Pham 5
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
139 Terms
1
New cards
ADHD is associated with
dopamine transporter gene and dopamine D4 gene
2
New cards
Causes for ADHD
–Genetic
–Perinatal stress
–Low birth weight
–Traumatic brain injury
–Maternal smoking during pregnancy
–Early deprivation
–Dietary intake of certain chemicals and sugar
3
New cards
four types of symptoms for ADHD
**Behavioral**
* Hyperactivity
* impulsivity
* risk behaviors and reward dependence
**Cognitive**
* Organizational issues,
* poor planning and execution skills,
* deficits in time management
**Social-emotional**
* Emotional impulsivity
* dysphoria, anger, anxiety
* emotional lability
* trouble reading social cues, and issues w/ keeping friends
\
**Deficits in executive function**
* Problems with self-regulation
* sequencing behaviors
* planning and organization,
* working memory and internalized speech
\
\
* Hyperactivity
* impulsivity
* risk behaviors and reward dependence
**Cognitive**
* Organizational issues,
* poor planning and execution skills,
* deficits in time management
**Social-emotional**
* Emotional impulsivity
* dysphoria, anger, anxiety
* emotional lability
* trouble reading social cues, and issues w/ keeping friends
\
**Deficits in executive function**
* Problems with self-regulation
* sequencing behaviors
* planning and organization,
* working memory and internalized speech
\
\
4
New cards
ADHD symptoms in adults cont.
•Interrupting conversations
•Frequent job changes
•Irritability
•Relationship discord
•Low frustration tolerance
5
New cards
non pharmacologic treatment ADHD
•Behavior modification
•Parent training
•Family therapy
•Social and academic skills training
•Individual psychotherapy
•Cognitive–behavior modification
•Therapeutic recreation
6
New cards
Name two types of stimulants
Dextroamphetamine (adderall)
**Methylphenidate** (Ritalin, Concerta, Methylin, and Metadate)
**Methylphenidate** (Ritalin, Concerta, Methylin, and Metadate)
7
New cards
Dextroamphetamine (adderall)
ex. Dextroamphetamine (adderall) FDA controlled substance class 2
\
Side effects
**Report CNS changes**
•Can cause physical dependency
•dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, altered libido
•Diabetes may need to monitor serum glucose can alter requirements
\
Interactions
•Avoid ETOH, caffeine, OTC meds that stimulate
\
Contraindications
•Pregnancy cautious use
\
Education
•Taper dose when discontinuing
\
Side effects
**Report CNS changes**
•Can cause physical dependency
•dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, altered libido
•Diabetes may need to monitor serum glucose can alter requirements
\
Interactions
•Avoid ETOH, caffeine, OTC meds that stimulate
\
Contraindications
•Pregnancy cautious use
\
Education
•Taper dose when discontinuing
8
New cards
**Methylphenidate** (Ritalin)
ex. **Methylphenidate** (Ritalin, Concerta, Methylin, and Metadate)
\
Side effects
•cardiovascular events, headache, insomnia, anorexia, nausea, tics, weight loss, vomiting, EPS, NMS
\
Interactions
–Anticonvulsants
\-Other ADHD medications
–Antidepressants
–Anticoagulants
Contraindications
•Caution with seizure disorders, monitor BP and CBC, growth
Education
•Do not mix with Alcohol, other CNS drugs, take on empty stomach.
\
Side effects
•cardiovascular events, headache, insomnia, anorexia, nausea, tics, weight loss, vomiting, EPS, NMS
\
Interactions
–Anticonvulsants
\-Other ADHD medications
–Antidepressants
–Anticoagulants
Contraindications
•Caution with seizure disorders, monitor BP and CBC, growth
Education
•Do not mix with Alcohol, other CNS drugs, take on empty stomach.
9
New cards
two types of Non-Stimulants
**Atomoxetine** (Strattera)
**Guanfacine** (Tenex)
**Guanfacine** (Tenex)
10
New cards
**Atomoxetine** (Strattera)
Side effects
•headache, insomnia, xerostomia, abdominal pain, vomiting, anorexia, nausea, cough.
**Box Warning**-may increase risk of suicide ideation in pediatric patients.
Interactions
•Multiple drug interactions
Contraindications
•Pregnancy cautious use
Education
used for adults or children over 6(weight based)
•Dose adjustment with hepatic impairment
•headache, insomnia, xerostomia, abdominal pain, vomiting, anorexia, nausea, cough.
**Box Warning**-may increase risk of suicide ideation in pediatric patients.
Interactions
•Multiple drug interactions
Contraindications
•Pregnancy cautious use
Education
used for adults or children over 6(weight based)
•Dose adjustment with hepatic impairment
11
New cards
**Guanfacine** (Tenex)
**ex. Guanfacine** (Intuniv® extended release tablets)
\
MOA
•Selective alpha-2A adrenergic receptor agonist. Directly engages receptors found in prefrontal cortex (area of brain linked to ADHD
Side effects
\-Somnolence, sedation, abdominal pain, dizziness, constipation, hypotension, drug mouth
\
Interactions
•Multiple drug interactions
\
Contraindications
•Use with caution in patients with hypotension, bradycardia and syncope.
Education
•Treatment of ADHD in children and adolescents ages 6 to 17 years
Dose adjustment with patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction
\
MOA
•Selective alpha-2A adrenergic receptor agonist. Directly engages receptors found in prefrontal cortex (area of brain linked to ADHD
Side effects
\-Somnolence, sedation, abdominal pain, dizziness, constipation, hypotension, drug mouth
\
Interactions
•Multiple drug interactions
\
Contraindications
•Use with caution in patients with hypotension, bradycardia and syncope.
Education
•Treatment of ADHD in children and adolescents ages 6 to 17 years
Dose adjustment with patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction
12
New cards
MOA
Side effects
Interactions
Contraindications
Education
Side effects
Interactions
Contraindications
Education
13
New cards
Antidepressants in ADHD
•Tricyclic Antidepressants may also be used.
ex bupropion (wellbutrin)
14
New cards
Clonidine in ADHD
•used for mood, activity level, cooperation and frustration
15
New cards
first line for ADHD
**stimulants**
–Methylphenidate
-amphetamine
–Methylphenidate
-amphetamine
16
New cards
Second line for ADHD
**nonstimulants**
–Atomoxetine
–Guanfacine or clonidine
17
New cards
Third line for ADHD
bupropion
18
New cards
neurotransmitters ADHD
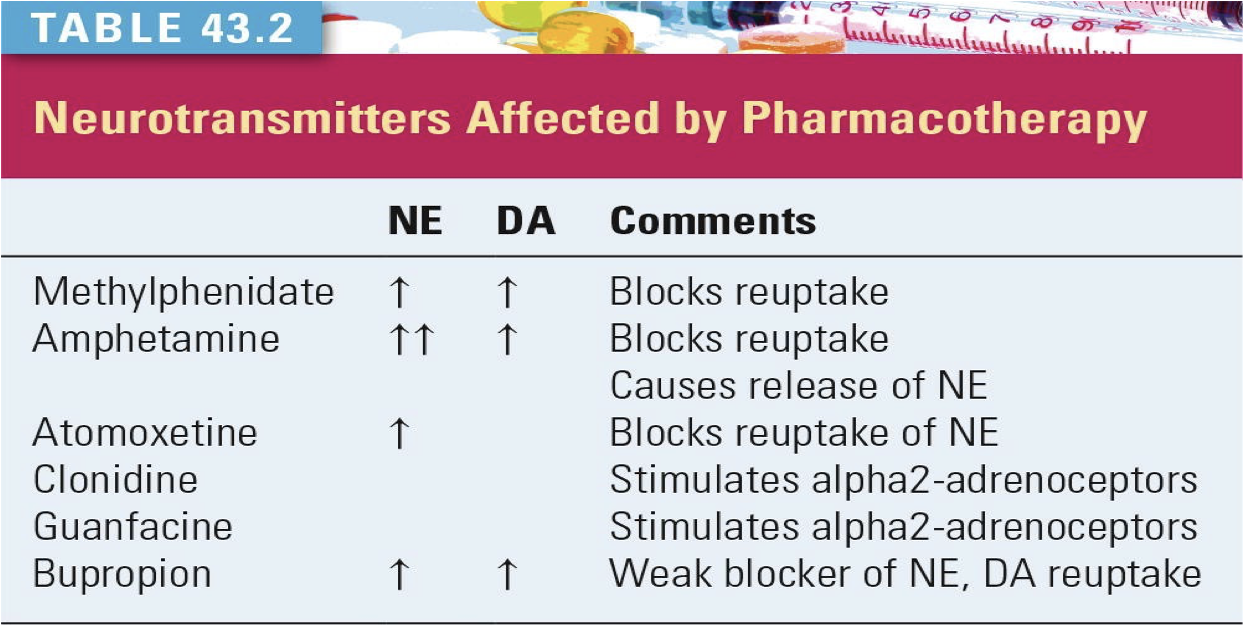
19
New cards
monitoring for ADHD
* Connor’s Rating Scale
* take drug exactly as prescribed
* Height and weight in children
* Monitor for change in behavior
* Cardiovascular risk factors- EKG, BP, P; monitor CBC
\
* take drug exactly as prescribed
* Height and weight in children
* Monitor for change in behavior
* Cardiovascular risk factors- EKG, BP, P; monitor CBC
\
20
New cards
education in ADHD
•If taken in multiple doses, last dose should be before 2:00 PM because of sleep issues.
•Teach parents which adverse effects to monitor for.
•Children may require more and higher calorie snacks.
•Screen for self medication with other substances in adolescents and adults.
21
New cards
Alzheimer’s facts
•Characterized by a slow, progressive decline in cognition
•The most common cause of dementia accounting for approximately 60% to 80% of all dementia
\
reduces life span and prevalence increases w/ age
\
22
New cards
risk for Alzheimer’s
**Advanced age**
•Apolipoprotein E (APOE)-e4 gene
•\*Family history (e.g., genetic abnormalities)
•Mild cognitive impairment
•Cardiovascular disease
•Low education
•Traumatic brain injury
•Lack of social and cognitive engagement
23
New cards
Alzheimer’s causes
* Apolipoprotein E (ApoE), a protein involved in cholesterol transport, is linked to the development of AD.
* The E4 allele (homozygote E4/E4) is thought to increase the risk of AD, whereas the E2 allele may be protective.
* age related changes: cortical atrophy in brain, vascular damage, free radicals, inflammation
* destruction of cholinergic neurons
* overstimulation of glutamatergic system in the synapse>>neuronal death
* formation of neurofibrillary tangles and plaque
24
New cards
Alzheimer’s late onset VS early onset
Late: 60s and up; most common; APOE gene
\
Early: 30-60s; rare; genetic from parents
\
•Cognitive symptoms, such as loss of short-term memory, usually present first in mild AD.
\
Early: 30-60s; rare; genetic from parents
\
•Cognitive symptoms, such as loss of short-term memory, usually present first in mild AD.
25
New cards
Diagnosis for Alzheimer’s
* only confirmed by autopsy
* DSM-5 ( *Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders)*
* Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE)
* Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA)
* Clock drawing task (CDT)
* DSM-5 ( *Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders)*
* Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE)
* Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA)
* Clock drawing task (CDT)
26
New cards
non pharmacologic for Alzheimer’s
Explore reversible causes:Meds, Metabolic, intracranial infection, toxins,Vitamin B12 def, depression, psychoses
\
Behavior oriented
•Emotion oriented
•Cognition oriented
•Stimulation oriented
•Using calendars, clocks, and written notes or instructions
•Patient and family education
27
New cards
first line for Alzheimer’s
Cholinesterase inhibitors (CIs) once daily
28
New cards
second line Alzheimer’s
•CIs; a trial of second CI may be warranted.
•Vitamin E: may be added to the CI or used as monotherapy in patients who cannot afford CIs.
29
New cards
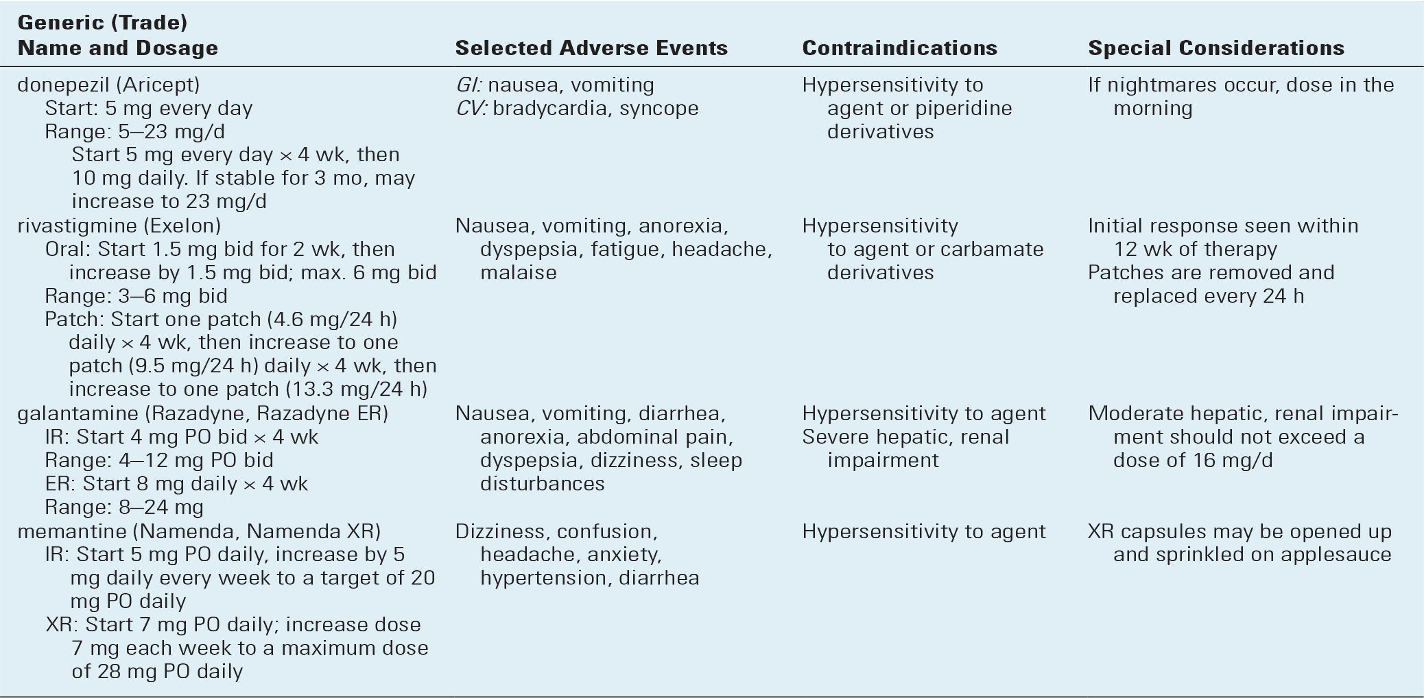
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
MOA
Prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine; keeps it high
\
\
Prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine; keeps it high
\
\
30
New cards
Memantine
Ex. Memantine (Namenda Namenda XR): __reserved for patients with moderate to severe AD__; may be used in conjunction with a CI.
\
MOA :Regulates the activity of glutamate
Side effects :headache, constipation, confusion and dizziness
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
Education extended release can be opened
\
\
MOA :Regulates the activity of glutamate
Side effects :headache, constipation, confusion and dizziness
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
Education extended release can be opened
\
31
New cards
treatment for Alzheimer’s non-cognitive
Examples of symptoms: agitation, psychosis, anxiety, depression, and sleep disorders. Agents to improve sx include:
* Antipsychotic Agents (all contain a **BBW** -they are associated with an increased risk of death in patients with dementia-related psychosis
* Benzodiazepines (reserve for episodic events)
* Antidepressants (may improve cognition, mood, apathy, function, behavior, appetite, sleep, and overall quality of life)
32
New cards
Alzheimer’s education and monitoring
•Appointments 3-6 months. If clinical improvement does not occur with a cholinesterase inhibitor after 3 to 6 months of treatment, the practitioner may consider switching to another cholinesterase inhibitor.
•They need to understand that __no currently available agents are curative__ and only __modest improvements can be expected__.
•Vitamin E and *Ginkgo biloba*, antioxidants, may be useful in AD treatment.
33
New cards
Parkinson’s fast facts
* Neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a set of hallmark motor and nonmotor symptoms
* drug-induced parkinsonism (DIP) must be considered and ruled out
* common w. 1st gen antipsychotics or neuroleptic drugs
34
New cards
DIP 1st gen
**80 % of patients taking a drug from this class present with more than one kind of extrapyramidal side effects (EPS)**
–Chlorpromazine (psychosis and NV)
–Haloperidol (psychosis, agitation, Tourette syndrome
–Perphenazine (schizophrenia, NV)
–Fluphenazine (psychosis)
–Pimozide (Tourette syndrome)
35
New cards
DIP 2nd gen
–Risperidone (psychosis, tics, bipolar)
–Olanzapine (Zyprexa-schizo, bipolar, agitation, major depression)
–Aripiprazole (Abilify-schizo, bipolar, major depression)
**These 2 alone are known to be lower risk for elderly**
–Clozapine (schizophrenia)
–Quetiapine (Seroquel-schizo, bipolar, anxiety)
36
New cards
other DIP offenders
–Metoclopramide (Reglan, a prokinetic used for NV, GERD)
–Valporic acid (bipolar, migraines, seizures)
–Methyldopa (Aldomet, for mod-severe HTN)
–Prochlorperazine (Compazine for anxiety, NV)
–Amiodorone and Lithium may cause tremors
37
New cards
patho of parkinsons
–degeneration of dopaminergic neurons
–Autophagy dysfunction
–The formation of Lewy bodies in the residual neurons
–Autophagy dysfunction
–The formation of Lewy bodies in the residual neurons
38
New cards
how to differentiate extrapyramidal symptoms
**Main neurotransmitter of EPS is dopamine**
Definition: Neural network located in the brain that is part of the motor system involved in movement coordination
\
Pyramidal System: pathway for **voluntary movement**
Extrapyramidal: pathway for **movement coordination**
Definition: Neural network located in the brain that is part of the motor system involved in movement coordination
\
Pyramidal System: pathway for **voluntary movement**
Extrapyramidal: pathway for **movement coordination**
39
New cards
diagnosis and testing for parkinsons
•Functional MRI
•Dopamine transporter imaging
•Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS)
•Clinical hx and assessment of risk factors
•Medical and medication history
•Exclusion of DIP
•Neurological exam
40
New cards
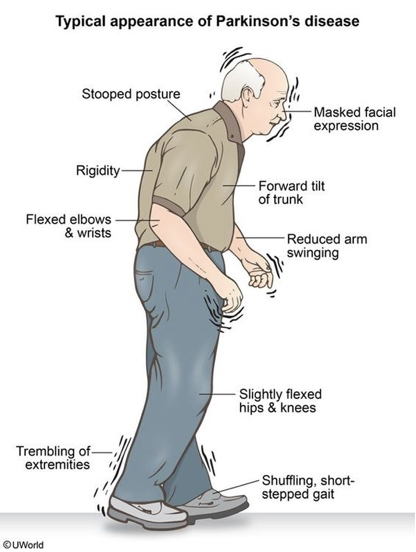
Parkinsons symptoms
* Classic Triad
-Resting Tremor
-Rigidity
-Bradykinesia
\
**S** huffling gait
**M** ask like
**A** kinesia (delayed response or freezing mid action)
**R** idgity
**T** remor
\
41
New cards
Dopaminergic Agents
ex Carbidopa-Levadopa (Sinmet)
\
MOA
•Levodopa is precursor to dopamine, it does not cross the BBB.
•Carbidopa-levadopa diffuses levodopa into the CNS, where it is converted in dopamine
\
Side effects
•GI, orthostatic hypotension, Abnormal movements-”bruxism, ballismus”
Bradykinetic episodes- known as “on-off”NMS (non motor symptoms)
Hyperventilation, bizarre breathing patterns, hoarseness, increased nasal secretions.
Interactions
–MAOI, TCA, phenothiazines, pyridoxine
Contraindications
•History of sensitivity
•Undiagnosed pigmented lesions or history of melanoma.
•Closed angle glaucoma
•Caution-cardiac disease, MI, pulmonary, DM, PUD, history of psychiatric disorders
Education
•Oral administration starts to take effect in 1-2 months but may take 6 months for noticeable effects
•Patients should avoid **high protein diet** and avoid foods with **large amounts of pyridoxine**. (ex fish, beef liver and other organ meats)
•Lose effectiveness after 2 to 5 years of therapy
\
MOA
•Levodopa is precursor to dopamine, it does not cross the BBB.
•Carbidopa-levadopa diffuses levodopa into the CNS, where it is converted in dopamine
\
Side effects
•GI, orthostatic hypotension, Abnormal movements-”bruxism, ballismus”
Bradykinetic episodes- known as “on-off”NMS (non motor symptoms)
Hyperventilation, bizarre breathing patterns, hoarseness, increased nasal secretions.
Interactions
–MAOI, TCA, phenothiazines, pyridoxine
Contraindications
•History of sensitivity
•Undiagnosed pigmented lesions or history of melanoma.
•Closed angle glaucoma
•Caution-cardiac disease, MI, pulmonary, DM, PUD, history of psychiatric disorders
Education
•Oral administration starts to take effect in 1-2 months but may take 6 months for noticeable effects
•Patients should avoid **high protein diet** and avoid foods with **large amounts of pyridoxine**. (ex fish, beef liver and other organ meats)
•Lose effectiveness after 2 to 5 years of therapy
42
New cards
•Dopamine Agonists
\
Pramipexole, bromocriptine, ropinirole (Requip and Mirapex)
MOA
Used as monotherapy to control symptoms and delay use of levodopa ( or when its wearing off.
\
Side effects
•GI, postural hypotension, dyskinesias, somnolence, dizziness unsteadiness, hallucinations and confusion
Interactions
•aminoglutethimide, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, ketoconazole, norfloxacine, ofloxacin, estrogen for ropinirole
\
Contraindications
•Renal impairment use caution
•Hepatic impairment use caution
Education
food does not effect bioavailability
•Avoid St. John’s Wort, Kava, Valerian
43
New cards
•Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors
ex. Selegiline-Eldypryl
MOA: Inhibits the metabolism of dopamine to increase blood concentration
\
Side effects
orthostatic hypotension, hallucinations, agitation, insomnia
Interactions
carbamazepine, SSRI’s, TCA’s, SNRI’s, meperidine.
Contraindications
-Increase BP with tyramine containing foods
\
MOA: Inhibits the metabolism of dopamine to increase blood concentration
\
Side effects
orthostatic hypotension, hallucinations, agitation, insomnia
Interactions
carbamazepine, SSRI’s, TCA’s, SNRI’s, meperidine.
Contraindications
-Increase BP with tyramine containing foods
\
44
New cards
•Anticholinergics
ex (Bentropine ( Cogentin), Trihexyphenidry (Artane)
MOA
•inhibiting the cholinergic neurons.
\
Not as effective as levodopa
MOA
•inhibiting the cholinergic neurons.
\
Not as effective as levodopa
45
New cards
•Amantadine
MOA (antiviral)
•mild PD and drug induced parkinsonism as well as late stage
Mainly for resting tremors and used in combo w/ levodopa
\
•mild PD and drug induced parkinsonism as well as late stage
Mainly for resting tremors and used in combo w/ levodopa
\
46
New cards
What do you NOT give with parkinsons meds
DO NOT give neuroleptics or any dopamine blocking meds\* (prochlorperazine, metoclopramide, promethazine)
47
New cards
complications of parkinsons meds
•Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)can occur with sudden withdrawal of levodopa or dopamine agonists
•Serotonin syndrome if MAOI’s combined with SSRIs or TCAs
•“On-Off” effect because medications eventually wane
48
New cards
treatment of non-motor parkinsons syptoms
•Psychological symptoms
–Depression, psychosis, and dementia.
–Pramipexole and venlafaxine have been shown to be efficacious, while tricyclic antidepressants and dopaminergic drugs have been labeled as likely efficacious.
•Sleep problems: insomnia
•Autonomic or other problems: orthostatic hypotension
–Depression, psychosis, and dementia.
–Pramipexole and venlafaxine have been shown to be efficacious, while tricyclic antidepressants and dopaminergic drugs have been labeled as likely efficacious.
•Sleep problems: insomnia
•Autonomic or other problems: orthostatic hypotension
49
New cards
monitoring during parkinsons
symptom journals
•Monitor for drugs that can exacerbate parkinsonism.
•MDS-UPDRS can be used to assess disability and impairment.
•Monitor for drugs that can exacerbate parkinsonism.
•MDS-UPDRS can be used to assess disability and impairment.
50
New cards
how do they work?
excitatory neurons>> decrease excitation of neurons
\
inhibitor neurotransmitter >> slow down neural impulses
\
inhibitor neurotransmitter >> slow down neural impulses
51
New cards
Phenytoins
ex Dilantin
One of the oldest and most effective aED's (Antiepileptic Drugs)
Use:
* Commonly used for generalized tonic-clonic (grand mal), but can be used for any type seizure
* prevents seizure post head trauma, neurosurgery, hemorrhagic stroke
MOA
◦Decreases the influx of sodium ions across cell membranes
◦Regulates neuronal excitability by inhibiting calcium conduction
Side effects
\*gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, anemia, Stevens-Johnson
(works too well)->>hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmias, CV collapse, thrombophlebitis (Causes inhibition = slowing)
Interactions
Multiple Interaction
Contraindications: allergy
\
Education
Monitor serum drug levels
52
New cards
Fosphenytoin (Cerebyx)
Prodrug of phenytoin
Short-term use when phenytoin unavailable, inappropriate, or less advantageous
WARNING: Do not confuse Cerebyx with Celebrex
53
New cards
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
MOA: Believed to limit influx of Na ions; several po forms;
Side effects: hematologic abnormalities, drowsiness, fatigue, SIADH, rash, GI upset, confusion; May exacerbate myoclonic szs; Increased risk SJS in asians with HLA-B 1502 allele
Interactions: Multiple
Contraindications: allergy to drug or TCA, bone marrow suppression, or recent MAOI
Education: Start low and increase weekly; Drug monitoring necessary
Side effects: hematologic abnormalities, drowsiness, fatigue, SIADH, rash, GI upset, confusion; May exacerbate myoclonic szs; Increased risk SJS in asians with HLA-B 1502 allele
Interactions: Multiple
Contraindications: allergy to drug or TCA, bone marrow suppression, or recent MAOI
Education: Start low and increase weekly; Drug monitoring necessary
54
New cards
Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal)
MOA: unknown, but thought to block Na channels to stabilize hyper neural membranes; used in Monotherapy or adjunctive partial szs in adults/children
Side effects: dizziness, somnolence, diplopia, n/v, ataxia, abd pain
Interactions: Multiple
Contraindications: Allergy
Education: Also used for Bipolar disorder, Trigeminal neuralgia
Side effects: dizziness, somnolence, diplopia, n/v, ataxia, abd pain
Interactions: Multiple
Contraindications: Allergy
Education: Also used for Bipolar disorder, Trigeminal neuralgia
55
New cards
Valproic Acid (Divalproex, Depakote)
MOA: unknown, but though to work on GABA; 1st line therapy for generalized tonic clonic, simple partial, complex partial, and absence
Side effects: fatigue, tremor, GI upset, behavioral changes, weight gain; Severe AE: thrombocytopenia, pancreatitis, encephalopathy, hepatotoxicity
Interactions: Multiple
Contraindications: hepatic disease, urea cycle disorders
Education: Also used for bipolar disorder-manic, migraine prophylaxis
Side effects: fatigue, tremor, GI upset, behavioral changes, weight gain; Severe AE: thrombocytopenia, pancreatitis, encephalopathy, hepatotoxicity
Interactions: Multiple
Contraindications: hepatic disease, urea cycle disorders
Education: Also used for bipolar disorder-manic, migraine prophylaxis
56
New cards
Ethosuximide (Zarontin)
Drug of choice for absence szs;
MOA: not known
Side effects: GI upset, fatigue
Interactions: CYP3A4
Contraindications: allergy
Education: Always used in combo with another drug
MOA: not known
Side effects: GI upset, fatigue
Interactions: CYP3A4
Contraindications: allergy
Education: Always used in combo with another drug
57
New cards
Barbiturates (Phenobarbital)
Alternative monotherapy in generalized tonic clonic; Sedating;
MOA: binds to GABA
Side effects: drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia, n/v, blurred vision, constipation, cognitive impairment, arryhthmias, dizziness
Interactions: Multiple, Increased toxicity of benzo’s, CNS depressants, methylphenidate
Contraindications: severe liver disease, respiratory disease, history of sedative or hypnotic addiction
Education: Cheap; loading dose followed by maintenance dose; frequent drug monitoring needed
MOA: binds to GABA
Side effects: drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia, n/v, blurred vision, constipation, cognitive impairment, arryhthmias, dizziness
Interactions: Multiple, Increased toxicity of benzo’s, CNS depressants, methylphenidate
Contraindications: severe liver disease, respiratory disease, history of sedative or hypnotic addiction
Education: Cheap; loading dose followed by maintenance dose; frequent drug monitoring needed
58
New cards
Gabapentin (neurontin)
adjunct therapy complex partial szs and generalized tonic-clonic
MOA: structurally related to GABA and is thought to reduce presynaptic GABA release
Side effects: fatigue, dizziness, blurred vision. May resolve over time; possible weight gain
Interactions: not many; Antacids may block absorption
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
Education: Mainly used in neuropathic pain control
MOA: structurally related to GABA and is thought to reduce presynaptic GABA release
Side effects: fatigue, dizziness, blurred vision. May resolve over time; possible weight gain
Interactions: not many; Antacids may block absorption
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
Education: Mainly used in neuropathic pain control
59
New cards
Pregabalin (Lyrica)
Adjunctive therapy for partial onset szs
MOA: Binds to ca channels to inhibit excitator neurotrans release
Side effects: peripheral edema, weight gain
Interactions: enhance sedative effect of CNS depressants
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
Education: one of the newest; other uses are Fibromyalgia, post-herpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain
MOA: Binds to ca channels to inhibit excitator neurotrans release
Side effects: peripheral edema, weight gain
Interactions: enhance sedative effect of CNS depressants
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
Education: one of the newest; other uses are Fibromyalgia, post-herpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain
60
New cards
Lamotrigine (Lamictal)
Generalized tonic-clonic, absence, complex partial
MOA: stabilizes neuronal membranes by acting on amino acid release and sodium channels
Side effects: n/v, fatigue, dizziness
Interactions: other aed’s
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
Education: also used for bipolar maintenance
MOA: stabilizes neuronal membranes by acting on amino acid release and sodium channels
Side effects: n/v, fatigue, dizziness
Interactions: other aed’s
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
Education: also used for bipolar maintenance
61
New cards
Levetiracetam (Keppra)
Adjunctive partial onset or primary generalized tonic-clonic
MOA: thought to facilitate GABA transmission, reduce K currents
Side effects: somnolence, HA, infection, usually within first 4 weeks; Behavioral changes
Interactions: No clinically relevant ones
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
MOA: thought to facilitate GABA transmission, reduce K currents
Side effects: somnolence, HA, infection, usually within first 4 weeks; Behavioral changes
Interactions: No clinically relevant ones
Contraindications: hypersensitivity
62
New cards
Topiramate (Topamax)
Monotherapy or adjunctive partial onset szs and generalized tonic-clonic szs
MOA: Block Na channels by enhancing GABA activity
Side effects: fatigue, dizziness, somnolence, psychomotor slowing (stupidimate), memory difficulty, nausea, weight loss, change in taste
Interactions: CYP2C19
Contraindications: hepatic or renal impairment, pregnancy, breast-feeding
Education: Also used for migraine prophylaxis; weight control
MOA: Block Na channels by enhancing GABA activity
Side effects: fatigue, dizziness, somnolence, psychomotor slowing (stupidimate), memory difficulty, nausea, weight loss, change in taste
Interactions: CYP2C19
Contraindications: hepatic or renal impairment, pregnancy, breast-feeding
Education: Also used for migraine prophylaxis; weight control
63
New cards
Amphetamines for weight loss
MOA: increase release norepi
Side effects: cardiovascular issues, High risk for abuse
Interactions:
Contraindications:
Education: Use at lowest effective dose; Schedule II; Not widely used
Side effects: cardiovascular issues, High risk for abuse
Interactions:
Contraindications:
Education: Use at lowest effective dose; Schedule II; Not widely used
64
New cards
Appetite Suppressants
Schedule III; Non-amphetamine derivatives; diethylpropion (Tenuate), phendimetrazine (Bontril), phentermine (Adipex)
MOA: decrease appetite by stimulating hypothalamus to release catecholamines norepi and dopamine
Side effects: CNS stimulation, dry mouth nausea, increase BP, tachycardia. Caution in DM’s
Interactions: None
Contraindications: MAOI
Education: Tolerance may develop after a few weeks; potential for abuse
MOA: decrease appetite by stimulating hypothalamus to release catecholamines norepi and dopamine
Side effects: CNS stimulation, dry mouth nausea, increase BP, tachycardia. Caution in DM’s
Interactions: None
Contraindications: MAOI
Education: Tolerance may develop after a few weeks; potential for abuse
65
New cards
Lipase Inhibitor
Example: Orlistat (Xenical, Alli)
MOA: Works locally in GI; blocks absorption of fats
Side effects: diarrhea, fatty stools, flatulence, leakage, nausea, abd pain, decrease absorption of fat soluble vitamins; Take MVI
Interactions: Caution on patients taking Coumadin b/c changes in Vitamin K
Contraindications: malabsorption syndrome, cholestasis
Education: Take during or 1 hr after fat containing meal. Meal should contain less than 30% fat
MOA: Works locally in GI; blocks absorption of fats
Side effects: diarrhea, fatty stools, flatulence, leakage, nausea, abd pain, decrease absorption of fat soluble vitamins; Take MVI
Interactions: Caution on patients taking Coumadin b/c changes in Vitamin K
Contraindications: malabsorption syndrome, cholestasis
Education: Take during or 1 hr after fat containing meal. Meal should contain less than 30% fat
66
New cards
Qsymia
(phentermine and topiramate)
(phentermine and topiramate)
MOA: combination of appetite suppressant & anti-seizure medication
Side effects: Tachycardia, suicidal behavior/ ideation, glaucoma, mood & sleep d/o, cognitive impairment, metabolic acidosis
Contraindications: Pregnancy Cat X
Education: Potential sz with abrupt withdrawal of medication
Side effects: Tachycardia, suicidal behavior/ ideation, glaucoma, mood & sleep d/o, cognitive impairment, metabolic acidosis
Contraindications: Pregnancy Cat X
Education: Potential sz with abrupt withdrawal of medication
67
New cards
Contrave
(Naltrexone Sustained Release/Bupropion
(Naltrexone Sustained Release/Bupropion
MOA: Naltroxene - narcotic antagonist; Bupoprion - dopamine/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; cause appetite suppression by working on 2 areas of brain involved with food regulation; hypothalamus & limbic systems
Side effects: Nausea, constipation, HA, vomiting, dizziness, potential suicidal ideations/ serious neuropsychiatric events
Interactions: opioid dependency/ opioids
Contraindications: uncontrolled HTN, seizure disorder, bulimia, anorexia nervosa, drug/ETOH withdrawal; MAOI use; pregnancy & lactation
Education: monitor for psychiatric changes; dose is titrated up when started & down when discontinuing
Side effects: Nausea, constipation, HA, vomiting, dizziness, potential suicidal ideations/ serious neuropsychiatric events
Interactions: opioid dependency/ opioids
Contraindications: uncontrolled HTN, seizure disorder, bulimia, anorexia nervosa, drug/ETOH withdrawal; MAOI use; pregnancy & lactation
Education: monitor for psychiatric changes; dose is titrated up when started & down when discontinuing
68
New cards
insomnia drug classes
Hypnotics:
* Benzodiazepines
-Short /Intermediate/Long acting (LA)
•Benzodiazepine receptor agonists
\-Orexin receptor antagonist
\-Melatonin receptor agonists
\-First generation antihistamines
\-Sedating antidepressants
69
New cards
fast facts for insomnia drugs
\*\*Hypnotics should be used at the lowest dose for the shortest period of time-can be habit forming
\
\*Provider should prescribe for as short a time as possible (Short term=2-3 weeks)
\*Wean pt’s slowly off hypnotics to prevent rebound effects
70
New cards
insomnia drugs benzos
Alprazolam (Xanax) SA
Estazolam (ProSom ) IA
Flurazepam (Dalmane)LA
Lorazepam (Ativan) IA
Temazepam (Restoril) IA
Triazolam (Halcion) SA
\
short= to initiate sleep
intermidiate= to maintain
Estazolam (ProSom ) IA
Flurazepam (Dalmane)LA
Lorazepam (Ativan) IA
Temazepam (Restoril) IA
Triazolam (Halcion) SA
\
short= to initiate sleep
intermidiate= to maintain
71
New cards
insomnia drugs bzra
\*\***Benzodiazepine receptor agonist**\*\*
Eszopiclone (Lunesta)
Zolpidem (Ambien, Ambien CR)
Zolpidem tartrate (Intermezzo
Zaleplon (Sonata)
Eszopiclone (Lunesta)
Zolpidem (Ambien, Ambien CR)
Zolpidem tartrate (Intermezzo
Zaleplon (Sonata)
72
New cards
drugs used for insomnia cont.
Suvorexant (Belsomra)
Ramelteon (Rozerem)
antihistamines
**Sedating antidepressants:**
***Use for pt’s with comorbid conditions***
•Mirtazapine (Remeron)
•Trazodone
•Doxepin (Silenor)
\
Ramelteon (Rozerem)
antihistamines
**Sedating antidepressants:**
***Use for pt’s with comorbid conditions***
•Mirtazapine (Remeron)
•Trazodone
•Doxepin (Silenor)
\
73
New cards
first line for insomnia
•benzodiazepine (e.g., alprazolam, lorazepam, temazepam)
• benzodiazepine receptor agonists (BZRAs) (zolpidem, zaleplon, escitalopram) or ramelteon
• first-generation antihistamine—doxylamine succinate
74
New cards
second line for insomnia
•alternating short-acting BZRAs (zaleplon, eszopiclone) with ramelteon;
•sedating antidepressants (trazodone, amitriptyline, doxepin, mirtazapine)
75
New cards
third line for insomnia
•sedating antiepilepsy agents (gabapentin)
•atypical antipsychotics (quetiapine, olanzapine);
•orexin receptor antagonist (suvorexant)
•atypical antipsychotics (quetiapine, olanzapine);
•orexin receptor antagonist (suvorexant)
76
New cards
restless leg treatment
•Ropinirole (Requip)
•Pramipexole (Mirapex)
•Rotigotine transdermal (Neupro)
\
anticonvulsants and benzos
77
New cards
narcolepsy treatment
•Psychostimulants (wake-promoting)
Armodafinil (Nuvigil)
•Amphetamines (wake-promoting)\\
•Modafinil (Provigil):
•Sodium oxybate (only distributed through manufacturer)
Sodium oxybate (Xyrem)
•Antidepressants-Venlafaxine (Effexor), Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
78
New cards
hypotheses of depression
•**Serotonin hypothesis:** a __functional or an absolute deficiency__ in the neurotransmitter **serotonin**
•**Catecholamine hypothesis:** a functional or an absolute deficiency in the neurotransmitter's **norepinephrine, serotonin, or dopamine**
•**Permissive hypothesis:** __diminished serotonin__ gives “permission” for a superimposed norepinephrine deficiency to manifest as depression
•**Beta-adrenergic receptor hypothesis:** depression results from __increased beta-adrenergic__ receptor sensitivity
•**Catecholamine hypothesis:** a functional or an absolute deficiency in the neurotransmitter's **norepinephrine, serotonin, or dopamine**
•**Permissive hypothesis:** __diminished serotonin__ gives “permission” for a superimposed norepinephrine deficiency to manifest as depression
•**Beta-adrenergic receptor hypothesis:** depression results from __increased beta-adrenergic__ receptor sensitivity
79
New cards
MDD diagnostic criteria
***A patient must exhibit at least** __**5 of these signs or symptoms in the same 2-week period along**__ **with symptoms of depressed mood or anhedonia, the inability to gain pleasure from normally pleasurable experiences.**
80
New cards
depression monitoring
•**Acute treatment phase**: 6 to 8 weeks up to 12 weeks
•The goal is to treat the patient until __full remission and a return to the premorbid level of function.__
•**Continuation phase:** the time after a treatment response is seen in the acute phase and usually lasts 9 months to 1 year
•The practitioner should continue antidepressant therapy for 4 to 6 months __after symptom resolution.__
•**Maintenance phase:** long-term or indefinite therapy
81
New cards
SSRI
Ex. Escitalopram (Lexapro);Fluoxetine (Prozac);Fluvoxamine (Luvox);Paroxetine (Paxil);Sertraline (Zoloft)
\
\
Side effects
•Weight gain
•Sexual dysfunction
•Discontinuation syndrome-flu-like symptoms, anxiety
•**BBW: increased risk for suicide**
\
Education
•Administer in the AM due to potential to induce insomnia and anxiety
•Inhibits CYP450 system, causing elevation of other medications that are metabolized by this system
•Must be tapered off
\
\
Side effects
•Weight gain
•Sexual dysfunction
•Discontinuation syndrome-flu-like symptoms, anxiety
•**BBW: increased risk for suicide**
\
Education
•Administer in the AM due to potential to induce insomnia and anxiety
•Inhibits CYP450 system, causing elevation of other medications that are metabolized by this system
•Must be tapered off
82
New cards
SNRI
ex. Venlafaxine (Effexor);Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq);Duloxetine (Cymbalta);Levomilnacipran (Fetzima)
\
Side effects
**r/t increased adrenergic effects**
•Dry mouth, constipation, nausea, HTN
•Sexual dysfunction
•Discontinuation syndrome-flu-like symptoms, anxiety
•**BBW: increased risk for suicide**
\
Education
•Do not administer with MAOI as can cause serotonin syndrome
•Inhibits CYP450 system, causing elevation of other medications that are metabolized by this system
•Must be tapered off
\
\
Side effects
**r/t increased adrenergic effects**
•Dry mouth, constipation, nausea, HTN
•Sexual dysfunction
•Discontinuation syndrome-flu-like symptoms, anxiety
•**BBW: increased risk for suicide**
\
Education
•Do not administer with MAOI as can cause serotonin syndrome
•Inhibits CYP450 system, causing elevation of other medications that are metabolized by this system
•Must be tapered off
\
83
New cards
TCAs
\
Ex. Amitriptyline (Elavil);Doxepin (Sinequan);Imipramine (Tofranil);Nortriptyline (Pamelor);Protriptyline (Vivactil);Trimipramine (Surmontil)
\
Side effects
•Weight gain, other adrenergic symptoms, gynecomastia, sexual, galactorrhea, epileptogenic
•Cardiac-QT prolongation, tachycardia, stroke, AV block, hypotension
•**BBW: increased risk for suicide**
\
Education
•Inhibits CYP450 system, causing elevation of other medications that are metabolized by this system
•Must be tapered off
•Blood levels for therapeutic range
Ex. Amitriptyline (Elavil);Doxepin (Sinequan);Imipramine (Tofranil);Nortriptyline (Pamelor);Protriptyline (Vivactil);Trimipramine (Surmontil)
\
Side effects
•Weight gain, other adrenergic symptoms, gynecomastia, sexual, galactorrhea, epileptogenic
•Cardiac-QT prolongation, tachycardia, stroke, AV block, hypotension
•**BBW: increased risk for suicide**
\
Education
•Inhibits CYP450 system, causing elevation of other medications that are metabolized by this system
•Must be tapered off
•Blood levels for therapeutic range
84
New cards
MAOIs
•Phenelzine (Nardil)
•Tranylcypromine(Parnate)
85
New cards
Atypicals
**Trazodone (Desyrel)**
•**adverse effects** include orthostatic hypotension, nausea, blurred vision, and priapism
**Bupropion (Wellbutrin**)
•Frequently used in patients __who cannot tolerate the sexual adverse effects__ of SSRIs and SNRIs
•**Adverse effects-** can lower the seizure threshold, especially when combined with alcohol.
**Mirtazapine (Remeron)**
better for low weight older or ill
•rare cases of reversible agranulocytosis
\
•**adverse effects** include orthostatic hypotension, nausea, blurred vision, and priapism
**Bupropion (Wellbutrin**)
•Frequently used in patients __who cannot tolerate the sexual adverse effects__ of SSRIs and SNRIs
•**Adverse effects-** can lower the seizure threshold, especially when combined with alcohol.
**Mirtazapine (Remeron)**
better for low weight older or ill
•rare cases of reversible agranulocytosis
\
86
New cards
Novel agents
**Vilazodone (Viibryd)**
**Adverse effects**-GI-nausea and diarrhea
\
**Vortioxetine (Trintellix)**
•**Adverse effects-** dizziness, diarrhea, vomiting, and xerostomia. Sexual dysfunction in men and women occurs at a rate of 34% to 50%’
\
**Esketamine (Spravato) (r/t Ketamine)**
\-add on therapy
•**Adverse effects**-increases in blood pressure, cognitive impairment and impaired ability to drive and operate machinery due to the risks of sedation and dissociation, and embryo-fetal toxicity
•**BBW**-sedation and dissociation (Schedule 3 drug)
\
87
New cards
warning signs of SI
•Pacing, agitated behavior, frequent mood changes, and chronic episodes of sleeplessness
•Actions or threats of assault, physical harm, or violence
•Delusions or hallucinations
•Threats or talk of death
•Putting affairs in order, such as giving possessions away or writing a new will
•Unusually risky behavior (e.g., unsafe driving, abuse of alcohol, or other drugs)
88
New cards
Special considerations for depression treatment
children older than 8 =Fluoxetine (Prozac)
children older than 12 =Escitalopram (Lexapro)
Black box warning for suicidal ideation in children taking SSRIs
* geriatrics
* start low and slow due to decreased renal and hepatic function
* woman
* young women more likely than older women
\
children older than 12 =Escitalopram (Lexapro)
Black box warning for suicidal ideation in children taking SSRIs
* geriatrics
* start low and slow due to decreased renal and hepatic function
* woman
* young women more likely than older women
\
89
New cards
first line for depression
•**First line: SSRIs and SNRI**
90
New cards
second line for depression
•**Second line: TCA (desipramine or nortriptyline) or atypical antidepressant**
91
New cards
third line for depression
•Depending on past response to other agents and side effect profile
92
New cards
patho of anxiety disorders
•**Norepinephrine, serotonin, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)** are the major neurotransmitters
\
they have __malfunctioning noradrenergic systems__ with a low threshold for arousal (hypersensitive)
93
New cards
non pharmacologic for anxiety
•Psychoeducation
•Supportive counseling
•Behavioral therapy
•Cognitive therapy
•Stress management techniques
•Meditation
•Exercise
94
New cards
antidepressants for anxiety
SNRI and SSRI
ex. Paroxetine (Paxil);Sertraline (Zoloft);Citalopram (Celexa);Escitalopram (Lexapro);Fluoxetine (Prozac)
SNRI Venlafaxine (Effexor XR);Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
\*\*Adverse Effects: weight gain, GI, insomnia, sexual dysfunction
\*\* 2-4 weeks until typical response seen
\
**(MAO-I)**
•Phenelzine (Nardil)
•Adverse Effects: anticholinergic (dryness of mouth, blurred vision, constipation, urinary hesitancy)
ex. Paroxetine (Paxil);Sertraline (Zoloft);Citalopram (Celexa);Escitalopram (Lexapro);Fluoxetine (Prozac)
SNRI Venlafaxine (Effexor XR);Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
\*\*Adverse Effects: weight gain, GI, insomnia, sexual dysfunction
\*\* 2-4 weeks until typical response seen
\
**(MAO-I)**
•Phenelzine (Nardil)
•Adverse Effects: anticholinergic (dryness of mouth, blurred vision, constipation, urinary hesitancy)
95
New cards
benzos for anxiety
ex. Alprazolam (Xanax);Chlordiazepoxide (Librium);Clonazepam (Klonopin);Clorazepate (Tranxene);Diazepam (Valium);Lorazepam (Ativan);Oxazepam (Serax)
**MOA:** binds ot GABA-A receptors in the brain-opens channels and causes increased endogenous GABA
Adverse Effects: drowsiness, psychomotor impairment, increased depression, confusion, habit forming
96
New cards
azapirones
Buspirone (buspar)
97
New cards
misc anxiety meds
Hydroxyzine HCl (Atarax)
Hydroxyzine Pamoate (Vistaril)
98
New cards
first line for anxiety GAD
•**First-Line**: SSRI’s and SNRI’s, and BZD’s-taper off until above working
99
New cards
second line for anxiety GAD
•**Second-Line:** Buspirone (BuSpar) or Imipramine (Tofranil)
100
New cards
first line for panic disorder
•**First-Line:** __Nonpharmacologic,__ SSRI’s or Venlafaxine (Effexor), BZD’s