Lecture 11: The Cytoskeleton Part 1
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Three kinds of filaments that make up our cytoskeleton
Intermediate Filaments
Actin Filaments
Microtubules
Cytoskeleton Definition
organized networks within cells that give cells structure
Polarity, meaning and what filaments are polar/non-polar
polarity relates to the top & bottom being the same (non polar) or not.
Actin & Microtubules are polar & Intermediate Filaments are non-polar
Subunits (what they are and how they’re held together)
the building blocks of each filaments, held thorough IMFS
Intermediate Filaments (Function) (TENSILE & ROPE LIKE)
prove strength and structure to the cell (MUSCLE CONTRACTION)
tensile and rope like
Intermediate Filaments subunit
a tetramer
staggered anti-parallel tetramer of two coiled dimers
NON-Polar
What gives intermediate filaments their noble strength
their side to side & lethal interactions make them tensile and rope like
The Two Types of Intermediate Filaments
Cytoplasmic (Keratin Filaments)
Nucelar Filaments
Keratin Filaments (function & location)
distributes stress between cells
anchored to the plasma membrane of the cell
The keratin filaments are linked together from cell to cell
Nuclear Filaments
nuclear lamina
provide strength and support for the nuclear membrane
Actin Filaments
highly dynamic because subunit can be removed real easy
Polar
MONOMER is the subunit (amino & carboxyl sides)
Microtubule Filaments
Hollow cylinders of tubular heterodimers (alpha & beta [on top])
highly dynamic
MT filaments subunit
a heterodimer, made up of alpha and beta tubulin where beta tubular is on the top
Actin Filament Subunit
a monomer; single protein
Plus & Minus Ends (what do they mean)
plus end: taste growing
minus end: slower growing
Why do filaments (actin & MTs) have polarity
so that motor proteins have google maps (know where to go)
Motor Proteins Anatomy
Heads that walk and tails that hold the cargo
Some idiot named this
Microtubule motor proteins
dynein (-) & kinesin (+)
dynein is nein in German which si no an negative and it goes to the negative side
Kinesin is like adding a phosphate which is happy happy and it goes to the positive side
How do MT motor proteins walk (what causes it)
ATP hydrolysis & exchange
How sliding MT’s & Actin works
there is an anchor attaches o the motor protein, when the motor walks it causes the filament to slide in the opposite direction
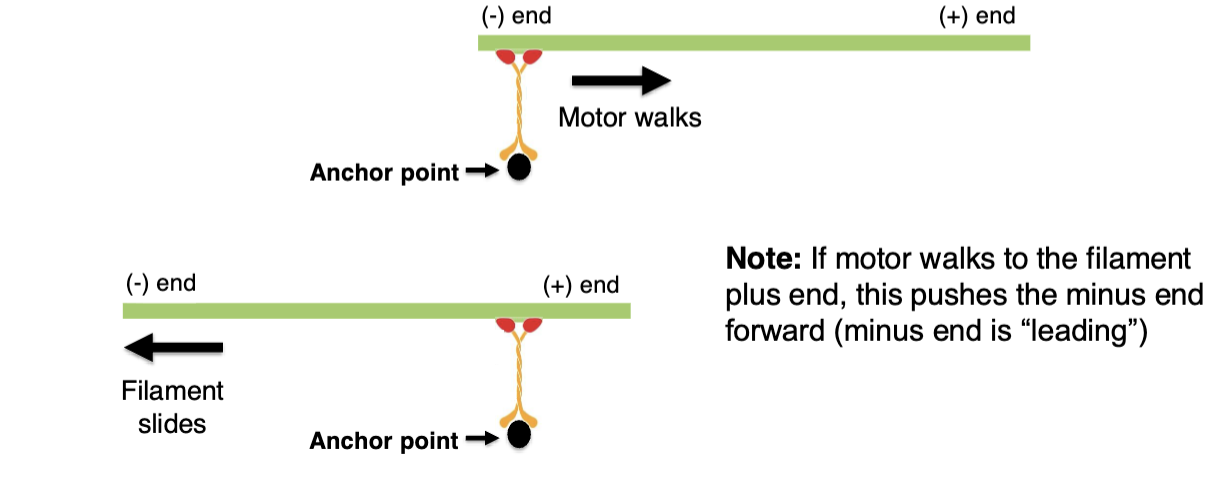
Actin Motor Protein
Myosin-
Walks to the plus end
Myosin 2
ENTIRE job is to slide actin filaments
dimer
heads walk on actin
multiple motors can assemble together to form a bipolar filament
Can form contractile structures
Job is to do muscle contraction