Empirical Social Research
1/368
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
369 Terms
What is empirical social research?
It is understood as a set of methods, techniques and instruments for the scientifically correct conduct of studies of human behavior and other social phenomena.
What are the key components of empirically social research?
- Theory
- Empiric
- Research method
Define the term theory
It is understood as a system or a network of contradiction-free statements to order knowledge about a fact, to explain facts and to predict them.
-> The task of science is to elaborate such theories, to test them and finally to improve them.
Define the term empiricism
It is a specific form of statements describing reality. Unlike theory, these have not yet been proven (sufficiently and comprehensively) in practice.
Name the characteristics of Empiricism
- Refers to knowledge based on systematic experience as well as theoretical models
- Ranges from historical source studies to quantitative and qualitative data collection and analysis
- Theory are in a dialectical relationship
Define the term research method
Represents systems of instructions and rules to be able to realize certain findings, respectively to achieve certain results or to collect information
What methodological approaches do you know?
- Qualitative
- Quantitative
- Mixed method
Name the goals of empirical social research
- describe and explain social life by providing reliable, valid, well-documented information
- develop and test theories
- build understanding about human behavior
- use of research as a solution to social problems
Give examples of empirical social research in the 21st century
Company: for new products or technologies
Parties/Politics: making election forecasts
Marketing: comparison of the success of different marketing measures
Medicine: experiments/studies for the introduction of a drug
Is the research process standardized?
No.
- the steps depend on the research context and research question
- the steps depend on the research context and research question
- the steps can be repeated
Name the individual steps of a research process
1) Literature research
2) Concept and theory
3) Research question
4) Selection of the unit of study
5) Data collection
6) Data analysis
7) Writing and publishing
What ideally happens in the literature review step? 1)
It involves a critical review of existing research on the phenomena and relevant theoretical ideas
What is ideally done in the step of conception and theory? 2)
Ideas emerge that drive the research process and inform the interpretation of the resulting findings
What does the research question step involve? 3)
the goal of a research project is formulated by elaborating a research question including possible sub-questions and hypothesis
What does the researcher consider in the step of selecting the unit of study? 4)
He considers which research direction (e.g., qualitative or quantitative) is best suited to address the problem and defines the sample
What happens in the data collection step? 5)
The researcher collects the data (e.g., interviews, surveys, data archives)
What takes place in the data analysis step? 6)
Managing, analyzing, and interpreting the data sets
What does the step Writing and Publishing entail? 7)
It involves writing up research and its results, as well as publishing in scientific journals
Graphically represent the exemplary process of a research project
1) plan your project schedule and scope
2) refine your research question
3) understand ethics, privacy, confidentiality
4) read, take notes, write up as you go along
5) choose your research
6) conduct a literature review
7) conduct your research and collect the data
8) analysis and interpret your data
9) read, redraft and proof your work
10) write a first draft of your report
Define the term research design
It outlines the plan for selecting subjects, the location of data collection, and the exact data collection methods needed to answer the research question(s) and test the hypothesis
Why is qualitative research used?
understanding, reconstructing situations, generating regularities
What is qualitative research?
Collection of non-standardized data and their analysis with special, non-statistical methods
What is qualitative research destined for?
Used for complex contexts, when little prior knowledge exists or when deep insights about a research subject are to be gained
What Survey methods are used for qualitative research ?
- Interview
- Group discussion
- Observation
- Qualitative content analysis
- Qualitative experiment
- Case study
What are the advantages of qualitative research ?
- Generating new knowledge
- Small sample
- Subjective/detailed/descriptive answers
What is quantitative research destined for?
explain connections, form causalities, check laws for validity
-> high comparability
What is quantitative research?
Extracts from reality are measured and quantified, i.e. translated into numerical values, and statistically evaluated
Why is quantitative research used?
Used when measuring the frequency of a phenomenon or its distribution, testing hypotheses, or seeking broad insight
What survey methods exist for quantitative research?
- Standardized interviewing
- Standardized observation
- Experiments
- Standardized content analysis
What are the advantages of quantitative research?
- High reliability
- Fast processing of a large amount of data
- Interval scale level responses
What is the examination order of qualitative research?
non-experimental
What is the closing procedure of qualitative research?
inductive (from specific to general), research logic is hypothesis developing
What is the scope of qualitative research?
holistic - holistic
What cognition mode is used for qualitative research?
explanatory, descriptive mode of knowledge
What is qualitative research's content?
open research process
How is data analysis conducted with qualitative research?
usually non-numeric and explicative, soft, realistic data
What is the research process of qualitative research?
dynamic
How is qualitative research investigated?
investigation of an individual case
What is the examination order of quantitative research?
non-experimental, experimental
What is the closing procedure of quantitative research?
deductible (from general to specific), research logic is hypothesis testing
What is the scope of quantitative research?
part concerning - particular
What cognition mode is used for quantitative research?
understanding, measuring mode of cognition
What is quantitative research's content?
testing of predefined hypothesis
How is data analysis conducted with quantitative research?
usually numerical and reductive, hard, replicable data
What is the research process of quantitative research?
static
How is quantitative research investigated?
study of sample
Describe the mixed-method approach
It combines aspects of quantitative and qualitative research to combine advantages of both approaches and provide a more comprehensive answer to the research question. The goal is to validate the results of one method by using another method and thus obtain more meaningful results.
Graph the mixed-method approach
Research: questions
1. Qualitative study: survey and analysis, conclusion (create hypothesis)
2. Quantitative study: survey and analysis, conclusion (test hypothesis)
= Joint: interpretation of the results
Name advantages of mixed methods
- Strengths and weaknesses ( limitations ) of qualitative and quantitative methods are balanced.
- Illumination of research subjects from different perspectives leads to more comprehensive understanding
- Suitable for questions that could not be answered by a purely quantitative or purely qualitative survey
- Validation function through triangulation
—> Results of one method are validated by the use of another method, this leads to more meaningful results.
Name disadvantages of mixed methods
- Paradigm War
- More methods do not necessarily lead to a better result.
- Mixed methods are not necessarily superior to one-method research.
- Researchers must have competencies in the execution of data collection, processing, and -evaluation of the respective methods.
Characterise Paradigm War
→ quantitative and qualitative research use different paradigms
→ approaches have different epistemologies
→ from epistemological point of view combination of the two approaches is not possible
When are qualitative methods are used ?
They are mostly used to generate new research questions and to open up new subject areas. They are less suitable for testing hypotheses and are therefore closely related to the inductive approach.
Give a sample question of qualitative methods
" What are the psychosocial effects of unemployment? " " What is the effect of unemployment following successful training? "
When are quantitative methods used ?
They are used when the research question refers to correlations of variables that are as concrete as possible and general statements are to be made.
Give a sample question of quantitative methods
"Is there a link between television viewing and school success ? " " Is frequent television viewing causative of lower school achievement ? "
What types of (raw) data are distinguished ?
-Primary data
→ What data must be obtained ?
- Secondary data
→ What data is already available ?
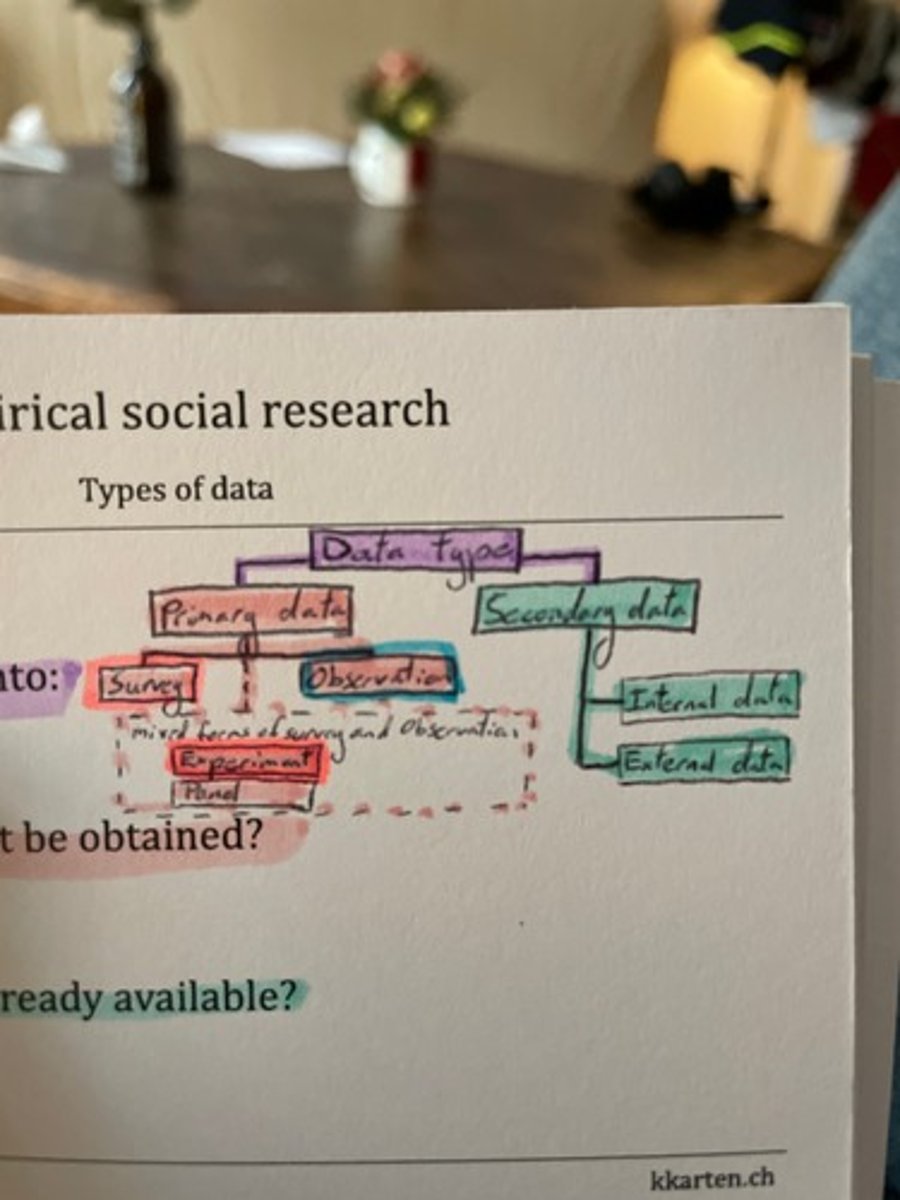
Distinguish the types of data in a graph
Data Type
1) Primary Data
a. Survey
b. Observation
c. Mixed forms of observation (Experiment; Panel)
2) Secondary Data
a. Internal Data
b. External Data
List goals for using primary data
- Know what is meant by observation, questioning, and experimentation
- Getting to know primary research methods (there's more than surveys!).
- Knowing the characteristics of the methods
- Knowledge of areas of application of these primary research methods
List goals for using primary and secondary data
- Know what possibilities (but also limitations) it has
- Recognize when and why it is not usable/useful
- Know how it is evaluated
In what ways can primary data be collected ? - qualitative studies
- Brainstorming
- Delphi technology
- In-depth interview
- Group discussion
- Focus Group
In what ways can primary data be collected ? -Survey
- Personal
- By phone
- Written
- Online survey
—> communicative!
Research Process In what ways can primary data be collected ? -observation
- Personal
- Apparative methods
- Non - reactive methods
- Eye tracking
- Neuroscience
- Click streams HPS
- Emotion- Recognition
- Netnography
- RFID
... non - communicativel
In what ways can primary data be collected ? -experiment
- Market test
- Product test
- Packaging test
- Advertising test
- Test market
—> No independent methods
In what ways can primary data be collected ? -panel suvey
- Consumer panel
- Retail Panel
- Special panel
—> No independent methods
What is a test market ?
A test market is a partial sales market in which newly developed products are introduced on a trial basis in order to make the introduction risk on the overall market calculable through accompanying surveys and / or market observations .
Where can secondary data be collected ?
- Blogs and forums
- Fan communities
- Social media
- Data mining platforms
- Data Contests
- Data search engines
Name strengths of primary data
- High topicality
- Good fit to the research question
- Influence on data quality
- Often proprietary
Name the weaknesses of primary data
- Longer time required
- Higher costs
- Higher personnel expenses
Name the strengths of secondary data
- Fast availability
- Low cost
- Low personnel expenses
- Large samples
Name the weaknesses of secondary data
- Lack of fit to the research question
- Little / no control during data collection
- Lack of documentation
List possible errors in the research process
- Research objectives and identified information needs do not correspond to the actual research question or are too ill-defined .
- During data preparation , data is entered incorrectly , participants are entered twice or overlooked, or data sets are merged incorrectly .
- Uncontrolled bias of the data by the participants
- Measurement errors during data collection
- Used systems (software and computers) work incorrectly .
- Incorrect interpretation of the results
Name general principles of scientific work
- Reliable backup and retention of primary data
- Objective evaluation and reference to the literature used
- No obstruction of the scientific work of others
- Clear and traceable documentation of the applied procedures
Summarize the most important points from lecture 1
- In empirical social research , the concepts of theory , empiricism , and research method are central .
- Qualitative research is about understanding meaning , whereas quantitative research is primarily about measuring events .
- When collecting data , it is important to distinguish between primary and secondary data , with observation and interviewing as two important primary data types
- Qualitative and quantitative research pursue different goals , the approach differs , and the two approaches bring different criticisms as well as advantages
Name requirements that are placed on a research topic
- Intrinsic motivation of the researcher (interest)
- Relevance for society
- Up-to-date and contemporary
- Not too much/little edited yet
What is a research question ?
Question around which the focus of the research revolves. The goal of a research question is to guide the research project and help construct a logical argument
→ It is central to the reader as it conveys the goal and framework of the paper
→ The constructed argument ideally results in hypothesis and conceptual model
Name the main types of research questions
- Comparison Question
- Causal question (cause-effect relationship )
- Descriptive question
Explain the comparison question
Attempts to examine the difference between two or more groups in terms of variables.
Explain the causal question
- Cause-effect relationship
- Compares two or more variables and investigates the existence of a causal relationship.
Explain the descriptive question
Aims to describe a phenomenon and often uses "how questions."
The question "What is the difference in caloric intake among high school students?" is a descriptive question. - True / False-
Wrong
example of a comparison question
The question "Does the amount of sugar in students ' diets affect the number of tooth cavities they have per year?" is a comparative question. - True / False-
Wrong
example of a causal question
The question "How often do students use social media platforms like Instagram?" is a descriptive question. - True / False-
Right
How do you find a research question ?
• Searching for a "gap" in the literature or for contradictions
• Review the "Limitations" or "Future Research" section of an article
→ They are often the result of deficiencies in existing research
What characterizes a good research question ?
- clear
- focused
- concise
- unambiguous
- exclusive
- ethical
→ A research question should provide suggestions, arguments, or solutions to a specific topic, making a concrete contribution to a scholarly debate to fill a gap in the literature
List key words for research questions
- Determinants, dimensions
- Conditions, criteria
- Advantages/Disadvantages
- Comparison, motives , goals
- Requirement, prerequisite
- Conclusions, consequences
- Types characteristics, types
- Success/influence factor
- Properties features
- Opportunities, risks limits
Is the question a good or bad research question? "How is global warming affecting the environment?"
The research question is poor
→ The question is not focused enough. What does environment mean in the question?
Is the question a good or bad research question?" What is the most significant effect of glacier melt on penguin life in Antarctica?"
The research question tends to be poor
→ The question is too specific. The "most significant" effect is difficult to find empirically; it would be better to use the phrase " significant effects." Mentioning Antarctica in the question is unnecessary
Is the question a good or bad research question? "Why are social networks harmful?"
The research question is poor
→ The question is too open: For whom are social networks harmful? A kind of hypothesis is already set up in the question or a valuation takes place. Networks are not defined - social networks can refer to online or offline environments.
Is the question a good or bad research question? "How do online users perceive privacy issues on social networks like Facebook and Twitter "
The research question is good
→ Perhaps "privacy issues" could be specified more precisely
Is the question a good or bad research question? "How does the amount of time children spend playing computer games each day affect childhood obesity rates in London?"
The research question tends to be poor
→ The question is very complex and convoluted
What is a hypothesis ?
Quantitative studies typically include one or more hypotheses in addition to the research question. "They are formulated based on theories and can be tested through an empirical investigation"
Deductive :
Theory -> Hypothesis -> Investigation -> Verification
What are the types of hypotheses ?
- Null hypothesis vs. alternative hypothesis
- Directed vs. non-directed hypothesis
- Specific vs. non-specific hypothesis
Explain the alternative hypothesis
It represents the actual expected effect.
→ Ex: Aliens have entered my house to steal my socks.
Explain the null hypothesis
It egates the alternative hypothesis and expresses that, for example, there is no correlation.
→ Ex: Aliens are not to blame for where my socks have gone. There is another explanation for the disappearance of my socks.
Explain the non-directed hypothesis
- Non-directional or directional hypothesis :
- No specification of the direction
→ Ex: " There is no difference between advertising measure A and advertising measure B. "
Explain the directed hypothesis (directional)
Hypothesis specifies direction of effect
→ Ex: "Advertising Measure A is better than Advertising Measure B."
Explain the specific hypothesis
Indication of expected difference/connection.
-> Ex: " Advertising measure A leads to at least a 10 % increase in sales compared to advertising measure B. "
Explain the non-specific hypothesis
No indication of the size of the difference
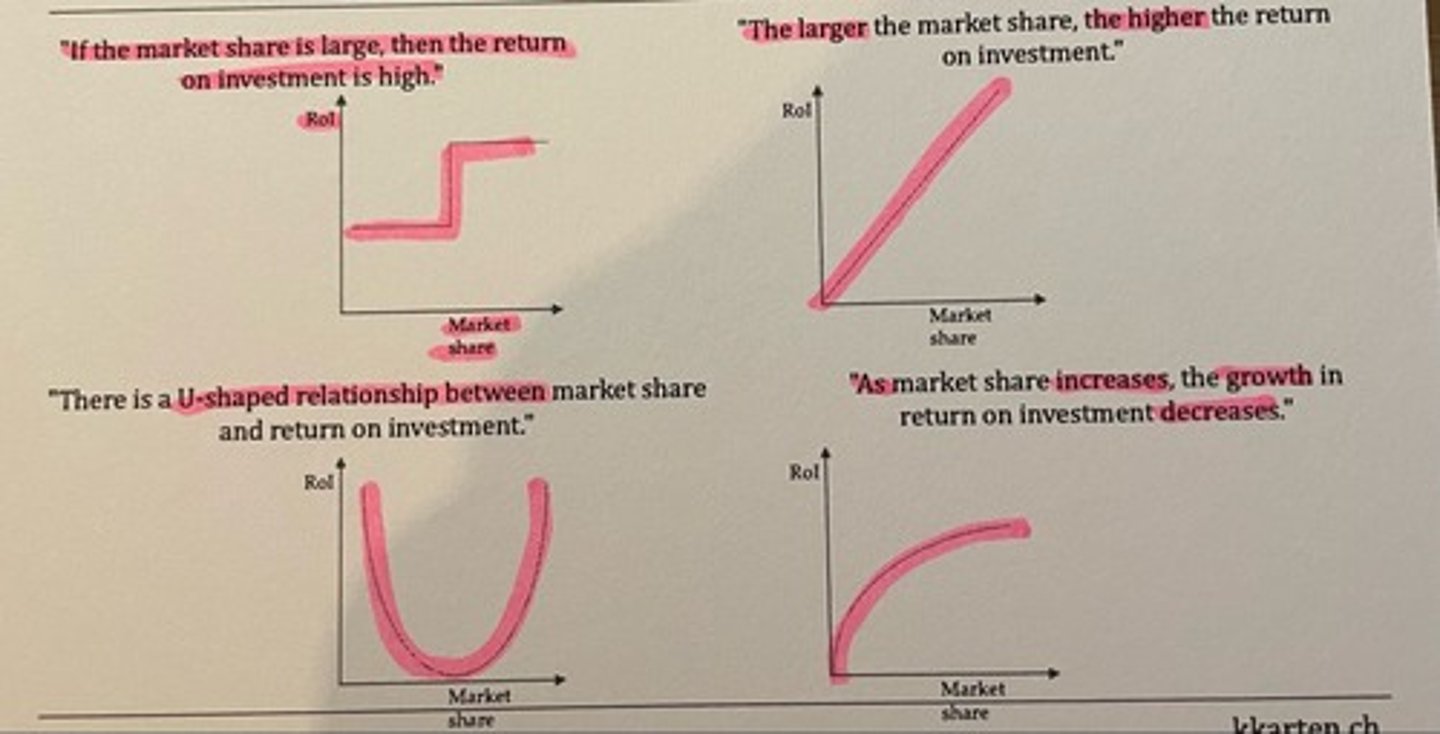
Show the possibilities of hypothesis formulation using the example of the relationship between ROI and market share
- If the market share is large, then the ROI in high (step line)
- The largest the market share, the higher the ROI (straight line)
- There is a U-shaped relationship between market share and ROI (convex curve)
- As market shares increases, the growth in ROI decreases (curve)
Name typical properties of hypotheses
- Used when there is already extensive knowledge on a particular topic
- Refer to real facts that can be tested empirically
- Usually valid statements that go beyond individual cases or singular events
- Inherently prognostic
- Should include the variables and populations chosen and the predicted relationships between these variables
- Framed as statements rather than questions and should be developed prior to data collection in order to know what data to collect
- Data is collected and analyzed to support or refute hypotheses to reach a conclusion