal GDP and Real GDP, And Gross National Product
What does the Change in Output Determine?
Whether the economy is in expansion or recession
What is it called when the tendency for GDP to fluctuate around a trend called?
Business Cycle
Nominal GDP
Measure the output produced using CURRENT PRICES
Real GDP
Measures of Output produced using CONSTANT PRICES/BASE YEAR PRICES
Gross National Product ( GNP )
Measures the output by the COUNTRIES CITIZENS no matter WHERE they are
Gross Domestic Product ( GDP )
Measure production IN THE COUNTRY no matter who it is
Inflation
Sustained increase in the average level of prices in an economy over time. Decreasing in the value of MONEY
What are the 4 primary measures of price level in the United States?
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) : publishes GDP price deflator
Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) : Price Index
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) : Consumer Price Index and Producer Price Index (2 measures of inflation)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) : Most widely reported Inflation measures
Producer Price Index (PPI) : Measures changes in wholesale prices received by producers
GDP Price Deflator
Measures overall inflation in the economy. Shows how much prices have changed compared to base year
The Unemployment Rate
Measure of the percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking for work but not finding work
(Number actively seeking but not finding work / Number in Labor force ) X 100
Can Foreign investor affect the value of assets in the home country and the cost of borrowing money?
Yes
Net Exports
Included in GDP. Important in determining how quickly economy is expanding or contracting
What are the important measure of the International Economy?
The Balance of payments
The Current Account
Exchange Rates
The Balance of Payments
The record of a country’s flows of goods, services, income , gifts, capital, and financial assets with rest of world
The Current Account
Is a subset of the balance of payments that’s used to measure a country’s trade deficit or surplus. Also measures flows of goods, services, gifts and income with rest of the world.
Current Account positive = Country has a trade SURPLUS
Current Account negative = Country has a trade DEFICIT
Exchange Rates
The value of one country’s currency in terms of another country’s currency
Currency is traded in Currency Markets or Foreign Exchange Markets
Interest Rate :
The Price of money, or the cost of borrowing funds/ the benefit of lending funds
Money Supply :
The Quantity of money in circulation at a given point of time. The rate of change in the money supply is an important determinant of several economic variables
3 major Macro Policy goals in : The Full employment and Stabilization Act of 1946 and the Humphrey Hawkins Act of 1978
Stable rate of GDP growth
High Employment ( or low unemployment)
A stable Price Level ( or low inflation )
How are these goals achieved?
The governments 2 policy tools:
Fiscal Policy
Monetary Policy
Fiscal Policy :
A change in government spending or taxes to influence a macroeconomic variable like GDP/ Inflation
Used by Administration
Can be used to to attempt in fights of recession
Aiming to promote growth, reduce unemployment and manage inflation
Monetary Policy :
Change in the money supply or interest rates to influence a macroeconomic variable
Exercised by the Federal Reserve System
Less of a lag for monetary policy compared to fiscal policy
Federal Government can use their tools of fiscal and monetary policy to help maintain a stable Macroeconomy
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) :
The Markets ALL FINAL GOODS AND SERVICES PRODUCED within a country’s borders in a year
What are the issues of Calculating GDP?
Market Value
Final Goods and Services
Value-added Approach
Produced within a country’s borders
In a Year
Non-Market Transactions are Excluded
Non-Productive Transactions are excluded
Second- Hand Goods are Excluded
Goods produced not sold
Market Value:
Some goods may not be market prices that exist to measure the value
Final Goods and Services :
Some goods may not be market prices that exist to measure the value
Value- Added Approach :
Measures the value that is ADDED to GDP stage of production process
Produced Within a Country’s Borders :
GDP measures ALL of the final output produced on a country’s soil, or domestically/ regardless of which country actually owns the resources used in the production
In a Year :
GDP is flow variable
Even though GDP stats are measured quarterly, they measure the amount of output that would be produced in a year if economy was operated at a quarterly rate
Non-Market Transaction :
Some transactions are excluded from GDP stats even though they provided value to economy
—> EX : value of domestic labor / work done inside the household by household members. If I cleaned my house and the other person cleans their house, they are excluded from GDP. If we pay to clean eachothers houses and reported an income from it , then it would be included in GDP
Non-Productive Transactions are excluded :
Exchanges that do not increase production are not included in GDP
—> EX: Gov’t transfer payments such as Social Security, Temporary assistance to Needy Families (TANF). These represent a redistribution of wealth from taxpayers to recipients , but not to production in the economy
Second-Hand Goods are excluded :
Second hands goods are not calculated in the current year’s GDP. This is so they are not counted more than once
—> EX: Used cars, used bikes, used clothing
Goods produced but not Sold :
This in included in GDP as part of inventory Changes or a good component of investment
Sold to US = consumption spending
Sold to foreign customer = export spending
—> EX : if a bicycle your selling remains unsold in the current year, it’s treated as increase in inventories as part of investment spending
What does the labor force consist of ?
over 16 years of age
Not students
Not retired
Not in prison
Not in hospitals
Not in military force
People actively seeking work or working
College students employed if they have a job
College students not considered unemployed if they are without work
How is unemployment measured ?
By using a household Current population survey conducted on telephone
What does the unemployment rate ignore?
Someone working fewer hours than desired/ below their skill level
People without homes or phones are more likely to be unemployed but arent counted
Ignores discouraged workers—> Someone given up to look for work
GDP : The Expenditure Approach
Total spending in an economy on goods and services
Consumption, investment, government spending, net exports
Expenditure GDP= C + I + G + ( X - M )
GDP : As Final Output
Total value of final goods and services PRODUCED
Intermediate goods excluded
Σ( Pi x Qi )
GDP : Sources as income
Production side of GDP
Calculates GDP based on who earns money from PRODUCTION (income earned in an economy)
Wages, Interest, Net Factor Income from Abroad, Capital Consumption Allowance , Statistical Discrepancy
Income GDP = W + i + profit - NFIA + CCA + SD
GDP Expenditures = GDP as Sources of Income
Everything spent by consumers businesses, and the government turns to income for workers, businesses, and the government
Every dollar spent in the economy ( Expenditures ) becomes someones income ( sources of income)
GDP : Uses of Income
Consumptions Side of GDP
Total of income earned is spent or saved
Consumption Spending, Saving, Taxes, and Import Spending
Use of Income GDP = C + S + T + M
What can be used to Illustrate GDP?
Circular Flow Model
What is Circular Flow Model?
Assumes only 2 sectors of economy are households and firms
Shows interaction between households and firms in 2 markets ( Product Markets and Resource Markets )
%Δ Nominal GDP = ( Nominal GDP other year - Nominal GDP base year / Nominal GDP base year ) x 100
Nominal GDP base year = Real GDP base year
this is to determine how much output really increased form one year to the other
So we have to look at real GDP for both years
To calculate the Real GDP on the other year we must do…
Σ( Base year prices x Output in the other years prices ( Q ) )
% Δ Real GDP = (Calculated Real GDP in other year - Base year) / Base year X 100
GDP Price Deflator Equation :
GDP Price Deflator t = ( Nominal GDP t / Real GDPt ) X 100
Real GDP - Base Year Approach
Used until 1995
BEA Used to calculate this way but sometimes can cause problems
Real GDP - Chain-Type Growth Rate
BEA developed new way to measure Real GDP
MODERN AND MORE ACCURATE WAY to Calculate real GDP
Uses information from both
Chain - Type growth rate ( NEW WAY)
THEN :
—> Chain - Type Real GDP 2 = g x Real GDP 1
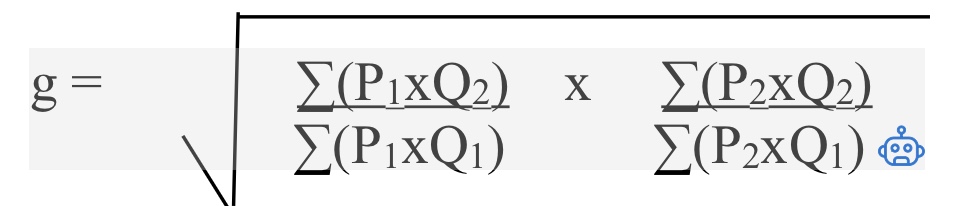
Chain - Real GDP Price Deflator
Chain - Type Real GDP Price Deflator t = ( Nominal GDP t / Chain - Type Real GDP t ) X 100
Chain - Type of Real GDP vs Base Year Approach
Measure of Real GDP = Chain - Type provides Lower estimate of Real GDP than Base Year Approach
Rate of inflation (GDP Price Deflator) = Chain - Type provides higher estimate of the rate of inflation compared to Base Year approach
Per Capita GDP
Per Capita = GDP / Population
Average Income Per Person in a Country
Countries with higher Per Capita GDP also have higher standards of living ( doesn’t always mean this though)
Doesn’t really acknowledge the distribution of wealth. It just shows the average. People with more money might oull up the per capita GDP
Factors of why GDP may not be accurate indicator of Social Welfare:
Defensive expenditures —→ people spend to protect themselves from perceived threats to their health and safety
Value of Leisure —→ benefits people get from free time when they aren’t working. Workers are not producing anything while consuming leisure time. Higher the GDP= less value of leisure
Population Differences —→ when comparing countries , one has to be careful. Countries could have high GDP due to population but the standard of living may not always be high (per capita GDP will be smaller )
Distribution of Income —→ Higher per capita GDP may disguise the great inequalities in income. Two countries might have same Per capita GDP but standards of living can be completely different. Doesn’t really tell us about the distribution of an economy which is important factor of determining quality of life
Cultural Differences—→ differences in cultures between countries make comparisons based on per capita GDP difficult. Countries where more goods are produced in the home (non-market transactions) then that country will have lower GDP since its not counted in the GDP. Countries have differences in whats legal and illegal. Also cultures differ in how they value leisure. Countries with higher divorce rates = higher GDP
Price and exchange rates —→ Changes in price/exchange rates can affect relative positions of countries that are being compared using per Capita GDP
Quality changes —→ GDP stats doesn’t always capture quality changes in the products included. Chnages how much value people get for their money
Wars and natural disasters—→ Changes GDP in way that doesn’t reflect change in happiness.
“GDP takes no account of increasing inequality, pollution or damage to peoples health and the environment. It treats crime, divorce, and other elements of social progress as economic gains”
Gini Coefficient
Measures income inequality in a country
Shows how evenly or unevenly income is distributed among people
Higher number means more inequality in a country
Gini Coefficient Equation :
Gini = (5000- A(area under lorenz curve ) / 5000
Lorenz Curve
graph where percent of total income earned ( y- axis)
And the percent of Population is plotted ( x - axis)