Multiple Myeloma (MM) And Detection Methods Part I and II
1/214
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
215 Terms
What is a tumor
An abnormal mass of tissue caused by cancer, inflammation, or infection
What are neoplasms
Tumors caused by uncontrolled cellular growth. They may form a mass or may not (Multiple Myeloma in the blood)
What is cancer
It refers to malignant neoplasms that invade surrounding tissues aggressively
What is multiple myeloma
A neoplasm of proliferating plasma cells that secrete Ig uncontrollably
How are plasma cells best distinguished from other populations
By their membrane expression of syndecan-1 which is CD138 a marker unique to plasma cells
What is CD138 and discuss the clinical utility of CD138 of syndecan-1
It is a surface marker expressed on mature plasma cells, playing a critical role in cell adhesion and antibody secretion. Clinically, CD138 is used to ID and quantify plasma cells in conditions like MM
What are the plasma cells dyscrasias or disorders of plasma cells
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
Multiple Myeloma
Immunoglobulin Light Chain (AL) amyloidosis
Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
What characterizes plasma cell dyscrasias
Overproduction of Ig, leading to hypergammaglobulinemia
What is hypergammaglobulinemia
The overproduction of Ig by plasma cells
What are the two types of hypergammaglobulinemia
Monoclonal and Polyclonal

Which hypergammaglobulinemia is this
Monoclonal
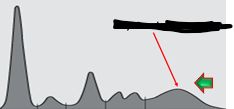
Which hypergammaglobulinemia is this
Polyclonal
What is elevated in monoclonal gammopathy
A single class of Ig
What types of cells are involved in monoclonal gammopathy
A single clone of B cells or plasma cells
What characterizes monoclonal gammopathy
The presence of an excessive amount of paraprotein or M protein
What does a discrete band in monoclonal gammopathy indicate
Excessive single monoclonal gamma globulin in the blood
What is elevated in polyclonal gammopathy
More than one class of Ig
What types of cells are involved in polyclonal gammopathy
Several clones of B cells or plasma cells
What characterizes polyclonal gammopathy
A broad diffuse band with no sharp or discrete band W
What are some causes of polyclonal gammopathy
Chronic infection
Hepatic cirrhosis
Decreased clearance of endotoxins/antigens
What is an example of an autoimmune disorder associated with polyclonal gammopathy
Rheumatoid
Is polyclonal gammopathy a primary or secondary disease
Secondary

What kind of band is this and what is it associated with
Discrete band. monoclonal gammopathy

What kind of band is this and what is it associated with
Broad diffused band, polyclonal gammopathy
What is the benign form of hypergammaglobulinemia
MGUS
What does a small spike in the gamma zone indicate
MGUS
What is the severe form of hypergammaglobulinemia
MM
What does a large spike in the gamma zone indicate
MM
What type of Ig is involved in Waldenstroms Macrogloublinemia
IgM
What does Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia involve
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (a mix of lymphocytes and plasma cells)
What is heavy chain disorder
Synthesis and secretion of incomplete Ig heavy chains
What is light chain disease
Synthesis and secretion of incomplete immunoglobulin light chains.
What is amyloidosis
Deposit of abnormal protein in multiple organs
What is AL amyloidosis caused by
Overproduction and misfolding of Ig light chains
What is AA amyloidosis caused by
Overproduction of amyloid A (acute phase proteins) in the liver during chronic inflammation (joint arthritis)
Is MGUS a premalignant condition
Yes a premalignant form and a precursor to myeloma
Does MGUS show the triad of MM
No
What is the level of M-protein in serum in MGUS
Less than 3g/dL
What is the percentage of marrow plasma cells in MGUS
Less than 10%
Are bone lesions present or end stage damage present in MGUS
No
Are Bence Jones Proteins present in MGUS
No
What is an important consideration for MGUS management
Long term follow-up is required, but no treatment is given
What % of asymptomatic MM cases does smoldering myeloma account for
About 15%
What is smoldering myeloma
It is an indolent (slow progressing) myeloma that exists in a concealed state
What is it important to follow cases of MGUS
To monitor if it develops into multiple myeloma
How long should cases of monoclonal protein be followed?
Follow up is required for years in some cases
How is smoldering myeloma initially diagnosed
It is initially diagnosed as MGUS
What is the percentage of marrow plasma cells in Smoldering myeloma
Greater than or equal to 10%
What is another name for MM
Plasma cell myeloma
What is multiple myeloma also known as, named after a doctor
Kahler’s disease, named after Austrian doctor Otto Kahler
What type of gammopathy is MM
Monoclonal gammopathy
What is the cause of MM
The exact cause is unknown
What are the suggested causes or risk factors for MM
Radiation
Viral Causes
Environmental stimulants
Genetic factors
What is the level of M-protein in serum in Smoldering Myeloma
Greater than or equal to 3g/dL
Are bone lesions present or end stage damage present in Smoldering myeloma
No
What is the percentage of marrow plasma cells in MM
Up to 90%
Are bone lesions present or end stage damage present in MM
Yes, there is a presence of end organ damage
What is the level of M-protein in serum in MM
M protein in serum and urine
What is the most common form of dysproteinemia
MM
What does dysproteinemia refer to
Excessive synthesis of Ig molecules or subunits
How common is MM
It accounts for 5-10 per 100,000 people
How does MM prevalence vary by ethnicity and sex
It is 2 times common in African Americans than whites and 1.6 times more common in males than females
What % of all malignancies does MM represent
1%
What % of hematological malignancies does MM account for
It accounts for 10% of hematological malignancies
What is the tumor burden in MM
Marrow plasma cells are 10%, and the tumor burden can increase up to 90%
What type of bone lesions are seen in MM
Ribs
Vertebrae
Skull
Long bones
What symptoms commonly accompanies bones lesions in MM
Bone pain and pathological fractures
What blood abnormality is present in MM related anemia
Normochromic, normocytic anemia
What causes fatigue in MM patients
Anemia and elevated ESR due to infection or inflammation
What protein damages kidney in MM
Free light chains, also known as Bence Jones Protein
What is a common cause of death in MM patients
Kidney failure due to free light chain deposition
What is another major cause of death in MM patients
Overwhelming infection or sepsis
What electrolyte balance is associated with MM
Hypercalcemia
What % of MM cases involve IgM
12%
Which Ig type is most common in MM
IgG, 52%
What % of cases involve IgA
22%
Are IgE and heavy chains common in MM
No they are rare
What % of MM cases involve light chains
11%
What type of disorder is Waldenstrom’s Macroglobulinemia
A low grade B cell lymphoplasmacytic disorder involving both lymphocytes and plasma cells
What type of lymphoma is WM classified as
Indolent lymphoma
What organ enlargements are associated with WM
Lymphadenopathy and Splenomegaly
What causes anemia in WM
Lymphoplasmacytic marrow infiltration disrupting erythropoiesis and increasing B cell proliferation
What are two common complications associated with WM
Hyper viscosity and Cryoglobulinemia
What type of anemia is seen in WM
Cold agglutinin hemolytic anemia
What is the main Ig implicated in WM
IgM
What bleeding disorder is associated with WM
Thrombocytopenic purpura (low platelet count)
What neurological condition is linked with WM
Peripheral neuropathy, present in 10% of patients with M-proteins
What patient population is WM more common in
Diabetes patients
What happens in cryoglobulinemia
Serum proteins precipitate at lower than normal body temperatures
What are the main tissue complications of cryoglobulinemia
Vasculitis and ischemic injury to peripheral tissue, which can lead to ischemic gangrene
What is “cold related gelling”
It refers to the blocking of blood vessels due to protein precipitation in cryoglobulinemia
What is Type I cryoglobulinemia
It involves monoclonal proteins, often IgM
What is type II cryoglobulinemia
It involves a mix of polyclonal and monoclonal Ig
What is type III cryoglobulinemia
It involves polyclonal Ig without monoclonal components
What is important when handling cryoglobulinemia lab specimens
The specimens must be transported, clotted, and centrifuged at temperatures near body temperature
A condition where abnormal misfolded protein produced in the bone marrow are deposited in tissues, leading to organ failure
Amyloidosis
What is the protein type involved in AL
Monoclonal light chain Ig, also known as monoclonal LC Ig deposition disease
What are the consequences of amyloid proteins deposition in tissue
Nephrosis
Cardiomyopathy
Pulmonary failure
Malabsorption
What are common physical signs of amyloidosis
Macroglossia (enlarged tongue)
Skin purpura
Vessel fragility
Carpal tunnel syndrome
What neurological symptoms may occur with amyloidosis
Peripheral neuropathy and autonomic insufficiency