ADV Chapters 1-4
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Marketing vs Advertising
Marketing = bring in revenue, Adv = inform and persuade into purchasing/acting
Advertising vs PR
Adv = inform and persuade into purchasing/acting, PR = communicate between organization and public
What is IMC and why do companies use it?
Integrated Marketing Communications. Building a profitable relationship between a company and a consumer through coordinated strategic communications. This helps form a consumer-centric perspective in brand messaging
Four sources of brand messages
Planned: ads, publicity releases, LOW impact
Product: selling products, HIGH impact
Service: employee interactions, POS or NEG impact
Unplanned: rumors, news, PR helps with response if neg
Advertising
Persuade and inform
Marketing
Bring in revenue
IMC
Profitable relationship building; Integrated Marketing Communications
Medium
non personal advertising method. Single specific channel delivering message, i.e. radio spot, billboard
Mass media
broad and collective main means of communication, i.e. internet, TV
Consumers
groups of people
Stakeholders
People interested in success/failure/actions of advertising campaign, i.e. employees, press, stockholders
target audience
segment of population (adv)
target market
segment of population (marketing)
What is the importance of relationship marketing?
keep customers coming back to spend more money - it’s easier to keep current customers than get new ones
How does the communication process apply to advertising?
source → encoding → message → channel + noise → decode → receiver -*gives feedback to source*→ source
4 Ps/Elements of marketing strategy
Product: features and benefits or purchasing
Price: emphasize the value
Place: distribution locations
Promotion: communication
Promotion categories
Personal selling: person to person
Product adv: advertise a product
Sales promotion: advertise a sale to gain interest, i.e. BOGO
PR: Communication
Collateral materials: flyers, brochures
What functions does advertising perform in a free market economy?
stimulate economic growth, foster competition, provide information
Brand
differentiate products from each other, helps companies charge more for a product and helps with customer loyalty
Brand vision
describes lasting impact a company wants to make
Brand personality
unique set of human traits/emotions/values
What are the benefits of having a strong brand?
make more money, more successful product, recruit higher talent, customer loyalty
Preindustrial age
FIRST; Chinese invent paper, Gutenberg’s printing press, Ben Franklin
Industrial age
SECOND; mass production, transportation through railroad and steamship, emergence of brands, Volney Palmer, Francis Ayer, catalogs, radio, George Gallup, AC Nielson
Golden age
THIRD; TV, market segmentation, positioning, Bill Bernbach, Mary Wells Lawerence
Postindustrial age
FOURTH; computer, information age, demarketing, internet
Global/interactive age
FIFTH; social media, TV narrowcasting, BK Subservient Chicken, Nike+
Market segmentation
divide potential customers into groups to target, i.e. age, income, location, values, etc.
Positioning
how target consumers perceive a brand/product in comparison to competitors; creating a memorable identity
What are assumptions of free-market economics?
self interest, complete information, many buyers and sellers, no externalities
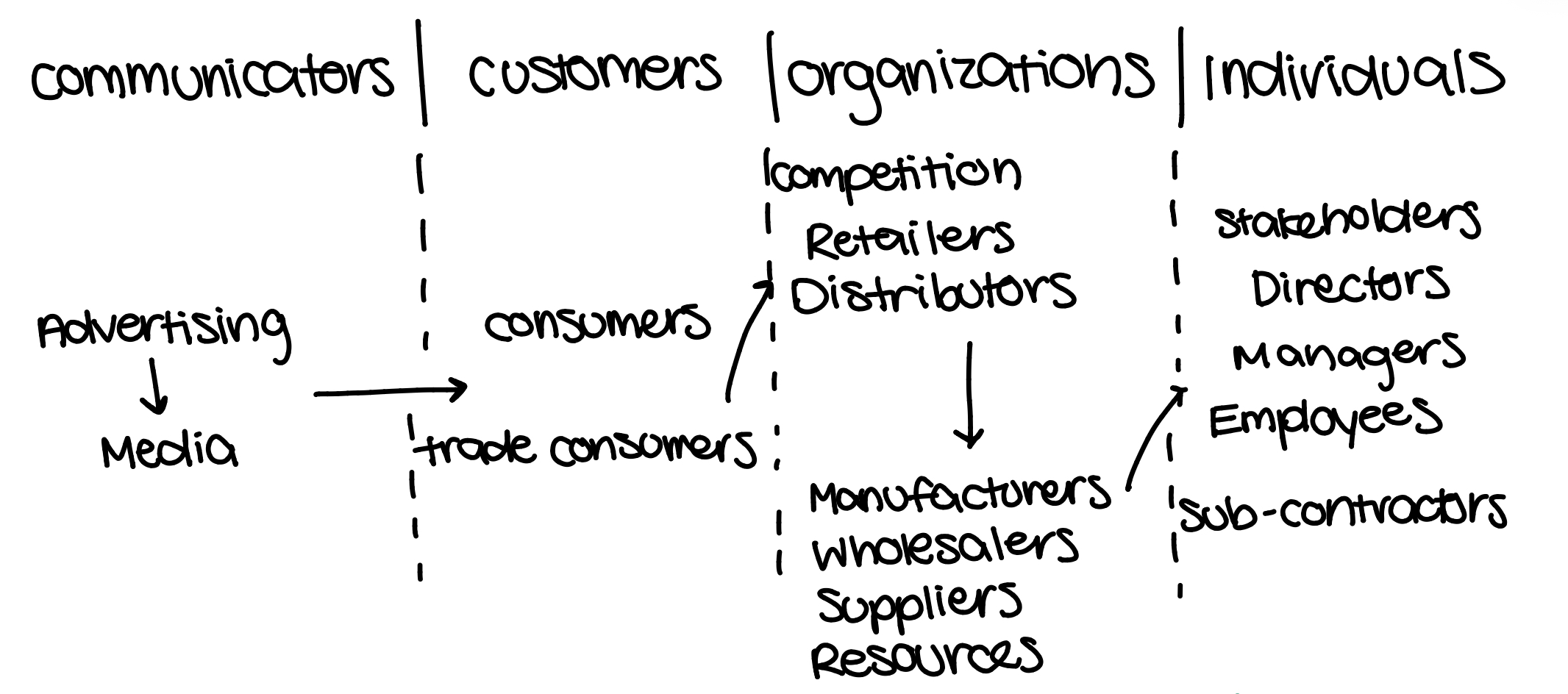
Economic Impact of ADV
Billiards model: Refer to image
- people pay for ads when paying for products, so adv. adds to value or product
- prices go up because of this
- restricts competition by encouraging brand loyalty
- consumer demand increases when people see others with a product they want
- consumer choice increases because there is so many options
Short term social impacts
deceptive, focus on advertising styles (unfair/deceptive practices)
Long term social impacts
environment, so many people see so many ads, materialism, manipulation, incomplete information, costs
Puffery
exaggerated claims that cant be proven true or false, i.e. “world’s best coffee”
Regulations through levels of government
Local: mayor, police
State/Regional: Attorney general
National: All 3 government branches
FTC
Federal Trade Commission
- protect consumers
- maintain competition and prevent monopolies
- advance organizational performace
FDA
Food and Drug Administration; truthful labeling on food and drugs, including pets
FCC
Federal Communications Commissions
- radio, TV, internet, satelites
- licensing, control profanity
USPTO
US Patent and Trademark Office; intellectual property
LOC
Library of Congress; copyrights, works of authorship
Deception
ad misleads consumer, i.e. Skechers Shape-Ups promising weight loss without exercise
Comparisons
compare product to another, must have data, i.e. 4 out of 5 dentists recommend this toothpaste brand over that one (but this stat must be true)
Endorsements
sponsored person, must be disclosed and honest, i.e. sponsored posts on social media must be clarified
Demonstrastions
honest and real representation, i.e. vacuum videos must be real and not faked
Bait-and-switch
promise you one thing but really sell you another, i.e. $499 sofa that is "sold out" to sell a more expensive one
FTC Consent Decree
first “warning,” document to stop ad
FTC cease-and-assist
second “warning,” prohibit further use of ad
FTC corrective advertising
most extreme warning, put out ad that corrects previous mistake
Advertiser
company being advertised, i.e. Nike, McDonalds, etc
Agencies
create the ad campaigns for advertisers
Suppliers
provide media to agency for ad campaign, i.e. photographers, artists, etc
Media
shares advertising message, i.e. TV, posters, etc
Account Management
core position in ad agency; communicator between the client and the agency, business oriented
Creative
core position in ad agency; come up with ideas for/execute the ads
Media (job position)
core position in ad agency; decides where the ad will run according to what will give best results
Strategy
core position in ad agency; research the consumers, be the voice of them
Production
core position in ad agency; turn ad idea into execution, organize and manage the ad production
Local advertisers
retail, small local stores. Short term thinking, advertise for specific people
Regional/National advertisers
larger chain stores. Long term thinking, advertise for groups of people
Consumer agency
sell to customers, i.e. clothing, food, etc
business-to-business agency (B2B)
sell to businesses, i.e. parts of marchinery, communication tools like slack, etc
3 models for how agencies make money
Media commissions: Agency buys ad for advertiser, agency takes a percent of profit
Markups: Agency buys materials for ad, charge advertiser extra
Fees: fee-commission = monthly fee + commission per ad, straight-fee = monthly fee, commission goes to client
Pros and Cons of an in-house agency
Pros: Cheaper, greater control, more attention to brand
Cons: lower creative quality, less experience + talent, no objectivity (more bias)