Geography - Coasts - Enquiry Question 1 - Why are coastal landscapes different and what processes cause these differences?
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is a concordant coastline?
Where layers of hard rock and soft rock are parallel to the coasts, meaning that the coastline is just hard rock or just soft rock.
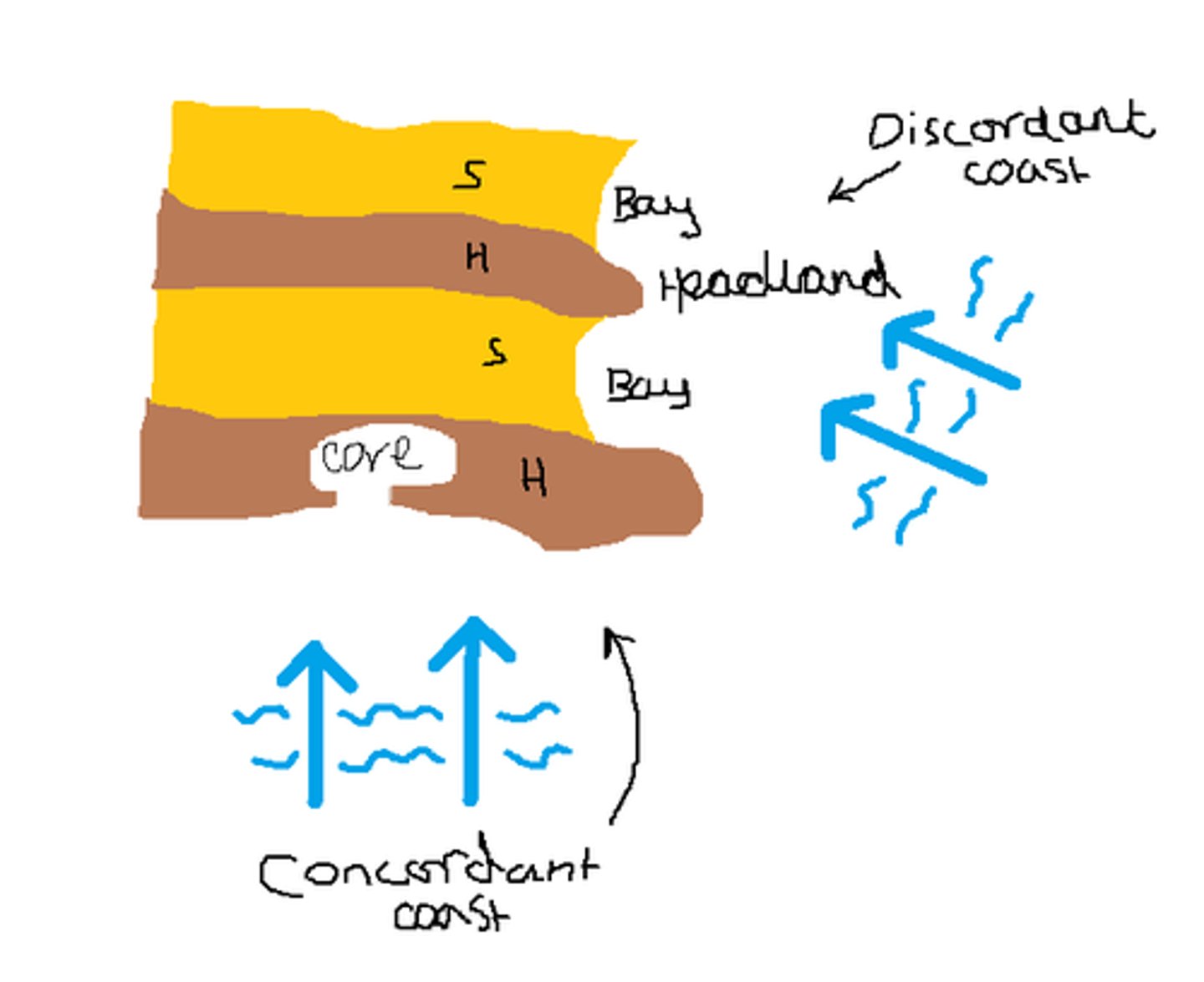
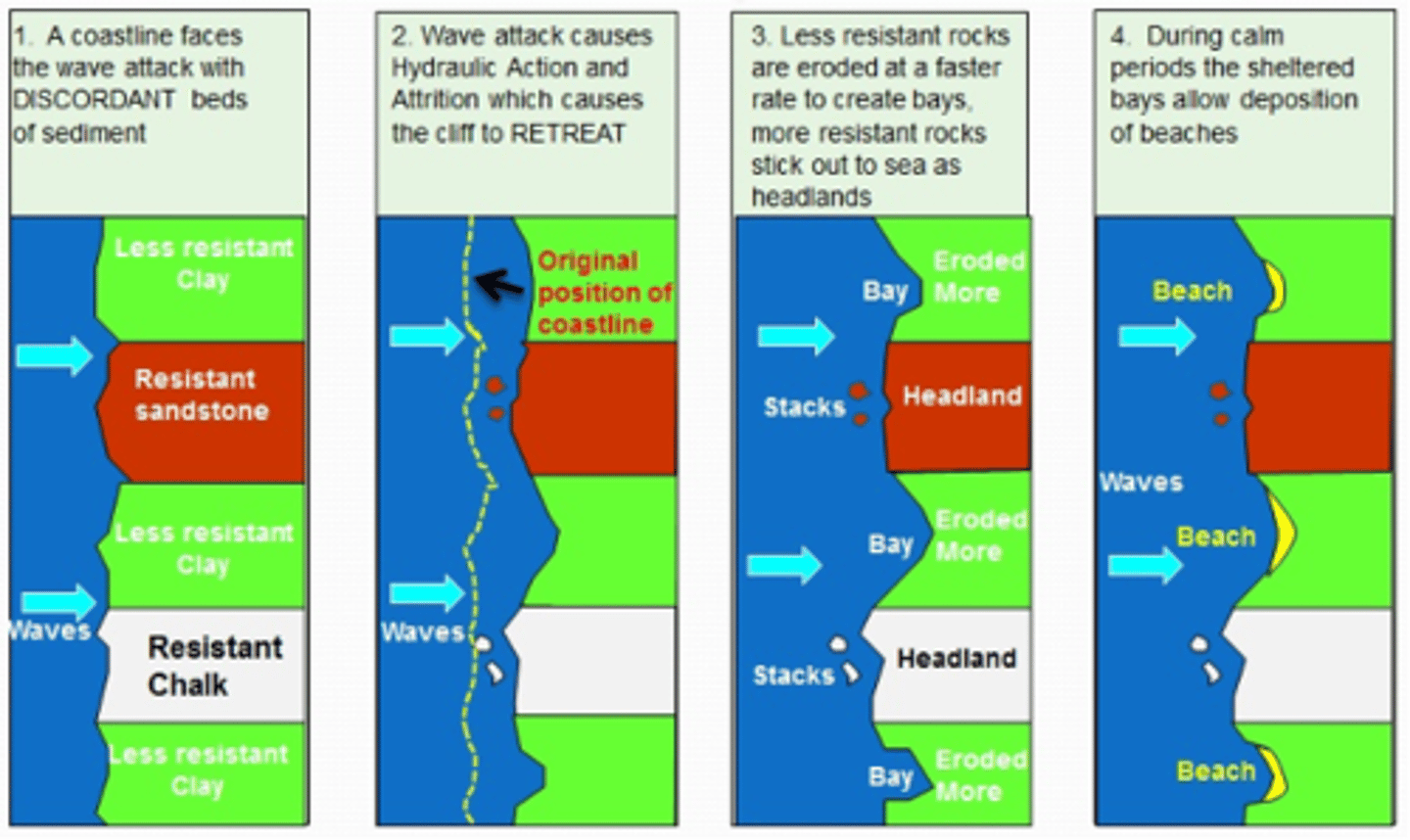
What is a discordant coastline?
Where layers of hard rock and soft rock are perpendicular to the coast, meaning that the coast is made up of multiple types of rock.
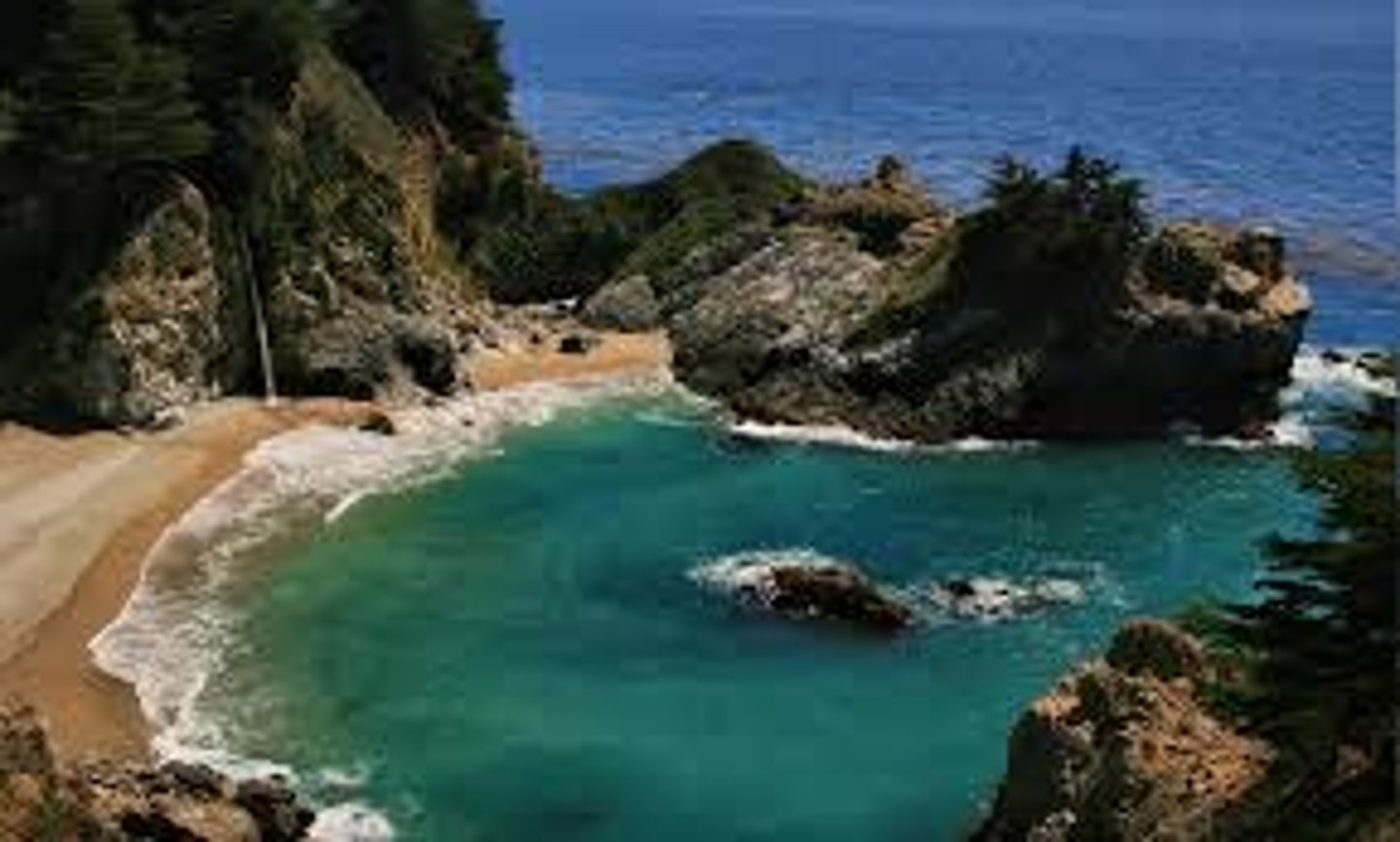
What landforms are formed on a concordant coastline?
Coves

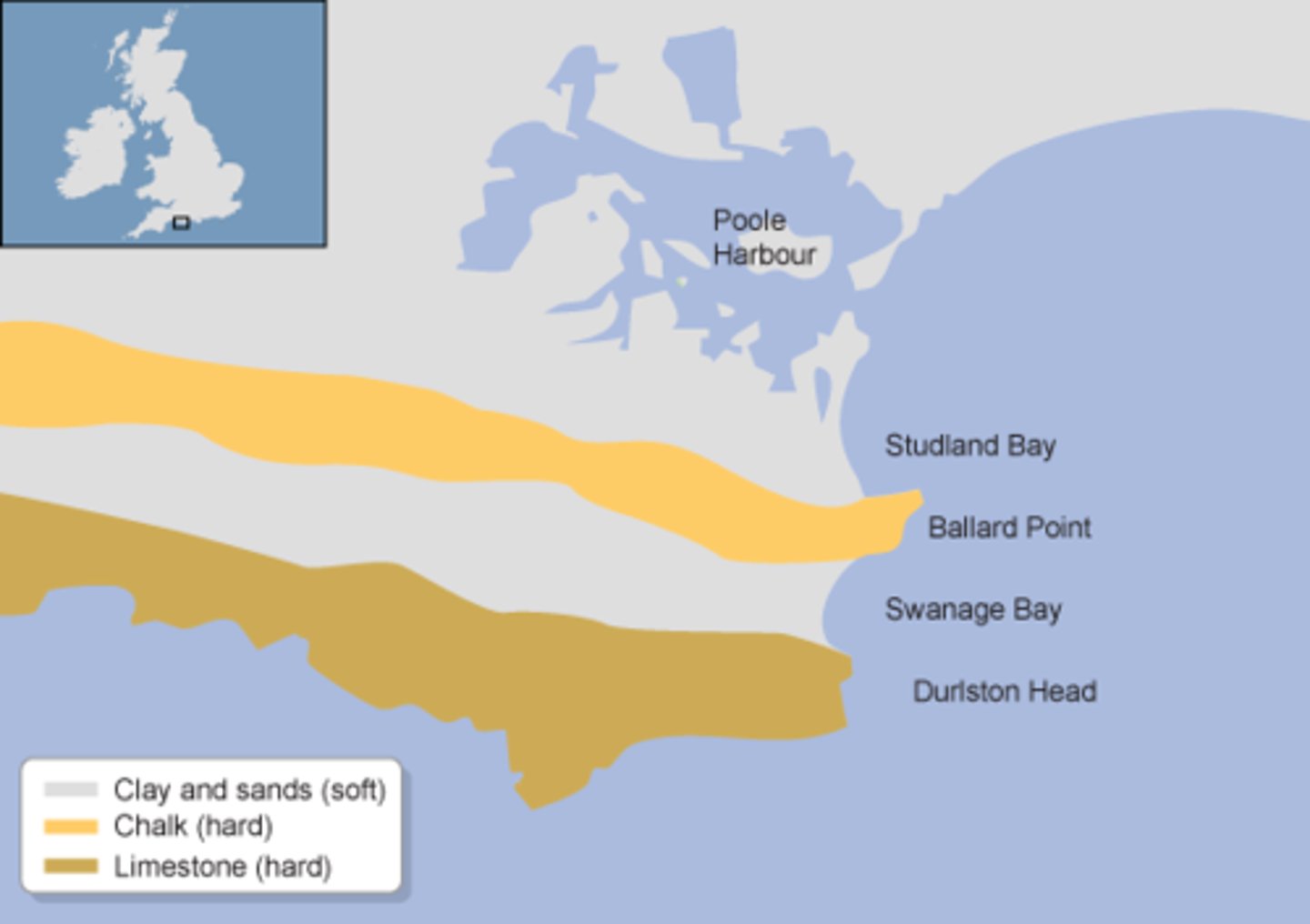
What landforms are formed on a discordant coastline?
Headlands and bays
Name an example of a concordant coastline.
Lulworth Cove
Name an example of a discordant coastline.
Swanage Bay and Durlston Head
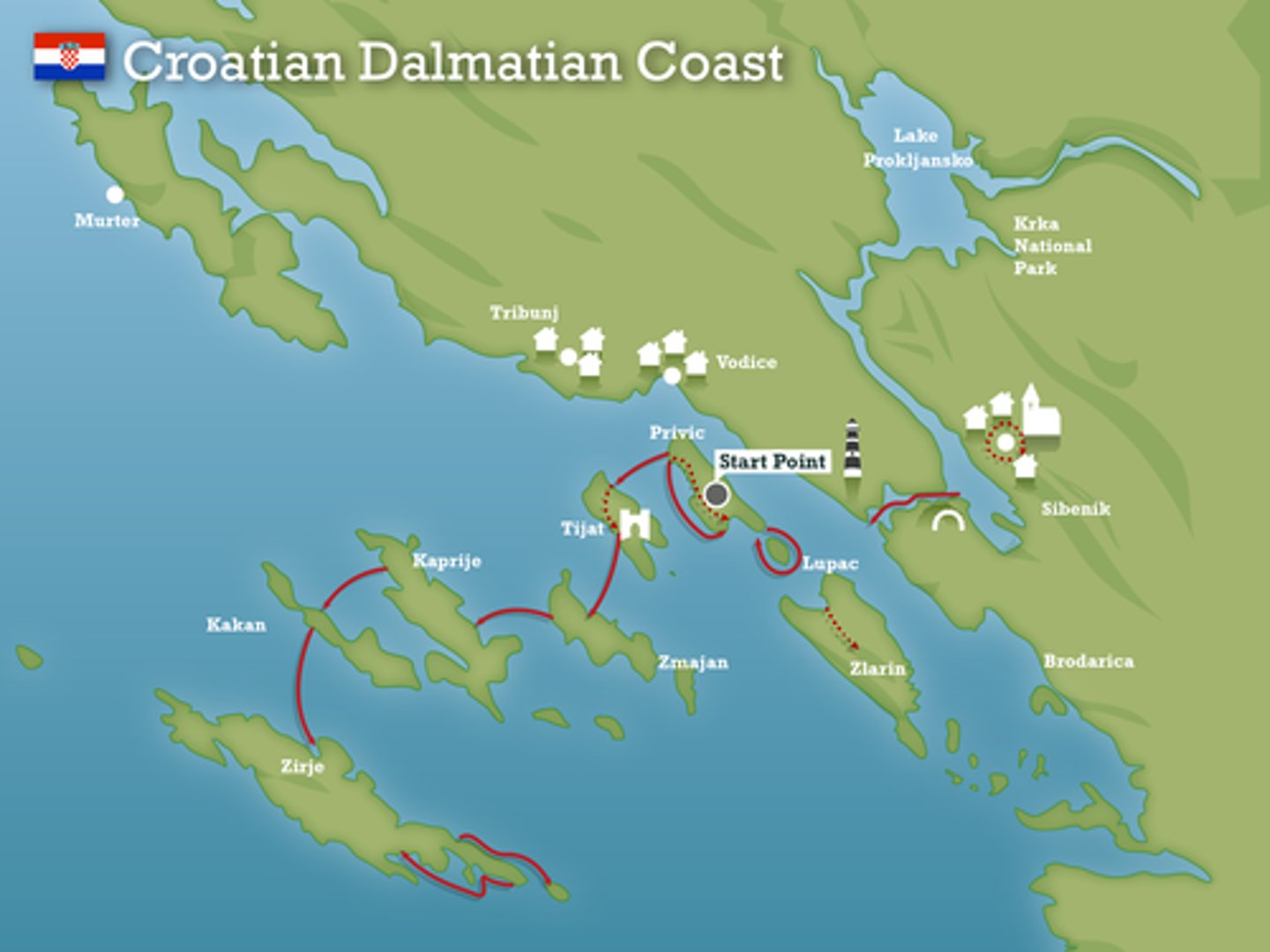
Describe and explain the Dalmatian coastline.
The Dalmatian coastline is caused by a concordant coastline being submerged and flooded, giving the view of a huge lake. It has left islands in the lake and in the sea.
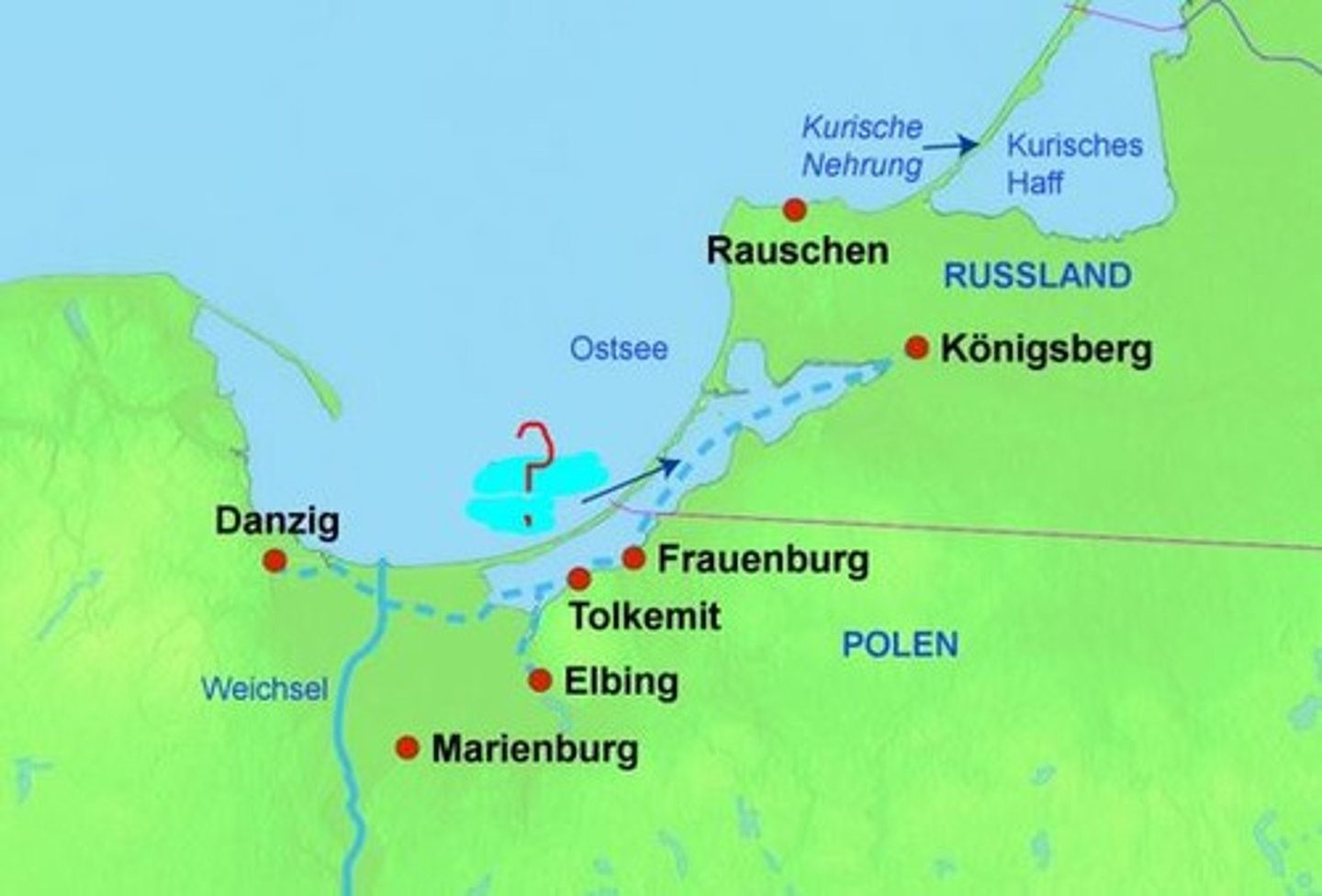
Describe and explain the Haff coastline.
The Haff coastline was formed by the flooding of the coast, creating a lake just behind the cliff. This leaves a thin strip of land between the lake and the sea.
Name two key geological factors that influence cliff profiles.
- The resistance of the rock.
- The dip of rock strata in relation to the coastlines.
Define fault.
A fracture zone between two blocks of rocks.
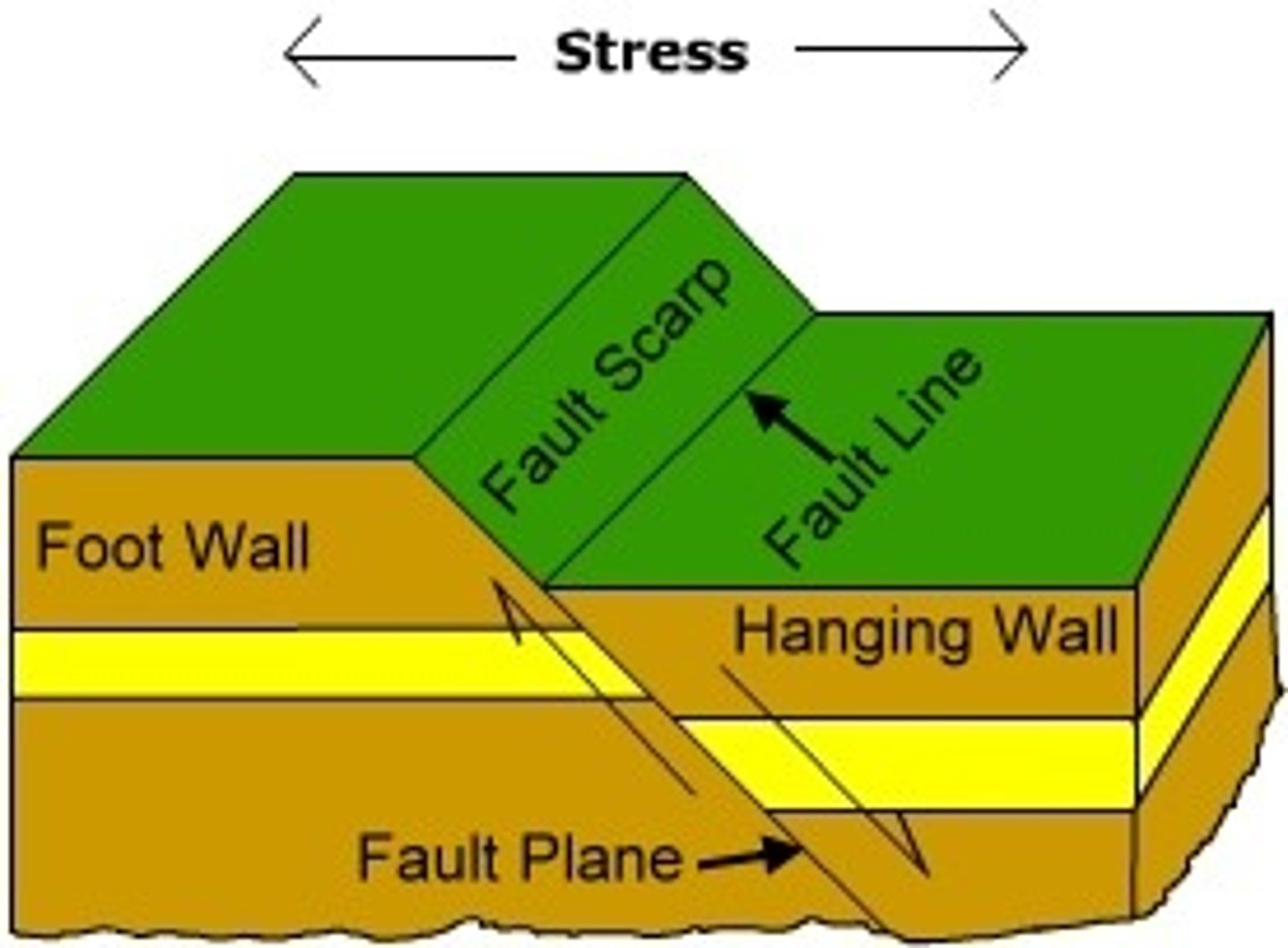
Define joint.
A fracture dividing into two sections that moved away from each other.
Define fissure.
A long narrow crack in the rock.
Define folding.
A fold is a bend in the rock strata and folding is a type of earth movement resulting from the horizontal compression of rock layers by internal forces of the earth along plate boundaries.
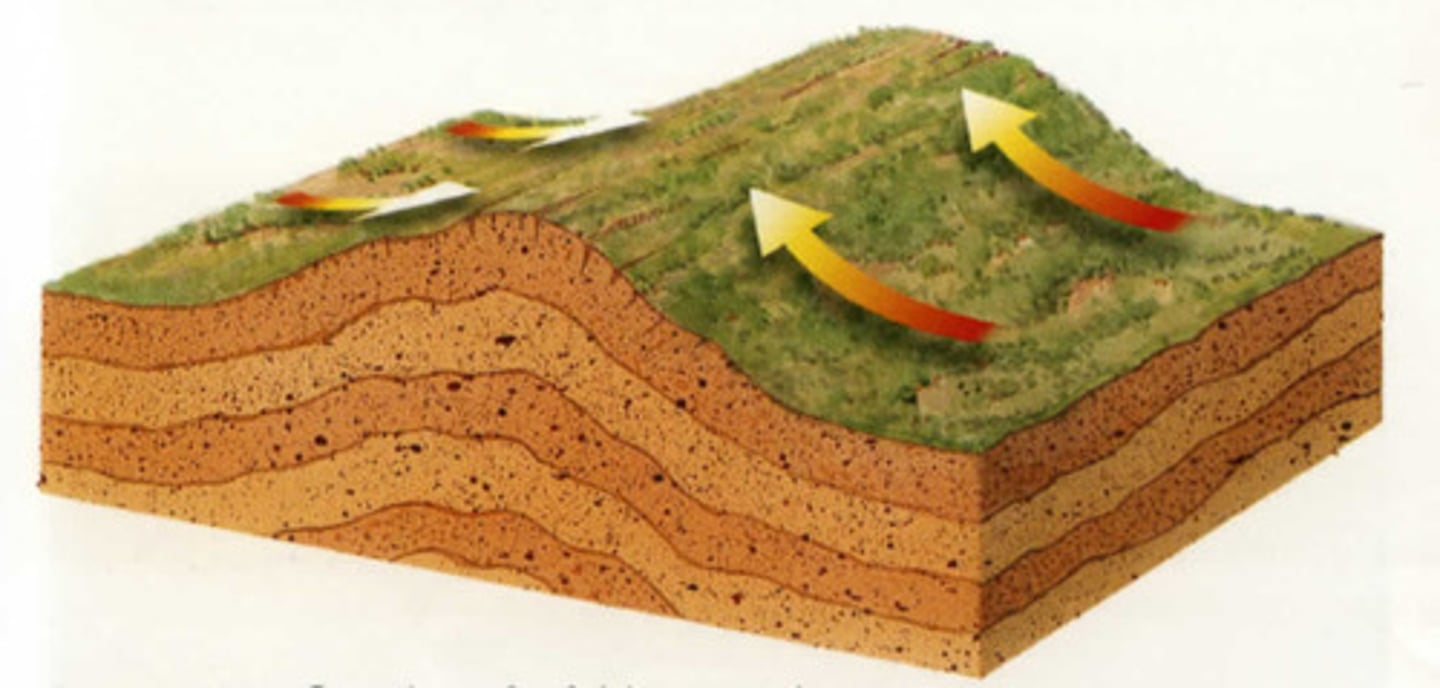

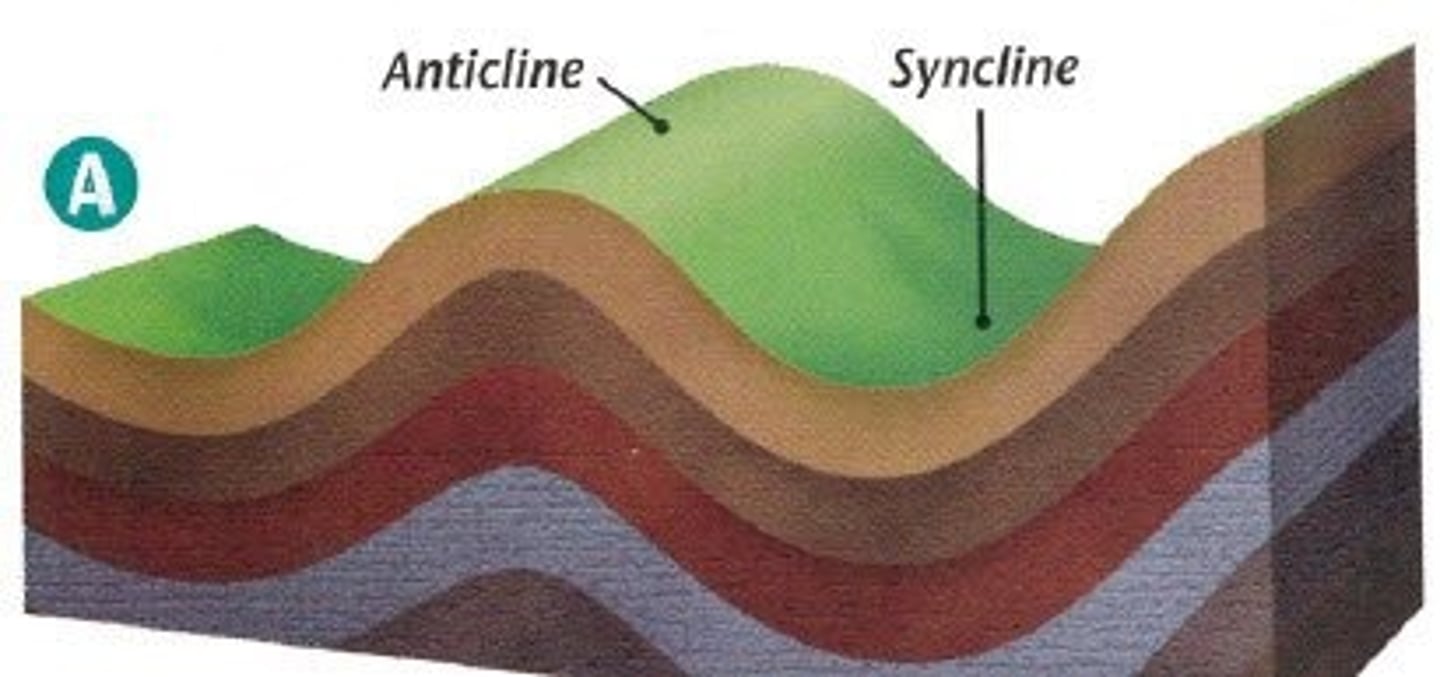
Define anticline.
A ridge-shaped fold of stratified rock in which the strata slope downward from the crest.
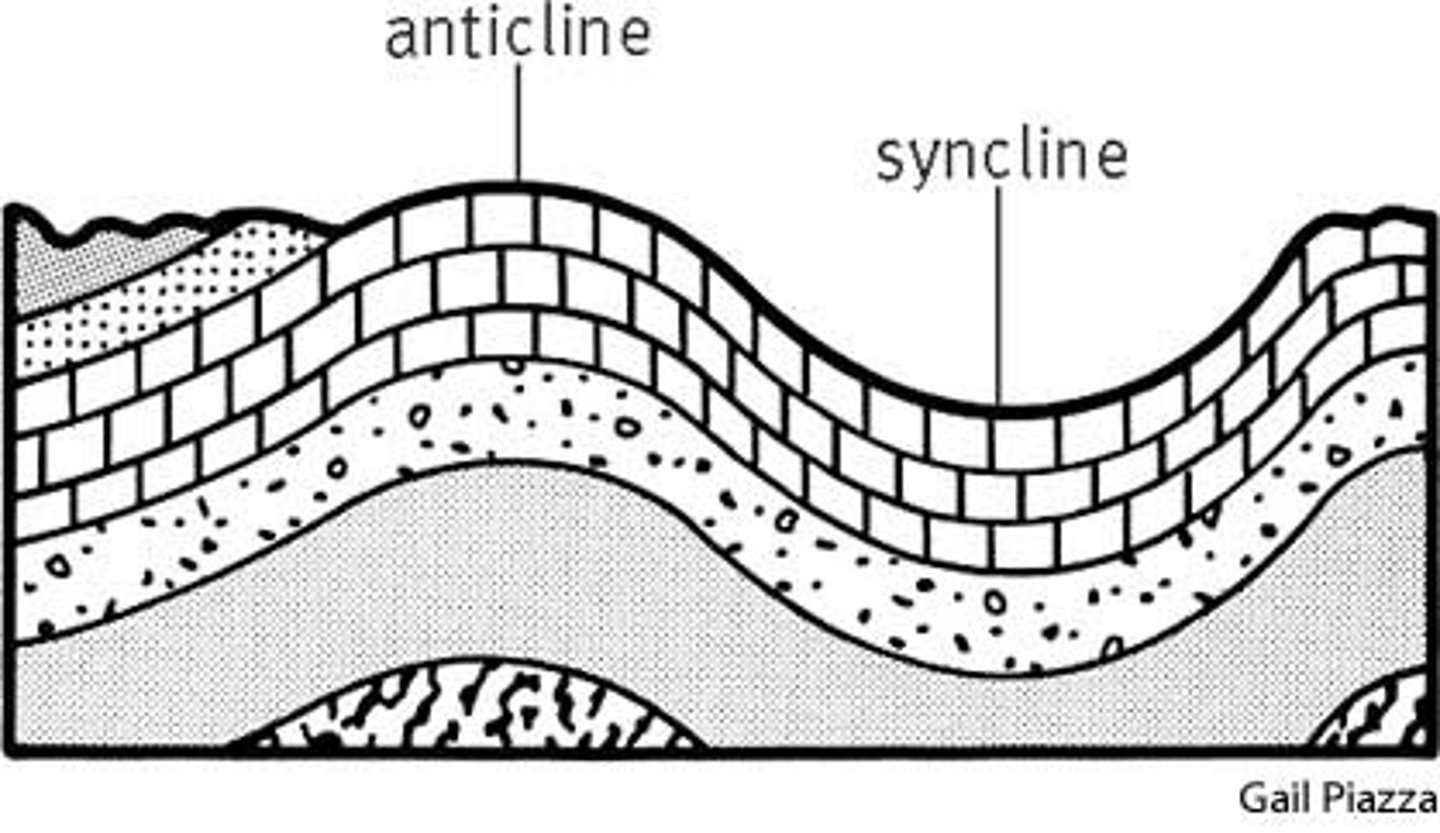
Define syncline.
A trough or fold of stratified rock in which the strata slope upward from the axis.
What are the characteristics of a low energy coastal environment?
- Lots of deposition
- Spits and bars formed from long shore drift
- Slow waves
- Alluvial plain
What are the characteristics of a high energy coastal environment?
- Fast waves
- Lots of erosion (especially hydraulic action)
- Rocky cliffs