chapter 5 pt. 2 - infection and disease
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
what are characteristics of transient microbes?
cling to surfaces that they don’t originally grow from
vary from person to person
can be any microbe that a person picks up
is greatly influenced by hygiene
what are characteristics of resident microbes?
lives and multiplies in deeper epidermal layers
lies in glands and follicles
more stable and less influenced by hygiene
examples include Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, Porpionibacterium, and yeast
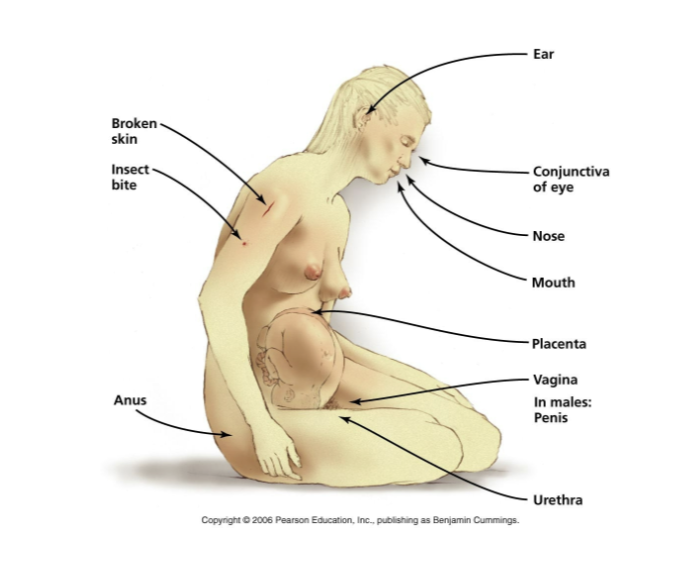
this is a diagram of portals of entry
what are some ways that pathogens can leave the host?
in secretions (such as earwax, tears, nasal secretions, saliva, sputum, respiratory droplets)
in blood (via arthropod bites, hypodermic needles, wounds)
in vaginal secretions or semen
in milk produced by mammary glands
in excreted bodily wastes (such as feces and urine)
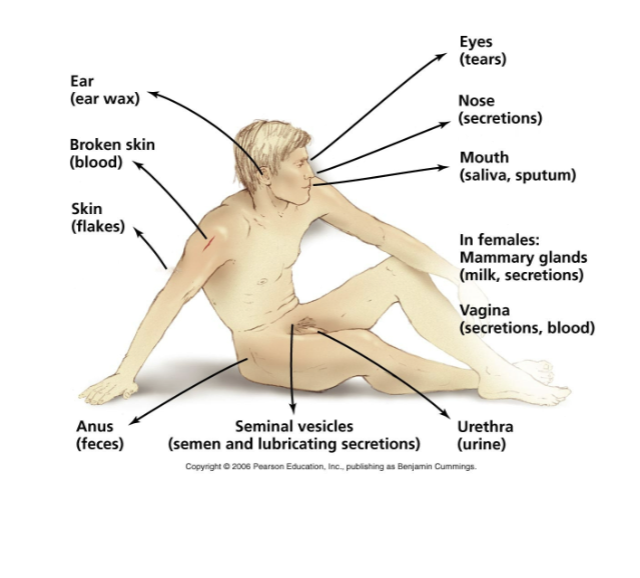
sources of infectious diseases in humans include
animal reservoirs and human carriers
what are animal reservoirs and how are they acquired?
they are zoonoses-diseases that spread naturally from usual animal hosts to humans. they are acquired by direct contact with animals and their wastes, the eating of animals, or bloodsucking arthropods
what are human carriers and a few examples?
humans who act as carriers of a pathogen. they may or may not be capable of transmitting the pathogen, because it depends on the stage of infection and the type of pathogen. asymptomatic humans can remain infective for years. examples include AIDS or syphilis
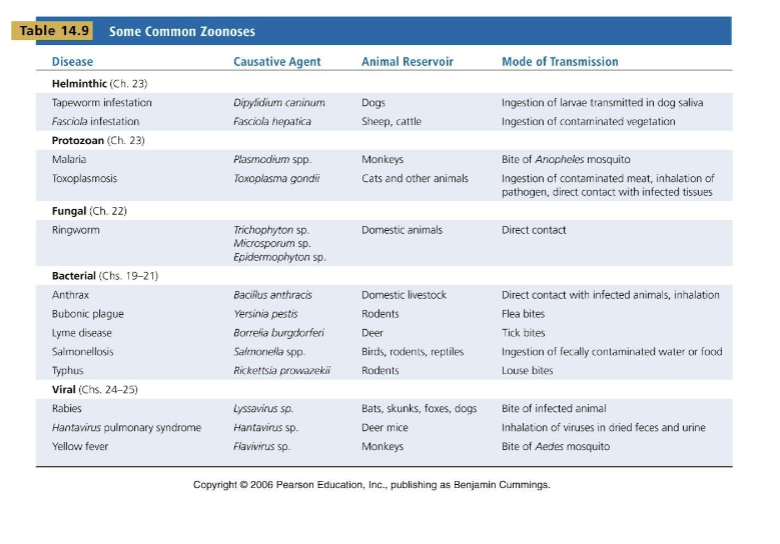
these are examples of zoonoses
what are examples of nonliving reservoirs?
soil, especially if contaminated by feces (such as Clostridium)
water, which can be contaminated with feces and urine that contain parasitic worm eggs, pathogenic protozoa, and viruses
food, because meats, milk, and veggies can harbor pathogens
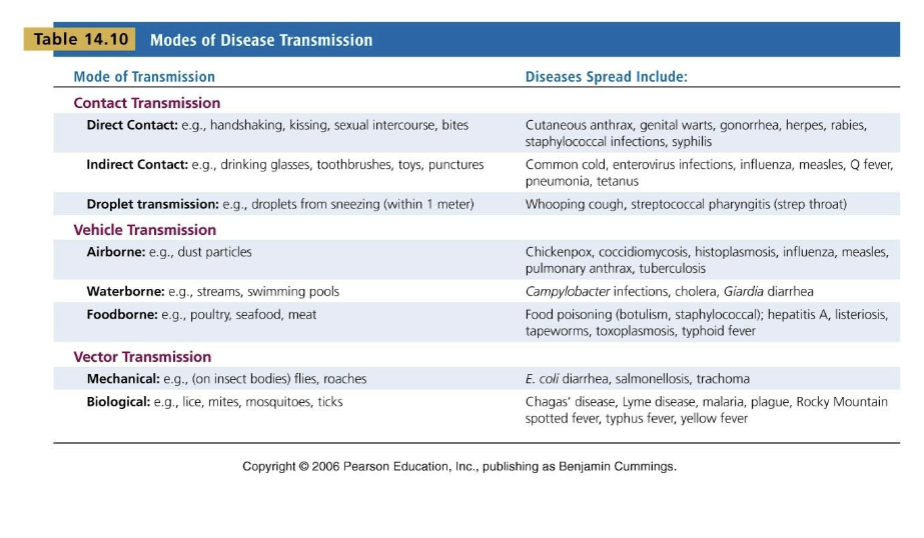
these are examples of modes of transmisson