occlusion final
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
1.5 - 2
(1 - 1.5 for gold)
how much reduction for a ceramic crown
the angle at which the condyle moves from a horizontal plane (The angle at which the condyle moves downward and forward along the articular eminence during mandibular protrusion.)
what is the condylar angle
the angle at which the non-working side moves away form the sagittal plane as viewed in the horizontal plane
what is the bennet angle
false
T or F
the intra-arch alignment means between the teeth in the opposing arch
premolar
which tooth int he maxillary arch has the least angulation when viewed from the sagittal plane?
curve of wilson
what is another name for the medial-lateral curve
occlusal table
the area defined by the cusp tips and M/D cusp arms
both statements are true
classify each statement as T or F
anterior class 1 has 2-3mm of horizontal overlap. Anterior class 1 has 2-3mm of vertical overlap.
false
T or F
anterior class 2 division 1 is when the maxillary incisors are lingually inclined
completely edentulous pt.
dentate pt. receiving extensive restorations that will alter occlusion
(also, in partially edentulous pt. that has an unstable MIP)
when is it necessary to restore in CR?
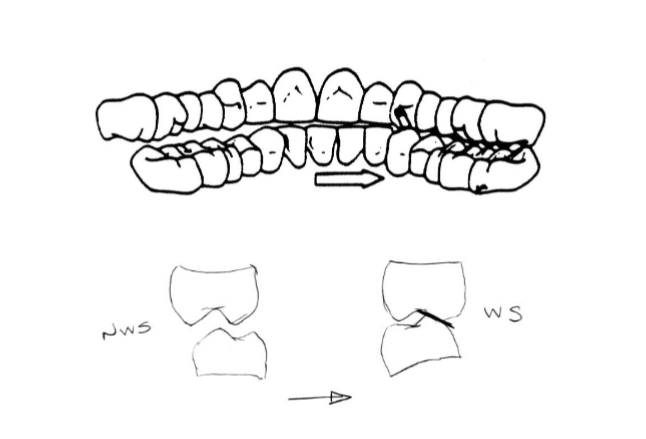
group function
occlusion for patients with:
no anterior vertical overlap (ant. open bite),
large anterior horizontal overlap (Class II div I),
and/or reverse overlap (Class III).
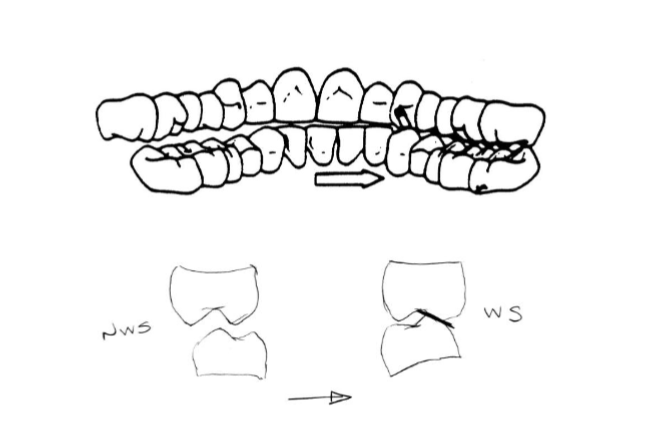
mutually protected occlusion (aka optimal functional occlusion)
acceptable occlusion for all patients
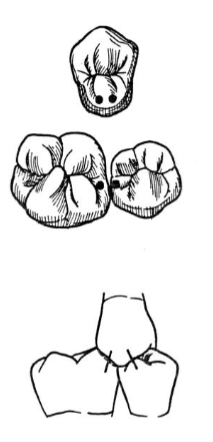
one tooth to two tooth arrangement
commonly used for single restorations
describe cusp-marginal ridge contact
What type of functional cusp relationship do we use when restoring both opposing quadrants of teeth
cusp-fossa
(tooth to tooth arrangement)
mandibular central incisor (max 3rd molar is only other)
which tooth only contacts one other tooth
distal marginal ridge of the mandibular second premolar and mesial marginal ridge of the mandibular first molar (cusp-marginal ridge)
distal fossa of mandibular second premolar (cusp-fossa)
where does the maxillary second premolar contact?
supero-infero movement
cusp height and fossa depths
the vertical component of occlusion affects?
anterior posterior and medial lateral movements
direction of grooves and ridges in occlusal plane, and placement of cusps in the horizontal plane
The horizontal component of occlusion affects?
plane of occlusion
curve of spee
mandibular lateral translation movement
(others: condylar guidance, anterior guidance, nearness of cusps to the controlling factors)
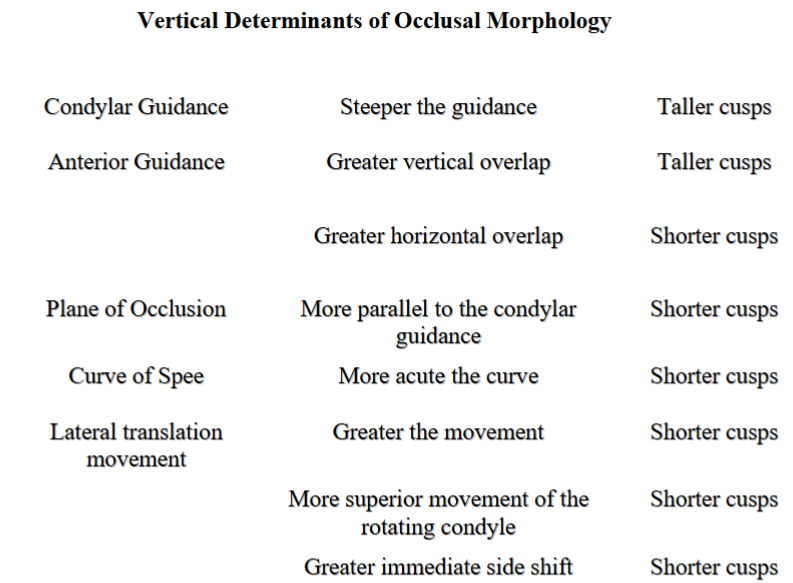
vertical determinants include:
effect of distance of tooth from rotating condyle and midsagittal plane
effect of mandibular lateral translation movement
effect of intercondylar distance
factors of horizontal determinants:
pharmacological therapy
(also, physical therapies that include thermotherapy, coolant, ultrasound, electrogalvanic, manual techniques, muscle conditioning, acupuncture)
examples of supportive therapy:
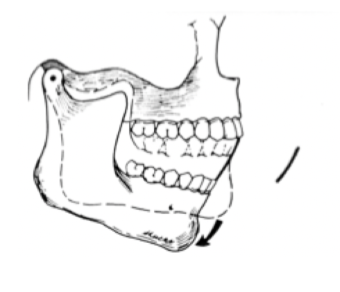
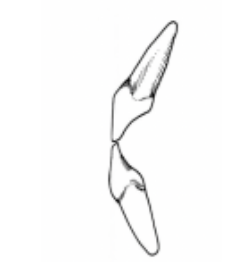
diagram on the left
in which diagram do MIP and CR not coincide
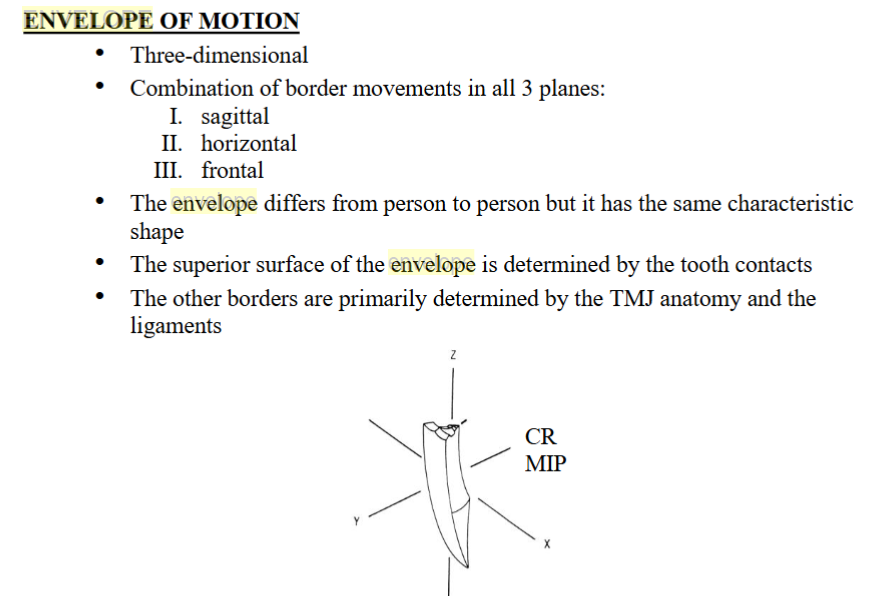
first statement false (determined by tooth contacts)
second statement true
classify each statement as T or F
the superior surface of the envelope is determined by the condyles. The other borders are primarily determined by the TMJ anatomy and ligaments.
- occur within the outer range of border movements and near MIP
- outer range of movement is greater in early stages of mastication
- outer range of movement is smaller in late stages of mastication
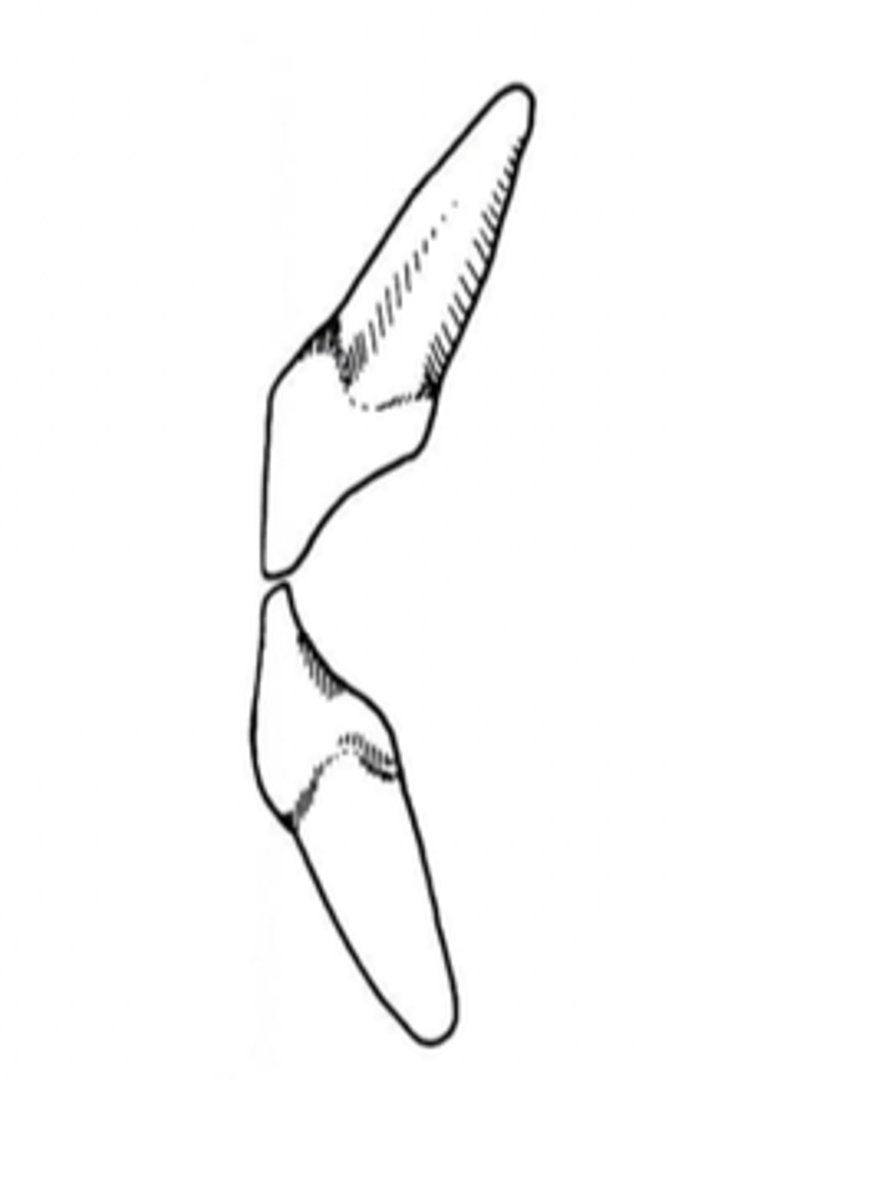
functional movements:
rotation
opening 20-25mm = what movement (picture given)
false (in a neutral unstrained position)
t or f
physiological rest position is a habitual postural of the mandible when the patient is resting comfortably in the upright position and the condyles are in a restrained position
superior joint compartment
translation of the condyles occurs in
false, trauma is no longer present. this would be true for microtrauma
t or f
for macrotrauma, definitive therapy is necessary and useful
definitive and supportive
treatment of TMD can be categorized as?
horizontal factors
__________ ____________ influence the direction of ridges and grooves on the occlusal surfaces
distance of tooth from rotating condyle
distance of tooth from midsagital plane
which of the following are horizontal factors
- distance of tooth from rotating condyle
- distance of tooth from midsaggital plane
- intercondylar height
restorations
ortho
extractions
caries
anterior guidance can be altered by what?
taller
the steeper the anterior guidance angle --> the ______________ posterior cusps
false
T or F
the further the tooth is from the TMJ, the more joint anatomy will influence its eccentric movements
patient has multiple, bilateral, even and simultaneous contacts in MIP/CR
patient has anterior guidance only in protrusion
MIP and CR and coincident
mutually protected occlusion is when:
true
t or f
non working side interferences occur between inner inclines of the maxillary lingual cusps and inner inclines of the mandibular buccal cusps
false
pt. can have class 1 angles and bad occlusion
t or f
a patient with ideal angles class 1 occlusion has optimal occlusal contacts, optimal condyle position and ideal contacts.
balanced occlusion
simultaneous contacts on working and nonworking during lateral excursive movements
muscles
genetics
habits
occlusal contacts
interproximal contacts
factors that affect tooth position
plane of occlusion
curves to fit the occlusal surfaces and incisal edges of all teeth
curve of spee
curve of wilson
compensating curve
true
t or f
posterior teeth are designed to be loaded axially, take heavy loads and support the occlusal vertical dimension
50-60%
the occlusal table is ____% of the BL width
class 3 end to end
what class
20-25mm
pure rotation occurs in the first
superior joint compartment
translation of condyles occurs in
terminal hinge axis
imaginary axis through the condyles that facilitates pure rotation
postural rest position
habitual posture of mandible when patient is sitting upright and condyles are in neutral unstrained position in the glenoid fossa
easy to mix and handle
non allergenic to patient
an ideal impression material...
impression compound
which of the following is not elastic
- impression compound
- polysulfide
- polyether
- condensation silicone
0.5-1mm
how much axial reduction on full gold crown prep
verifying occlusal clearance
what are these used for
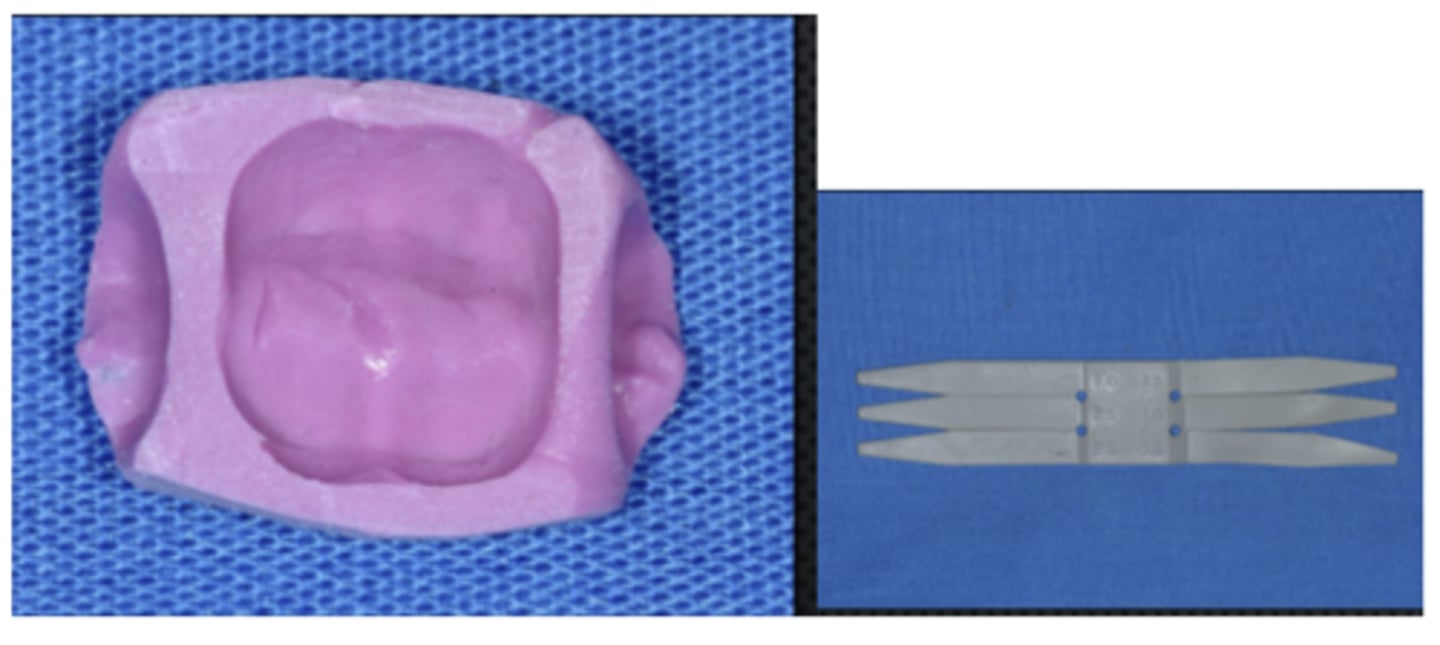
checking reduction
what is putty used for
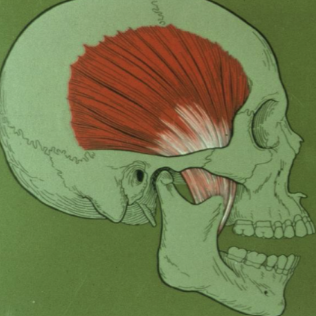
elevates mandible and provides chewing forces
what is the function of the masseter
patient education
diagnosis
treatment planning
purposes of articualtor
convex
occlusal plane in maxilla is (curve of spee)
The mandible and TMJs act as a Class III lever system
The more anterior (away from the fulcrum), the resistance (load) occurs, the
lesser the impact (magnitude)
The canine has the longest root, and best bone support (canine eminence) and
therefore can tolerate higher load
Why is Canine Guidance-Anterior Guidance considered the optimal occlusal scheme?
variable
anterior guidance is (vertical overlap)
balancing
Which type of occlusion
posterior controlling factor. It is a fixed factor as it is controlled by two anatomical factors amongst the two TMJs. it is the steeper eminence = taller
articular eminence and
(medial wall of articular fossa and articular eminence)
What is the condylar guidance
axial loading; light contact and guidance
posterior teeth are meant for:
anterior teeth are meant for:
border movements
The mandibular movements are limited by ligaments, the articular surfaces of the
TMJ, and the morphology and alignment of the teeth. The outer range of movement is
reproducible and called…
Condyles are in the most antero-superior position in the glenoid fossa.
Condyles rest against the posterior slope of the articular eminence (thickest bone)
therefore can tolerate higher stresses.
In the TMJ, during CR, where is the condyle?
D. A and B
Which of the following are horizontal factors
a. Distance of tooth from rotating condyle
b. Distance of tooth from midsagittal plane
c. Intercondylar height
d. A and B
taller posterior cusps
A steeper anterior guidance angle means
B. Distal marginal ridge of maxillary second premolar and mesial marginal ridge of maxillary first molar (MB cusp during cusp-MR occlusion)
In class I, the mandibular first molar can contact?
a. Central fossa of maxillary first molar (DB cusp)
b. Distal marginal ridge of maxillary second premolar and mesial marginal ridge of maxillary first molar (MB cusp during cusp-MR occlusion)
c. Triangular mesial fossa of first maxillary molar (MB during cusp-fossa occlusion)
d. all true
Mutually protected occlusion is when
a. The patient has multiple, bilateral, even and simultaneous contacts in MIP/CR
b. Patient has anterior guidance only in protrusion
c. MIP and CR are coincident
d. All true
NW side between inner inclines of the maxillary lingual cusps and inner inclines of the mandibular buccal cusps
Non working side interferences occur on
false, can have bad occlusion
T/F a patient with ideal angles class I occlusion has optimal occlusal contacts, optimal condyle position, and ideal contacts
group function (WS hits)
what type of occlusion
balancing (only used in denture pt)
What type of occlusion: Simultaneous contacts on working and nonworking during lateral excursive movements
plane of occlusion
Curves to fit the occlusal surfaces and incisal edges of all teeth
true
T/F Posterior teeth are designed to be loaded axially, take heavy loads, support the occlusal vertical dimension
facilitates axial loading
question about occlusal table definition
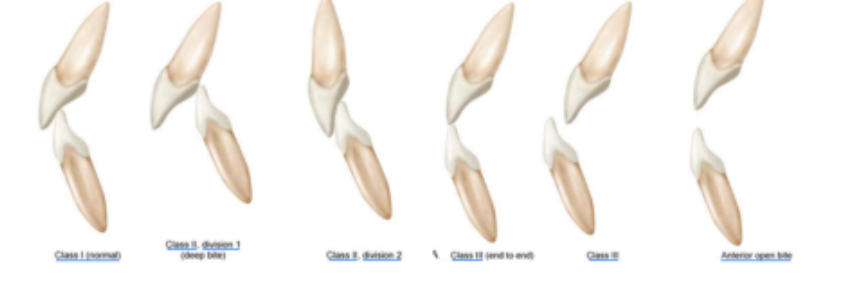
class III end to end
which class
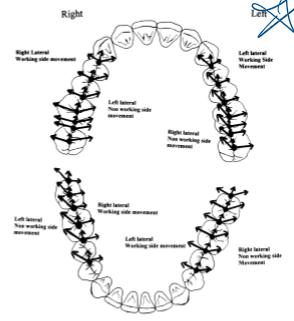
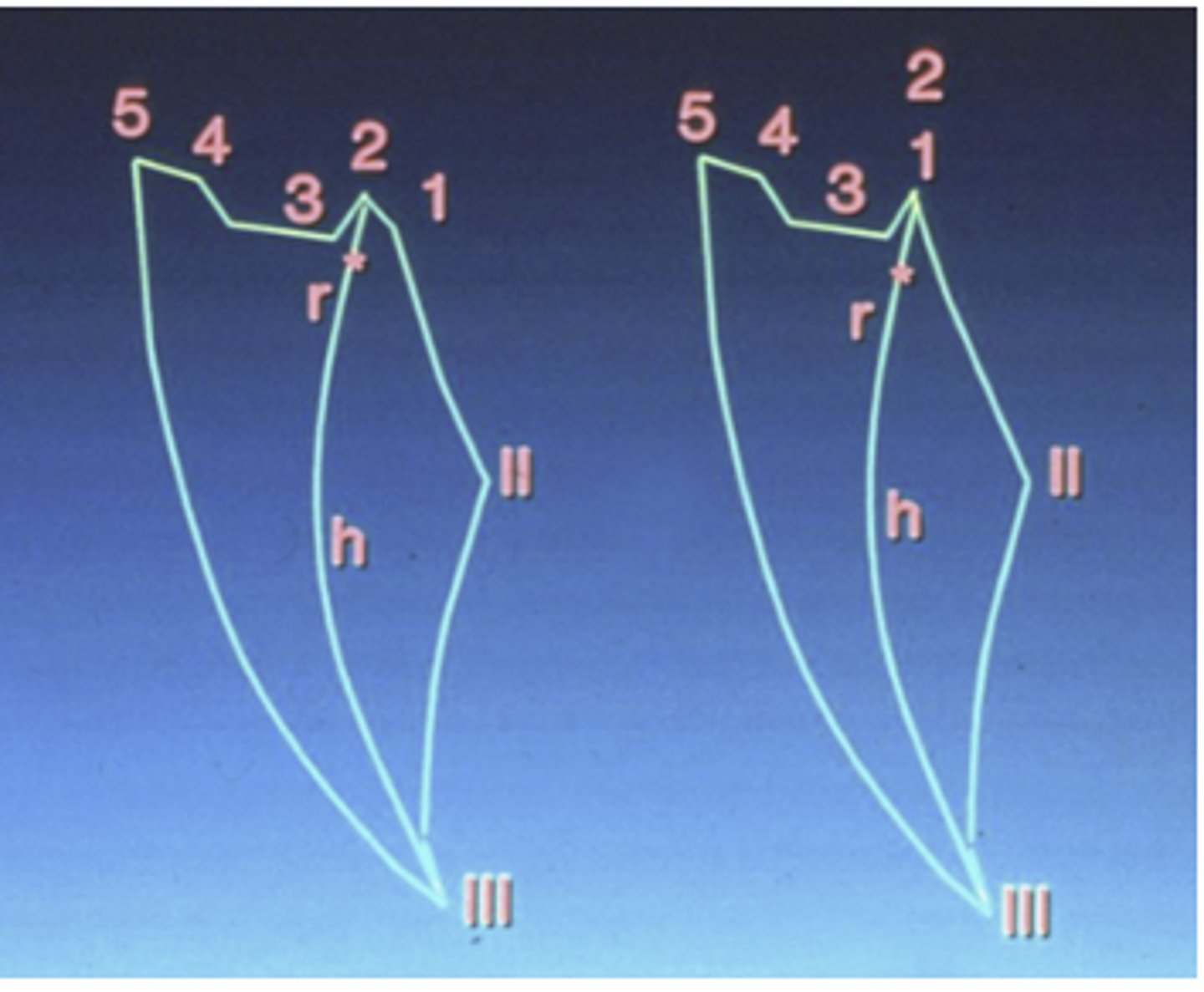
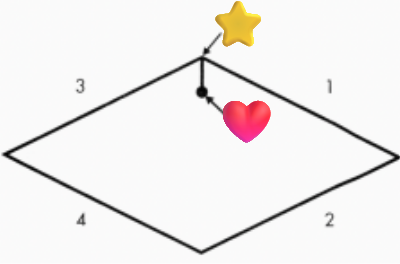
star = CR, heart = MIP, 1 = pure left lateral movement, 2 = left lateral with protrustion, 3 = right lateral movement, 4 = right lateral with protrusion
ID all structures
d. B and C (near MIP, not CR)
Functional movements
a. Occur near CR
b. The outer range is greater in early stages of mastication
c. The outer range is smaller in late stages of mastication
d. B and C
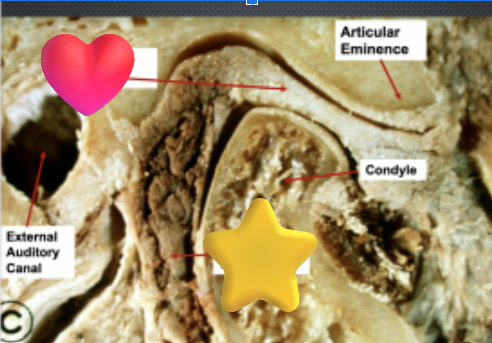
star = retroarticular tissue, heart = articular disc
ID the two features
a. impression compound (along with zinc oxide eugenol, gypsum, impression wax)
Which of the following is not elastic
a. Impression compound
b. Polysulfide
c. Polyether
d. Condensation silicone
true
T or F Masseter elevates the mandible and provides force for chewing
temporalis
ID
3rd point of reference
This should be repeatable and reproducible. It orients cast to reference plane or something like that
d. all of the above
When is a facebow indicated
a. Cusp teeth are present
b. Interocclusal records are made at an increased OVD
c. OVD is subject to change
d. All of the above
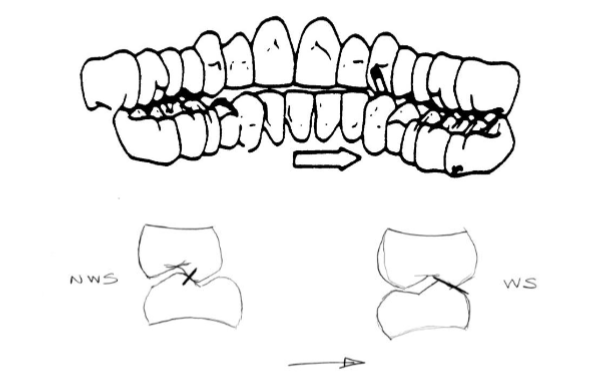
premature contact; centric interference
what is this showing/what type of interference
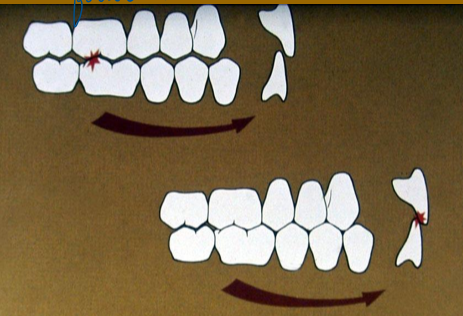
maxillary - working out of mouth, protrusive out
mand - working in towards mouth, protrusive in
ID the working, nonworking, and protrusive paths