Prokaryotic Genomes and Organelles
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
some bits of wisdom abt bacteria (5 points)
they are everywhere and do everything
snottite eats rocks and spits acid
permafrost
in clouds
we only know v little abt them
only 10^4 cultured
10^5 sequences
(vs tot estimation of spp being 10^7-10^12)
v huge impact on our lives good and bad
we are partly bacteria
in our body we have abt 10 more bacteria than humans cells or same number
mitochondria used to be free living bacteria
some of most amazing bio tools from bacteria
i.e. CRISPR
what is the most diverse grp of organism
bacteria
(also archaea but less)
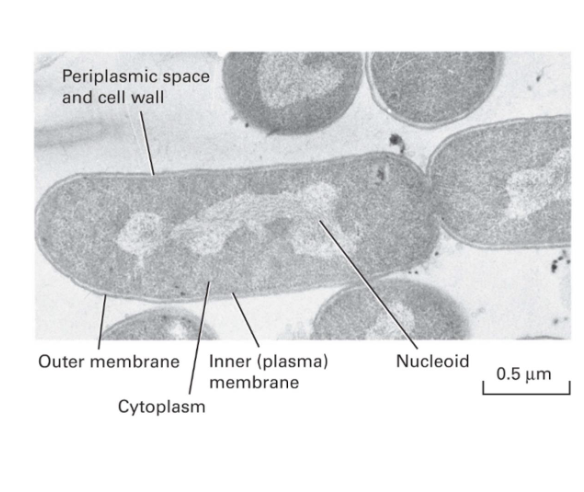
what is the prokaryotic cell organization
cell wall surrounding the cellular membrane
gramm negative bacteria contian outer membrane that surrounds cell wall
typically no membrane bound organelles in the cell
chromosomes are in the cytoplasm
allows translation to occur on RNA before transcription even finished
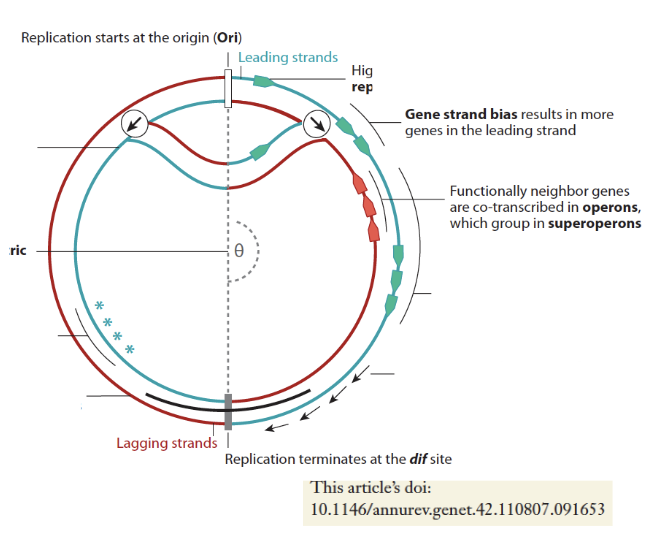
bacterial chromosomes
most contain single circular chromosome
abt 10% of the known spp contain more than one
each chromosome contains a single origin of replication
each half of chromosome is replicated by replisome
length of known ones ranges few hundred kbp to mroe than 14Mbp
highly transcribed genes are oriented in same direction as the replication fork progression
to avoid conflicts
how are genes organized in the bacterial chromosome?
DNA is gene rich
very little intergenic regions
unlike eukaryotes that have a lot of non coding DNA
no introns
genes are grouped with operons
share common promoter
are transcribed together to form polycistronic mRNA
How is bacterial DNA compacted and organized?
use DNA binding proteins to cover DNA (like eukaryotes)
BUT do not have histones
so DNA not wrapped around nucleosome
Gyrase required to introduce torsion (negative supercoiling) to compact DNA
SMC proteins generate loops to organize DNA
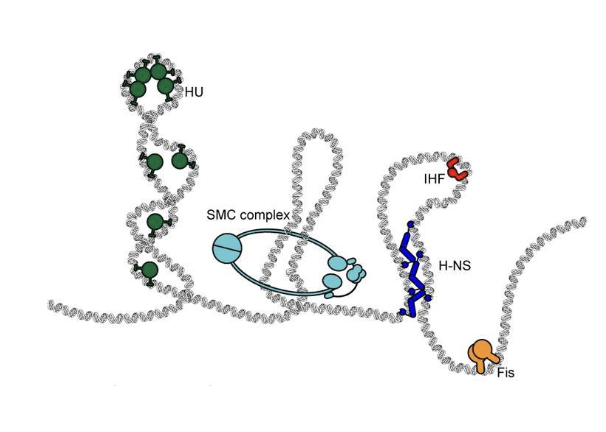
gyrase
a special type of DNA topoisomerase that introduces torsion (negative supercoiling) to compact bacterial DNA
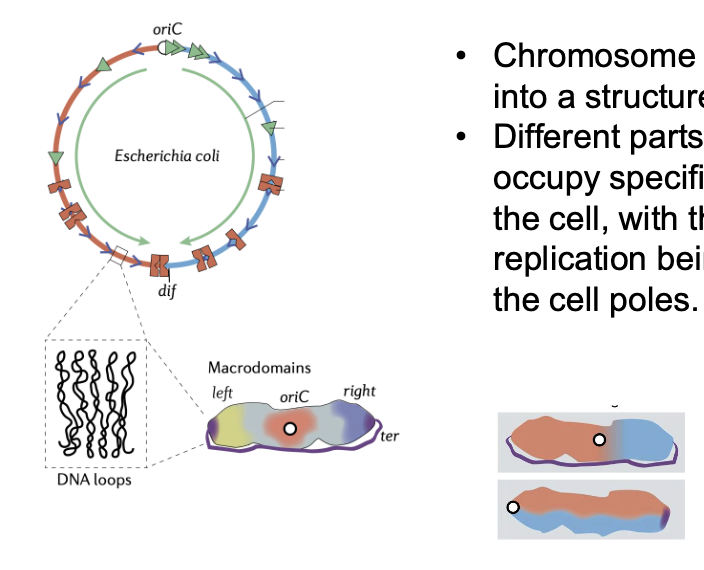
how are chromosomes organized in bacteria (originally surprising because we didn’t think they were organized)
nucleoid structure of chromosome and protein
difft parts of the chromsome occupy specific parts of the nucleoid in the cell
origin of DNA replication is at the cell center or at the cell poles
this is analogous to eukaryotic higher order organization
Organellar DNAs
genetic material found in organelles outside of the cell nucleus
found in mitochondria and chloroplasts
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
Mitochondria important for respiraion
Chloroplasts imp for photosynthesis
originally free organisms that were endocytosed and became endosymbionts
how do mitochondria and chloroplasts ressemble prokaryotes in terms of their genomes?
circular
genes typically lack introns
gene products resemble prokaryotic RNAs and proteins
where in the mitochondria do we find DNA molecules
in the mitochondrial matrix
how many organelles do cells usually have? what can we say about each organelle’s genome?
there are usually many mitochondria (and chloroplasts) per cell
each organelle may have multiple genomes
Human Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
16,569bp
37 genes only in mtDNA (other organisms can have more or less)
many encode components needed for respiration and translation
have their own ribosomes for translation
have many genes coding for tRNA molecules
no introns
gene products stay within mitochondria
Chloroplast genome (cpDNA)
DNA molecules also inside organelle
100-200 genes
100-200kb
Lynn Margulis
evo theorist and biologist and author
using info at the time proposed that mitochondria and chloroplasts originiated from free living bacteria
was motivated to explain how eukaryotes acquired their organelles (contrast w bacteria and archea that do not have membrane bound organelles)
her paper was rejected 12+ times
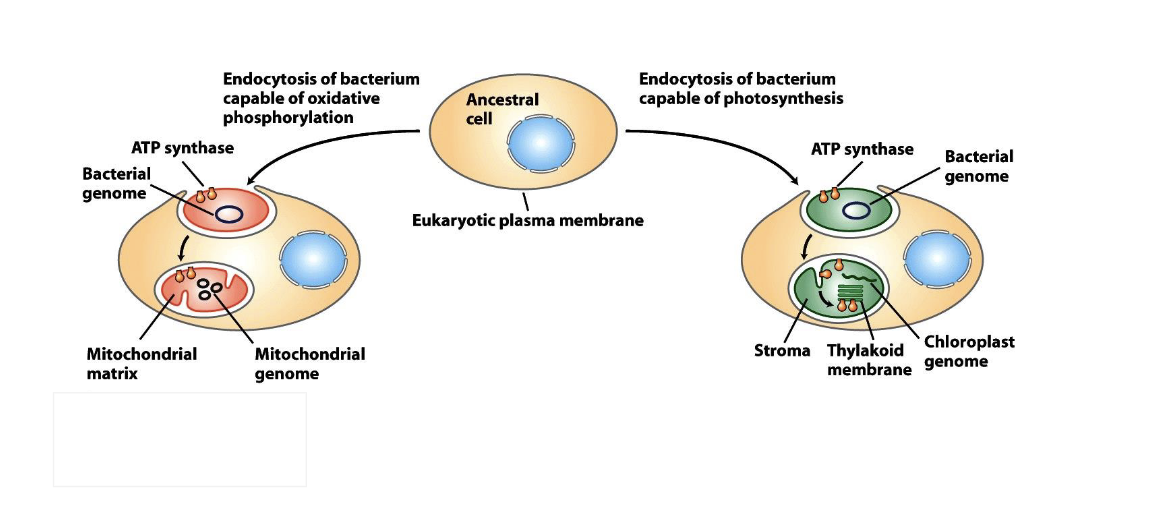
What is the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of chloroplasts and mitochondria
ancestral cell endocytosis of bacterium
capable of oxidative phosphorilation
(or)
capable of photosynthesis
what is evidence of endosymbiotic theory for mitochondria we have now?
bacteria from the Rickettsia genus
relatives to the ancestor of mitochondria
These are intracellular parasites
cause typhus fever
what are thought to be the closest relatives to the recipient cell that generated the first eukaryotes
Lokiarchea
found near the Loki’s Castle hydrothermal vent site in the Acrtic Ocean
identified from metagenomic sequence data
(as most prokaryotes) cannot be cultured
Other examples of bacterial endosymbionts
many insects
esp those that eat from plant saps => the bacterial endosymbiont help them produce the nutrients lacking in their diet
other organisms with bacterial endosymbionts include:
cockroaches
clams
blood feeding flies
etc
obligate endosymbiont
can no longer survive wirthout a host cell
undergoes a reduction in their genome
genes that are not necessary for bacterial function are lost
reductive evolution
how do sea slugs (dinoflagellates) use endosymbiosis?
they eat algae and corals and keep the chloroplasts so that they can photosynthesize
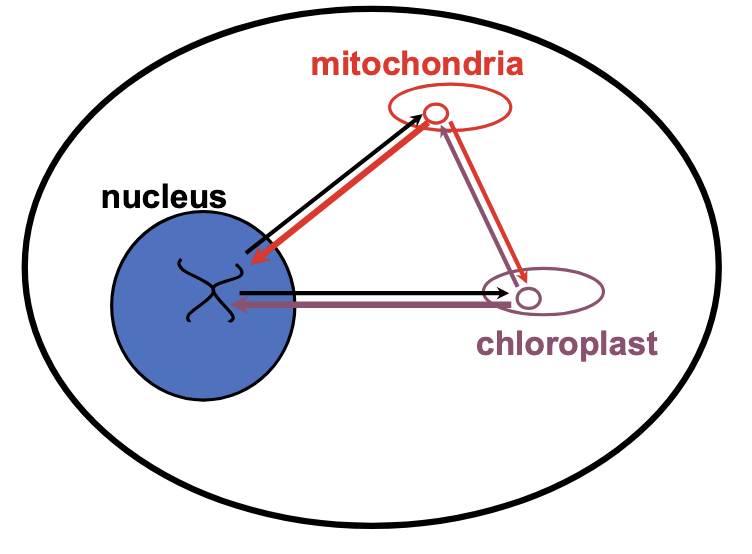
where are most of the proteins in mitochondria and chloroplasts cloded
in the nucleus
there has been gene mvmnt to nucleus over evolution
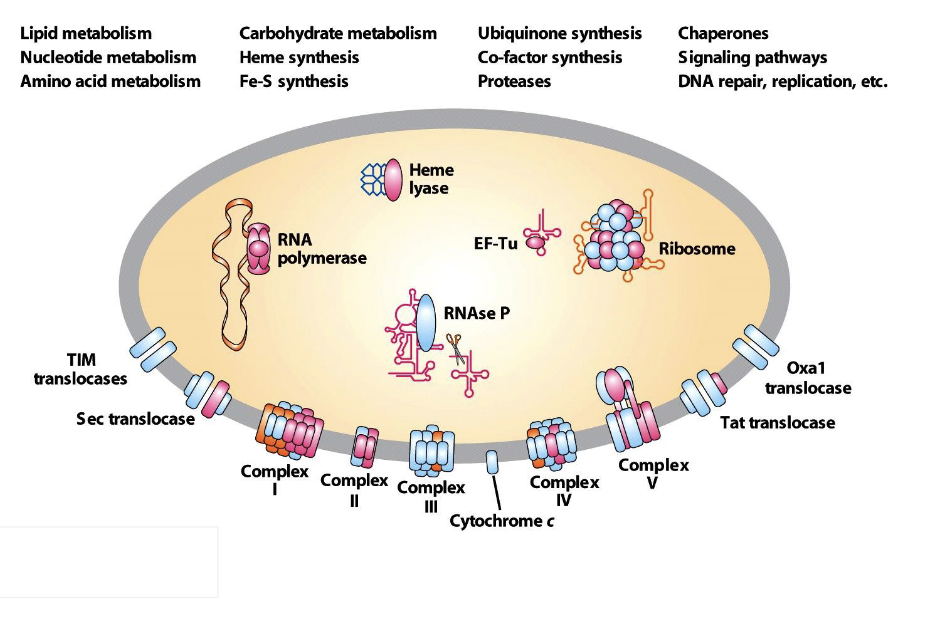
what can we say about mitcochondrial ribosomes?
Mitochondria have their own ribosomes
they have sequence similarity to those in bacteria
all proteins coded in the mitochondria stay in this organelle
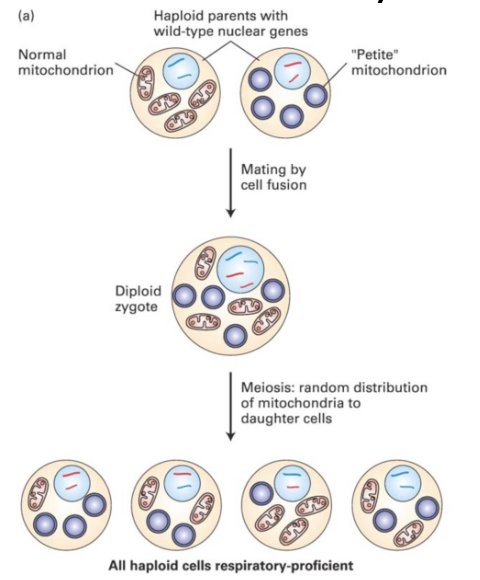
how are mitochondria inherited?
cytoplasmic inheritance
different from that of DNA in the nucleus
Mitochondria are distributed evenly among daughter cells
this is random
if once cell has no mitochondria or non functional one then won’t survive in most scenarios
Why do mitochondria not have the same constraints as the genetic code?
alternation of genetic code
i.e. stop codon used for an AA
What are mutations in mtDNA related to in mammals?
aging
Mice with a mitochondrial DNA polymerase defective
for proofreading exhibit premature agin