Introduction to psychological research
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is empirical research?
Gathering and analysing original research, using real-world evidence
What is a hypothesis?
Clear, testable prediction or idea about what you expect to happen
What is a theory?
A broader, established explanation of behavior/experience based on multiple studies
What is quantitative research?
Numerical data
What is qualitative research?
Non-numerical data
What is experimental research? (3)
Quantitative
Manipulate control variables
Random assignment
What is quasi-experimental research? (3)
Quantitative
No random assignment
Measuring cause and effect relationships
What are the 4 types of non-experimental research?
Correlation
Descriptive
Survey
Observational
What is ethnography research?
Qualitative
Immersion into culture/daily life of participants
What is phenomenology research?
Qualitative
Studying an event or activity as it happens from different perspectives/insights
What is a case study?
Qualitative
In-depth understanding of one participant
What is narrative research?
Qualitative
Gathers data from participant(s) over time, focusing on the experience of the individual
What is an extraneous variable?
Other factors that could influence the DV but are not the main focus (should be controlled)
What is a confounding variable?
A variable which overlaps with the IV and affects the DV
What are demand charactersits?
Participants chanting their behaviour
What 6 ways can we control for extraneous variables?
Control groups
Randomization
Grouping participants based on certain characteristics
Statistical control
Holding variables constant
Pre-screening participants
What is volunteer sampling?
Participants sign up through adverts
What is opportunity sampling?
People who are available and willing to take part
What is random sampling?
When everyone from the target population has an equal chance of being picked
What is systematic sampling?
A system to pick participants (eg. The Nth person)
What are the 3 types of reliability?
Test-retest- the test produces similar results over time
Inter-rater- degree of agreement among different raters when assessing the same phenomenon
Internal consistency- How well the items on the test measure the same concept
What are the 4 types of validity?
Face- does it measure what it is meant to
Construct- does it measure the theory it’s meant to
Criterion- how well one measure predicts an outcome based on another measure
External- can the findings be generalised/used in other contexts
What are the pros of qualitative research? (4)
Detailed
Patterns and themes
Flexible
Contextualises data
What are the cons of qualitative research? (5)
Limited generalisability
Time consuming
Bias
Complexity in analysis
Researcher presence
What is primary qualitative data?
Collected through interviews or first hand descriptions
What is secondary qualitative data?
Analysing existing documents
What is a structured interview?
Highly controlled with closed-ended questions
What is a semi-structured interview?
Has a guide for questions but can ask additional questions
What is an unstructured interview?
No set questions (just a topic) just open ended ones, with natural flow
What is thematic analysis?
Identifying patterns or ideas across data
What is content analysis?
Analysing various sources of data to quantify data (counting occurrences of themes/words)
What is narrative analysis?
Examines stories from individuals to understand how they contrast
What is grounded theory?
To develop a theory grounded in data collected
What is discourse analysis?
To study language use and communication
What is interpretative phenomenological analysis?
Lived experience of individuals
What are Braun and Clarke’s 6 steps to thematic analysis?
Data Familiarisation
Initial coding generation
Search for themes
Review of themes
Theme definition and labelling
Report writing
What is nominal data?
Categories/lables
(E.g. fruit: Apples, Bannanas, Oranges…)
What is ordinal data?
Categories are ranked/ordered with a logical relationship
(E.g. Eduation: High school, Bachelor’s, Master’s, PhD
What is interval data?
Numerical values with no ‘true zero’
(E.g. Dates on a calendar)
What is ratio data?
Numerical data with ‘true zero’ were all mathematical operations work- you can calculate ratios
(E.g. Income)
What is true zero?
Represents complete absence of the measure- 0° doesn’t mean ‘no heat’
What are inferential statistics?
Uses sample data to make predictions, decisions or generalisations about a population
What does variance tell us?
Higher variance= data points more spread out
Lower variance= data points closer together/clustered
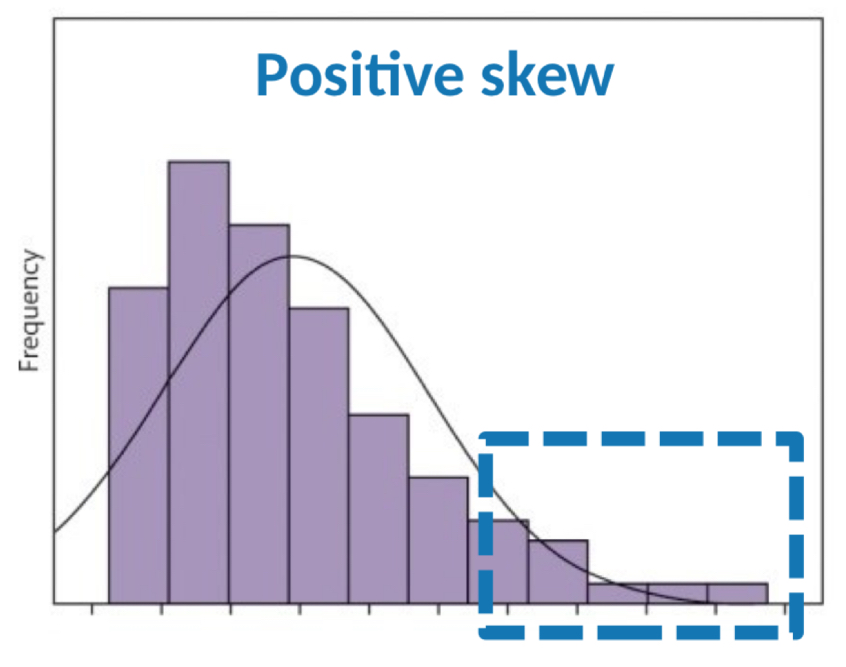
What is positively skewed data?
Data skewed to the right- tail is longer on the right, but most data is on the left
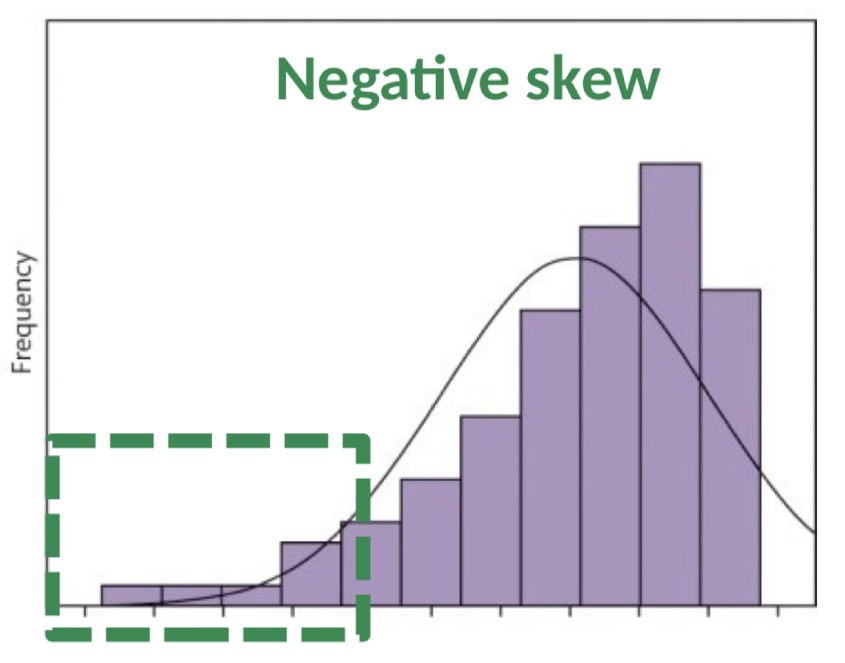
What is negatively skewed data?
Data skewed to the left- tail is longer on the left, but most data is on the right
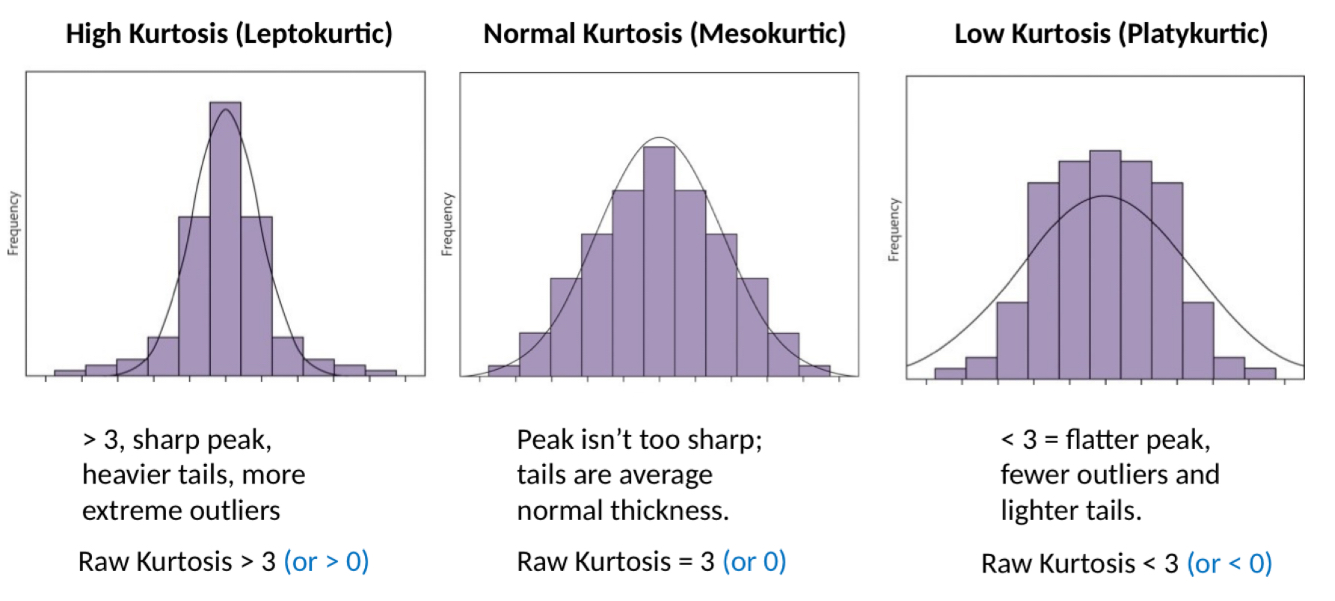
What is kurtosis?
How sharp the shape of the distribution is
What is Bimodal Distribution?
Data with two clear peaks- typically occurs when data comes from two different groups
How do we calculate the Z-score?
Z=\frac{X-\mu}{\sigma} where X = observed score, \mu = population mean, \sigma = standard deviation
What is the Empiral Rule?
68% of data falls within 1 standard deviation of the mean
95% of data falls within 2 standard deviations
99.7% of data falls within 3 standard deviations
What is the central limit theorem?
The sampling distribution of the mean approaches a normal distribution, as the sample size increases
What are the 3 key features of a hypothesis?
Tesatble
Specific
Falsifiable
What is a null hypothesis?
There is no effect or relationship
What is an alternative hypothesis?
There will be an effect or relationship
When should your alternative hypothesis be one tailed?
When there is a specific direction of change
When do you reject the null hypothesis?
If p<0.05 this is a significant result so you can reject null hypothesis
What is a type 1 error?
Rejecting the null hypothesis when you should accept it
What is a type 2 error?
There is an effect, but we fail to reject the null hypothesis
What is statistical power?
If an effect truly exists, power is the likelyhood you will detect it
What is a Chi-squared test called when there is 1 variable?
Goodness of fit
What is a Chi-squared test called when there are two variables?
Test of association
What must the expected frequency of a cell be in the Chi squared test?
At least 5
What does the chi squared test tell us?
Whether the observed frequency is different from the expected frequency (yes or no)
How do you know degrees of freedom?
For one variable: Number of cells - 1
For two variables: (Number of rows - 1)(Number of columns - 1)
How do you write up a Chi-squared test in APA standard?
\chi2 (df, N=XX) = XX.XX, p = .XXX
N = number of participants
What result should you put if JASP gives .000?
p < 0.001