Anatomy Week 2 - Neck Muscles and Cervical Triangles
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Neck Muscles
Divided into 3 divisions: anterior, lateral, and posterior
Anterior Neck Muscles
divided into 4 divisions: superficial, suprahyoid, infrahyoid, and vertebral
Platysma
inserts at multiple points on skin of the lower face
muscle of facial expression
vascularized by submental branch of facial artery + suprascapular branch of thyrocervical trunk
innervation by cervical branch of facial nerve
Which nerve innervates all muscles responsible for facial expression?
Facial Nerve (CN VII)
Sternocleidomastoid
two heads
inserts on mastoid process
assists with forced respiration when head and neck and fixed
innervated by spinal accessory nerve (XI) and ventral rami
multiple blood sources: occipital, posterior auricular, superior thyroid and suprascapular artery
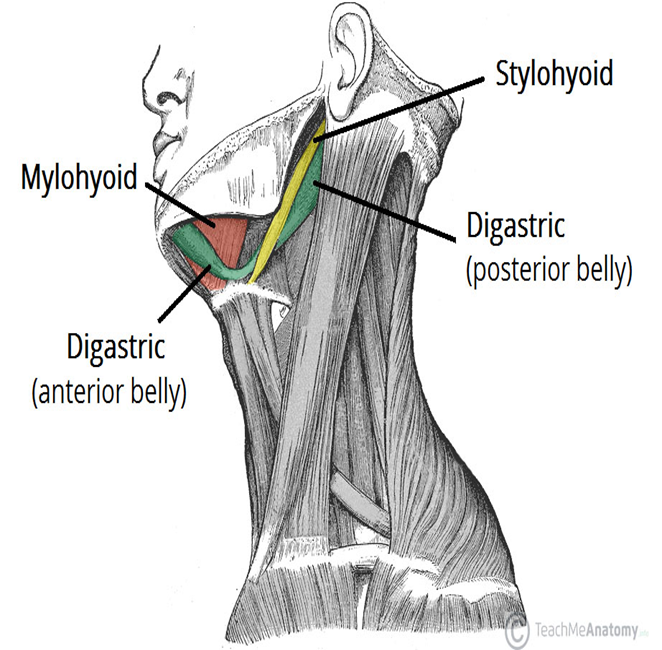
Suprahyoid Muscles
digastric, mylohyoid, geniohyoid and stylohyoid muscles
form floor of oral cavity
main function is to elevate the hyoid, which closes/depresses the epiglottis
Digastric Muscle
suprahyoid muscle
separated into an anterior and posterior belly; connected by intermediate tendon at hyoid bone
posterior originates at mastoid process, anterior originates at mandible
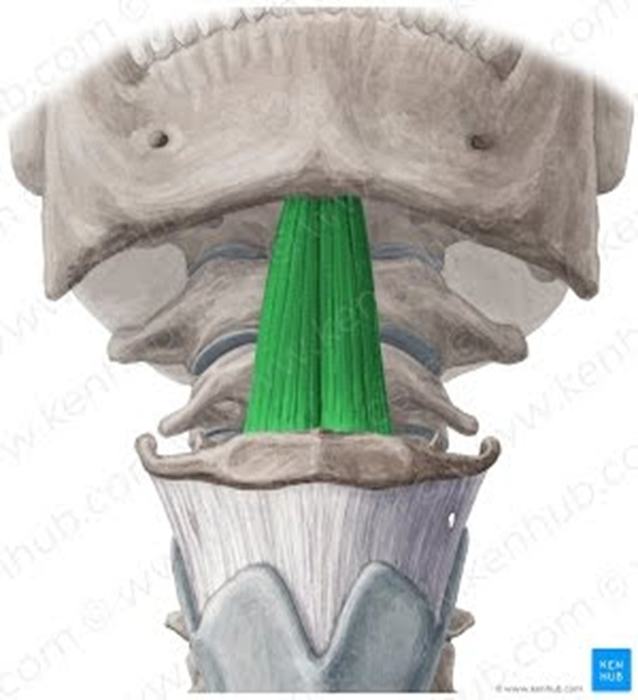
Geniohyoid Muscle
suprahyoid muscle
short, narrow muscle
connects from mandible to body of the hyoid
same function as others
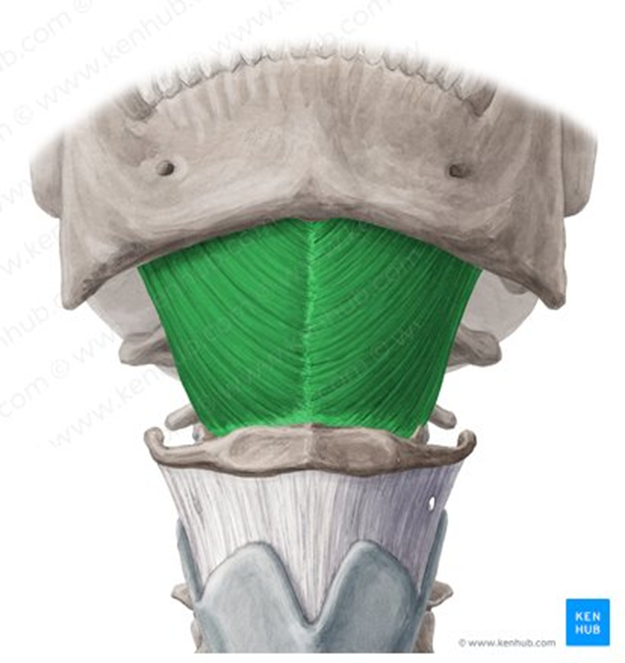
Mylohyoid Muscle
suprahyoid muscle
sheet-like muscle; forms much of the floor of the mouth
same functions
Stylohyoid Muscle
suprahyoid muscle
originates on styloid process of temporal bone
Infrahyoid Muscles
sternohyoid, omohyoid, sternothyroid and thyrohyoid muscles.
function to depress the hyoid, reopening the airway (allowing respiration), and play a role in vocalization
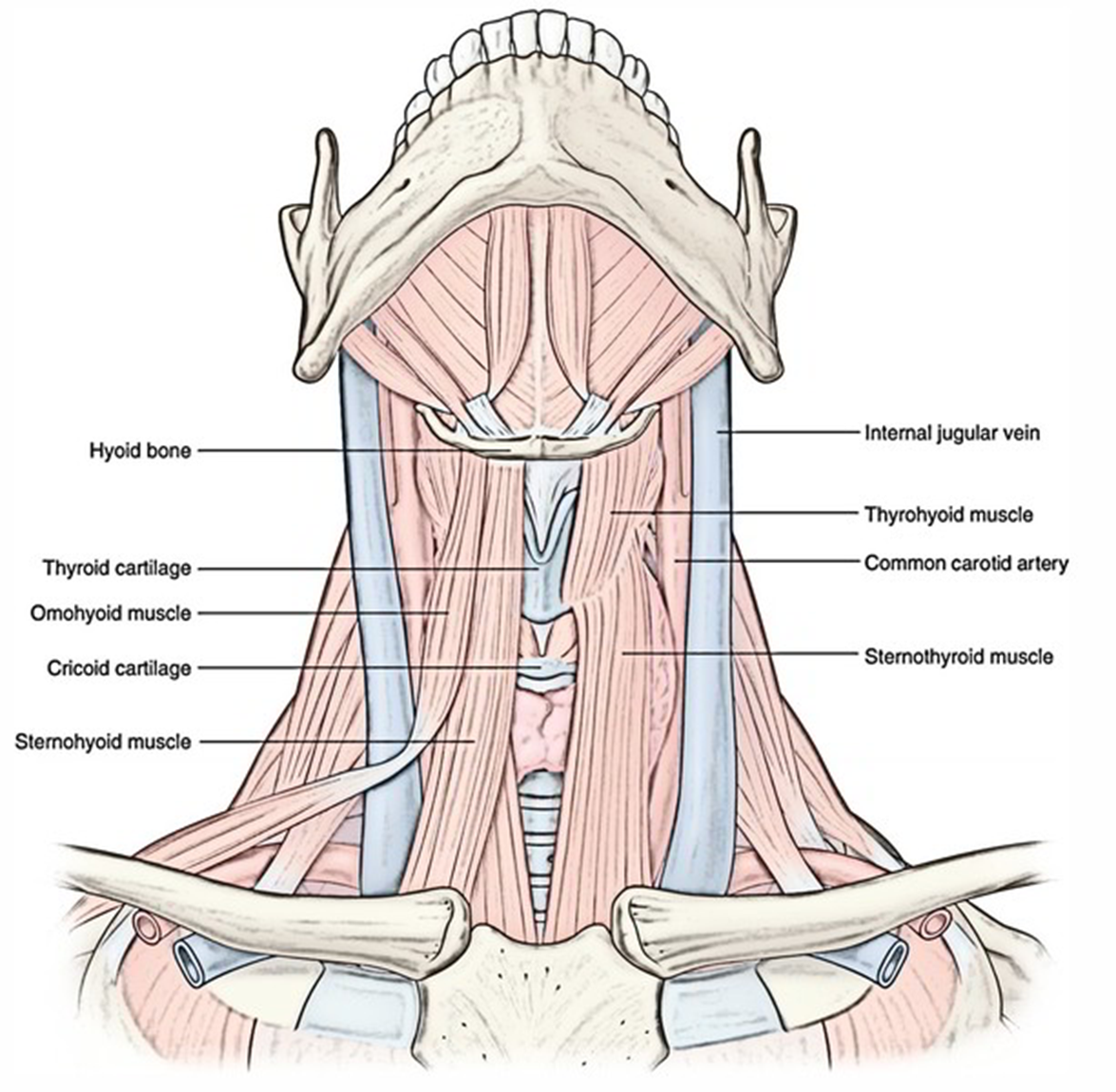
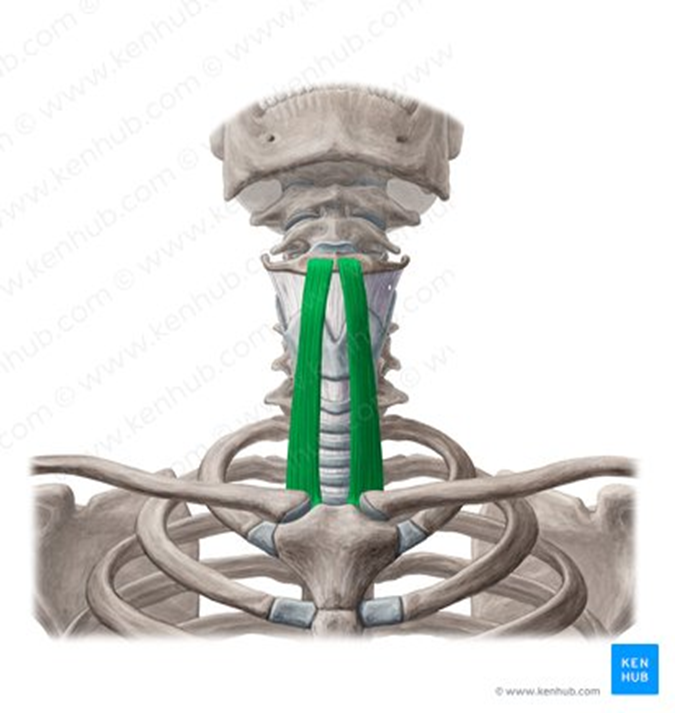
Sternohyoid Muscle
strap-like muscles; have to be moved during thyroid procedures
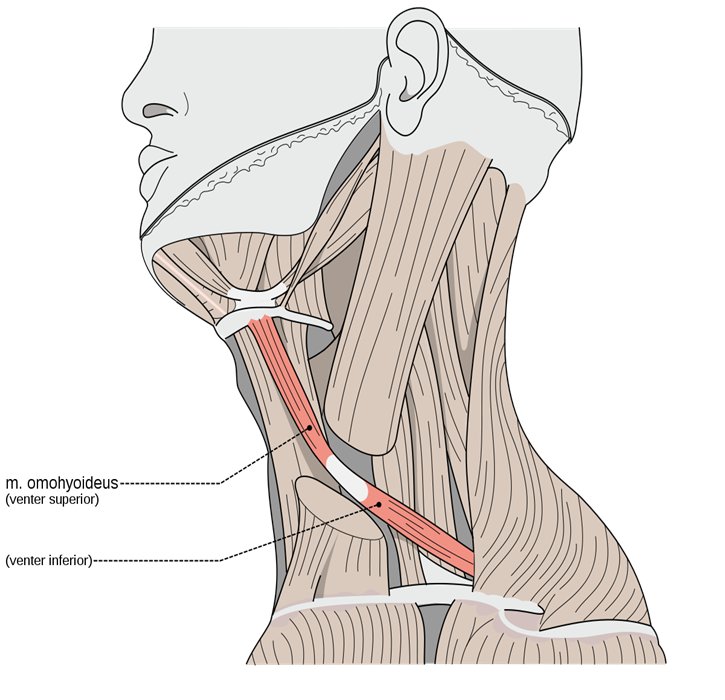
Omohyoid Muscle
divided into two bellies: inferior and superior which are connected by an intermediate tendon
inferior belly originates at superior border of scapula, superior belly originates from the tendon
“Om(o)ha(yoid), set, hut!” Muscle is curved like a football
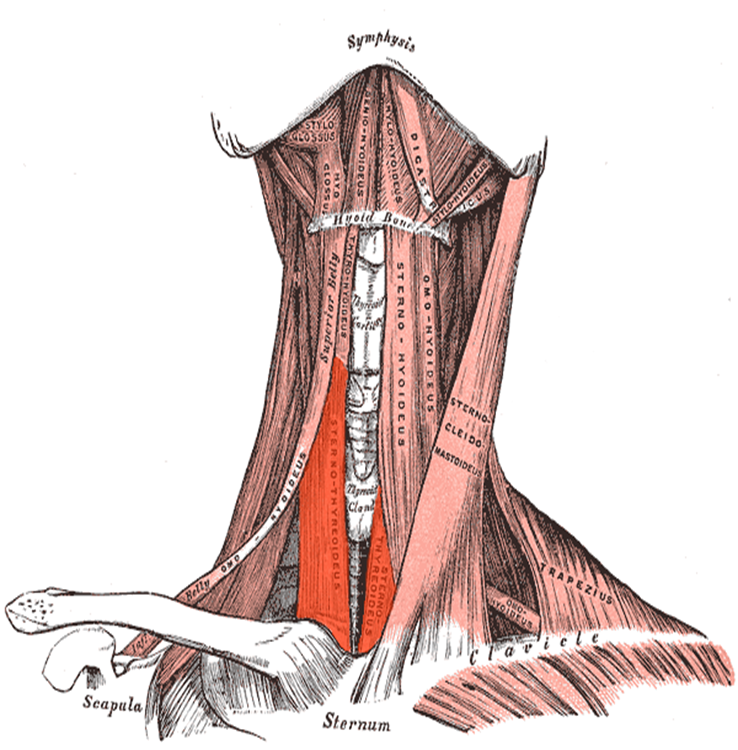
Sternothyroid muscle
strap-like muscle that runs from sternum to thyroid cartilage
doesn’t directly insert onto hyoid
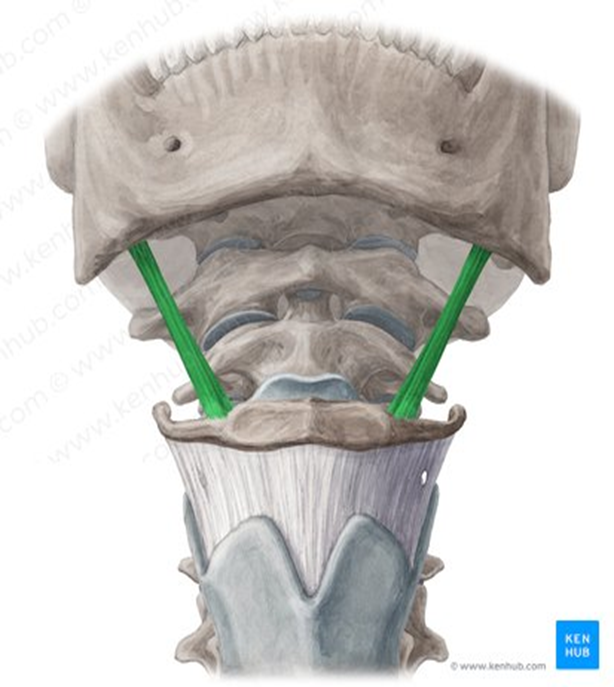
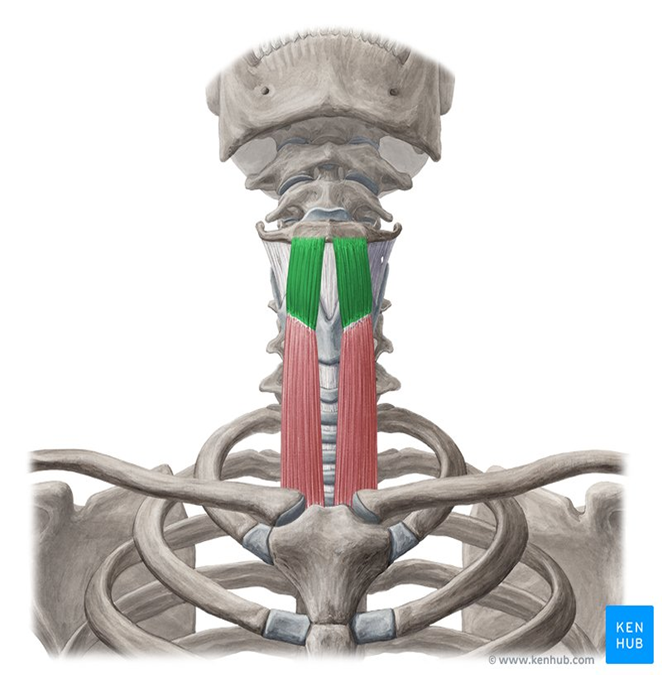
Thyrohyoid Muscle
highlighted in green
runs from thyroid cartilage to hyoid bone
has an additional function of elevating the larynx when the hyoid bone is fixed, important for singing high notes
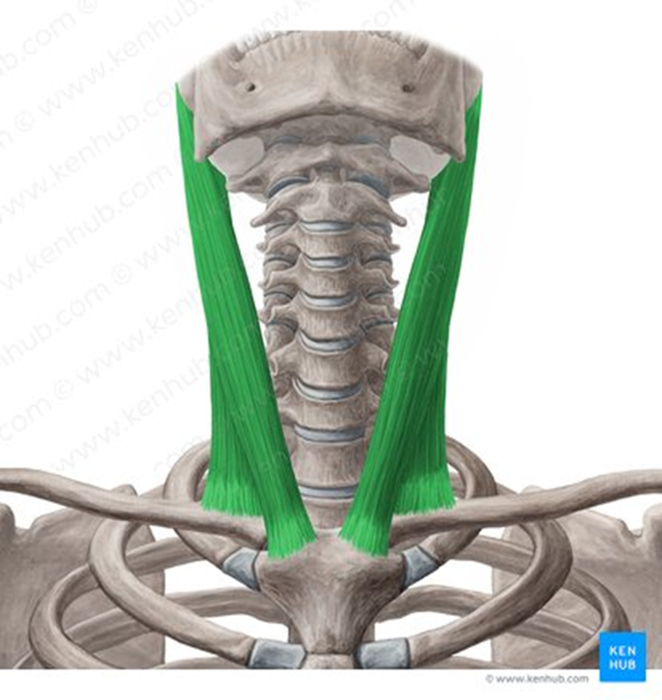
Vertebral Neck Muscles
include the rectus capitis anterior, rectus capitis lateralis, longus capitis and longus colli
mainly responsible for head flexion
also called prevertebral muscles (surrounded by prevertebral fascia)
Rectus Capitis Anterior
runs from anterior surface of lateral mass of C1 to occipital bone (anterior to foramen magnum)
flexion at the atlanto-occipital joint + stabilization
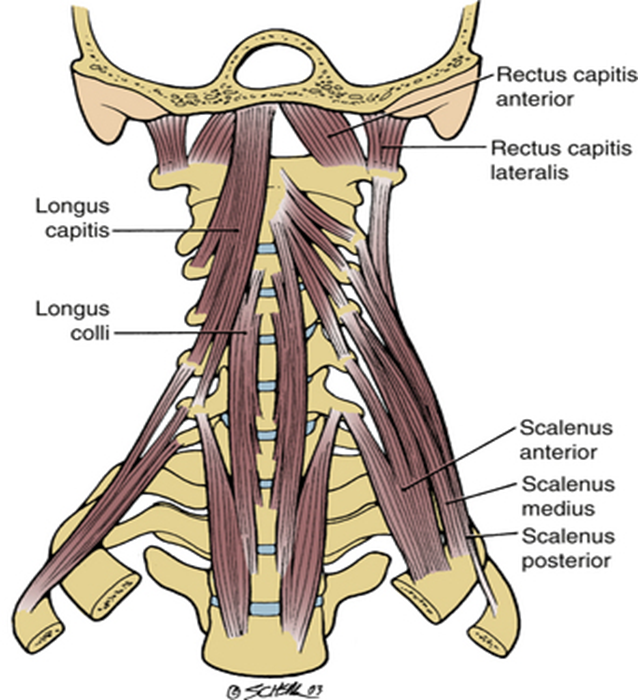
Rectus Capitus Lateralis
runs from transverse processes of C1 to inferior surface of jugular process on occipital bone
lateral flexion of the atlanto-occipital joint, stabilization
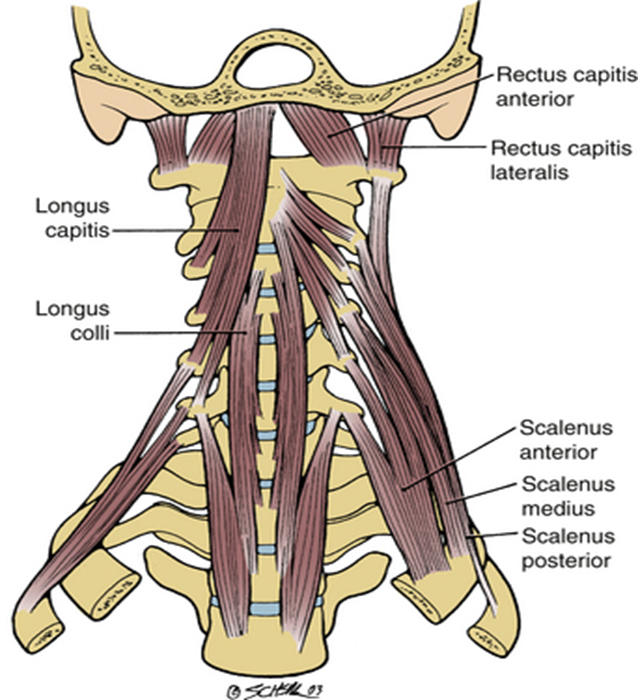
Longus Capitis
runs from cervical vertebrae to occipital bone, curves superomedially
weak flexion of head (bilaterally) + ipsilateral rotation (unilaterally)
Longus Colli / Longus Cervicis
stretches along all cervical vertebrae + upper portion of thoracic vertebrae
stronger head flexion, weak ipsilateral flexion + contralateral rotation
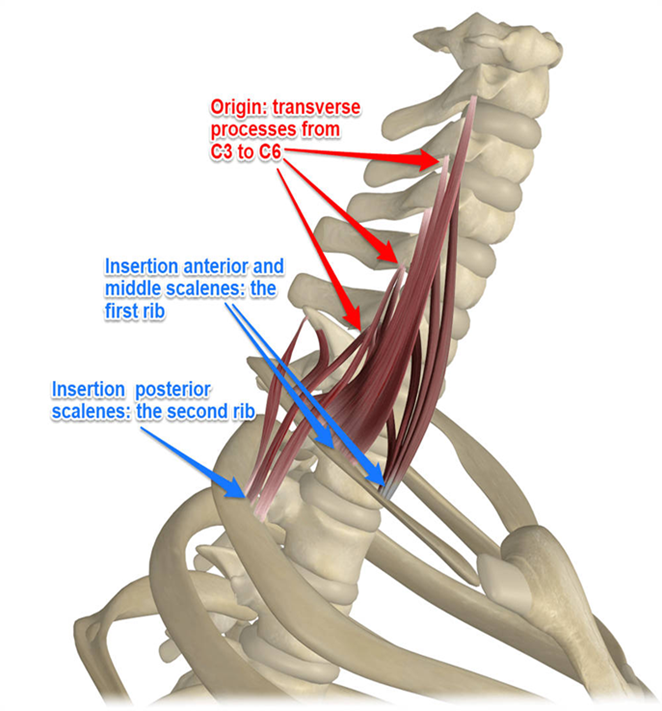
Lateral Neck Muscles - Scalenes
divided into anterior, middle, and posterior scalenes muscles
general + lateral neck flexion
also elevates ribs during forced inspiration (w/ fixed vertebral column)
Notes:
Anterior and middle scalenes insert on 1st rib, posterior scalenes on 2nd
Middle scalenes is the largest, posterior scalenes is the smallest
Posterior Neck Muscles (review)
Superficial — trapezius and splenius muscles
Deep — transversospinalis muscles
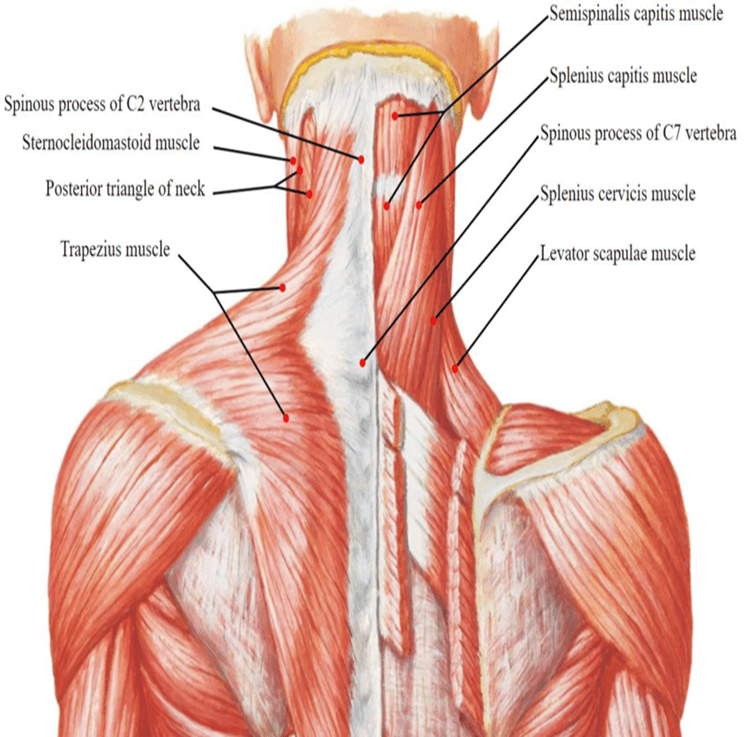
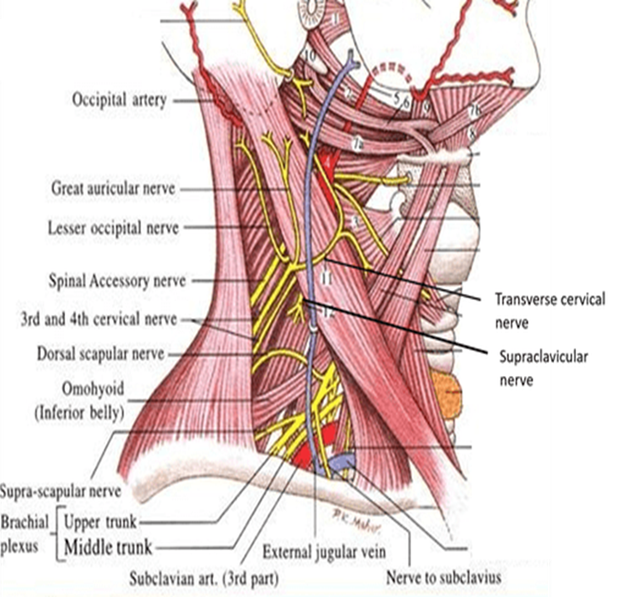
Cervical Triangles
The neck is divided into two large triangles by the sternocleidomastoid muscle: Anterior Triangle and Posterior
These main triangles are further subdivided into smaller triangles recognized by their specific boundaries and contents.
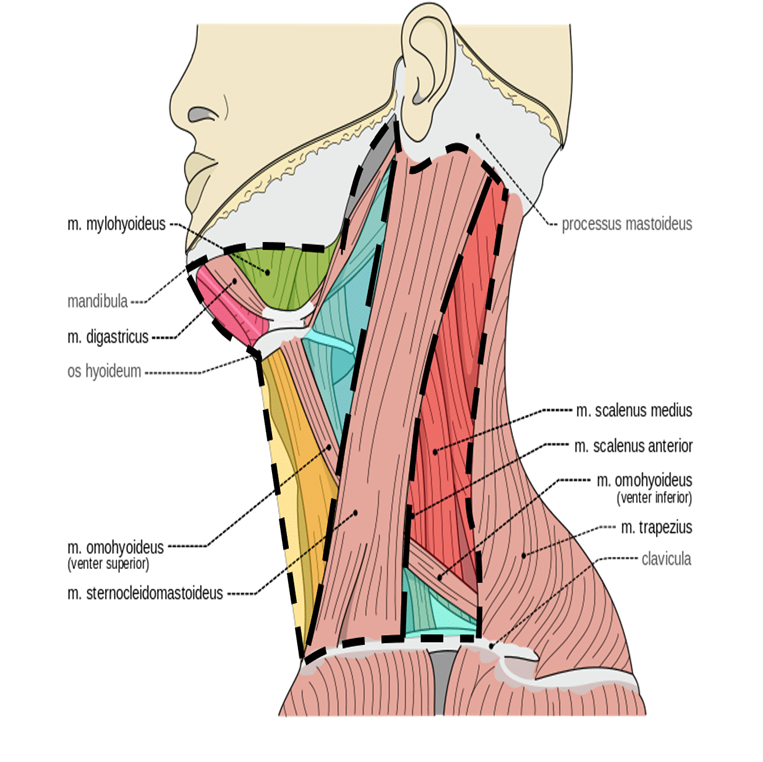
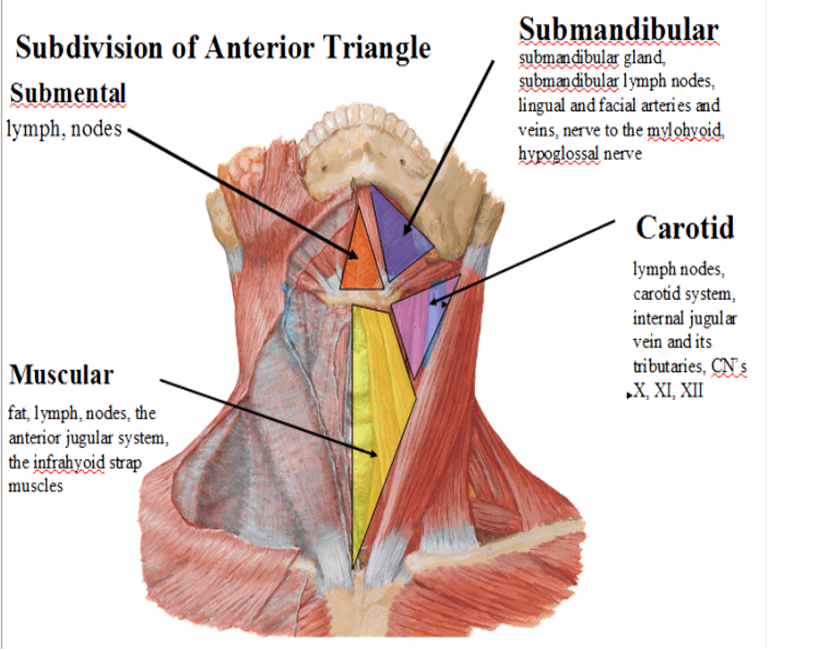
Anterior Triangle
formed by the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid laterally, the median line of the neck medially and by the inferior border of the mandible superiorly
further subdivided into muscular, submandibular, submental, and carotid triangles
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Thoracic outlet syndrome is not the name of a single entity but rather a collective title for a variety of conditions attributed to the compression of neurovascular structures as they traverse the thoracic outlet. The thoracic outlet is bordered by the scalene muscles, first rib, and clavicle.
Relevant structures: brachial plexus, subclavian artery + vein, scalenes muscles
Posterior Triangle
borders = trapezius posteriorly, SCM anteriorly, clavicle inferiorly
further divided into occipital triangle and supraclavicular triangle
Relevant structures of the muscular triangle
infrahyoid muscles
thyroid + its vessels (thyroid arteries), anterior jugular vein
larynx, trachea, esophagus
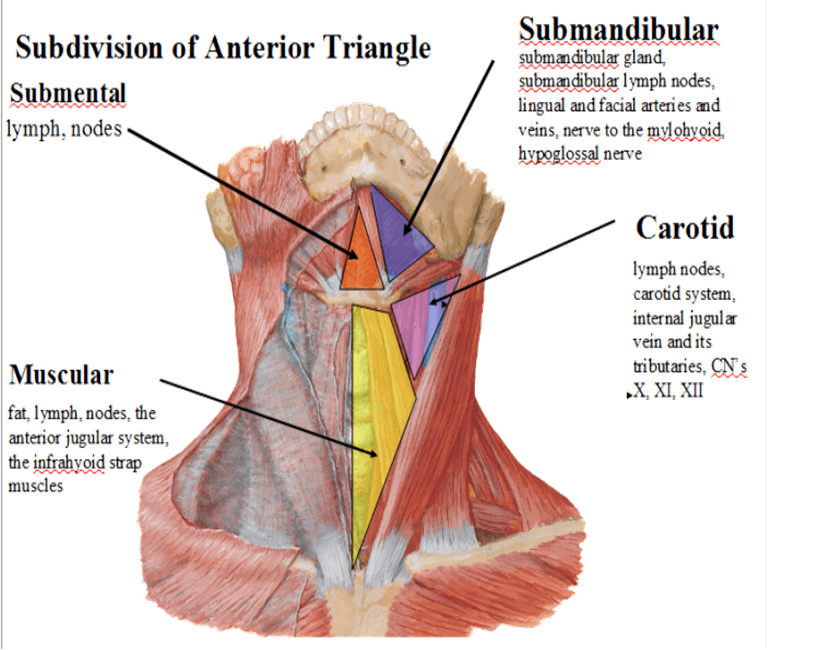
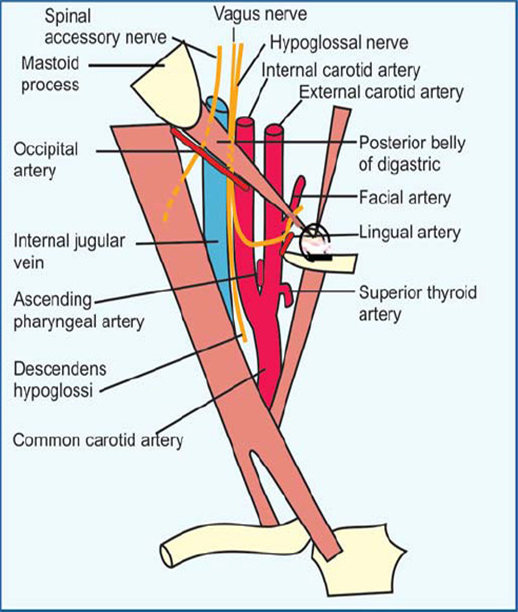
Relevant structures of the carotid triangle
Arteries: common, internal, external carotid (sinus at the base of internal)
Veins: internal jugular, common facial, lingual, superior/middle thyroid
Nerves: vagus (X), hypoglossal (XII), sympathetic trunk
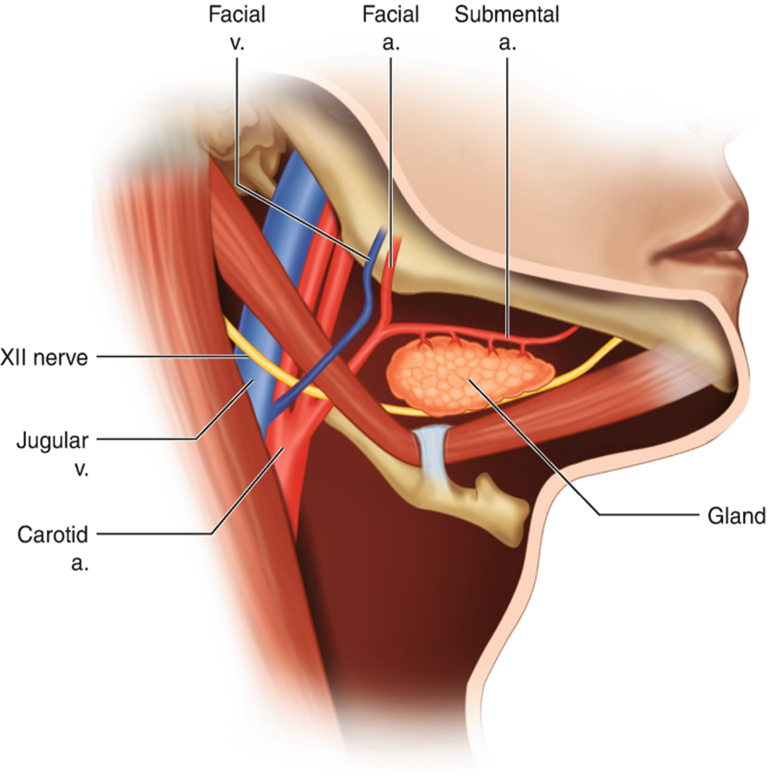
Relevant structures of the submandibular triangle
dental abscesses*
submandibular lymph nodes, and part of the parotid gland
facial artery + vein, submental artery + vein, lingual artery + vein
mylohyoid nerve and hypoglossal nerve (XII)
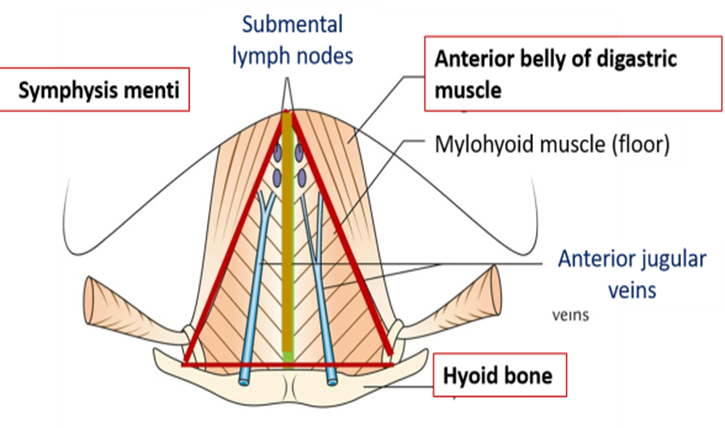
Relevant structures of the submental triangle
Anterior jugular vein and submental lymph nodes
Relevant structures of the occipital triangle
spinal accessory nerve (XI), cervical plexus + part of brachial plexus
supraclavicular nerve
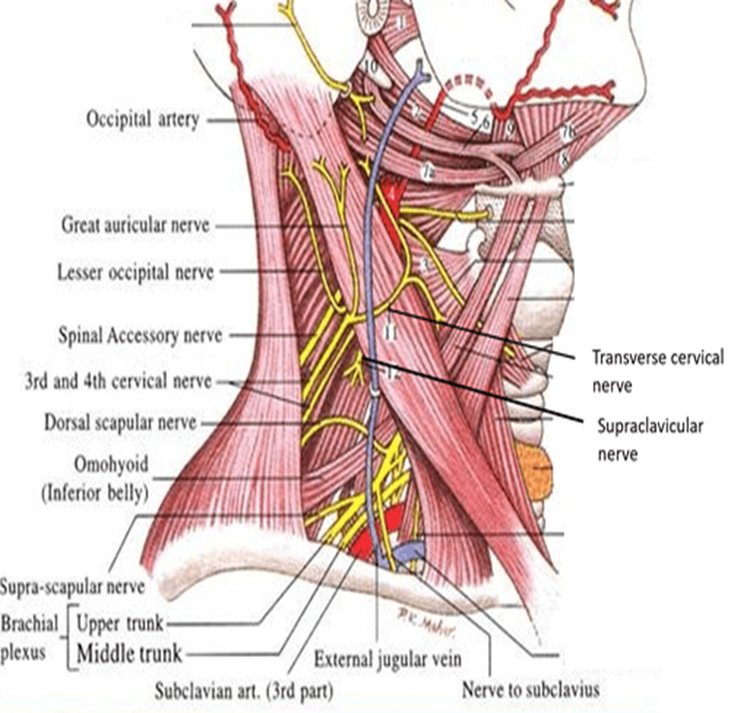
Relevant structures of the supraclavicular triangle
Third part of the subclavian artery, brachial plexus trunks, nerve to subclavius muscle, lymph nodes