Hybrid Imaging PET/CT & PET/MRI Slide 30-59
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
What is the typical diameter of the detector ring in most whole-body PET systems?
80–90 cm
What is the typical diameter of the clear bore that patients lie in during a PET scan?
55–60 cm
What component surrounds the patient in a ring configuration to detect annihilation photons?
Scintillator blocks
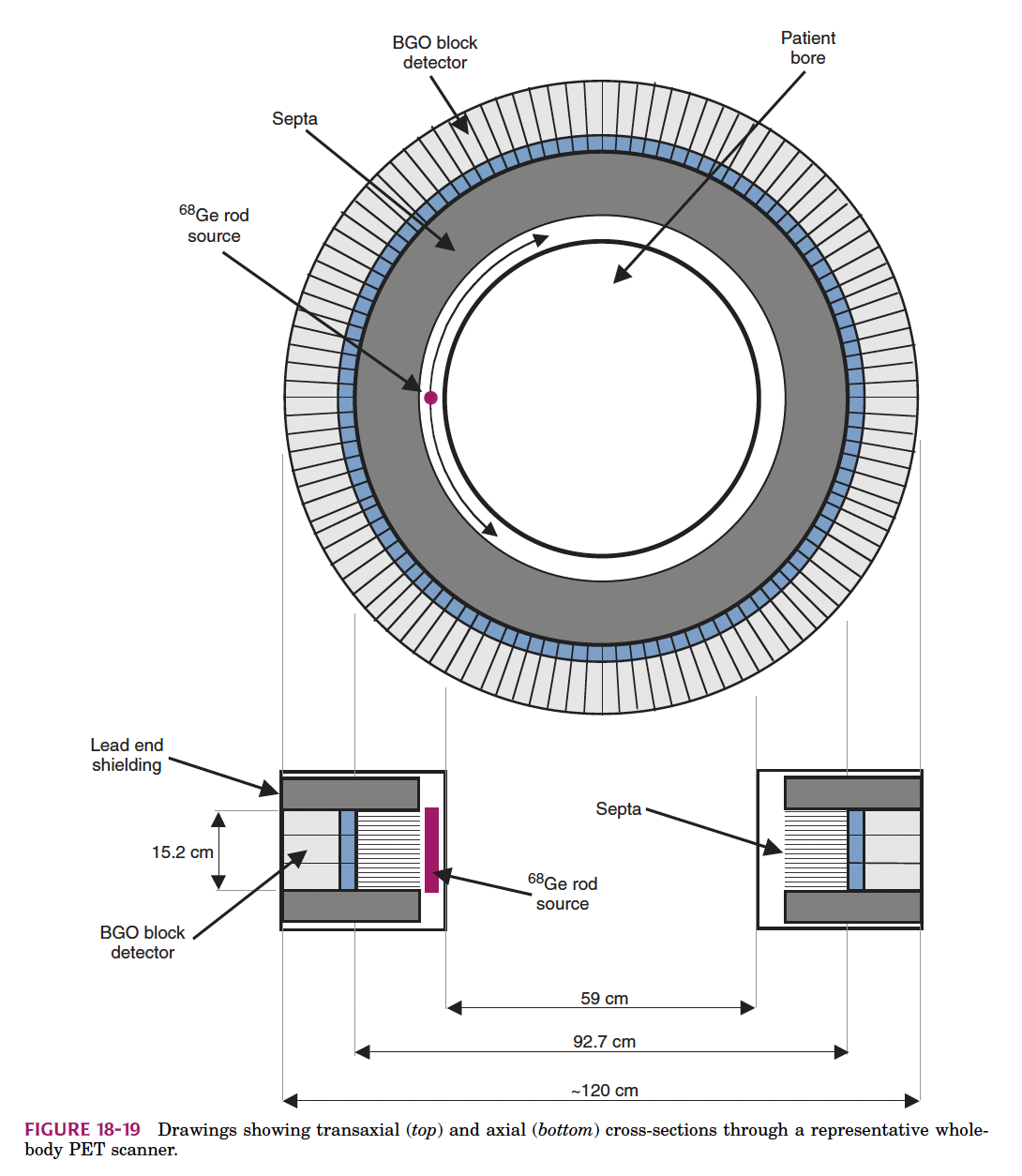
In the diagram, which material is used for the PET detector blocks?
BGO
Why is the ring diameter larger than the bore diameter?
To house detector elements
Which of the following is not true about the bore of a PET scanner?
It is wider than the ring
The design of a PET scanner is most optimized for detecting which type of event?
Coincidence detection of annihilation photons
What is the purpose of axial collimators or septa in traditional PET scanners?
To allow only photons emitted parallel to the detector plane
What type of PET acquisition removes the septa to allow more photon detection?
3D acquisition
What do septa help reject in 2D PET acquisition?
Scattered photons
What reconstruction methods are used in PET? (Select all that apply)
Iterative reconstruction and Filtered Backprojection
What are cross planes in PET?
Coincidences detected from detectors on adjacent rings
What is a benefit of using cross planes in PET acquisition?
Roughly double the sensitivity
What is the result of stacking 2D transaxial image planes from a PET scanner?
A full 3D image volume
Which statement best describes direct planes?
Coincidence data from the same detector ring
What is the primary role of septa in 2D PET acquisition systems?
To reject scattered photons and reduce random coincidence events
In 3D PET acquisition, which component is removed to allow more lines of response?
Septa
How many times greater is the sensitivity of 3D acquisition compared to 2D acquisition?
4x to 8x
What drawback is associated with increased sensitivity in 3D PET mode?
Increased scatter and dead time
In the image of axial planes shown, which configuration corresponds to Δ = ±1?
2D direct and cross planes
What is the main reason cross planes have higher counting rates than direct planes?
They receive data from two rings instead of one
Which of the following is a correct pairing of acquisition mode and detector behavior?
2D Acquisition – septa present – restricted LOR
What term describes the number of rings included in line-of-response calculations in 3D acquisition?
Axial span
What is the main advantage of PET scanners with detectors surrounding the patient?
They can acquire projection angles simultaneously
What does dynamic scanning in PET imaging allow for?
Timed acquisition of frame-based data
What must be entered into the system before starting a dynamic PET scan?
Number of time frames and frame length
What is "List Mode" acquisition in PET?
A method of logging individual events with timestamps
How are coincidence events recorded in List Mode?
Written sequentially with a timestamp
What is one benefit of using List Mode over static acquisition?
Ability to adjust frame lengths after scanning
Which of the following best describes dynamic PET imaging?
Requires pre-defined time frames for image reconstruction
What does List Mode allow you to do with the data after acquisition?
Integrate events over any time interval
What is the primary purpose of attenuation correction in PET?
To correct for photon loss due to tissue absorption
Which of the following is used in a transmission (blank) scan for PET attenuation correction?
Ge-68
When is a post-injection transmission scan performed?
Immediately after the emission scan
What does the variable T represent in the attenuation correction diagram?
Total distance between the two detectors
What does x represent in the attenuation diagram?
Distance from the point source to Detector 1
Which method provides counts for all acquisition pairs including true, false, and scattered events?
Blank scan
Why is Ge-68 used in blank scans?
It provides a consistent, long-lived positron source for calibration
What’s a risk of performing a post-injection transmission scan?
Interference from remaining radiotracer activity
What is the primary purpose of PET and SPECT imaging?
To provide functional information about metabolic or physiological processes
Which type of imaging provides the highest spatial resolution?
CT or MRI
What is one major limitation of nuclear medicine imaging compared to CT/MRI?
It has poor spatial resolution for anatomy
In which scenario is the regional anatomy obvious without hybrid imaging?
Cardiac scans
What additional imaging unit is built into almost every PET scanner today?
CT unit
What is the main advantage of hybrid PET/CT or SPECT/CT imaging?
Combines functional and anatomical imaging in one study
True or False: Only PET scanners are available with integrated CT units.
False
What is meant by “spatially registered CT images” in hybrid imaging?
CT and PET/SPECT images are aligned to the same coordinates in the body
Which hybrid system is becoming increasingly common aside from PET/CT?
SPECT/CT
True or False: PET/CT scans are performed at separate visits to ensure accuracy.
False
Why is spatial and temporal registration better in hybrid imaging?
Because the scans are done in quick succession on the same system
What extra function can CT provide in hybrid PET/CT?
Attenuation correction
What type of CT is used in hybrid imaging for attenuation correction?
X-ray computed tomography
Which statement about X-ray CT in hybrid imaging is TRUE?
It uses an external x-ray tube to generate a narrow beam
How is X-ray CT similar to PET/SPECT transmission scanning?
Measures attenuation for reconstruction
What is the key difference between CT and nuclear medicine imaging?
CT uses external x-rays; NM uses internal radiotracers
Why is a “high flux” of x-rays used in CT?
To ensure enough photons penetrate for image reconstruction
What is the purpose of the filament in the x-ray tube?
Heat and release electrons via thermionic emission
What material is typically used for the filament in an x-ray tube?
Tungsten
What happens when electrons strike the anode target?
Bremsstrahlung and characteristic x-rays are generated
What determines the energies of characteristic x-rays?
Atomic structure of the anode material
What is Bremsstrahlung radiation?
Continuous spectrum from deceleration of electrons in the anode
Why is the anode in many x-ray tubes designed to rotate?
To spread heat over a larger area and prevent damage
What is the typical anode material in a medical x-ray tube?
Tungsten
What component drives the rotation of the anode?
Rotor
Which of the following is not a benefit of a rotating anode?
Lower patient dose
The most common detector material in modern CT scanners is:
CsI(Tl) scintillators read by silicon photodiodes
Which older detector type uses high-pressure xenon gas?
Ionization chambers
The main function of CT detectors is to:
Convert X-ray photons into an electrical signal proportional to the X-ray flux
In CT detectors, high-pressure xenon gas is used because:
It increases the probability of X-ray interaction
Ceramic scintillators in CT scanners are primarily used because they:
Have high light output and fast decay time
The proportionality between detector output and tube current means:
Detector signal increases linearly with X-ray tube current
In CT detectors, light produced in the scintillator is:
Converted into electrical signals by silicon photodiodes
The rotating anode in an X-ray tube helps to:
Spread heat over a larger area to prevent damage
The focal spot is:
The area on the anode where electrons strike to produce X-rays
The material most often used for the anode in CT X-ray tubes is:
Tungsten
Why is tungsten used as the anode material?
High atomic number and high melting point
The purpose of the vacuum in an X-ray tube is to:
Prevent electron scattering before reaching the anode
The electron beam is produced by:
Heating the cathode filament (thermionic emission)
When electrons hit the anode, they produce:
Bremsstrahlung and characteristic X-rays
The CT scanner’s gantry contains:
X-ray tube, detector, and high-voltage power supply
Slip ring technology allows:
Continuous gantry rotation without cable rewinding
Typical CT gantry rotation speeds are:
1–3 revolutions per second
In slip ring systems, electrical contact is made using:
Conductive brushes sliding on the slip ring surface
The main advantage of continuous rotation in CT is:
Faster acquisition of large axial image sets
Slip ring technology in CT scanners was developed to:
Eliminate the need to stop and unwind cables
Before slip rings, technologists had to:
Manually unwind the scanner cables between rotations
Slip rings make electrical contact via:
Conductive brushes
Slip ring innovation mainly improved:
Scan speed and workflow efficiency
Slip rings allow data transmission:
Without physically stopping the gantry
Which of the following is a direct result of slip ring technology?
Helical CT scanning
The circular component in the gantry that the brushes contact is the:
Slip ring
The primary purpose of CT imaging is to:
Create cross-sectional images without superimposed structures
CT differs from conventional X-ray because it:
Removes overlapping structures in the image
The human body appears differently in CT images mainly because:
Different tissues have varying densities and attenuation
In CT imaging, bone appears differently from soft tissue because:
Bone has a higher density and attenuates X-rays more
Which statement about CT images is correct?
CT allows imaging in multiple planes without superimposition
The density differences in tissues that allow CT to work are measured in:
Hounsfield units
CT scanning is particularly useful for complex anatomy because:
It provides detailed visualization without overlapping structures