Unit 2 Test Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Radio isotopes, free radicals, artificial foods
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is a protein?
A biomolecule composed of amino acids that participate in nearly all cellular activities
What are the functions of proteins?
Enzymes - speed up reactions
Structural support
Storage of extra energy
Defense against disease
Regulation passage of fluids through cell membrane
Signaling in cells
What is an amino acid and its structure?
Amino acids make up proteins,
Made up of a central carbon atom attached to a hydrogen, an acidic carboxyl group
How many amino acids are there in the body, and how do the amino acids differ?
There are 20 different types of amino acid.
They differ in which R chain is connected to them. This R chain determines their function
What are the four levels of structure in a protein?
Primary - amino acid sequence
Secondary - local folding patterns
Tertiary - Provides overall shape of protein at this point
Quaternary - Quaternary structure occurs in proteins that are made up of more than one polypeptide chain.
Why is protein structure important?
It allows them to do their job. Proteins are like keys. They fit together with other molecules to complete a job.
When a protein loses it’s shape it becomes denatured.
What happens to proteins with changes in ionic composition, temperature, and pH?
It becomes denatured and loses its shape
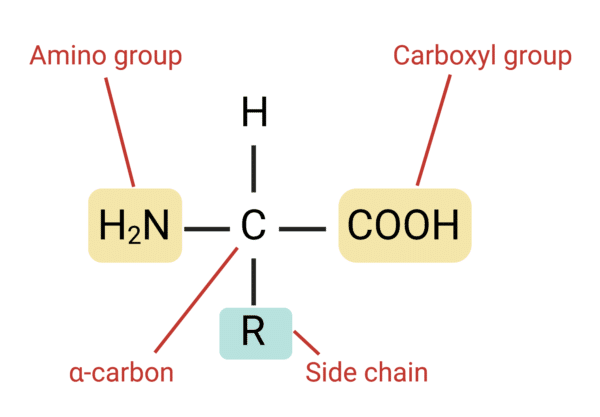
Be able to identify a protein (both amino acid)
Central Carbon, Hydrogens coming off of it, Carboxyl group and R chain
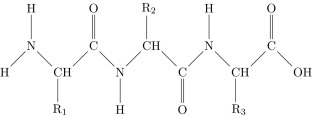
Be able to identify a protein (polypeptide)
Look for nitrogen, long snaking chains
What is a nucleic acid?
A chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems
-creates DNA/RNA
What elements make up a nucleic acid?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus
What is DNA and what is its function? What is RNA and what is its function?
DNA is responsible for storing and transferring genetic information
RNA directly codes for amino acids and as acts as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes to make proteins.
What is a nucleotide? What are the three parts of a nucleotide?
Nucleotides are organic molecules that serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid
they are made up of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base
What are the 5 types of N-bases?
Adenine (A),
Cytosine (C),
Guanine (G),
Thymine (T)
and Uracil (U).
What is a purine and pyrimidine?
They are nitrogenous bases that make up the two different nucleotides in DNA and RNA.
Purines (adenine and guanine) are two-carbon nitrogen ring bases
Pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) are one-carbon nitrogen ring bases.
What structural differences are there between DNA and RNA?
DNA
Double Stranded, Thymine base
RNA
Single Stranded, Uracil Base
What is complementary base pairing?
What bond holds the complementary base pairs together?
These bonds hold the two strands of the molecule together. Bases pair up with each other in a consistent way
-Hydrogen bonds
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element whose nuclei contain different number of neutrons (same properties different masses)
What is a radioisotope?
A radioactive isotope that has nuclei that are unstable and spontaneously break down.
How are radioisotopes used in medicine?
Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radiation to provide information about a person's body and the functioning of specific organs, ongoing biological processes, or the disease state of a specific illness
(can also break down specific tissues and cells around reaction, such as cancer cells)
What are free radicals?
a molecule with one or more unpaired electrons in its outer shell (missing one valence shell electrons)
How do free radicals enter the body?
Endogenously (created in the body, but body can healthily regulate them)
Exogenously (excessive buildup)
water/air pollution
cig smoke
cooking methods, smoking meats, fats/oils in food
radiation
heavy metals entering body
How are free radicals beneficial? Harmful?
Beneficial
Fights disease, Defeats invading pathogens, Involved in inflammation responses
Harmful
Alters DNA/protein activity, lipids, and membranes. Increases aging/chronic diseases, Loss of enzyme activity
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants are minerals, compounds that when broken apart have an extra electron.
Antioxidants neutralize free radicals and protect cells against their toxic effects by adding an extra electron to balance them.
Endogenous, produced in body’s enzymes
Exogenous, from diet (ex. Tomato)
What is a trans fat? Describe its chemical structure.
A transfat is a fat that has been saturated with hydrogen.
Chemical structure: unsaturated fats with trans double bonds instead of cis bonds. The carbon chain isn’t bent and can’t be broken down.
What is hydrogenation?
Adding hydrogen into the unsaturated bonds of a fat. this forms transfats
Why are trans fats harmful?
They can’t be broken down in our body because the carbon chain isn’t bent
Why do companies use artificial fats and sugars like Olestra and sucralose? How does these fake foods affect our bodies?
To enhance taste of food without adding harmful fats and sugars.
Sugar substitutes also don't raise the level of sugar in the blood.
Products made with sugar substitutes also may give you the wrong message about processed foods. A snack labeled low sugar or no sugar may not be the most nutritious choice