TMOD (Lids/Lashes)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Dermatochalasis
Skin becomes laxative with age due to weakened orbital septum
Complaints of heavy eyelids and reduced superior VF
Deramatochalasis Treatment/Management
Blepharoplasty
Ectropion
Outward rolling of the lid (usually lower lid) due to age/involutional (lid laxity due to loss of muscle tone of orbicularis oculi), trauma, bells palsy
asymptomatic or epiphora and ocular irritation
Presents with inferior exposure keratopathy
Ectropion Treatment/Management
Sx to tighten lateral tarsal strip
Tx exposure keratopathy
If cause is bells palsy, it will resolve spontaneously
Entropion
Inward rolling of the eyelid due to involution/age
Complaints of ocular irritation, FB sensation, epiphora
Exposure keratopathy and trichiasis,
Entropion Treatment/Management
If cornea is compromised, top antibiotic ointment as a preventative measure
Abnormal position of lid can be tx with tape temporaily or botox temporarily, sx for permanent fix
Can epilate lash
Trichiasis
Misdirected eyelashes that rubs the globe due to entropion or idiopathic
Complaints of ocular irritation, FB sensation, epiphora
Presents with SPK, injection, possible corneal scarring
Trichiasis Treatment/Management
Epilation
If chronic, lashes can be permanently removed by cryotherapy, cautery or electrolysis
If cornea is compromised, top antibiotic ointment as preventative measures
Blepharospasm
Idiopathic uncontrollable eyelid closure
Spasm of orbicularis oculi, corrugator, procerus
Absent during sleep
Blepharospasm + lower facial abnormalities = Meige’s Syndrome
Blepharospasm Treatment/Management
Botox inject every 12 wks (3mths)
Bell’s Palsy
Flaccid paralysis of lower motor neuron CN 7
Usually idiopathic but also neural inflammation, herpes
Signs and symptoms develop over 24 hours
Unilateral epiphora, dry eye (affect secretion and blinking), drooling, inability to close one eye, exposure keratoconjunctivitis
Bells phenomenon is still present
Bell’s Palsy Treatment/Management
Spontaneously improve within 4 months and complete resolution within 1 yr
If due to neural inflammation, tx with oral steroid
If due to herpes, tx with oral antiviral
Tape eyelid shut while asleep but if chronic, consider gold weight implant. during the day, PF AT Q1H and AT ointment QHS
FU in 6 wks
Floppy Eyelid Syndrome
Decrease elastin within tarsal plate
Excessive lid laxity in overweight men and is a sign of sleep apnea
May present with exposure keratoconjunctivitis of inferior cornea and conjunctiva, papillae
Floppy Eyelid Syndrome Treatment/Management
Sx for definitive tx
Refer to rule out sleep apnea
Tape eyelid shut or wear eye shield while sleeping
During the day, PF AT Q1H and AT ointment QHS
If cornea is compromised, top antibiotic ointment
Xanthelasma
Seen in elderly pt with hyperlipidemia
Creamy yellow plaques found in superior nasal eyelids
Xanthelasma Treatment/Management
Not necessary
Plaques can be removed with excision or carbon dioxide laser tx but recurrence is high
Blepharitis (anterior)/Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (posterior)
Inflammation of the sebaceous glands due to staphylococcus infection
Anterior bleph afflicting glands of zeis and moll
Posteriopr bleph afflicting meibomian gland
Causes evaporative dry eye
Blepharitis (anterior)/Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (posterior) Treatment/Management
Anterior bleph
Warm compress
lid scrubs
erythromycin or bacitracin ung QHS
tobradex for severe cases
Posterior bleph
warm compress and digital massage
eyelid scrub
tobradex for short term
oral azithromycin or oral doxy or minocycline for pts with ocular rosacea
Inflammation can be controlled with Xiidra or Restasis
AT and omegag-3 fatty acids
Hordeolum
“Stye” pimple of the eyelid or infection of sebaceous gland
Complaint of pain and eyelid tenderness
Internal hordeolum: meibomian gland
External hordeolum: zeis or moll
Hordeolum Treatment/Management
Ask about rosacea
Hot compress as much as possible with digital massage
Rx anitbiotic ointment or top steroid-antibiotic ointment (tobradex) if persisten
Chalazion
Sterile inflmmation of sebaceous gland
Painless, nontender bump and lid does not appear red, hard and immobile
Chalazion Treatment/Management
Hot compress
If persists for a month, remove via biopsy
If recurrent and in the same location, suspect sebaceous gland carcinoma dn refer for biopsy
Steroid injection is also an option but CI in AA due to high risk of hypopigmentation
Pediculosis/Phthiriasis
Eyelash infection of lice
If in children, suspect sexual abuse
Presnts with burrowing lice, spots fo dried blood, tiny brown deposits (feces), white/translucent nits (eggs), +PAN
Pediculosis/Phthiriasis Treatment/Management
Remove lce with jeweler’s forceps
Antibiotic ointment (erythromycin or bacitracin) for 2 wks
Can recommended kwell (for genitals)
Instruct pt to thoroughly wash towels and linens
If child, optometrists are mandated reporters and must notify authroities of child abuse
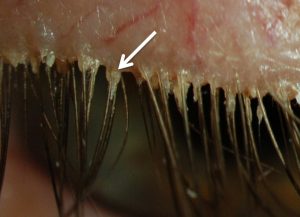
Demodicosis
Caused by parasite Demodex folliculorum
Demodicosis Treatment/Management
Lid hygeine + tea tree oil
Sebaceous Gland Carcinoma
Remember suspect SGC if chalazion is recurrent
Usually in women between 50-70
Risk factor for mortality:
tumors >2cm
superior and inferior involvement
duration >6mths
Presents with yellow, hard tumor (usually superior lid), madarosis, poliosis, possible lymphadenopathy (which indicates malignancy)
Sebaceous Gland Carcinoma Treatment/Management
Full thickness excision with biopsy
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Mostly on the inferior eyelid/sun exposed areas of the skin
Older white pts
Most common malignant eyelid tumor (rarely metastasizes
Layers of the epidermis from superficial to deep: corneum → lucidum → granulosum → spinosum → basale
Pearly umbilicated nodule that can progress to include central ulcerative telangiectasia (“rodent ulcer”)
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment/Management
Full thickness excision with biopsy
Advise to use sun protection
Actinic Keratosis → Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Usually on the inferior eyelid/sun exposed area
Usually older white pts who also smokes
Actinic keratosis is the most common precancerous skin lesion
SCC is the 2nd most common malignant eyelid tumor
SCC is more invasive than BCC
Metastasis to lymph nodes (submandibular or preauricular)
Actinic keratosis: scaly, round erythematous lesion
SCC: scaly, erythematous, ulcerated plaque (flat or elevated) rarely contains surface vascularization
Actinic Keratosis → Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment/Management
Full thickness excision with biopsy
Cryotherapy can be used as further tx once dx has been confirmed
Advise to use sun protection
Malignant Melanoma
Rare but most lethal primary skin tumor
Presents with pigmented, elevate, lesions with irregular borders
Due to abnormal proliferation of melanocytes
ABCDE: asymmetry, boarders, color, diameter, enlargement
Malignant Melanoma Treatment/Management
Full thickness excision with biopsy
Severe cases require orbital exenteration with neck dissection
Advise pt on sun protection and refer to dermatology for an evaluation
Malignant Melanoma prognosis
Based on thickness and depth of lesion
Capillary Hemangioma
Most common benign orbital tumors in children (in adults is cavernous hemangiomas)
Presents within the first month of life
Superficial vascular lesion (strawberry nevus) with rapid growth
May cause amblyopia if they block visual axis or press against the cornea and induce astigmatism
Capillary Hemangioma Treatment/Management
Spontaneously resolve by the time pt is10yo