Human biology year 10
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
cells contain
cells contain smaller structures called organelles
Cells
are the basic building blocks of all living things
Organelles
have specific functions within a cell
Cell membrane
barrier around the cell and allows materials to pass in and out of the cell
Cytoplasm
jelly like substance inside the cell that provides structure and contains organelles
Nucleus
contains DNA and controls cellular functions
Nuclear membrane
membrane that encloses the nucleus
Genetics
is the study of how the characteristics and qualities of parents are given to their offspring through their genes.
The way in which traits are passed on from one generation to another was first explained by
Gregor Mendel
how did gregor mendel explain the way traits are passed down, In the 1850’s
Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants to investigate the inheritance patterns of different features.
Mendel's experiment
Mendel cross-pollinated tall pea plants with short pea plants.
The offspring of the parent plants were all tall, none were short.
Mendel allowed the first generation of offspring plants to self-pollinate.
Some of the second generation offspring plants were short.
on average, for every three tall plants, there was one short plant.
Mendel repeated the experiment studying other traits
such as flower colour, seed colour and pod shape.
In these experiments he observed similar patterns, he concluded that
Inherited traits are controlled by factors (now known as genes)
Individuals have two copies of each factor.
history of genetics
In 1869, Friedrich Miescher first isolated the substance which we now know as DNA.
In the 1940’s, scientists discovered that DNA is responsible for inherited characteristics
By the mid 1950’s, the structure of DNA was determined – it looks like a twisted ladder, called a helix.
DNA is called
Deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA is found in
the nucleus of cells
DNA contains
the genetic code for every structure and function in an organism.
DNA also determines
the inherited characteristics of an organism.
DNA in a person is
unique
Your DNA is
a unique of combination of genetic material passed down from both of your parents
Is it possible for two people to have the same DNA
- Yes.
•Identical twins.
•Same cell, contains same DNA.
•Divides so each have same DNA
DNA is made of
of smaller molecules called nucleotides
Nucleotide molecules have three main parts:
‐A Phosphate group
‐A Deoxyribose sugar
‐A Nitrogenous base
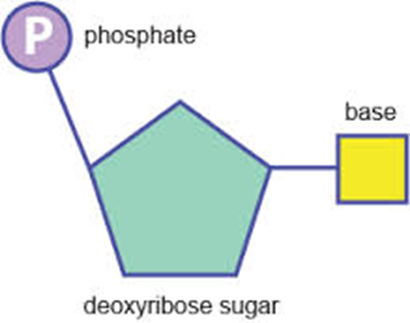
The nucleotides are arranged in a spiral, ladder like structure, called a
helix
sides of the ladder are made of
alternating sugar and phosphate
steps of the ladder
nitrogenous bases
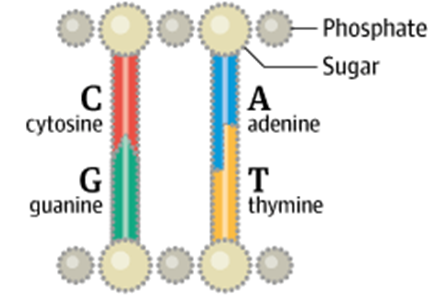
in DNA there are 4 nitrogenous bases
Adenine A
Thymine T
Guanine G
Cytosine C
each nitrogenous base will only bond with
one other specific base
known as a complementary base pair
complementary base pairs
Adenine and Thymine
Cytosine and Guanine
all the cells in your body except red blood cells have
a nucleus that contains DNA
The DNA is identical in each cell which means that
it must be possible to copy DNA molecules perfectly
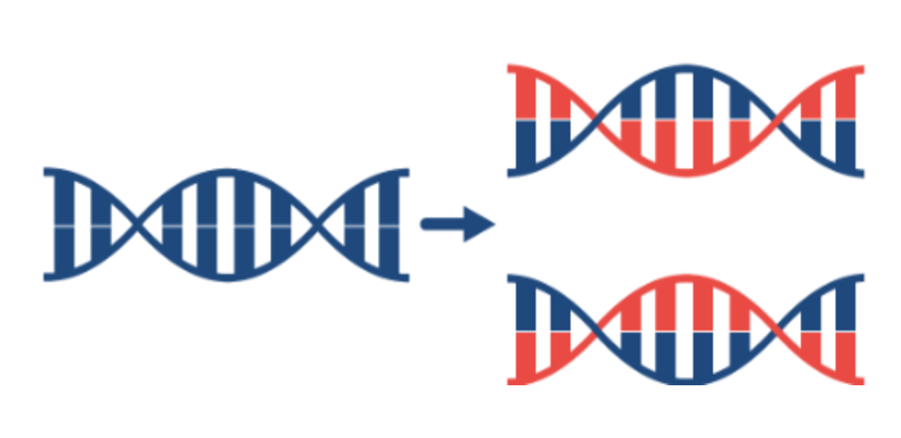
DNA replication is the process by which
DNA makes a copy of itself
this occurs just before the cell divides into 2 new cells
DNA replication occurs in stages
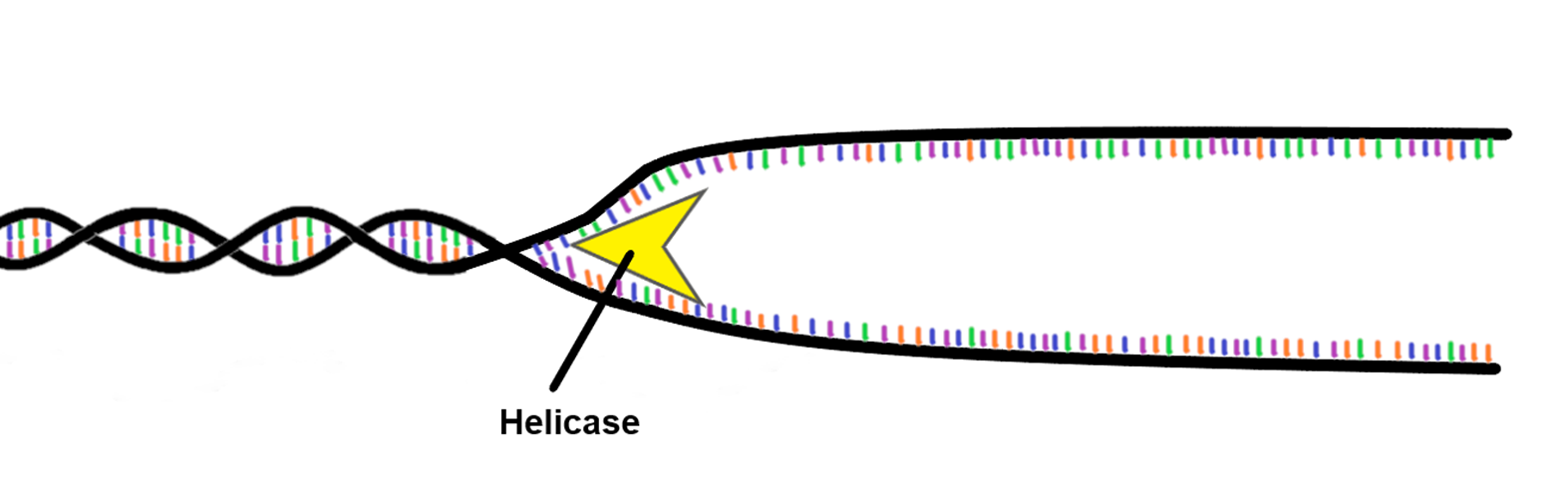
Stage 1: straightening and separation
the double helix untwists
an enzyme separates the individual strands of the double helix
This exposes the nitrogenous bases
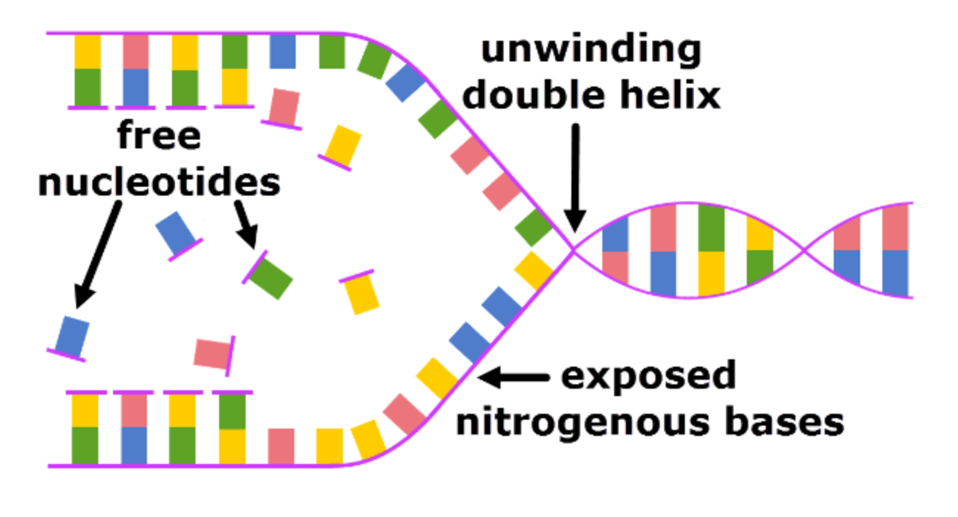
Stage 2: constructing copies
within the nucleus there are free nucleotides which are not part of a DNA chain
The free nucleotides connect to the exposed nitrogenous bases following complementary base pairing rules (A with T and C with G).
This forms two strands of DNA which are both identical to the original.
Stage 3: Checking for mistakes
•The replication process is now complete, with two identical double helixes being formed.
•The two new DNA strands are “proofread” by enzymes.
•Any errors in base sequencing are corrected
explain what the study of genetics is
genetics is the study of how the characteristics and traits of parents are given to their children through their genes.
state what the acronym DNA stands for
Deoxyribonucleic acid
explain the function of DNA
DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell
DNA contains the genetic code for every structure and function in an organism
DNA determines the inherited characteristics of an organism
your DNA is
a unique combination of genetic material passed down from both of your parents
Describe the structure of DNA
DNA is in a helix structure, and it looks like a twisted ladder.