Tympanometry and Middle Ear Assessment
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A series of flashcards designed to test knowledge on tympanometry, middle ear assessment, and associated concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What does tympanometry measure?
Changes in admittance as a function of pressure changes.
What is the optimal condition for sound transmission through the eardrum?
The pressure in front of the eardrum matches the pressure behind the eardrum.
What does a normal middle ear pressure typically indicate?
Balanced pressure on both sides of the eardrum, usually around 0 decapascals.
What might negative pressure in the ear indicate?
Eustachian tube dysfunction.
What might positive pressure in the ear suggest?
Conditions like fluid buildup or ear infections.
What could cause an unusually large ear canal volume?
Perforation of the ear drum, PE tube, or surgical alteration of the ear canal.
What could cause an unusually small ear canal volume?
Wax or debris in ear canal, atresia of the ear canal, or inaccurate probe placement.
What characterizes a Type A tympanogram?
Normal middle ear pressure, normal admittance, and normal tympanometric width.
What does a Type B tympanogram indicate?
Flat response with low or no admittance, indicating middle ear effusion or extreme negative pressure.
What does a Type C tympanogram suggest?
Normal admittance with negative middle ear pressure, often due to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
What is the goal of Middle Ear Muscle Reflex (MEMR) testing?
To assess changes in admittance of the middle ear based on muscle contraction in response to loud stimuli.
How is the Acoustic Reflex Threshold (ART) determined?
By presenting sound at a loud level and measuring the softest sound that elicits a reflex contraction.
What does a wideband acoustic immittance measure?
The reflectance, absorption, and resonance of the middle ear space.
What is a key frequency used for tympanometric testing in infants?
1000 Hz.
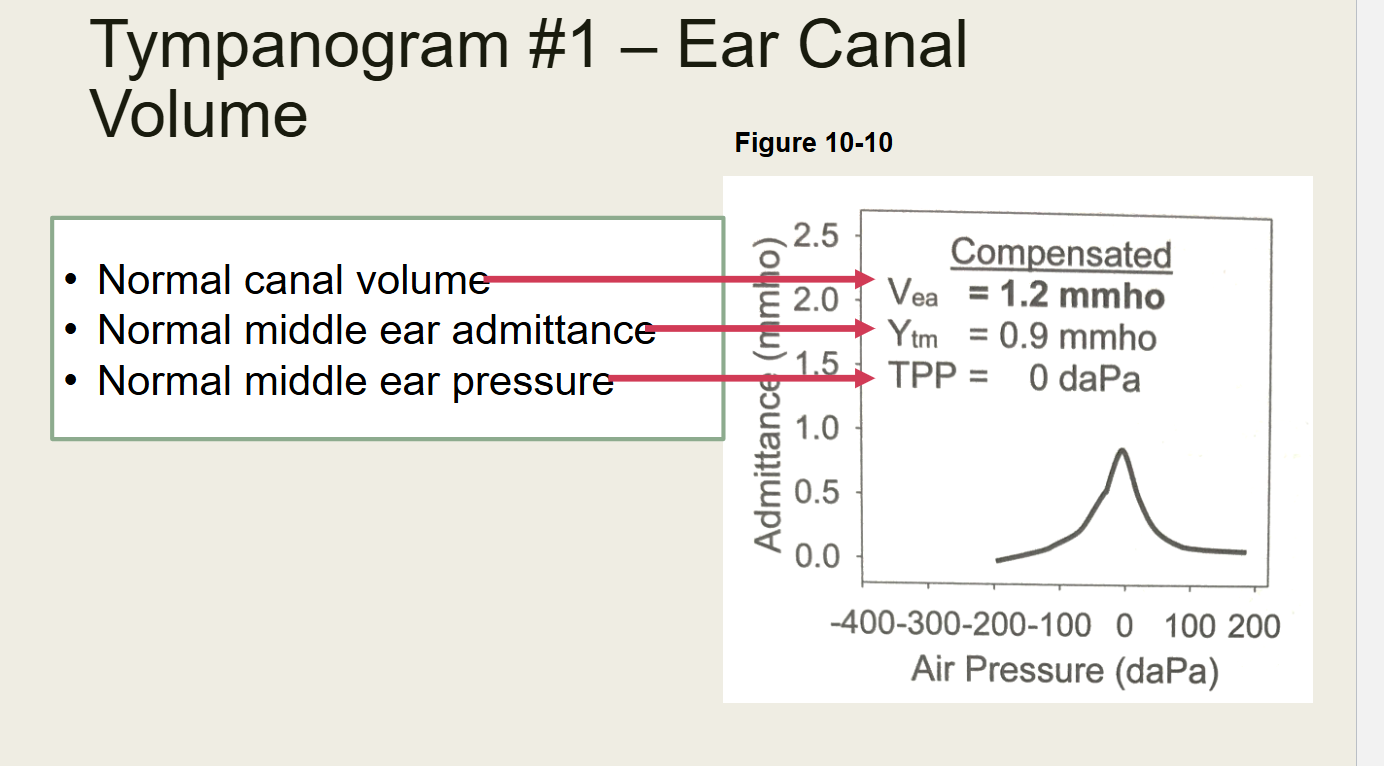
What does this test show
Normal test
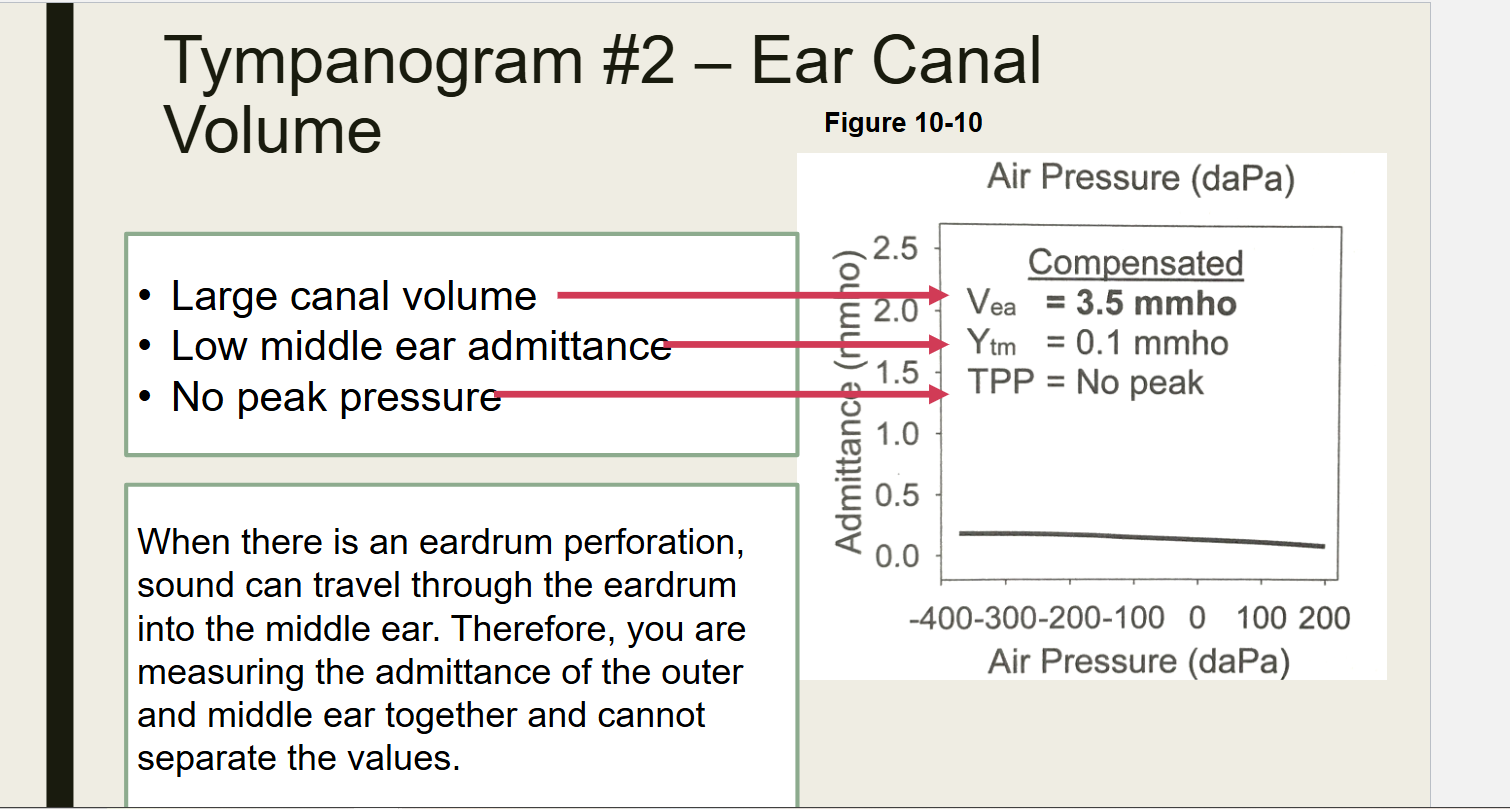
What does this test show
Large Ear Canal Eardrum Perforation
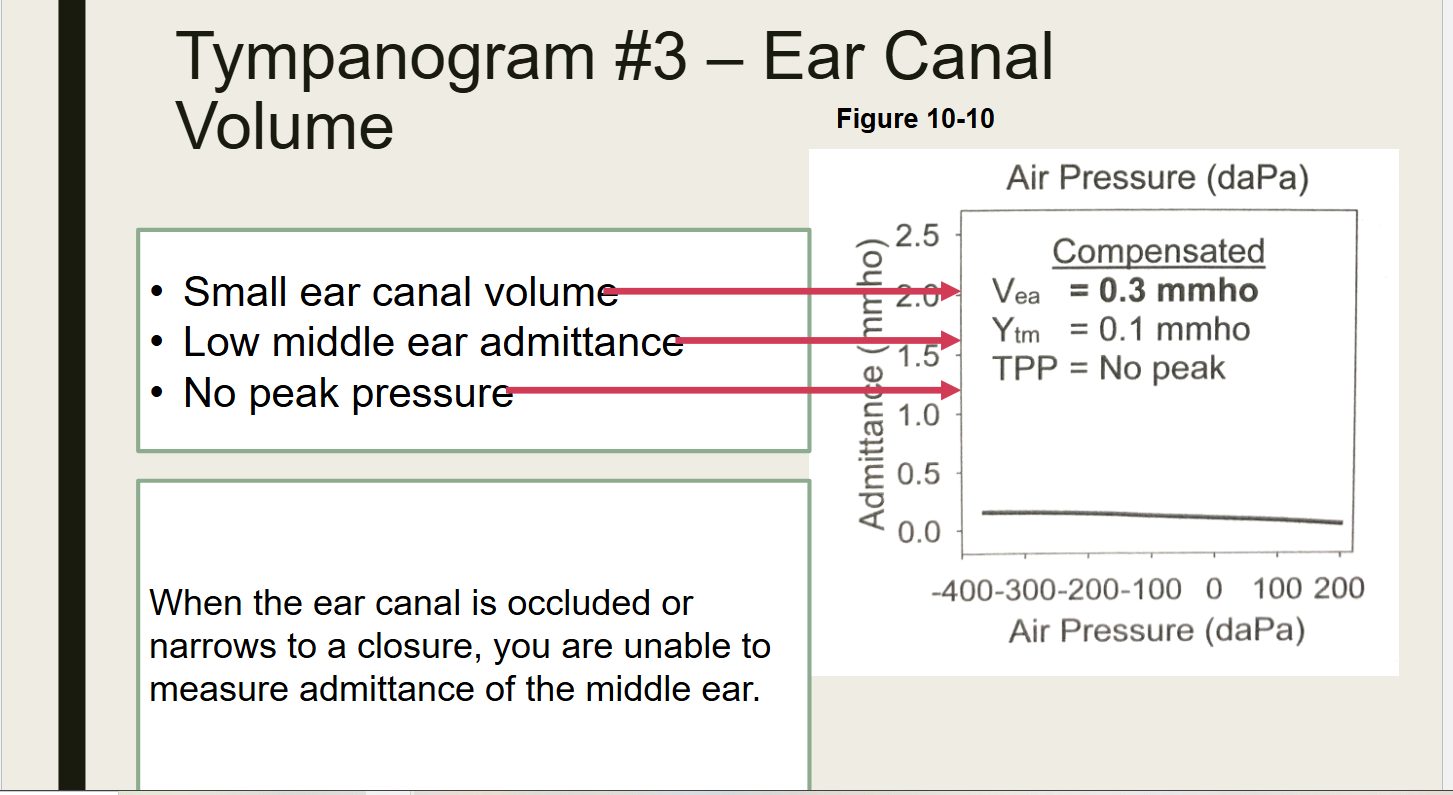
What does this test show
Ear Canal is blocked
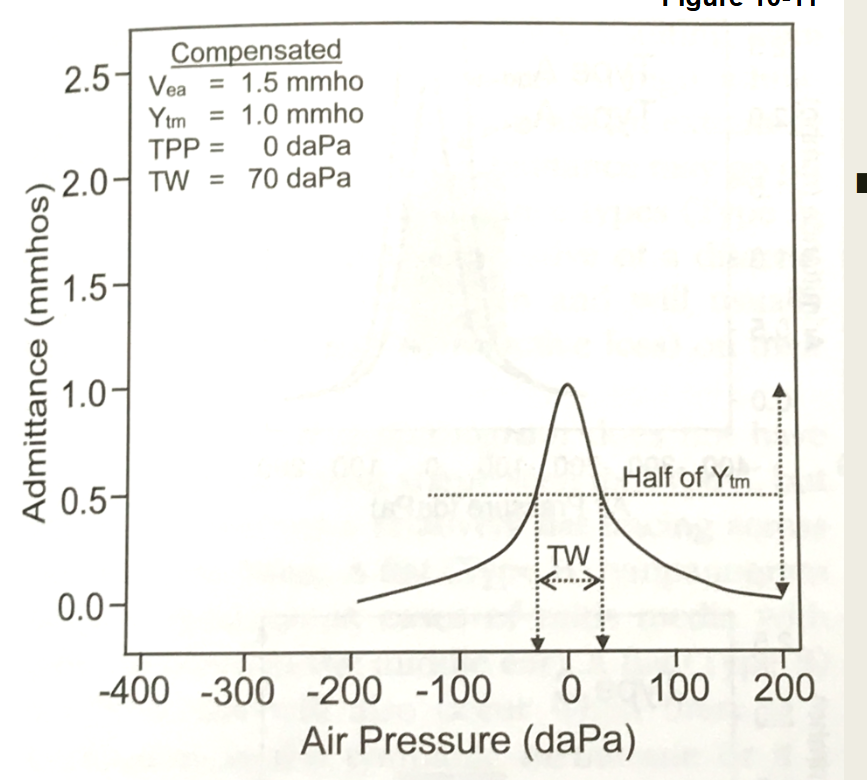
What type of Tympnogram is this
Type A: Normal
Normal middle ear pressure
Normal admittance
Normal tympanometric width
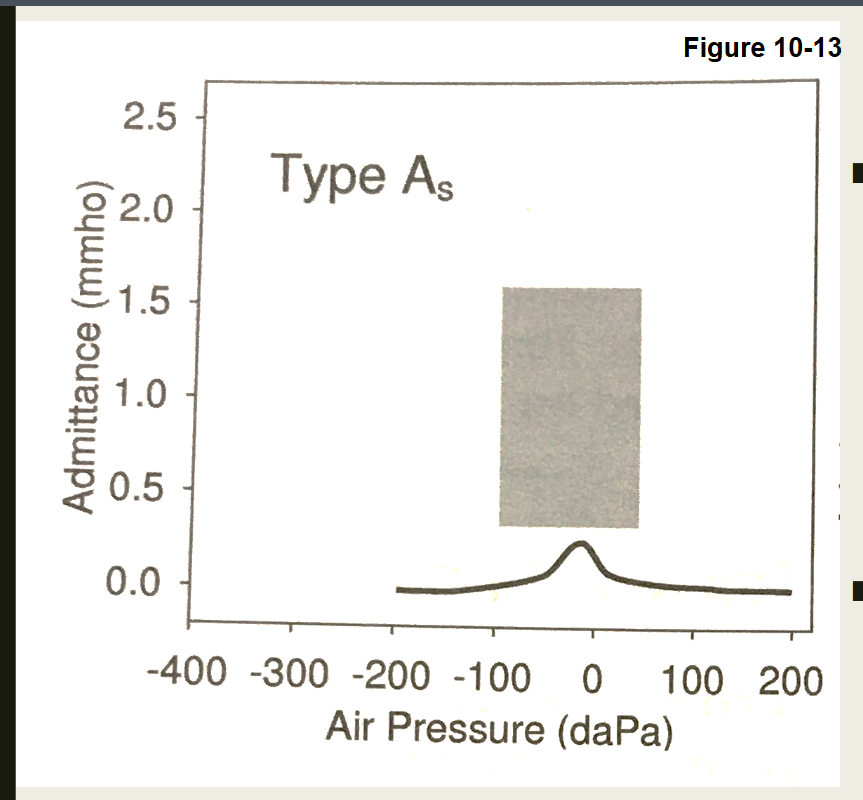
What type of Tympnogram is this
Type: As " Shallow"
Normal middle ear pressure
Reduced admittance
Normal tympanometric width
Causes
Middle ear fluid
Ossicular chain dysfunction
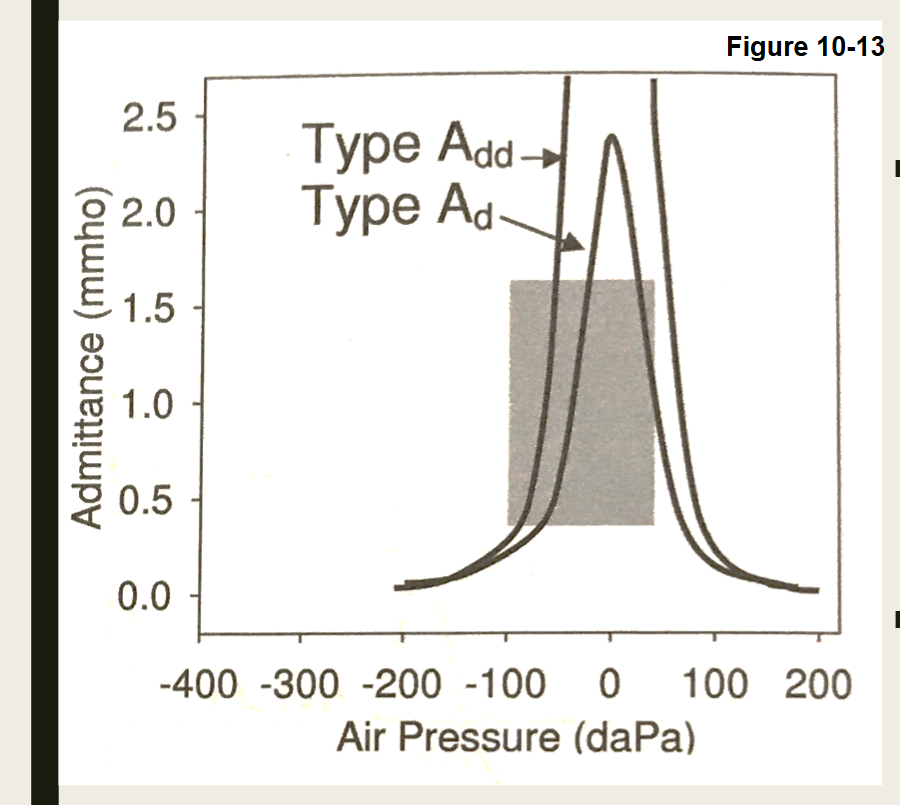
What type of Tympnogram is this
Type: Ad or Add: " High admittance"
Normal middle ear pressure
High admittance or hypercompliant
Normal tympanometric width
Causes:
Disarticulation of ossicles
Abnormally thin TM
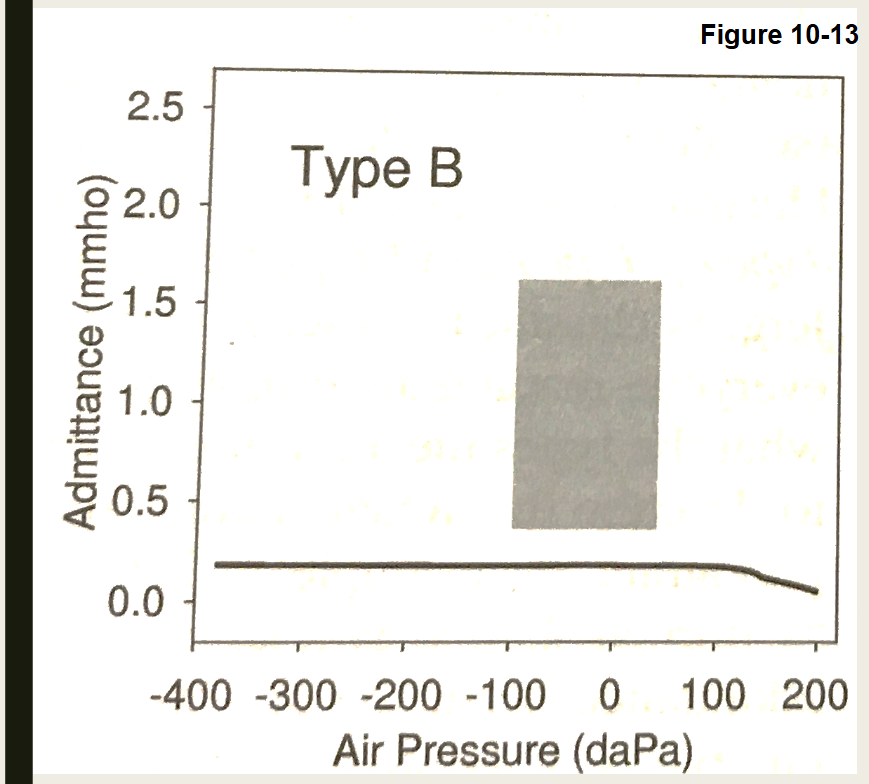
What type of Tympnogram is this
Type: B: "Flat"
Low (no) admittance
Cannot assess TPP
TW does not apply
Causes
With normla ear canal volume
Middle ear effusion
Extreme negative pressure
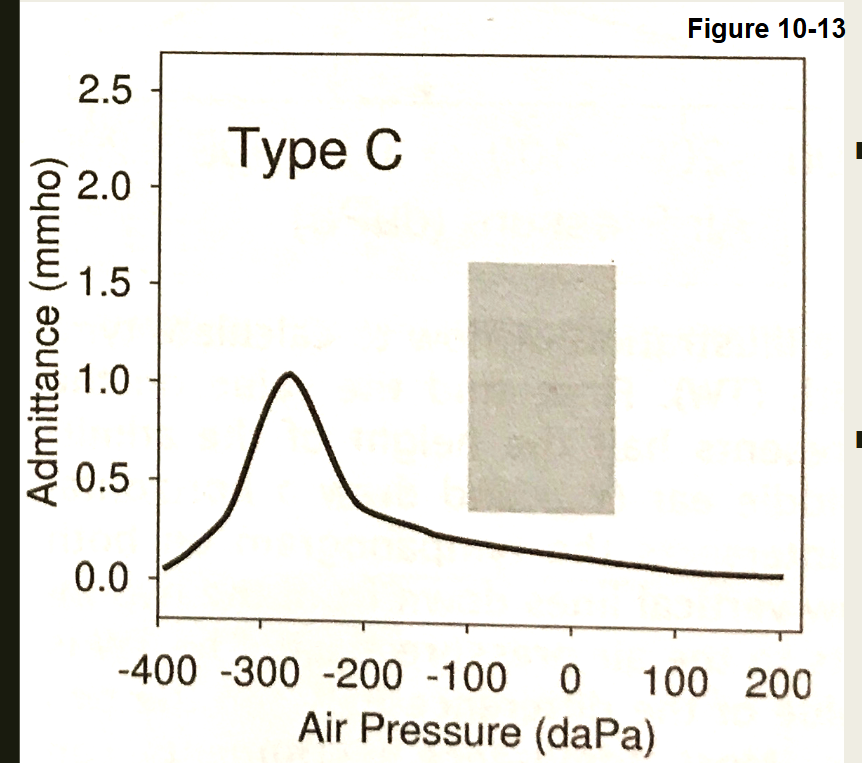
What type of Tympnogram is this
Type C: "Negative Pressure"
Normal admittance
Negative middle ear pressure
Normal TW
Causes:
Eustachian tube dysfunction
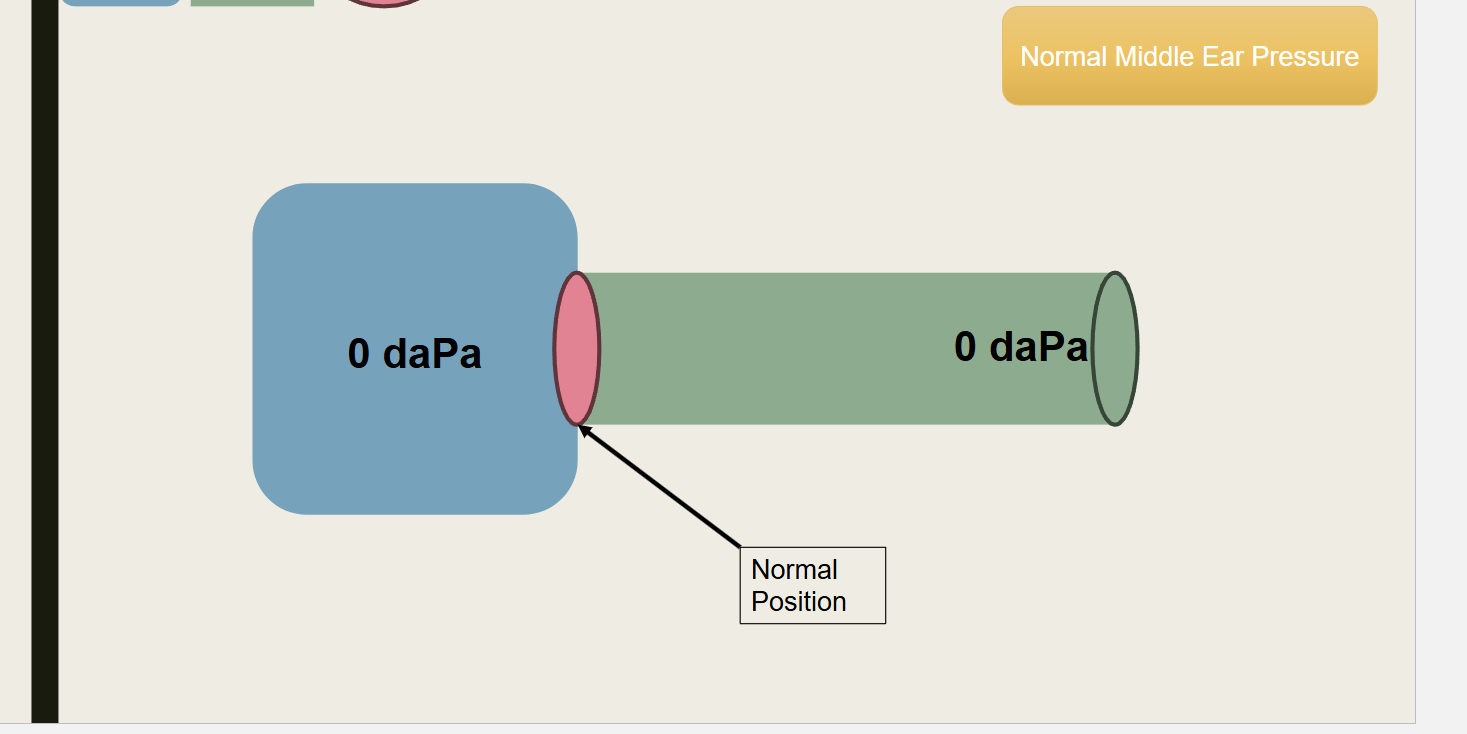
What type of pressure is this?
normal middle ear pressure
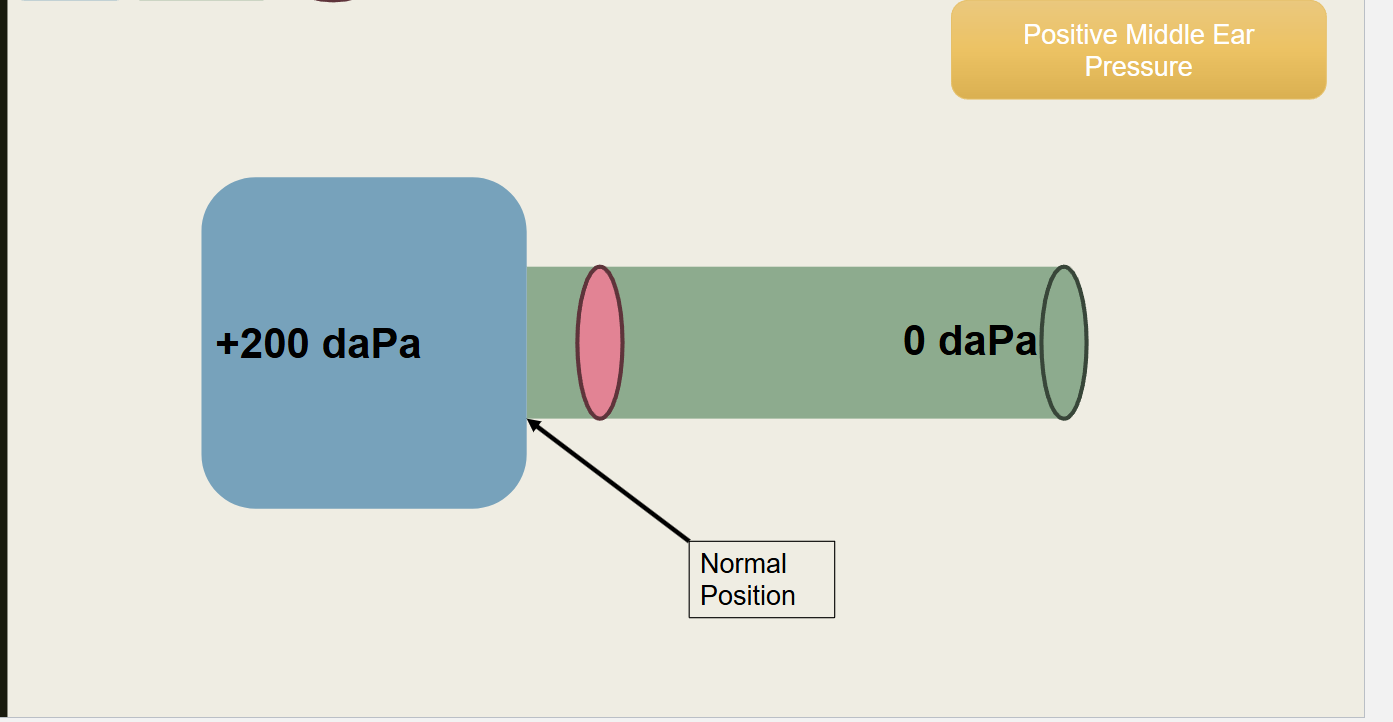
What type of pressure is this?
Positive Middle Ear Pressure
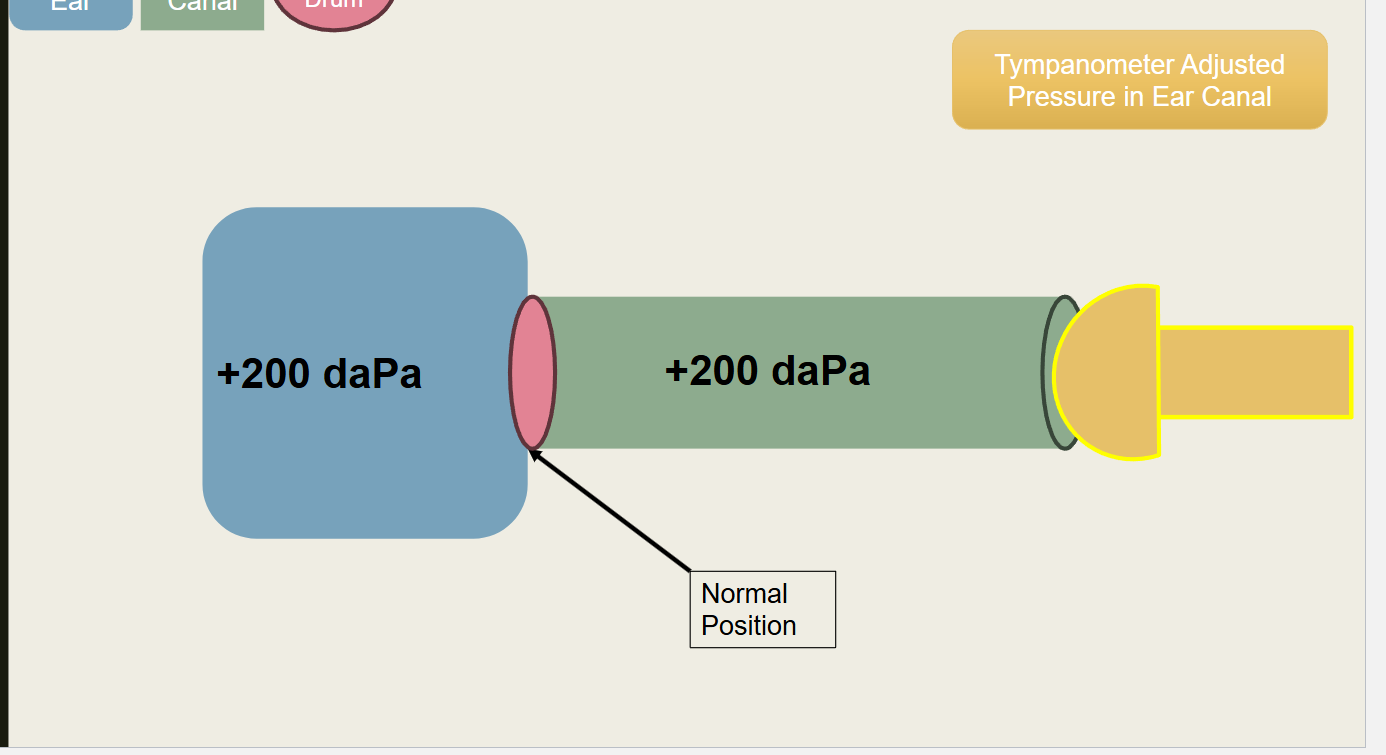
What type of pressure is this?
Tympanometer adjusted pressure
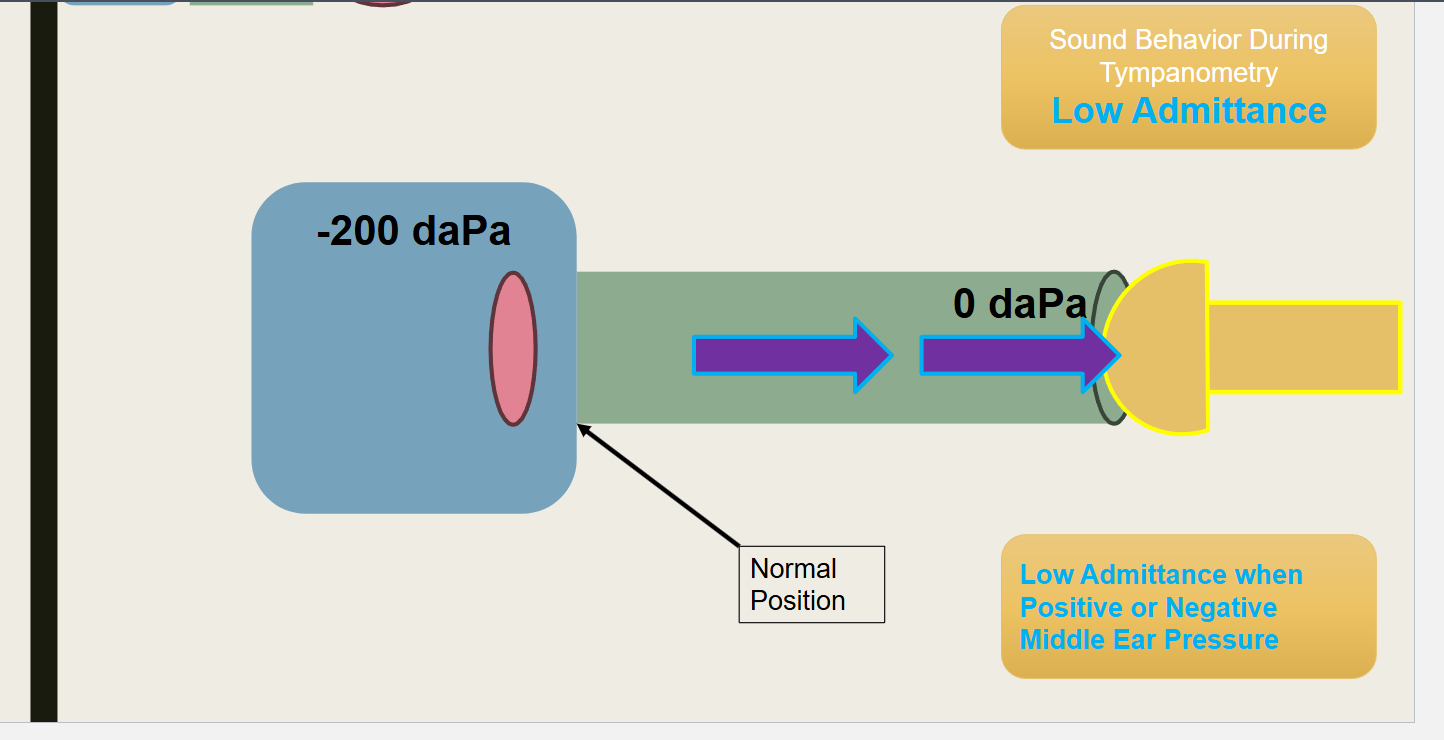
What type of pressure is this?
Low admittance during tympanometer
TPOAEs are better at finding
milder hearing loss
DPOAEs
can only diagnose
focus on specific areas where problem is occurring
focus on individual regions of outer hair cells
What is the term for passing and failing a hearing test
pass and refer
TEOAEs
The first screening done on babies
tests many regions of outer hair cells all at once
This test better at catching milder hearing loss