ANTH 105 EXAM 3
1/157
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
Who can pronounce death?
M.E. - forensic pathologist
Coroner - elected or appointed
Doctor
First US Coroner
Maryland 1637
Training for coroner
no formal medical training required
First US M.E.
1890 Baltimore Maryland appointed 2 doctors
M.E training
Physicians with specialized training in forensic pathology
NAS recommendations for coroners and M.E.
Get rid of coroner system, replace coroner with M.E. in every jurisdiction
Why is the coroner system not gone yet?
political reasons, can be used as a political stepping stone, used in the south to cover up lynching
Forensic pathologist
a pathologist who studies disease and trauma that lead to death = M.E.
Pathologist
doctor who studies and diagnoses diseases in humans. = M.E.
Autopsy
Greek for seeing with ones own eyes , standard dissection of body to determine cause and manner of death
Hospital Autopsy
Did doctor make mistake
Medicolegal Autopsy
investigate sudden, unexpected, or suspicious deaths
External Autopsy
Older individual that lives alone, also draw blood
Authority to investigate deaths
from criminal violence, accident or suicide, sudden nature when otherwise in good health, unattended by a physician, custody of state/city, in a suspicious or unusual manner, family can request autopsy
Religion except from autopsy
Judaism, Islam = M.E. can override this, some jurisdictions try to respect religious practices
Death certificate
legally dead for voting, insurance, and tax purposes
Death investigation
Scene investigation, examination of the deceased, identification of the deceased, determine cause of death, manner of death, produce death certificate
Death
Irreversible cessation of circulatory. and respiratory function
Cause of Death
injury or disease responsible for the pathological and physiological disturbances that resulted in death (Medical reason for death)
Examples of cause of death
The final disease or injury causing the death
Natural causes of death
Heart disease, diabetes, cancer
Asphyxiation
interruption of oxygenation of the brain. ex: strangulation or positional
Exsanguination
death by loss of blood
Manner of death
the circumstances under which the cause of death occured
Manner of death classifications
natural or unnatural
Manner of death: natural
natural disease, dies under care of doctor
Manner of death: unnatural
homicide, suicide, accident, undetermined, therapeutic complication
Manner of death: therapeutic complication
person dies during operation, normal complications that may occur during medical interventions
Manner of death: accidental
died by car crash/ accidental mistake
Manner of death: suicide
killing yourself
Manner of death: homocide
dying at the hands of another, can potentially be accidental,
Homicide
Not all homicides are murder
All murders are
homicides
Manner of death: undetermined
not enough evidence
Injury: Antemortem
sustained prior to death, may have healed or shown signs of healing
Injury: Perimortem
occurred at or near the time of death, no signs of healing
Injury: Postmortem
occurred after death, considered “modifications” from events such as carnivore gnawing/freeze or thaw/weathering
Mechanical Trauma
Applied force exceeds the strength of tissue (sharp force + blunt force)
Chemical trauma
damage and death resulting from the interaction of chemicals with the body
Gunshot Trauma
Gunshot wound, bone fractures
Thermal trauma
extreme heat or cold
Hypothermia
too cold
hyperthermia
too much heat
electrical trauma
injuries or death caused by electricity passing through the body
Decomposition is
variable/predictable
Decomposition is used to
predict how long someone has been dead for
Taphonomy
The laws of burial, greek: taphos = burial or grave + nomos = law
Generally human decomposition follows…
a set of processes
Post Mortem Interval
Time since death, assessing time since death
Post Mortem Interval: What factors caused
the destruction of remains, the dispersion of remains, are there modifications to bone, are the bones human or non human
Forensic Taphonomy
Time and circumstances of death
Rodents prefer when bones are
dry
Decomposition Definition
systematic continuum of tissue breakdown
Two Significant decomposition processes
External and internal
external decomposition
soft tissue decomposition or desiccation
Internal decomposition
cell death and prolification
Stages of decomposition
Fresh, bloat , active decay, advanced decay, dry remains/skeletonized
Estimated PMI on
degree hours, summer vs. winter temperatures, accumulated degree of hours
External (Extrinsic) decomposition processes
environment, animal activity
Internal (Intrinsic) decomposition proccesses
autolysis, gut bacteria, green belly
Initial phases of fresh
Livor,algor, and rigor mortis
Livor-mortis
blood settles, discoloration, well formed in 3-4 hours , fixed 6-8 hours, highly variable, important to determine if body has been moved
algor mortis
body cooling, cold death, determined by liver or rectal temperature, highly affected by location/room temperature, drop about 2 degrees per hour, does not start immediately following death, drops to equal room temp, influenced by body size
rigor mortis
stiff muscles, the period of time that a body goes through a state of rigidity, usually starts 2-4 hours post death, peaks then subsides, 12 hours for whole body to go rigid, 2-36 hours body can show rigor
rigor mortis starts…
at head and goes down to toes
Fresh stage - eyes
fluid in eyes become cloudy
bloat
putric faction begins, autolysis causes cells to self-digest and bacteria proliferates
bloat: bacteria
as bacteria feeds, they produce CO2, causing abdominal swelling/bloat
Active Decomposition
Putrefaction - bacterial activity leading to destruction of surrounding tissue
Active Decomposition - marbling
red—> darker red—> purple—> green, large scale discoloration
Active Decomposition - Degloving
skin slippage
Active Decomposition - bugs start
flies attracted within minutes, lay eggs in eyes/nose, once eggs hatch turn into maggots
Advanced decomposition - decay
intense and increased soft tissue decomposition
advanced decomposition
most of fluids have leaked out, decomposition island
advanced decomposition - purge
liquefaction
advanced decomposition- hair mat
hair slips off
advanced decomposition
skin cracking
The dry stage of decomposition - skeletonization
exposure of bone to outside environment
The dry stage of decomposition
longest lasting stage, eventual breakdown of skeletal material, commonly affected by taphonomic process
Decomposition Variation
The formation of “grave wax” due to hydrolysis of lipids (fat), typically occurs in moist/ colder environments, can co-occur with “typical” decomposition
Decomposition Environmental effects
temperatures, sunlight vs. shade, insect access, humidity
Additional influence on decomp
geography, seasonality
Individual variations - decomp
disease factors, trauma, age, size, ratio of muscle to fat tissue, medications
PMI is the time between
death and discovery of corpse
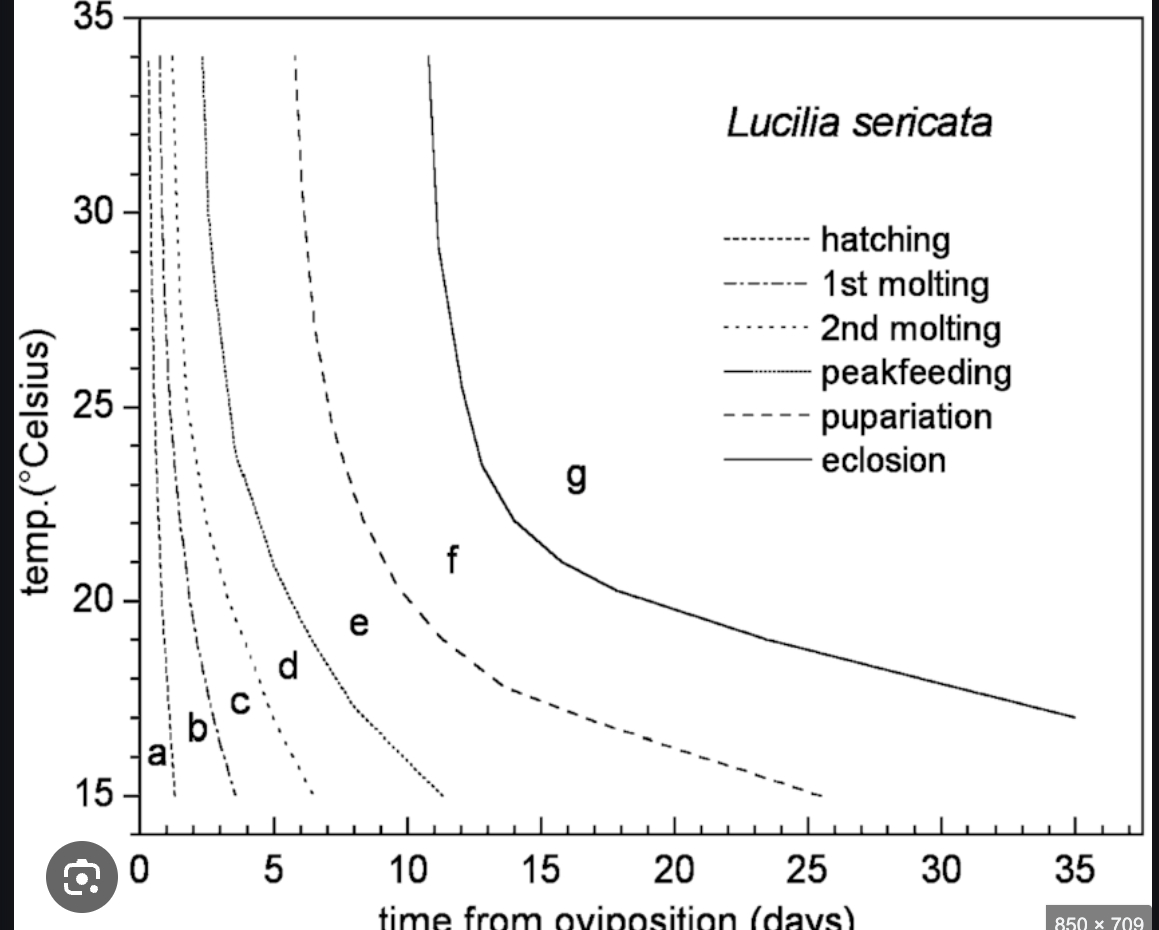
Isomorphe diagram
represents all the structural stages from hatching of eggs to eclosion phase
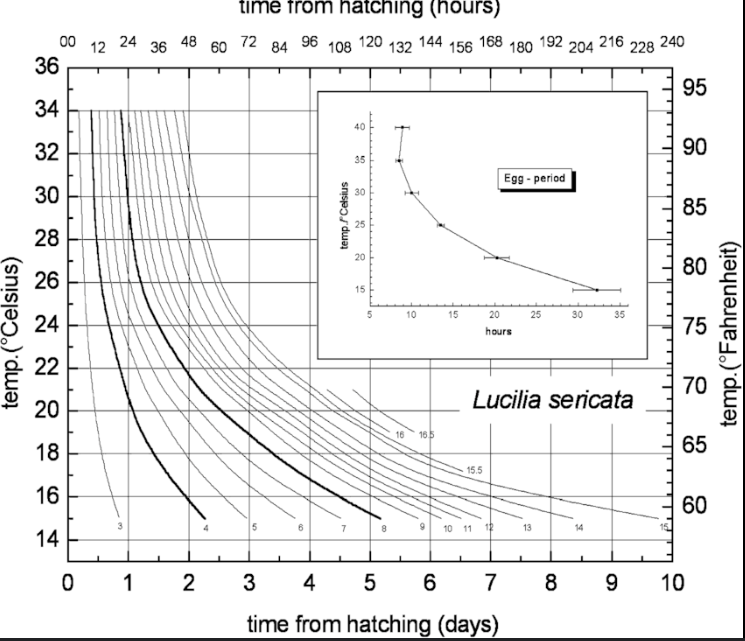
Isomegalem diagram
a chart that plots the size of larvae over time while accounting for environmental temperature less accurate than isomorphe graph
Forensic Entomology
study of insects and their arthropod relatives as applied to the legal system
Main application of forensic entomology
the determination of the minimum time since death
General areas for Forensic entomology
Urban - home infestations, Stored products pest - restaurants, medicolegal - criminal investigations
Medicolegal forensic entomology
criminal investigations
necrophagous
carrion feeding insects that typically infest human remains
Myiasis
infestation of live humans, ex. nursing homes
Entomotoxicology
drugs in insects feeding on humans, toxicology in insects = drugs in human being fed on by insects
Insect evidence is the most accurate method to estimate time of death up to…
72 hours
Post Mortem Interval
time since death
Insect activity can reveal
presence of drugs & toxins in the body, if body was moved from original location, if the presence of insects are not native to the area
Position of wound sites
can point out openings that are there other than typical eyes, mouth,ears
PMI can determine…
seasonality: temp, weather, humidity - development of insect
Development of insects
larval, weight, length, age - maggot eggs at 23 hours, blowfly at 143 hours
Diptera (flies)
four life stages: egg, larva (maggots), pupa, adult - show up within minutes of death