Osmoregulation and the Excretory System in Animals
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Osmolality
The total moles of solute per kilogram of water in a solution.
Osmotic Balance
The ability of the extracellular compartment of an animal's body to take water from its environment or to excrete excess water into its environment.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a membrane from a more dilute solution to a less dilute solution.
Isoosmotic
Solutions that have the same osmolality.
Hypoosmotic
A solution with a lower osmolality than another.
Hyperosmotic
A solution with a higher osmolality than another.
Osmoconformers
Marine invertebrates whose body fluids have the same osmolality as seawater.
Osmotic Equilibrium
A state where there is no osmotic gradient and no tendency for water to leave or enter the body.
Osmoregulators
Animals that maintain a relatively constant blood osmolality despite different concentrations in the surrounding environment.
Hypertonic
A condition where freshwater vertebrates have a higher solute concentration in their body fluids than that of the surrounding water.
Dilute Urine
A large volume of urine excreted by freshwater fish to eliminate excess water.
Hypotonic
A condition where most marine vertebrates have body fluids with only about one-third the osmolality of the surrounding seawater.
Dehydration Prevention
The process by which marine vertebrates retain water by drinking seawater and eliminating excess ions.
Evaporation Loss
The tendency of terrestrial vertebrates to lose water to the air by evaporation from the skin and lungs.
Terrestrial Vertebrates
Reptiles, birds, mammals, and amphibians that face water loss problems when living on land.
Kidneys and Gills
Organs through which marine vertebrates eliminate excess ions.
Extracellular Compartment
The part of an animal's body that includes blood plasma and is involved in maintaining osmotic balance.
Epithelial Cells
Specialized cells across which exchanges of water and electrolytes occur.
Osmoregulatory Organs
In many animals, the removal of water or salts from the body is coupled with the removal of metabolic wastes through the excretory system.
Contractile vacuoles
Protists employ contractile vacuoles for the removal of water and salts.
Excretory tubules
Other multicellular animals have a system of excretory tubules (little tubes) that expel fluid and wastes from the body.
Malpighian tubules
The excretory organs in insects are the Malpighian tubules.
Kidneys of vertebrates
The kidneys create a tubular fluid by filtration of the blood under pressure, containing waste products and water, as well as valuable small molecules.
Nephrons
The kidney is a complex organ made up of thousands of repeating units called nephrons, each with the structure of a bent tube.
Glomerulus
Blood pressure forces the fluid in blood past a filter called the glomerulus, which retains blood cells and proteins while allowing water and small molecules to pass through.
Urine
The final waste product eliminated from the body after filtration and reabsorption processes in the kidneys.
Human kidneys
In humans, the kidneys are fist-sized organs located in the region of the lower back that receive blood from a renal artery to produce urine.
Ureter
Urine drains from each kidney through a ureter, which carries the urine to a urinary bladder.
Renal pelvis
The mouth of the ureter flares open to form a funnel-like structure called the renal pelvis, which receives urine from the renal tissue.
Renal cortex
The outer part of the kidney tissue.
Renal medulla
The inner part of the kidney tissue.
Afferent arteriole
Blood is carried by an afferent arteriole to a tuft of capillaries in the renal cortex, known as the glomerulus.
Bowman's capsule
The first region of the nephron tubules that envelops the glomerulus, allowing glomerular filtrate to enter the nephron system.
Proximal convoluted tubule
A portion of the nephron located in the cortex where the filtrate enters after Bowman's capsule.
Glomerular filtrate
The fluid that enters the nephron system after being filtered through the glomerulus.
Filtration
The process by which blood pressure forces fluid through the porous capillary walls in the glomerulus.
Active transport
The process by which useful sugars and ions are recovered from the filtered fluid in the nephron.
Metabolic wastes
Substances left behind in the fluid urine after useful molecules are reabsorbed in the nephron.
Loop of Henle
A structure in the kidneys of mammals and birds that allows for the concentration of urine.
Cortex
The outer part of the kidney where the distal convoluted tubule drains into the collecting duct.
Medulla
The inner part of the kidney where the collecting ducts merge to empty urine into the renal pelvis.
Glomerular filtration
The initial process in urine production where blood is filtered in the glomerulus.
Active transport of Na+
The process that drives the reabsorption of Na+ out of the filtrate in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Osmotic gradient
Created by the extrusion of NaCl from the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, allowing passive water reabsorption.
Peritubular capillaries
The second bed of capillaries that surrounds the tubules in the kidneys.
Substances not filtered by glomerulus
Pollutants and drugs, such as pesticides and penicillin, that are moved into the proximal and distal convoluted tubules.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
A hormone produced by the hypothalamus that causes water retention in the kidneys when blood osmolality increases.
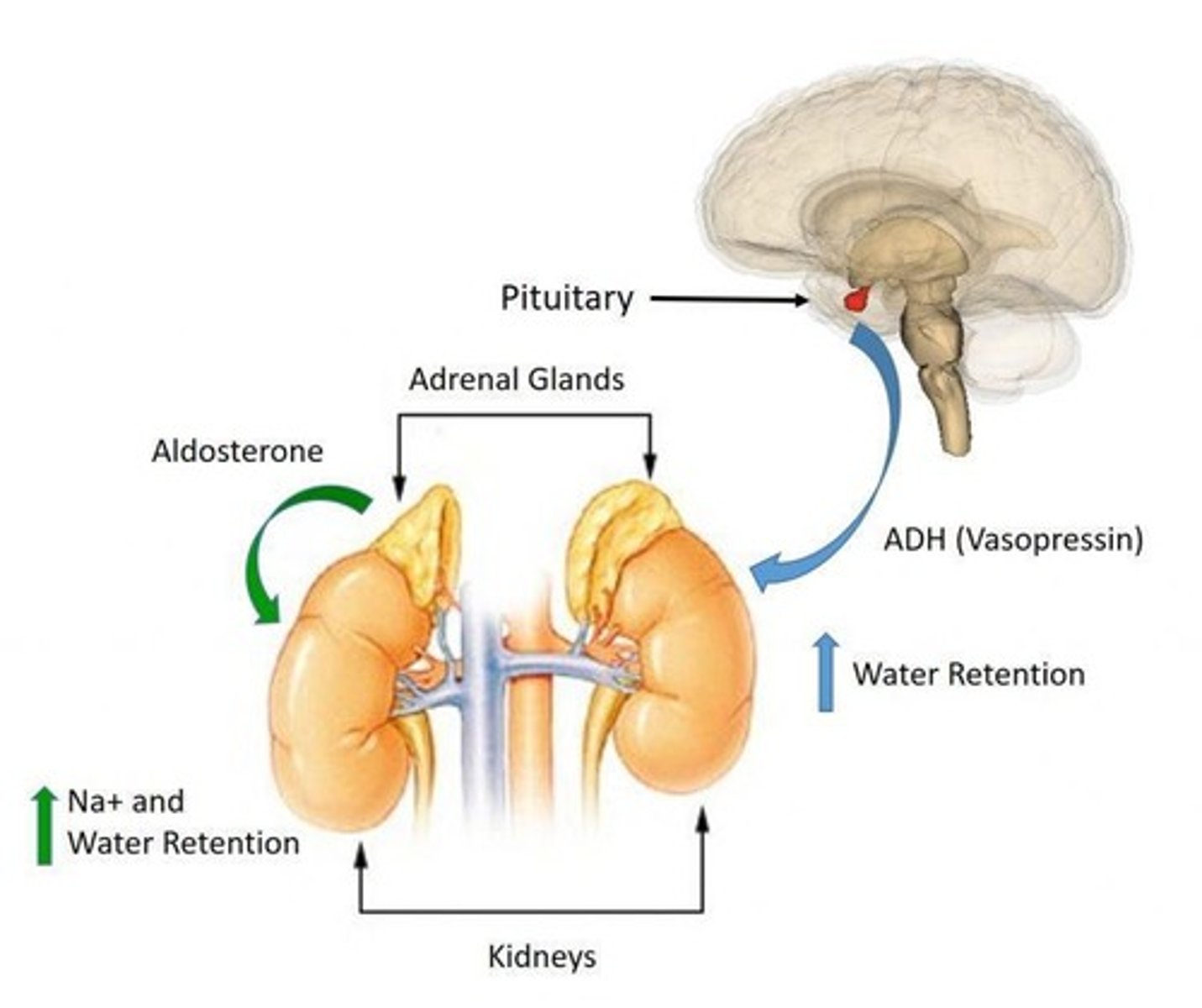
Aldosterone
A hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex that stimulates Na+ reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubules.
NaCl and water reabsorption
Occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule where approximately two-thirds of these substances are reabsorbed.
ADH activation
Occurs when blood osmolality is increased, prompting water retention in the kidneys.
Abnormal substances in urine
Glucose, blood, proteins, bilirubin, and ketones are examples of substances that should not be present in urine.
Collecting duct
The structure in the kidney that descends into the medulla and merges to empty urine into the renal pelvis.
Distal convoluted tubule
The part of the nephron that drains into the collecting duct after the loop of Henle.
Blood concentration of Na+
A decrease in this concentration activates aldosterone, promoting Na+ reabsorption.