Forensics - fingerprints
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms

plain arch
no deltas

tented arch
delta is present, what makes it tented

radial loop
one core
one delta
bottom of loop points towards the thumb

ulnar loop
one core
one delta
bottom of loop point towards the pinky

central pocket whorl
2 deltas

plain whorl
2 deltas
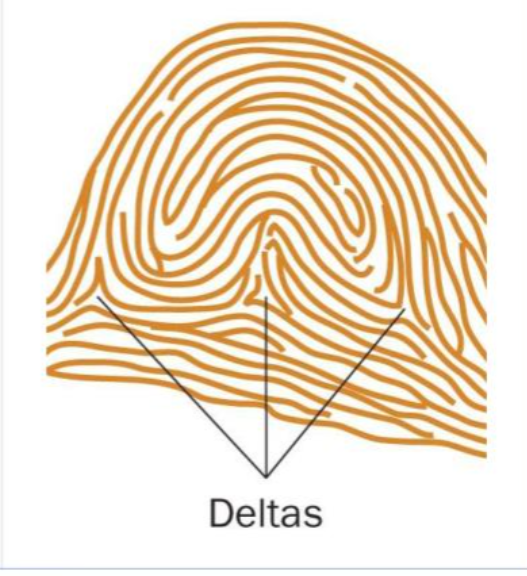
accidental whorl
2 or more deltas
combines 2 or more other patterns, but not a tented arch

double loop whorl
2 loops
2 cores
2 deltas

bifurcation
looks like a fork

island

enclosure

eye

spur
hook

trifurcation

delta

double bifurcation
dusting
fine dust (often charcoal) stick to the sweat and oils on prints
works best on smooth surfaces
excess dust blown away, then photographed
lifted with tape then placed on collection card
can be messy, too faint
iodine fuming
get print from porous surface ( paper, cardboard, wood)
solid iodine is heated in vapor tend and produces vapor (sublimation)
Iodine crystalizes on prints, form brown color
fades unless sprayed with starch solution
not common, toxic and not sensitive
ninhydrin
best for prints off of paper
sprayed with solution of ninhydrin in acetone or alcohol
reacts with amino acids in sweat and becomes purple-blue
takes up to 24 hours to form, toxic and flammable
cyanoacrylate fuming
prints on plastic, metal, or glass
items put in “vapor tent” and exposed latent fingerprints to cyanoacrylate by heating superglue
reacts with amino acids and water and becomes a white solid (harder to see)
good for preserving the print
How/when do fingerprints form?
form on the fetus in the womb
the basal layer of the skin grows faster than the epidermis and the dermis, which makes it wrinkle into patterns
twins don’t have the same prints and they are not genetic
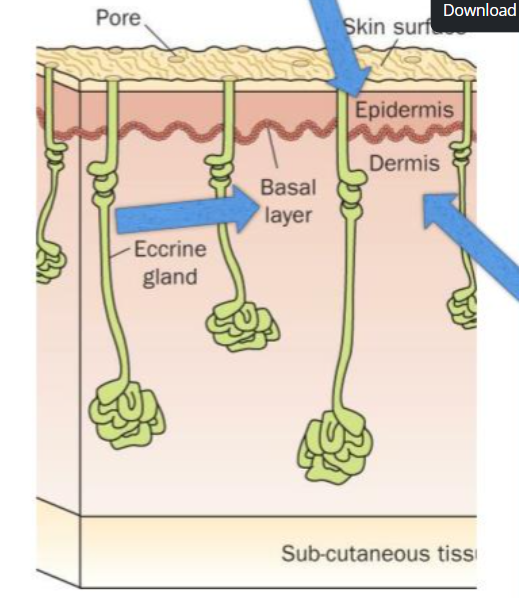
epidermis
Outermost layer, protection against environmental hazards, pathogens, and water loss.
produces melanin for skin pigmentation
dermis
Middle layer, blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. Provides structural support and has hair and sweat follicles.
temp regulation and sensation
hypodermis(subcutaneous layer)
Innermost layer, has fat and connective tissues. Acts as an insulator, absorbs shock, and anchors the skin to inner structures.
Basal layer
Between Epidermis and Dermis, important for skin regeneration, pigmentation, and treating wounds.