U4: orbital motion
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what is a geosynchronous satellite
satellite with an orbital period the same as earth’s rotation period (1 day)
placed directly over the equator
stays in a fixed position over the earth’s surface
why are geostationary satellites so useful
a reciever can be aimed at the satellite at all times
reciever can constantly recieve a signal from the satellite
can construct a large, stationary satellite dish
used in communication and navigation
what is the period of a geostationary satellite
1 day / 86400 s
a) How far away is a geostationary
satellite from the surface of the
earth (in m and km)?
b) What is its velocity in m/s and
km/h?

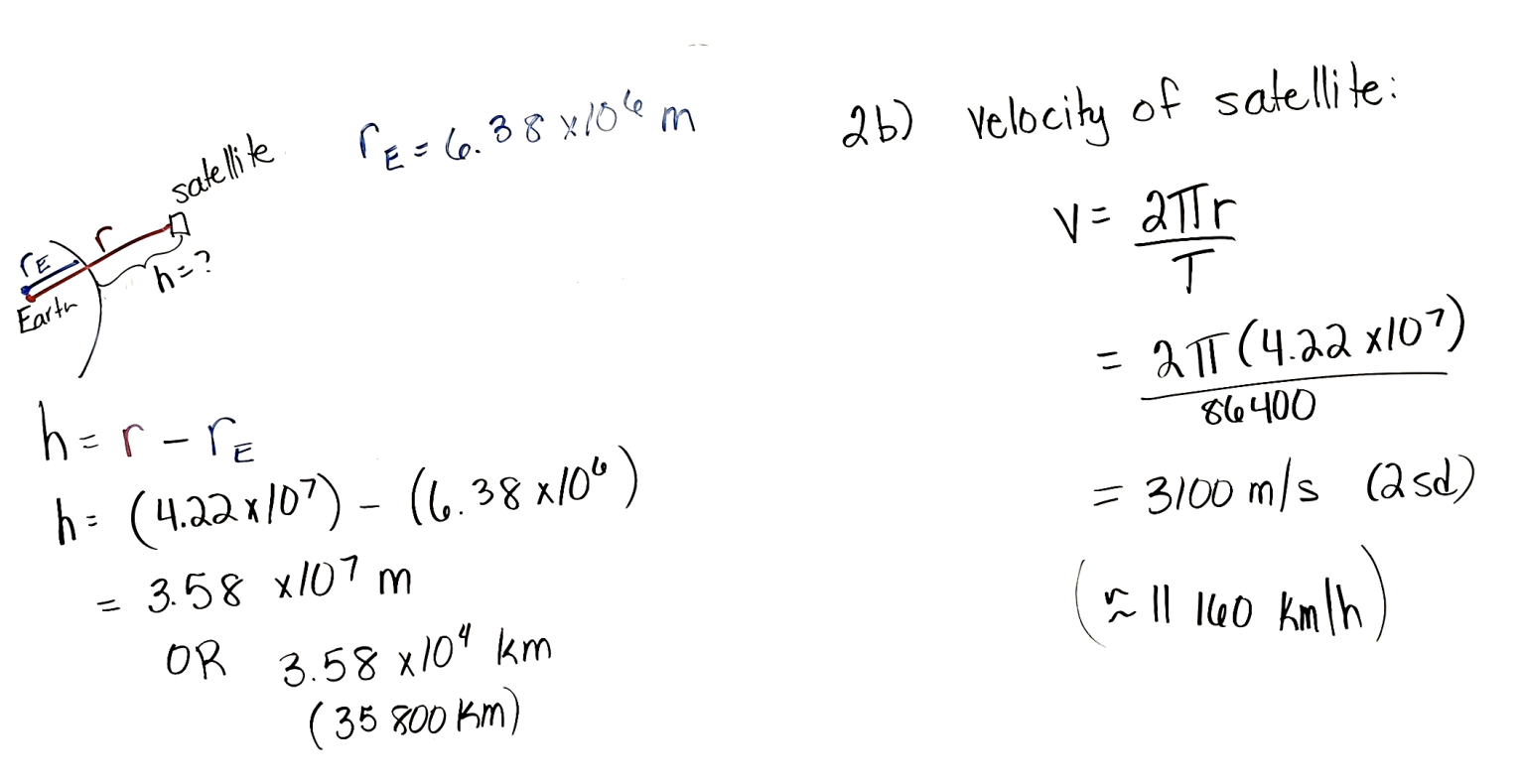
how do you calculate the height of a geostationary satellite above the surface of earth
radius of the satellite orbital radius - radius of earth
what are the 2 ways to find the velocity of a geostationary satellite
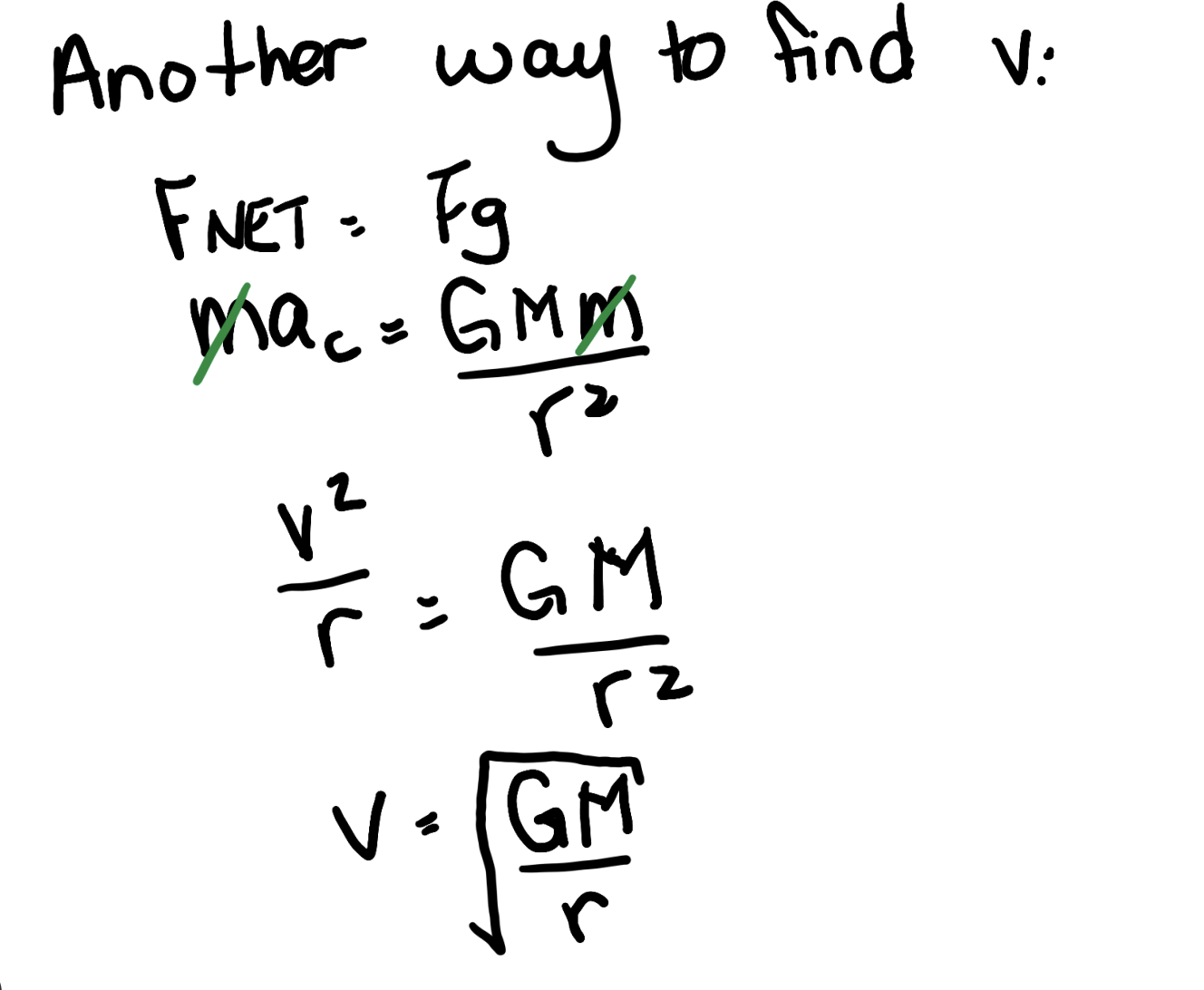
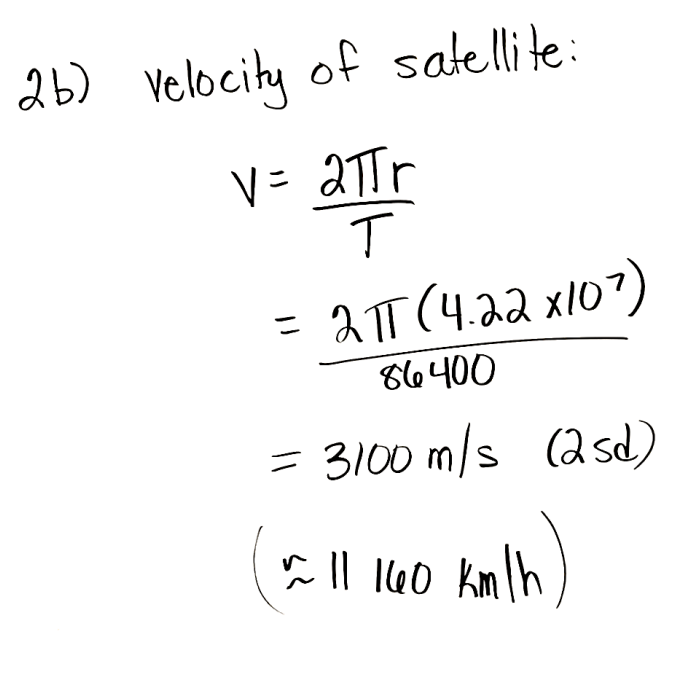
explain artificial gravity
Artificial gravity is a way of creating a gravity-like effect without using a massive planet, usually by rotation.
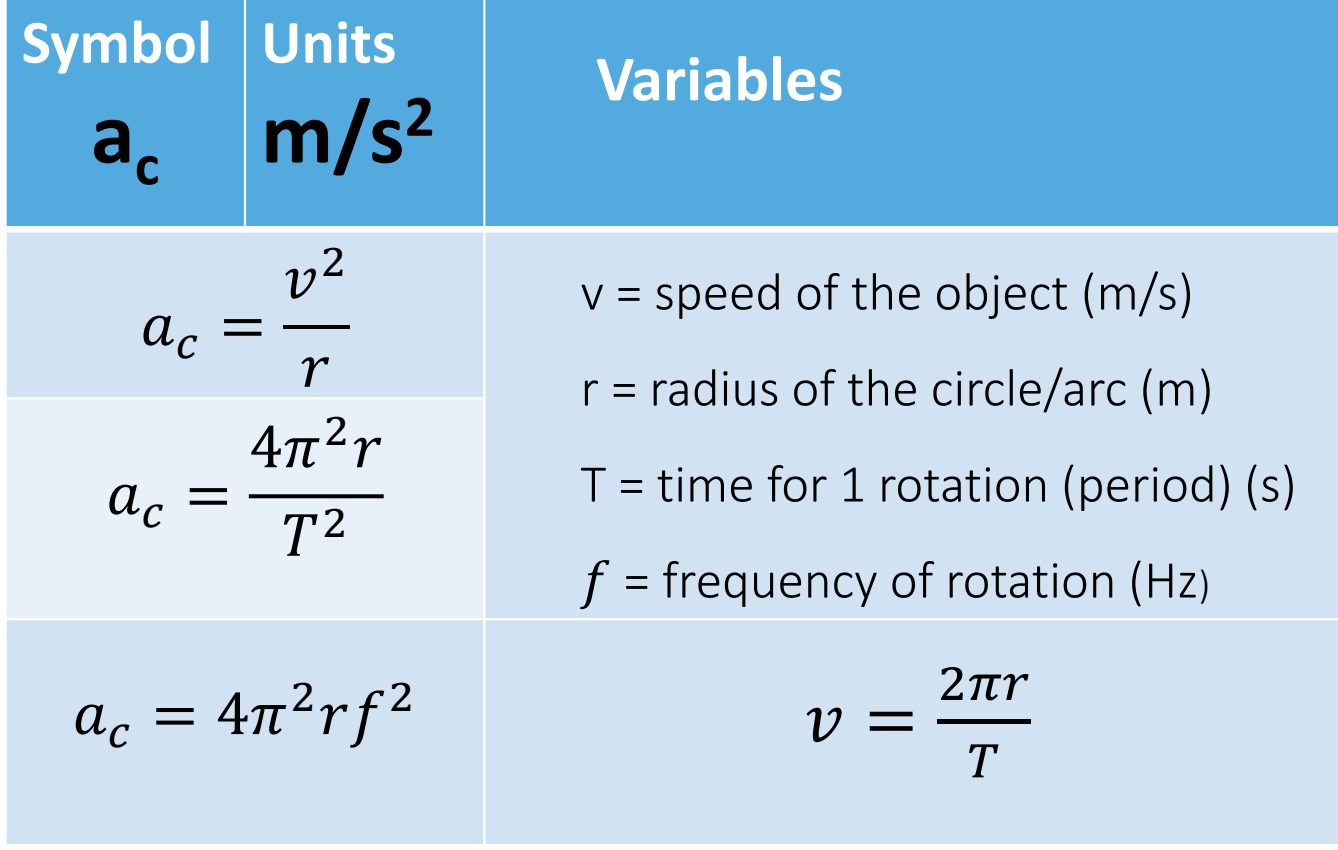
centripetal acceleration formulae
ac = v²/r → v = speed of the object, r = radius of its circular orbit
ac tells you the inward accerlation required to keep an object moving in a circle
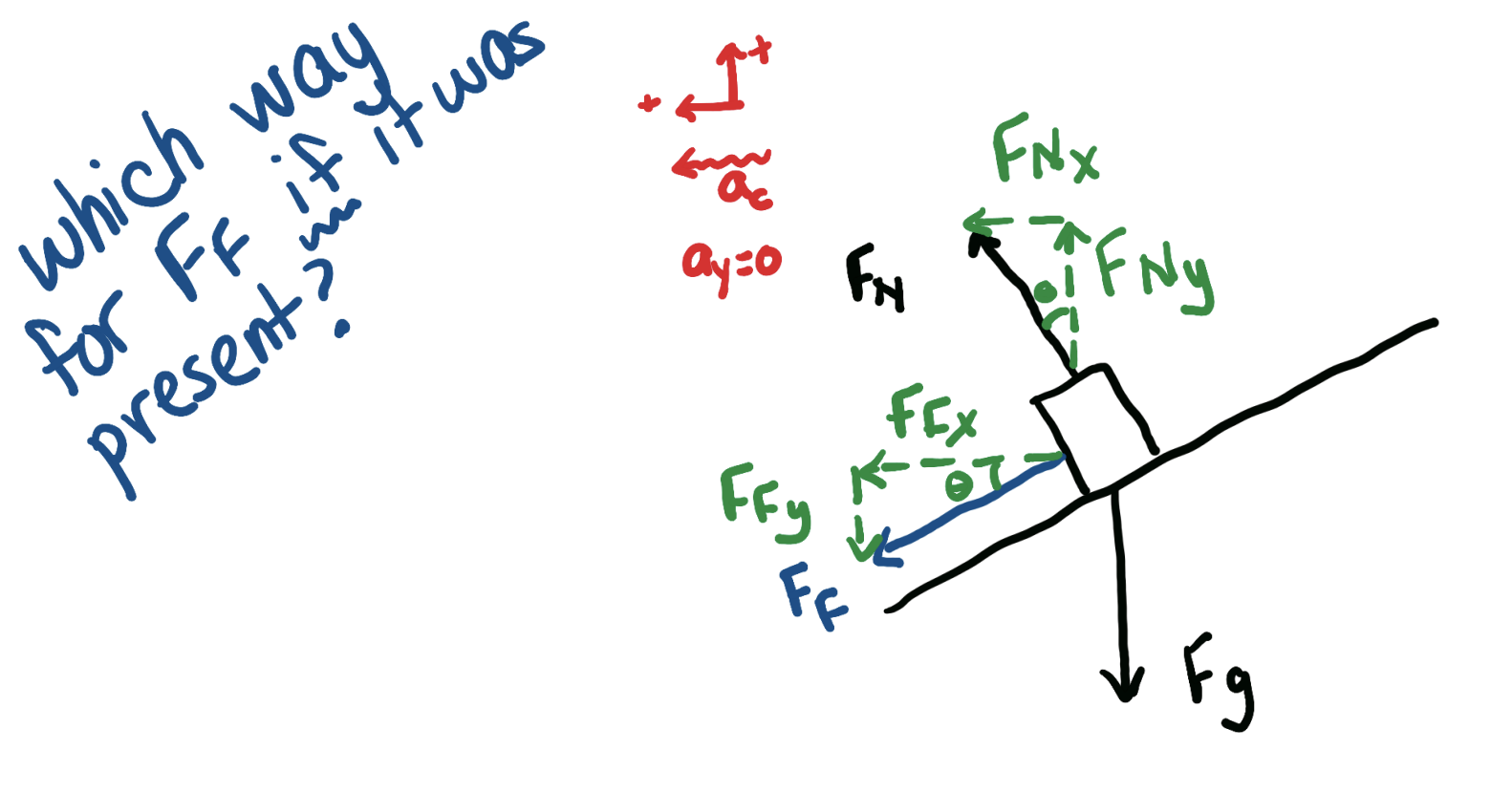
how are the axes different for a ramp vs a banked curve?
how does this affect the FBD and Fnet?
for a ramp, the forces are acting along the ramp, so the axes are tilted so the x axis is parallel to the ramp
for a banked curve, the centripetal force (and acceleration) is acting directly towards the centre so the x axis is not tilted! the forces are not acting at a tilted angle!
Fnet acts along the axes, so make sure that when your writing Fnet equations, the forces ALONG the axes are being added up
draw the FBD for a banked curve
which direction does friction act along
positive directions? ac, ay?
notice that friction acts along the ramp because its the force between the object and the surface, gravity acts down ALWAYS, and Fn is perpendicular to the surface
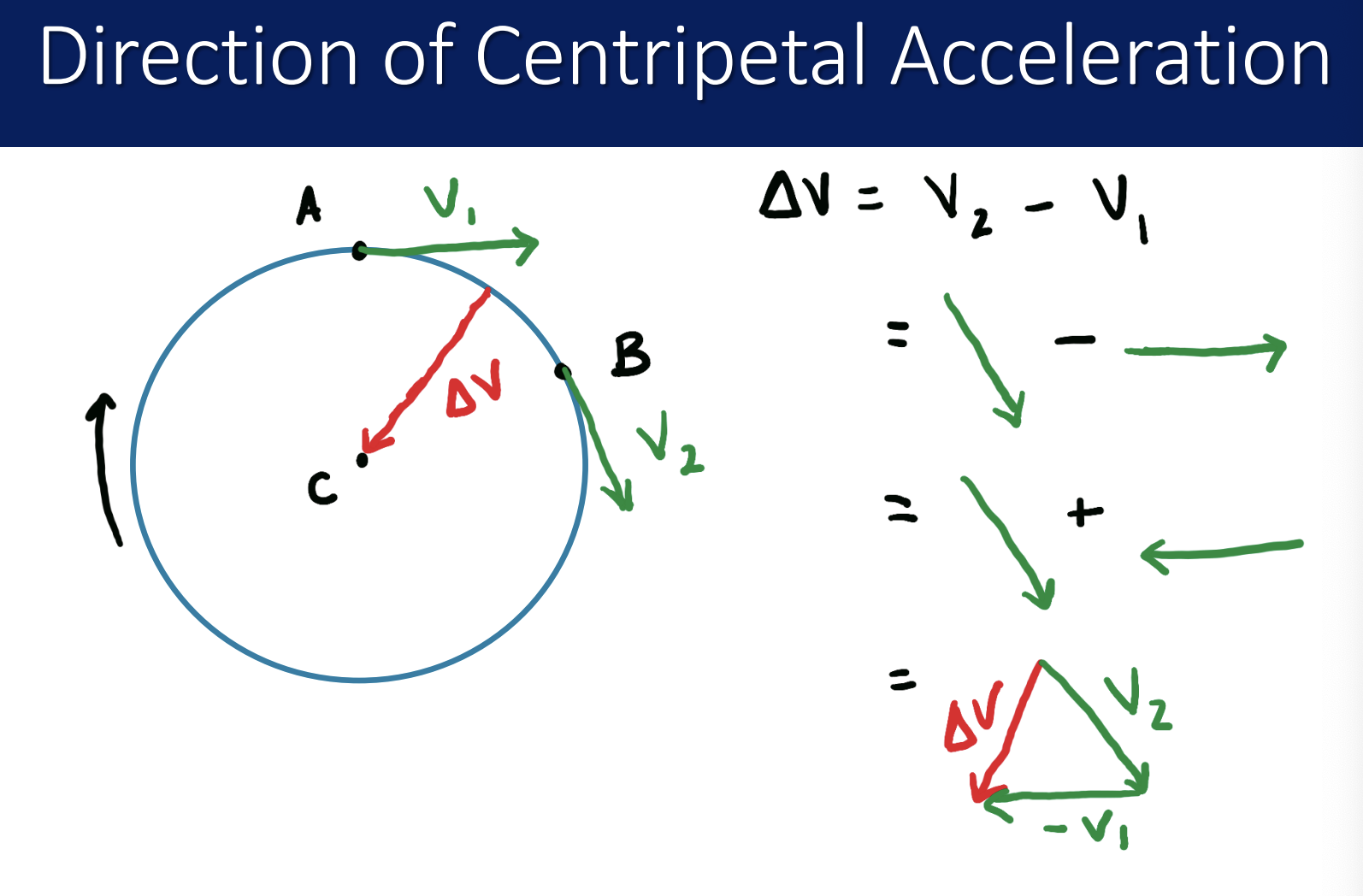
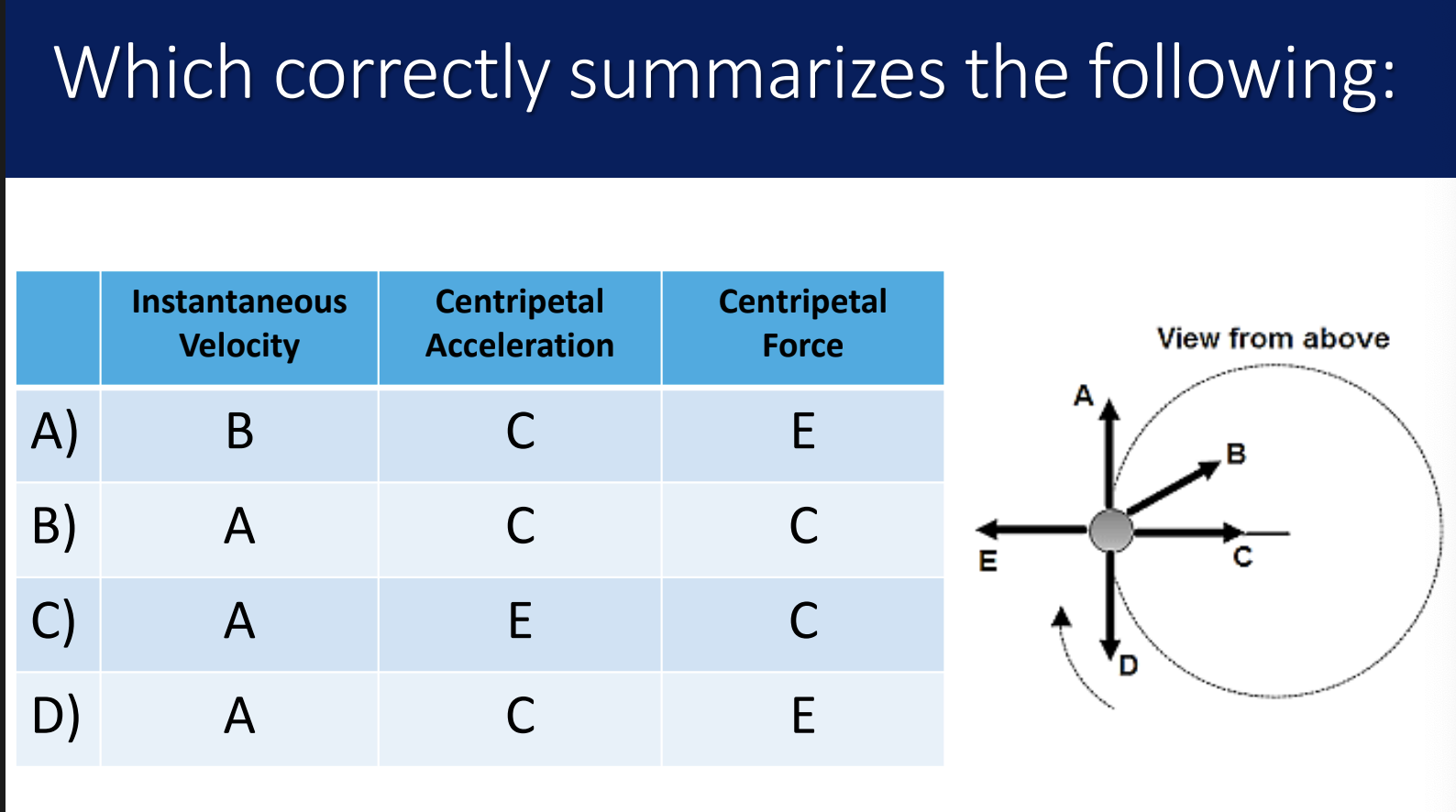
show how the direction of centripetal acceleration is in the same direction as ∆v
what are the 3 formula for centripetal acceleration
what is centripetal force
centripetal force is a synonym for the net force towards the centre of a circle
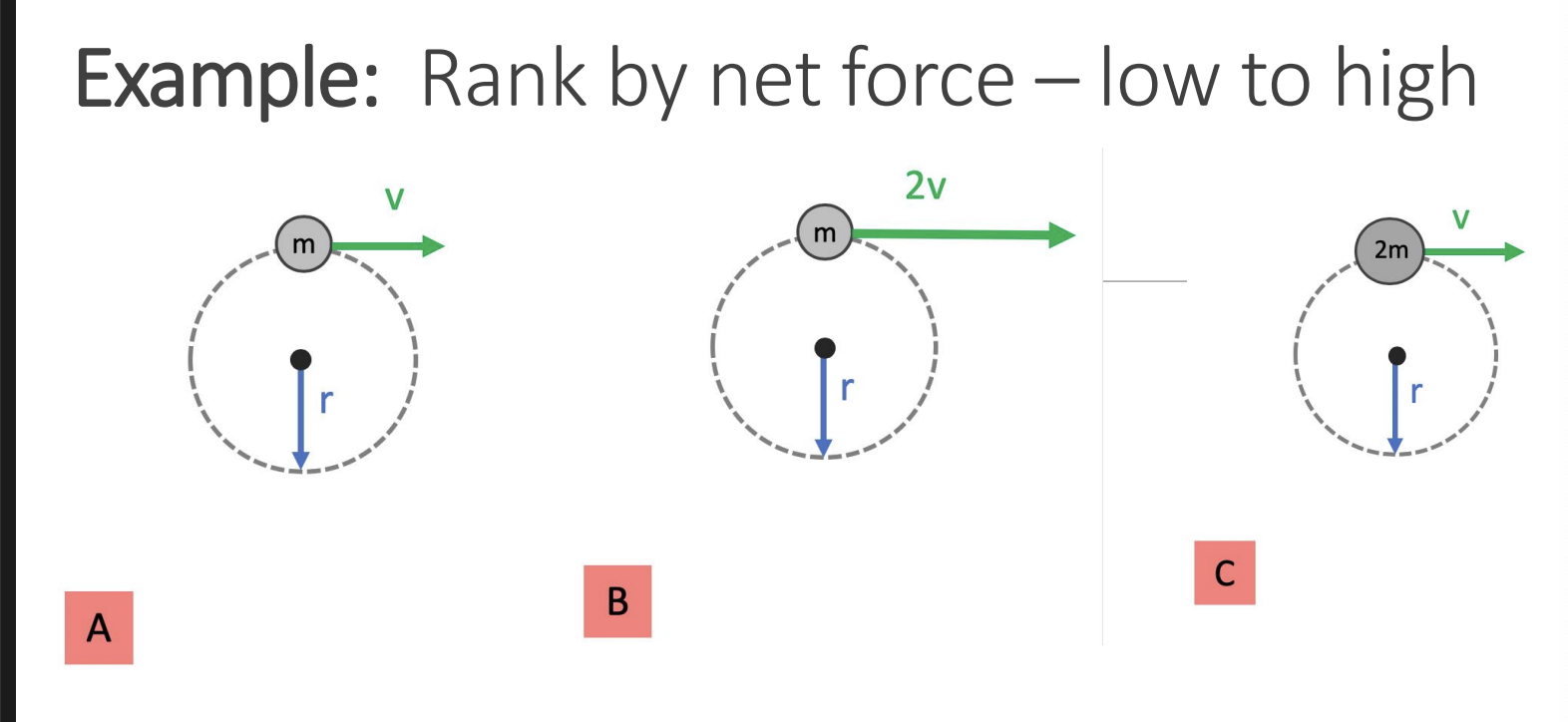
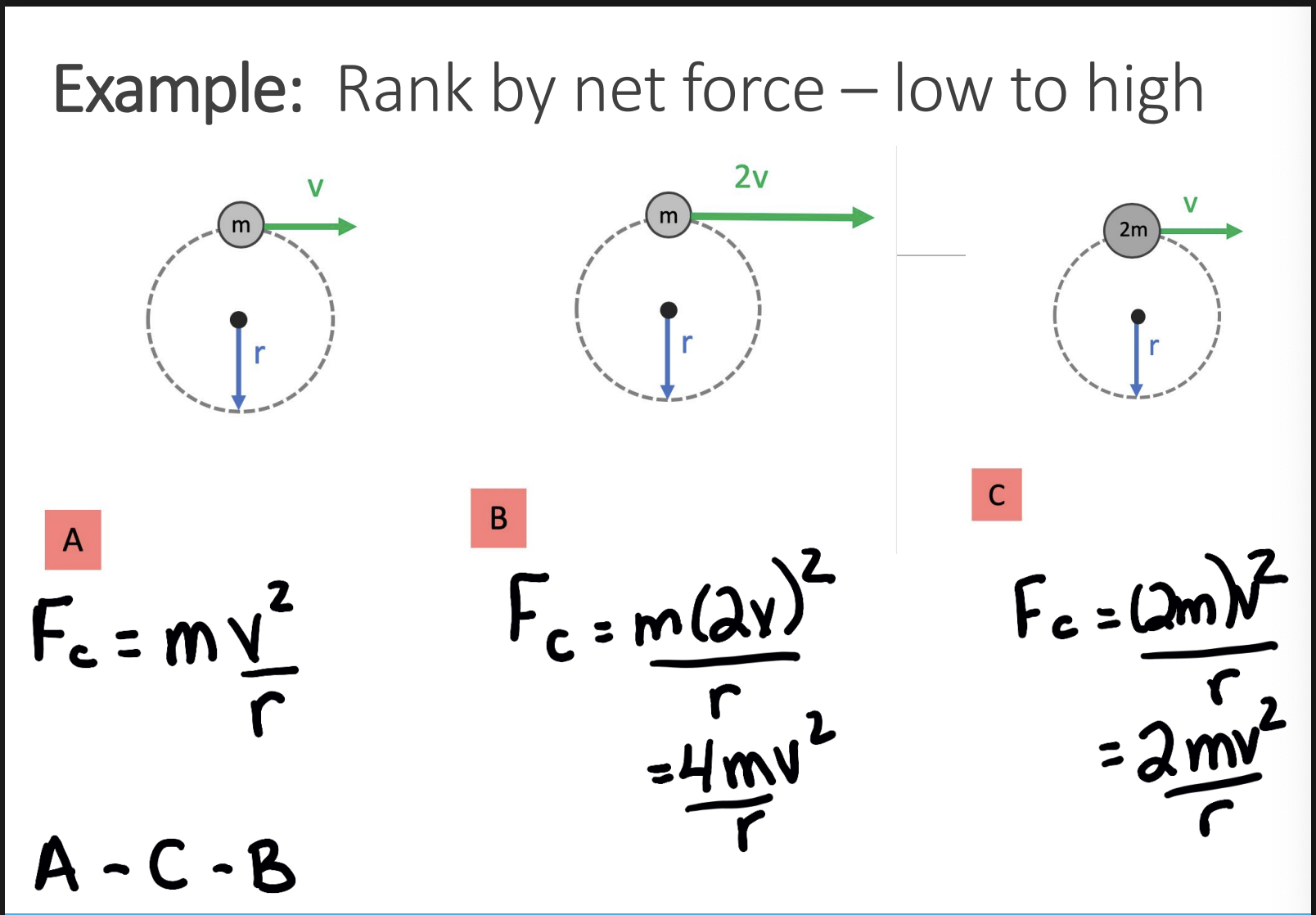
B
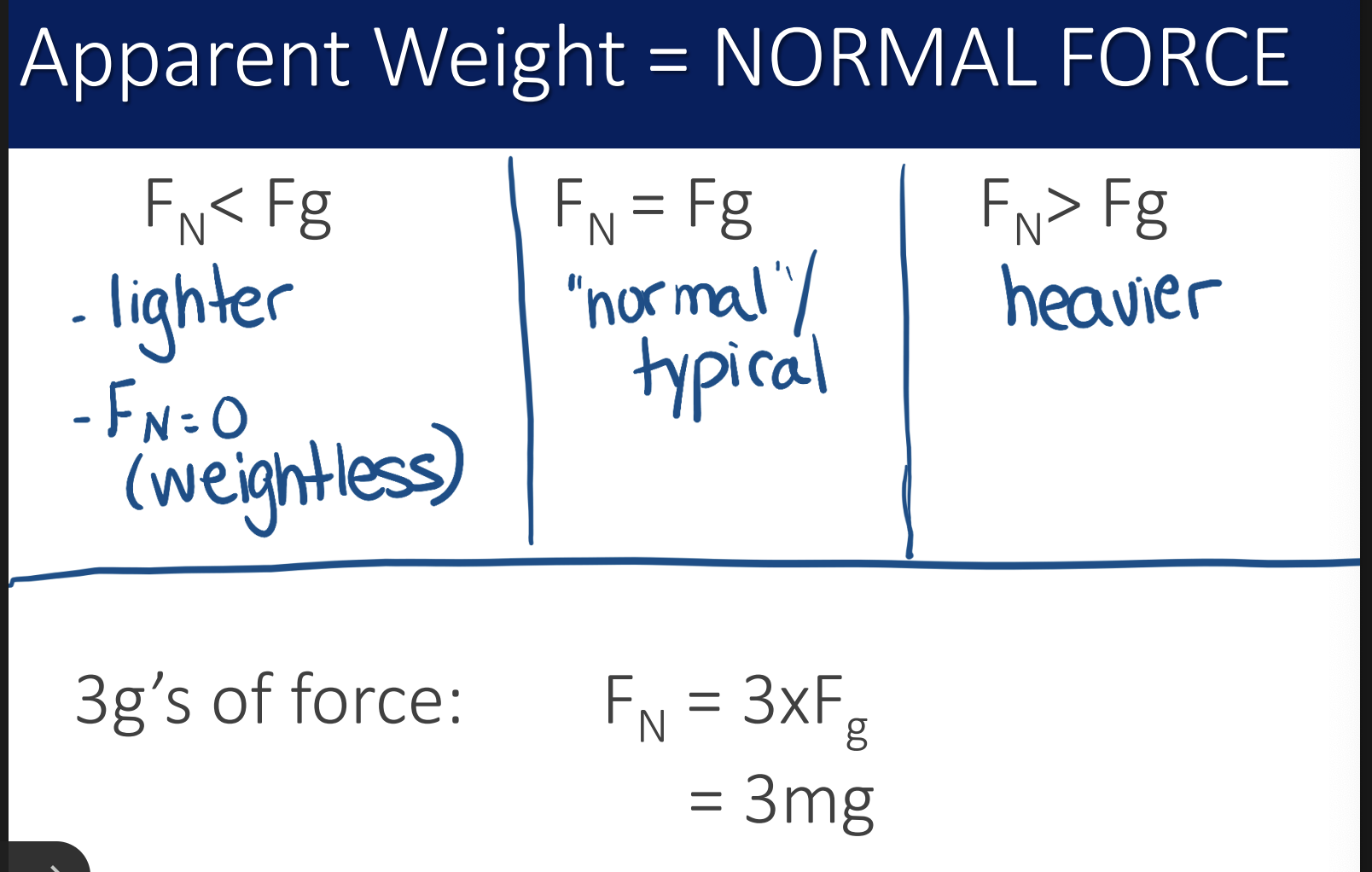
what is apparent weight
this is the normal force
what you feel is the apparent weight. what are the 3 scenarios that you should feel?
what is g of force?
g = Fn/Fg
what features do you need in an explain question
-Definition (IF RELEVANT)
-Point form
-Diagram(s)
-Equations
-Summary/Conclusion