ECO 304L UEX Final Exam
1/271
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
272 Terms
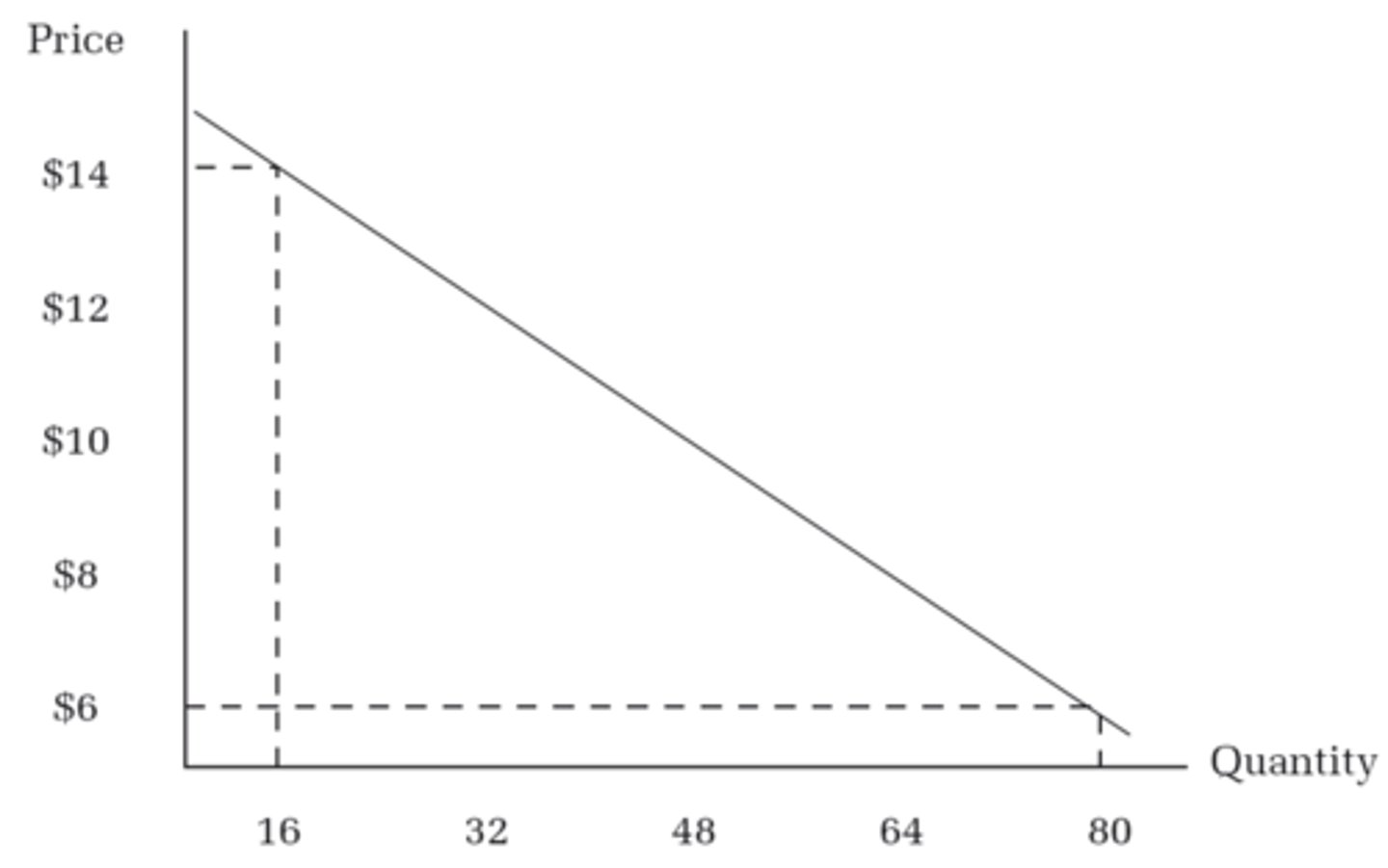
Law of Demand
other things equal, as price falls, quantity demanded RISES, and as price rises, quantity demanded FALLS
Demand Curve
-downward sloping
-inverse relationship
-shift to the right= increase
-shift to the left=decrease
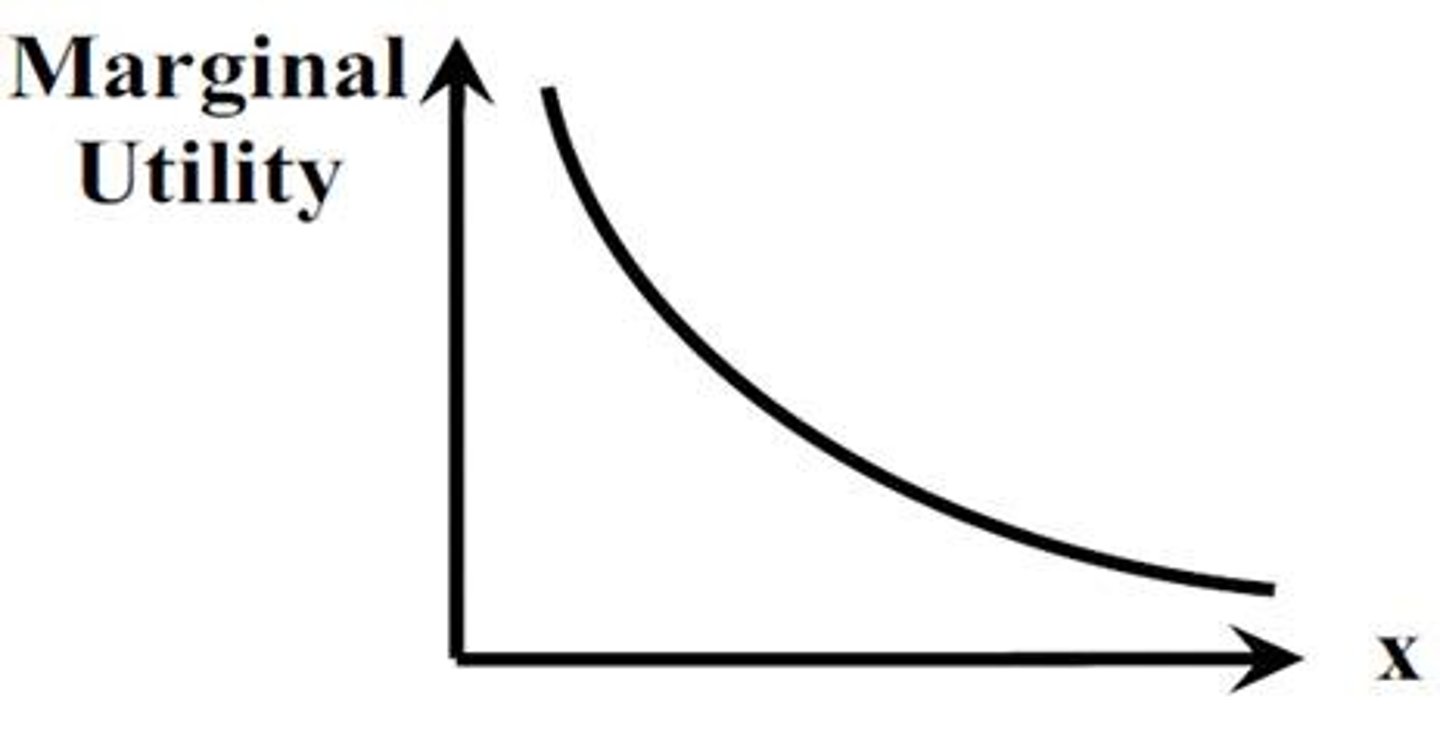
Diminishing Marginal Utility
successive units of a particular product yield less and less marginal utility, consumers will buy additional units only if price is reduced (think Costco)
Income Effect
indicates that a lower price increases the purchasing power of a buyer's money income, enabling the buyer to purchase more of the product than before
Substitution Effect
suggests that at a lower price buyers have the incentive to substitute what is now a less expensive product for other products that are now relatively more expensive
Determinants of Demand
factors that affect purchases:
-consumer preferences
-# of buyers in a market
-consumer incomes
-prices of related goods
-consumer expectations
Superior Goods (Normal Goods)
products whose demand varies DIRECTLY with money income
Inferior Goods
products whose demand varies INVERSELY with money income
Substitute Good
used in place of another good; example: two brands of ice cream

Complimentary Good
used with another good; example: tennis ball and racquet

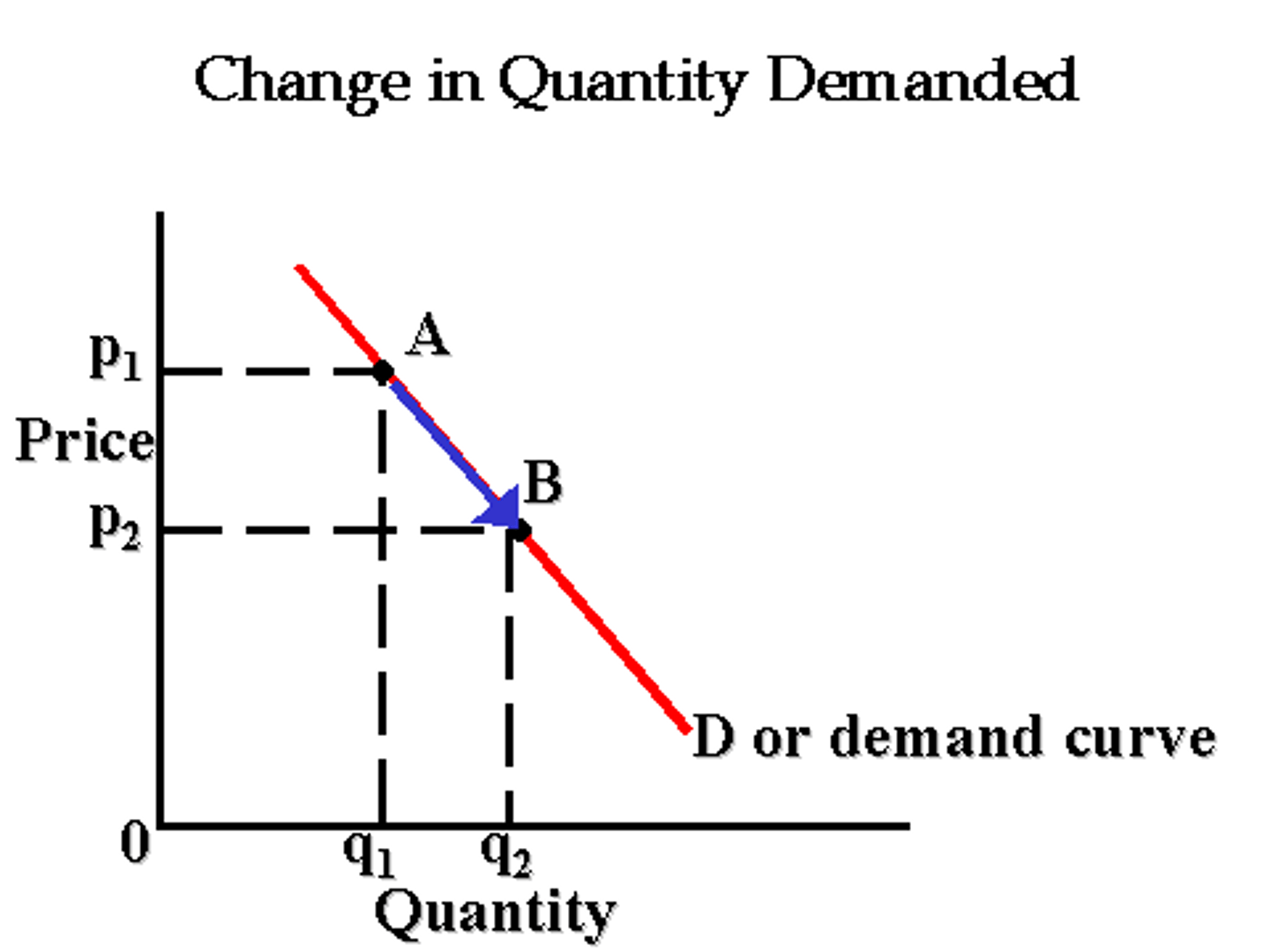
Change in Quantity Demanded
movement from one point to another point on the fixed demand curve; reflects change in price, not consumer tastes
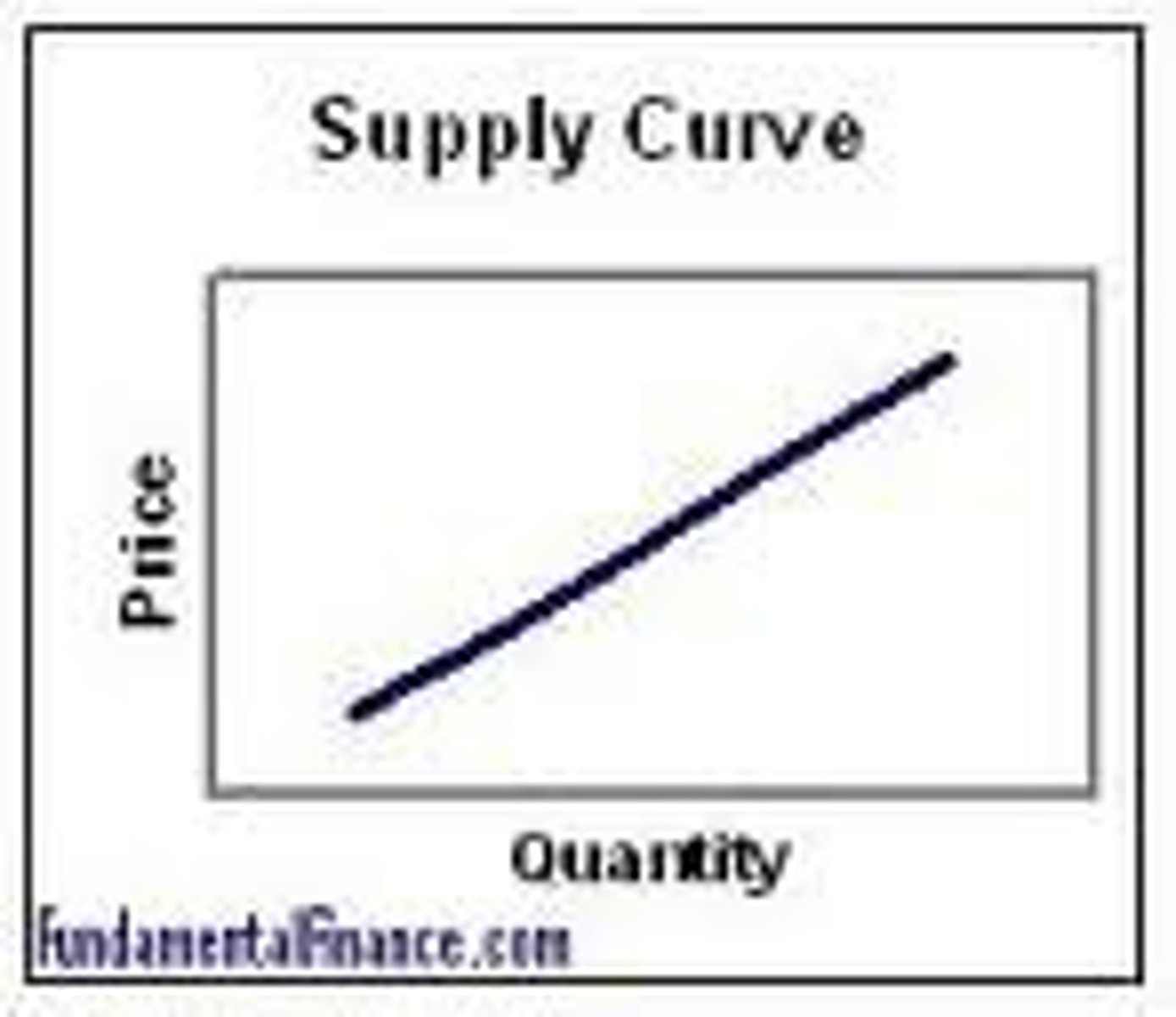
Law of Supply
as price rises, quantity supplied RISES, and as price falls, quantity supplied FALLS
Supply Curve
-upward sloping
-direct relationship
-shift to the right= increase
-shift to the left= decrease
Determinants of Supply
factors other than price that determine the quantities supplied of a good or service:
-resource prices
-technology
-taxes/subsidies
-prices of other goods
-producer expectations
-# of sellers in a market
As firms leave an industry, the supply curve shifts to the ____?
left
Change in Quantity Supplied
a movement from one point to another on a fixed supply curve; reflects change in price
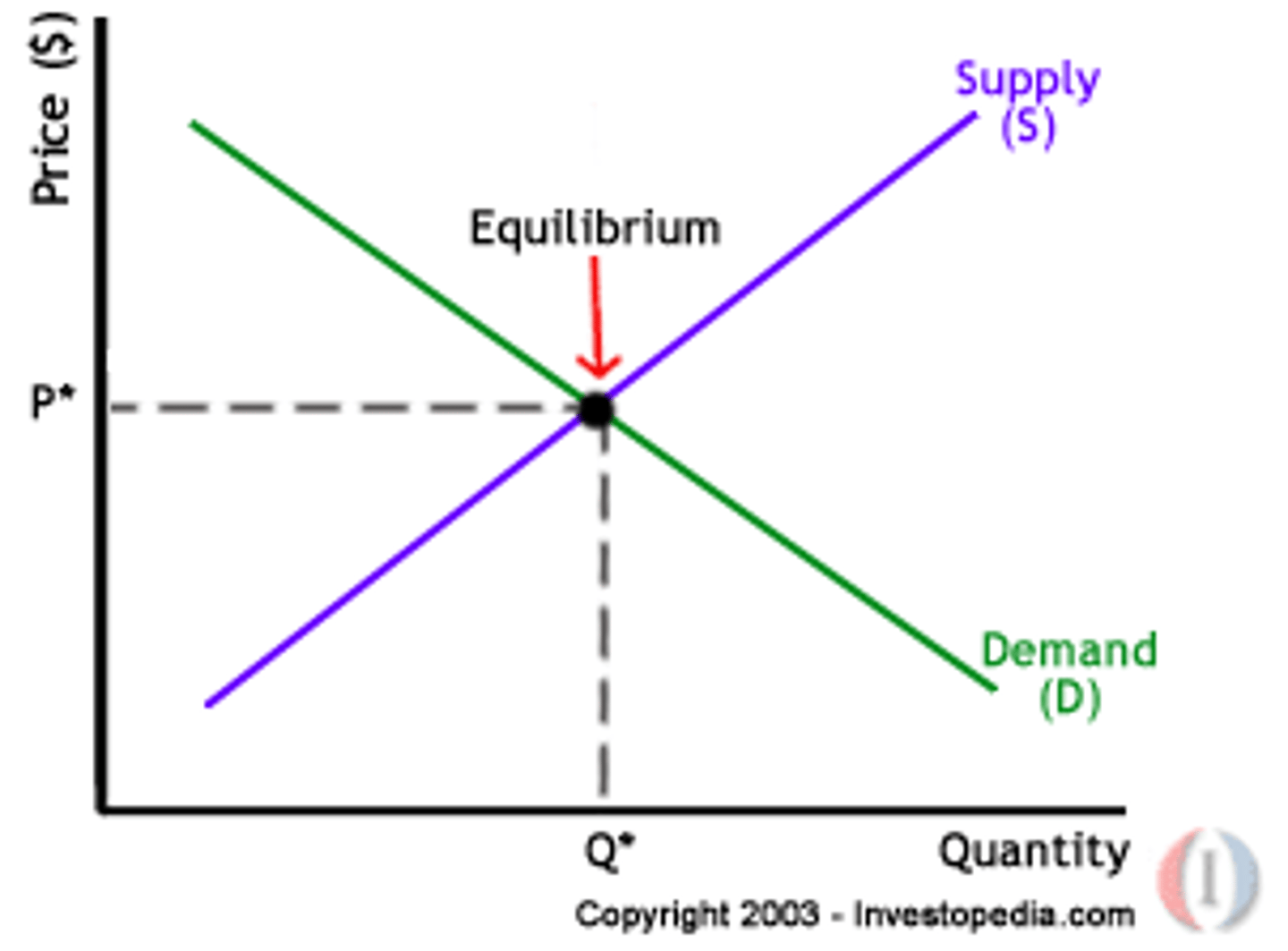
Equilibrium Quantity
the quantity at which the intentions of buyers and sellers match, so quantity demanded = quantity supplied
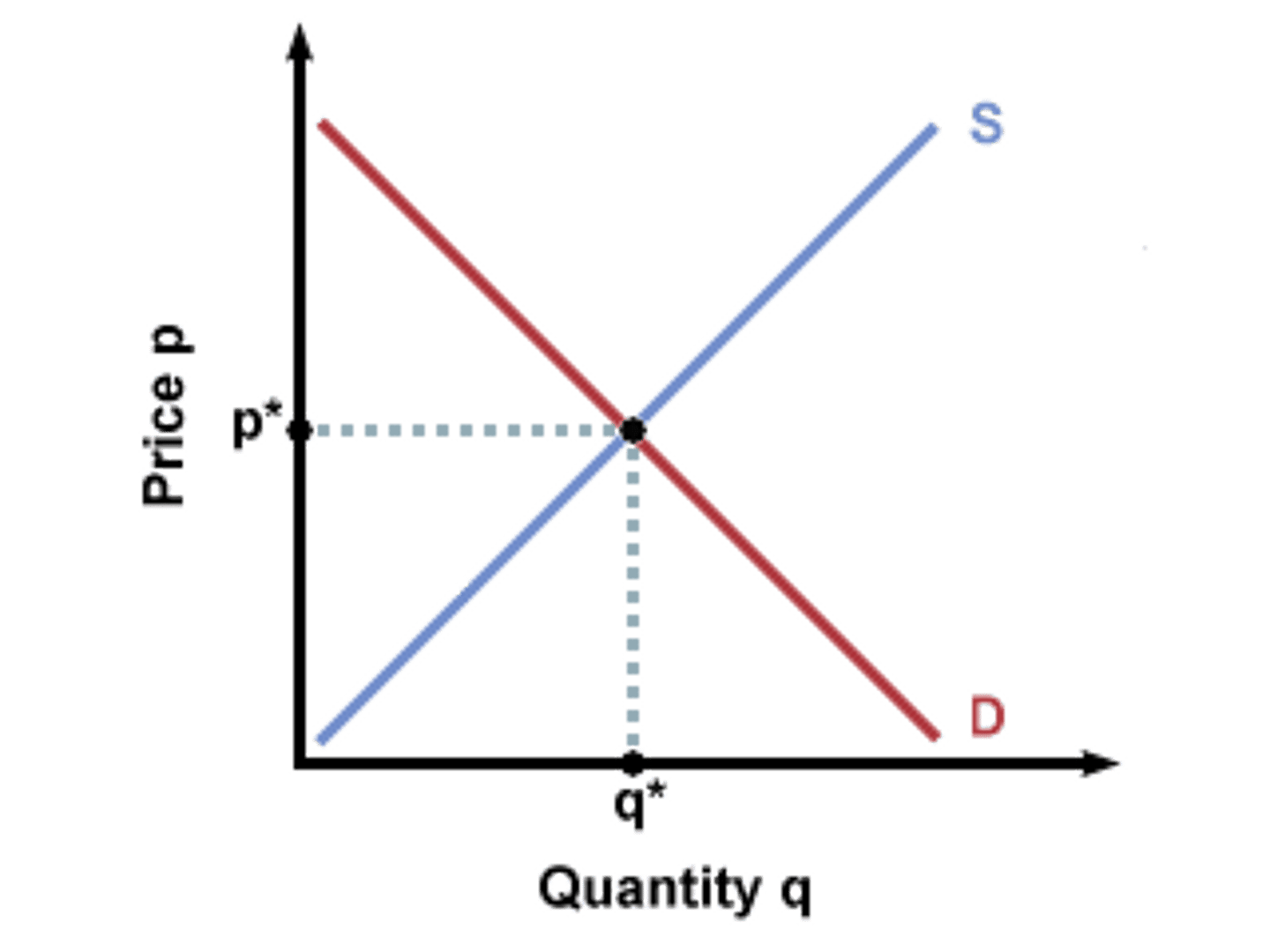
Equilibrium Price
the price where the intentions of buyers and sellers match
Surplus
quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
Shortage
quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
Productive Efficiency
the production of any particular good in the least costly way
Allocative Efficiency
the particular mix of goods and services most highly valued by society
Price Ceiling
sets the maximum legal price a seller may charge for a product or service; price above ceiling would be illegal
Rent Controls
maximum rents established by law (maximum rent increases for existing tenants)
Price Floor
minimum price fixed by the government; price below floor is illegal; used when society feels the free functioning of the competitive market is not providing sufficient income for certain producers
Price Elasticity of Demand
the measure of responsiveness (or sensitivity) of consumers to a price change
Price Elasticity of Demand Formula
Ed= (%change in quantity demanded of good X)/(%change in the price of good X)
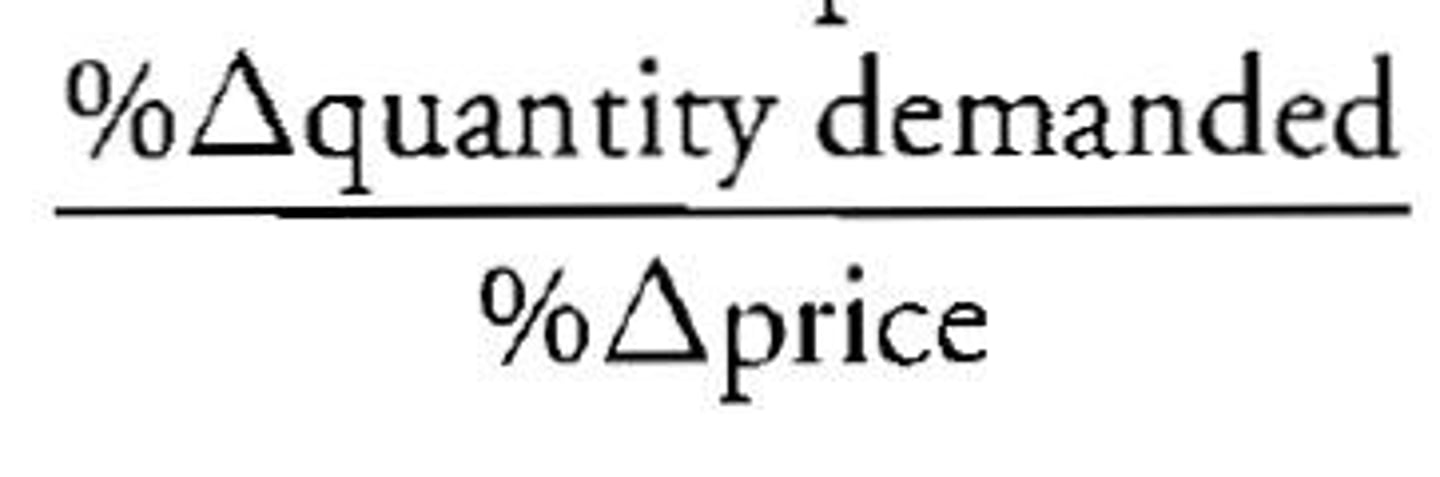
Elastic Demand
a situation in which consumer demand is sensitive to changes in price
Inelastic Demand
a situation in which an increase or a decrease in price will not significantly affect demand for the product
Unit Elasticity
demand or supply for which the elasticity coefficient is equal to 1; means that the percentage change in the quantity demanded or supplied is equal to the percentage change in price.
Perfectly Inelastic Demand
when a price change results in no change whatsoever in quantity demanded; price-elasticity coefficient is zero
Perfectly Elastic Demand
situation where a small price reduction causes buyers to increase their purchases from zero to all they can obtain; price-elasticity coefficient is infinity
Total Revenue
total amount the seller receives from the sale of a product in a particular time period
Total Revenue Formula
TR= (price) x (quantity sold)
Total Revenue Test
a method of measuring whether demand is elastic or inelastic; if TR changes in opposite direction of price, demand is elastic, if TR changes in same direction of price, demand is inelastic
If demand is elastic, a decrease in price will ________ total revenue?
increase
If demand is inelastic, a price decrease will ______ total revenue?
reduce
At the top of the linear demand curve, demand is _______?
elastic
At the bottom of the linear demand curve, demand is _________?
inelastic
Determinants of Price Elasticity of Demand
-substitutability
-proportion of income
-luxuries vs necessities
-time
Luxury items tend to have ________ demand, and necessities tend to have ________ demand.
elastic; inelastic
Price Elasticity of Supply
a measure of how much the quantity supplied of a good responds to a change in the price of that good
Price Elasticity of Supply Formula
Es = (%change in quantity supplied of good X) / (%change in the price of good X)
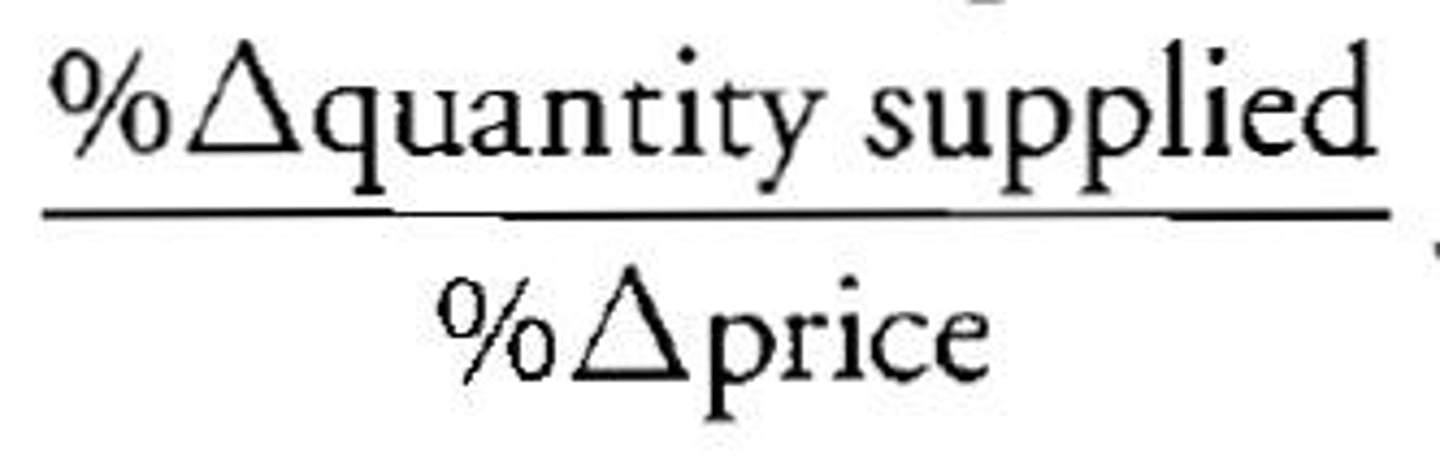
Market Period
the period that occurs when the time immediately after a change in market price is too short for producers to respond with a change in quantity supplied
Short Run
a period of time too short to change plant capacity but long enough to use the fixed-size plant more or less intensively
Long Run
a period of time long enough for firms to adjust their plant sizes and fore new firms to enter or exit
Cross Elasticity of Demand
measures how sensitive consumer purchases of one product are to a change in the price of some other product
Coefficient of Cross Elasticity of Demand Formula
Exy= (%change in quantity demanded of good X)/(%change in price of good Y)
If the cross elasticity of demand is positive for two goods, this means the two goods are ___________?
substitutes
If the cross elasticity of demand is negative for two goods, this means the two goods are ___________?
complements
Income Elasticity of Demand
measures the degree to which consumers respond to a change in their incomes by buying more or less of a particular good
Income Elasticity of Demand Formula
Ei= (%change in Qd) / (%change in Income)
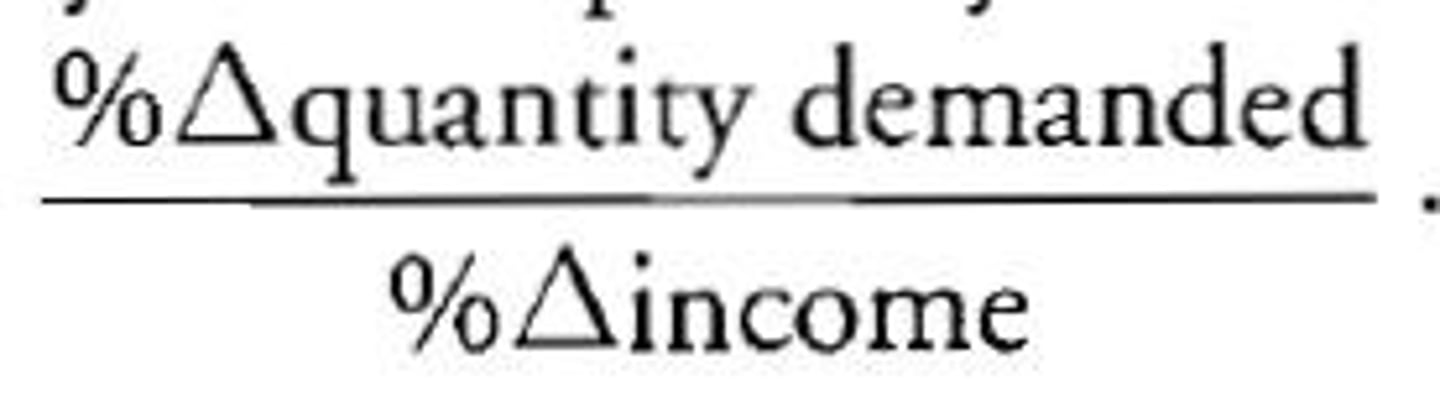
Demand-side Market Failures
happen when demand curves do not reflect consumers' full willingness to pay for a good or service; example: fire work displays; people can watch them without paying for them since they are outside
Supply-side Market Failures
occur when supply curves do not reflect the full cost of producing a good or service
Consumer Surplus
difference between the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for a product and the actual price they end up paying
Consumer surplus and price are _________ related?
inversely
Producer Surplus
difference between the actual price a producer receives & the minimum acceptable price that a consumer would have to pay the producer to make a particular unit of output available
Producer surplus and price are ________ related?
directly
Public Good
a shared good or service for which it would be impractical to make consumers pay individually and to exclude non-payers
Private Good
goods offered for sale in stores, shops, and on the Internet
Rivalry
when one person buys and consumes a product, it is not available for another person to buy and consume
Excludability
sellers can keep people who do not pay for a product from obtaining its benefits
Efficiency Losses (Deadweight Losses)
reductions of combined consumer and producer surplus, result from both underproduction and overproduction
At equilibrium price and quantity in a competitive market, marginal benefit is ________ to marginal cost?
equal to
Cost-Benefit Analysis
a decision-making process in which you compare what you will sacrifice and gain by a specific action
Externalities
occur when some of the costs or benefits of a good or service are passed onto or "spill-over to" someone other than the immediate buyer or seller
___________ externalities cause supply-side market failures?
negative
___________ externalities cause demand-side market failures?
positive
Optimal Reduction of an Externality
occurs when society's marginal cost and marginal benefit of reducing that externality are equal
Real GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
measures the value of final goods and services produced within the borders of a country during a specific period of time, typically a year; adjusted for inflation
Nominal GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
totals the dollar value of all goods and services produced within the borders of a country using current prices during the year that the products were produced; can increase from one year to the next, EVEN if there is no new output; doesn't account for inflation
Inflation
increase in the overall level of prices
Saving
occurs when current consumption is less than current output
Investment
when resources are devoted to increasing future output
Households
source of savings
Banks
collect savings of households and reward savers with interest, dividends, and sometimes capital gains; lend funds to businesses, which invest in capital goods
Demand Shock
unexpected changes in the demand for goods and services; more prevalent since prices of many goods and services are inflexible
Supply Shock
unexpected changes in the supply of goods and services
Inventory
store of output that has been produced but not yet sold
Flexible Prices
product prices that freely move upward or downward when product demand or supply changes; examples: corn, oil, airline tickets, natural gas
Sticky Prices
prices that do not always adjust rapidly to maintain equality between quantity supplied and quantity demanded; examples: final goods
National Income Accounting
measures the economy's overall performance
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
primary measure of the economy's performance is its annual total output of goods and services, or aggregate output; only counts FINAL goods and excludes non-production transactions
Intermediate Good
products that are purchased for resale or further processing/manufacturing; example: crude oil

Final Good
products that are purchased by their end user; example: gasoline used for transport

Non-production Transactions
not included in GDP:
-public transfer payments (social security, welfare)
-private transfer payments (Christmas gifts)
-stock market transactions (doesn't contribute to output)
Expenditures Approach
looking at GDP as the sum of all money spent in buying it; "output approach"
Income Approach
looking at GDP in terms of income derived or created from producing it; "earnings approach"
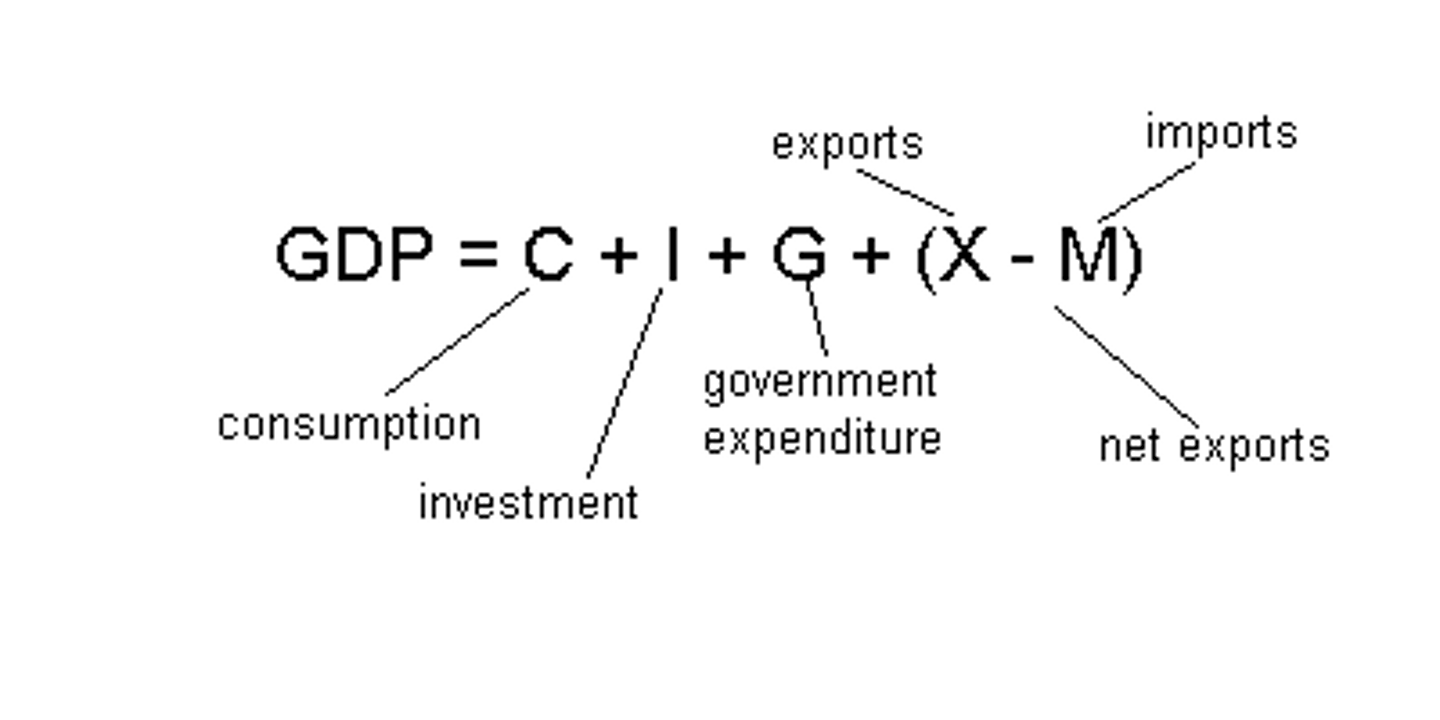
Expenditures Approach to GDP
GDP = consumption + investment + government purchase + net exports
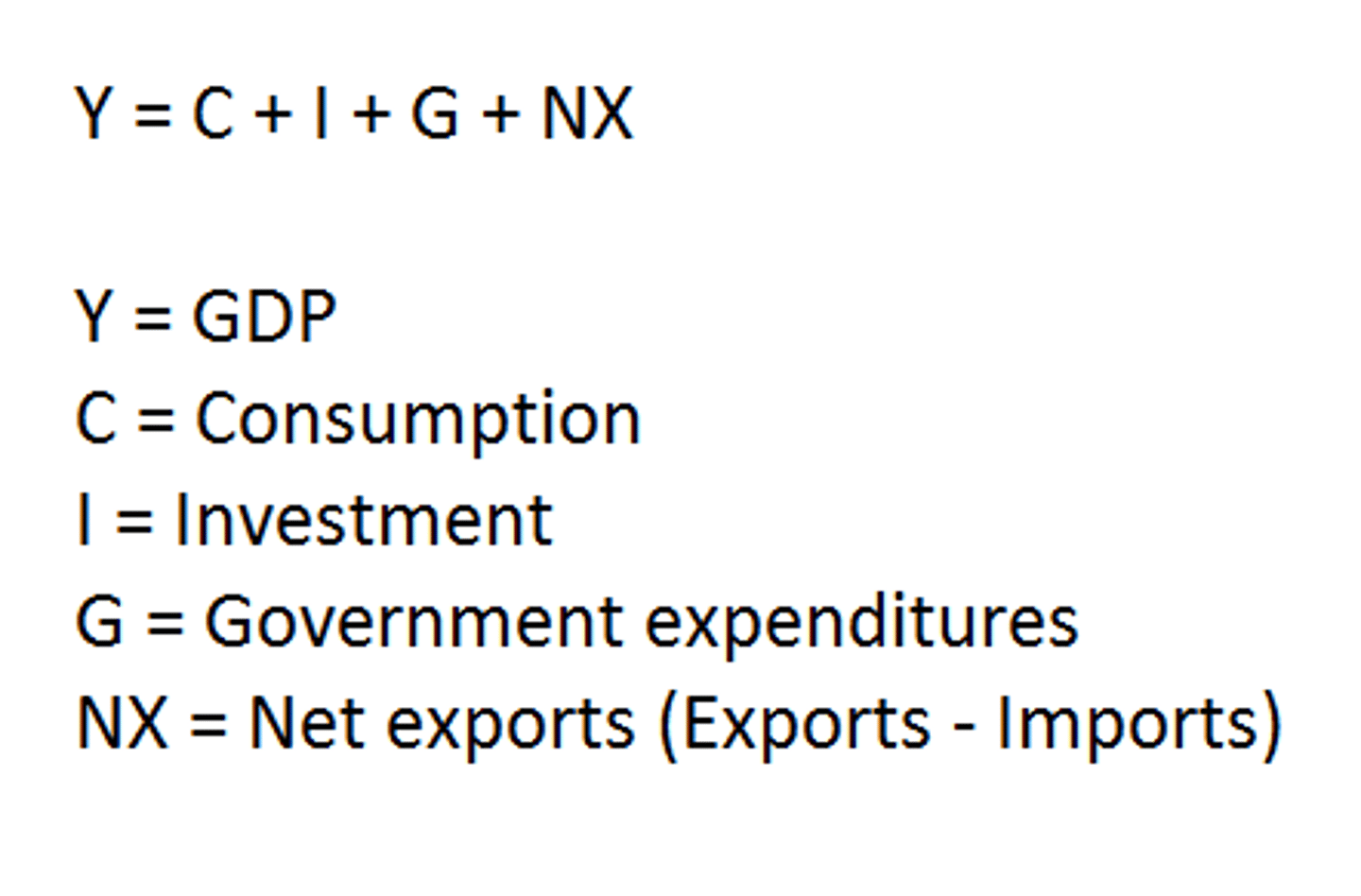
Income Approach to GDP
GDP= wages + rents + interest + profits + statistical adjustments
Personal Consumption (C)
includes all expenditures by households on goods and services; 10% of expenditures are on durable goods, 30% spent on nondurables, and 60% spent on services
Gross Private Domestic Investment (I)
all final purchases of machinery, equipment, and tools by business enterprises (investment of private business, not government agencies)
Government Purchases (G)
government consumption expenditures and gross investment (not including gov. transfer payments)
Net Exports
Net Exports = Exports - Imports
National Income
the total of all sources of private income (employee compensation, rents, interest, proprietors' income, and corporate profits) plus government revenue from taxes on production and imports

Consumption of Fixed Capital
the huge depreciation charge made against private and publicly owned capital each year
Personal Income
includes all income received, whether earned or unearned
Net Domestic Product
NDP = GDP - depreciation
Disposable Income
personal income less personal taxes; DI= Consumption + Savings
Price Index
a measure of the price of a specified collection of goods and services, called a "market basket," in a given year as compared to the price of an identical (or highly similar) collection of goods and services in a reference year.