African American History: Chapter 1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
geographical characteristics of Africa
highland, deserts, rivers, lakes, rain forests, savannas, chaparrals, and the great rift valley
Where did humans originate?
Africa
Out of Africa model of human origins
A theory in which human life originated from Africa and then spread around the globe.
Which direction does the Nile River flow?
South to North
Where is Lower Egypt located?
At the top, closer to the Nile delta.
"Ardi"
Nickname for the fossilized skeleton of female, Ardipithecus ramidus, an early species hominid who lived approx. 4.5 mya. This 1992 Afar, Ethiopia discovery shows hominids diverged from apes much earlier than previously believed.
Savanna
An area of grassland with scattered trees and bushes
rain forest biome
a dense evergreen forest found in tropical areas of heavy rainfall
hunting and gathering societies
societies whose mode of subsistence is gained from hunting animals, fishing, and gathering edible plants
West Africans began making iron tools
long before Europeans arrived in Africa
Hieroglyphics
a writing system based on pictures and symbols
Patrilineal
based on or tracing descent through the male line
Patriarchal
society ruled by a senior man
Semitic
Refers to languages, such as Arabic and Hebrew, native to southwest Asia
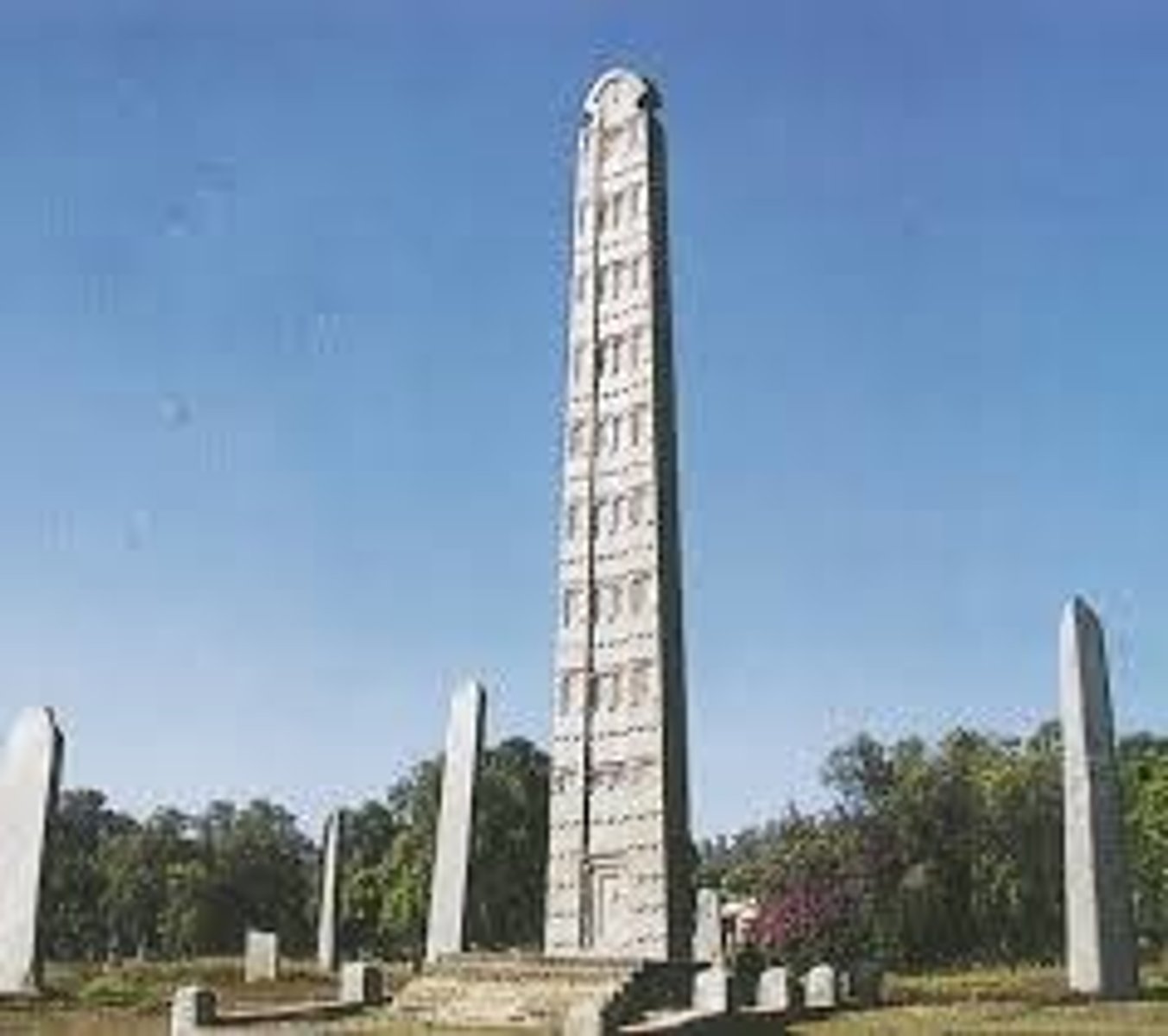
Axum Stele

Berbers
A people native to North Africa and the Sahara Desert
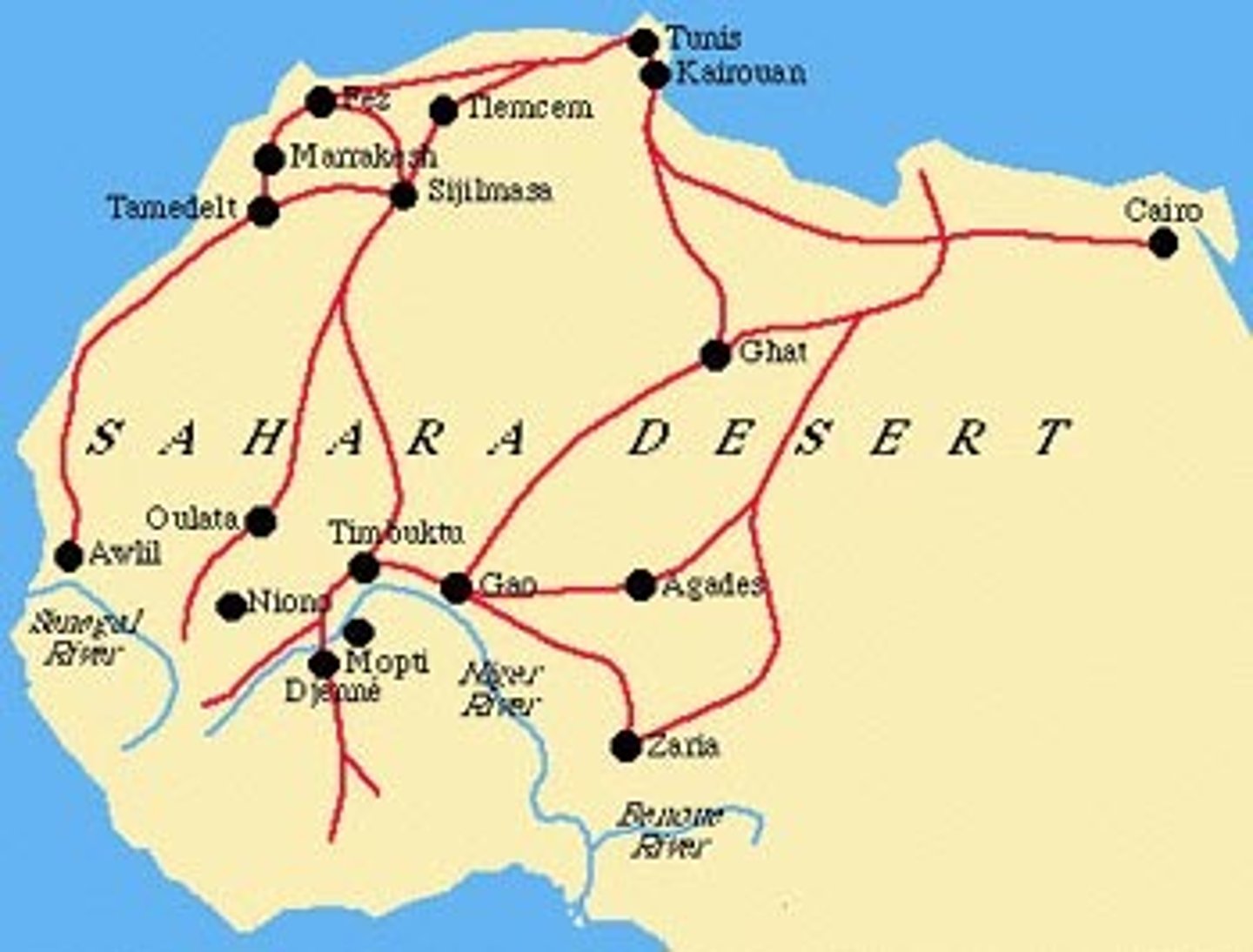
Ghana, Mali, Songhai
• West African kingdoms that built wealth and power through trans-Saharan trade of salt and gold
Mansa Musa
Ruler of Mali (r. 1312-1337). His extravagant pilgrimage through Egypt to Mecca in 1324-1325 established the empire's reputation for wealth in the Mediterranean world.
Kumbi Saleh
The capital city in the Empire
of Ghana
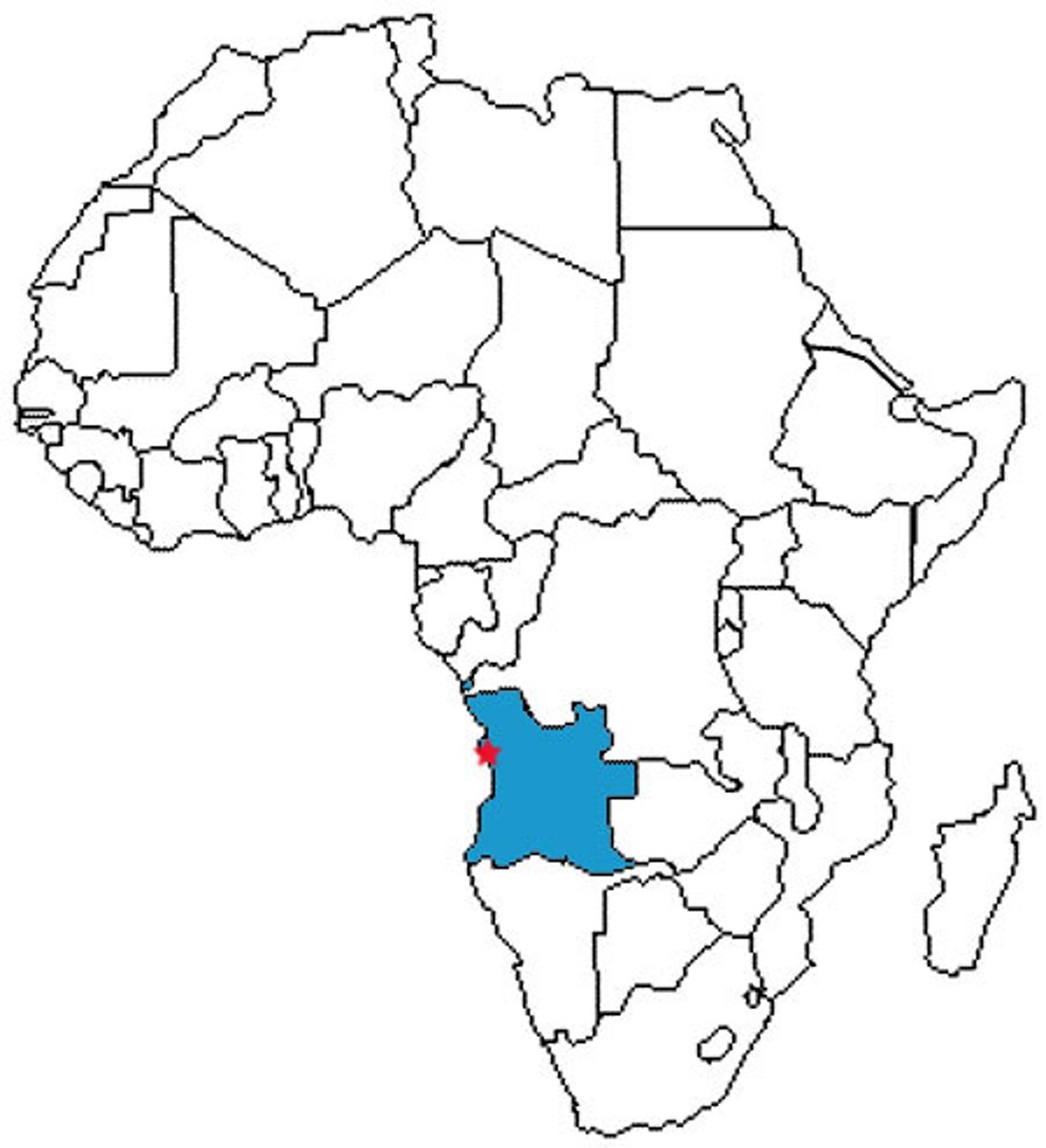
Kongo Kingdom
Large agricultural state on the lower Congo River; capital at Mbanza Kongo.
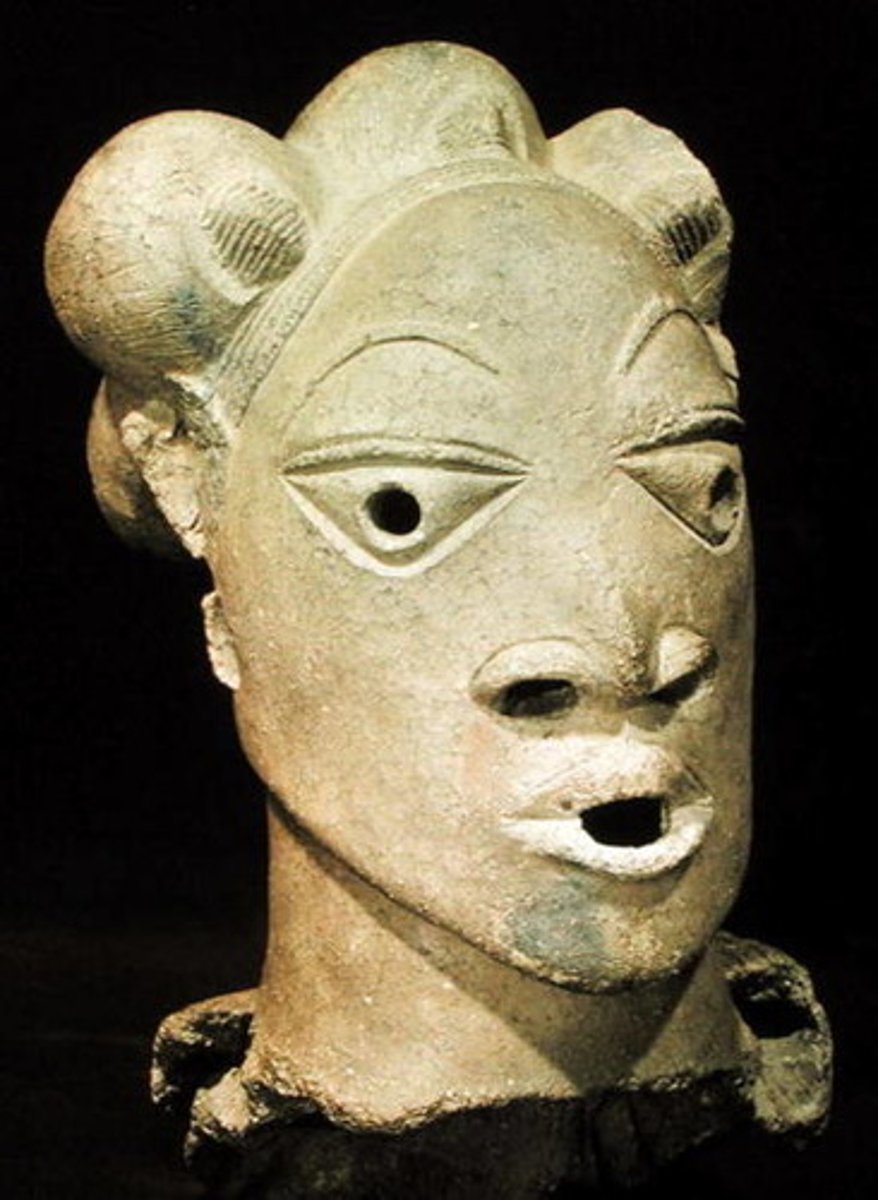
Nok people
the first known West Africans to smelt iron - was used for tools and hunting weapons.

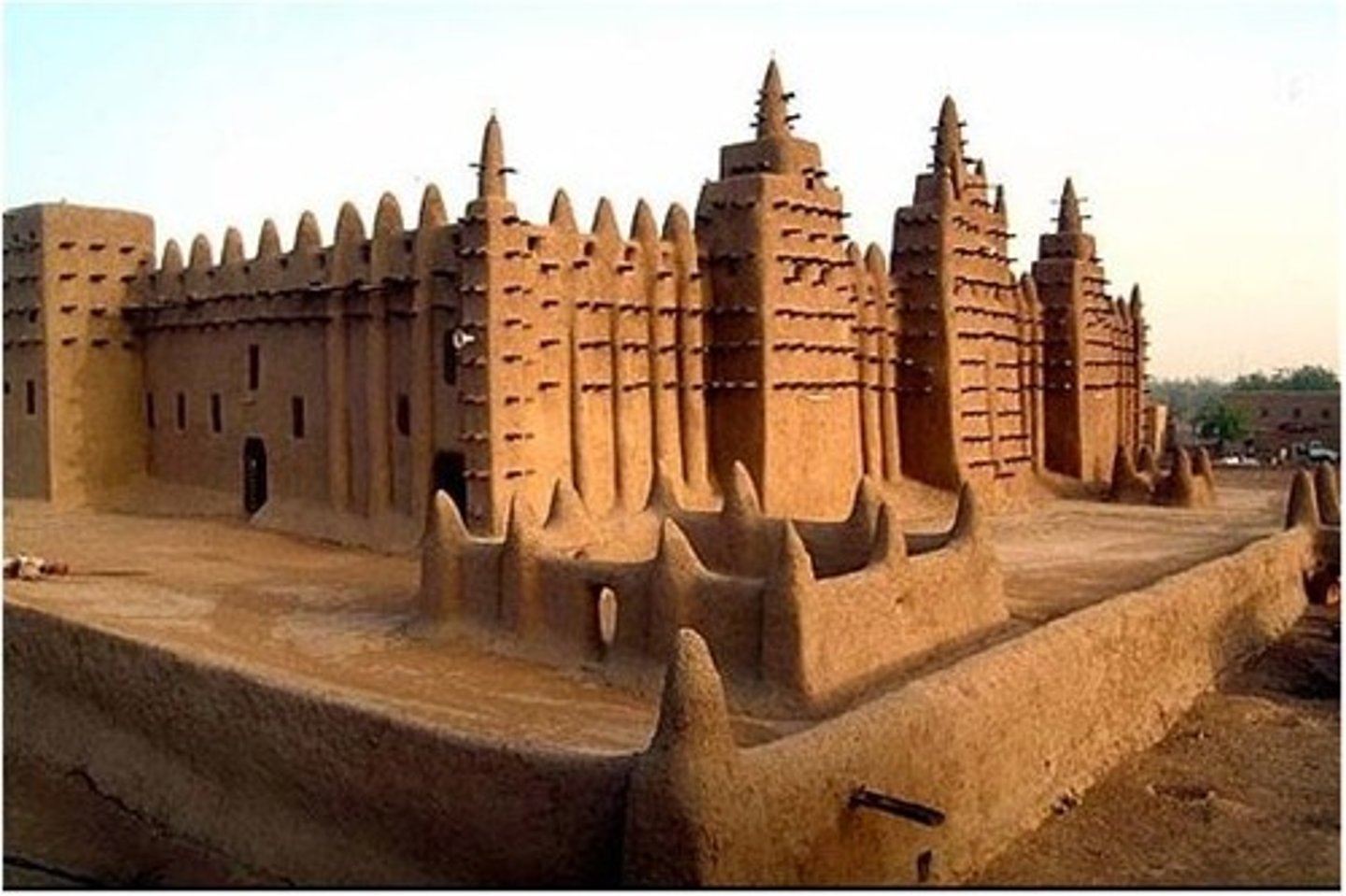
Great Mosque of Jenne
Largest Muslim architecture in (Sub-Sahara), was constructed during the Mali King Mansu Musa's reign.

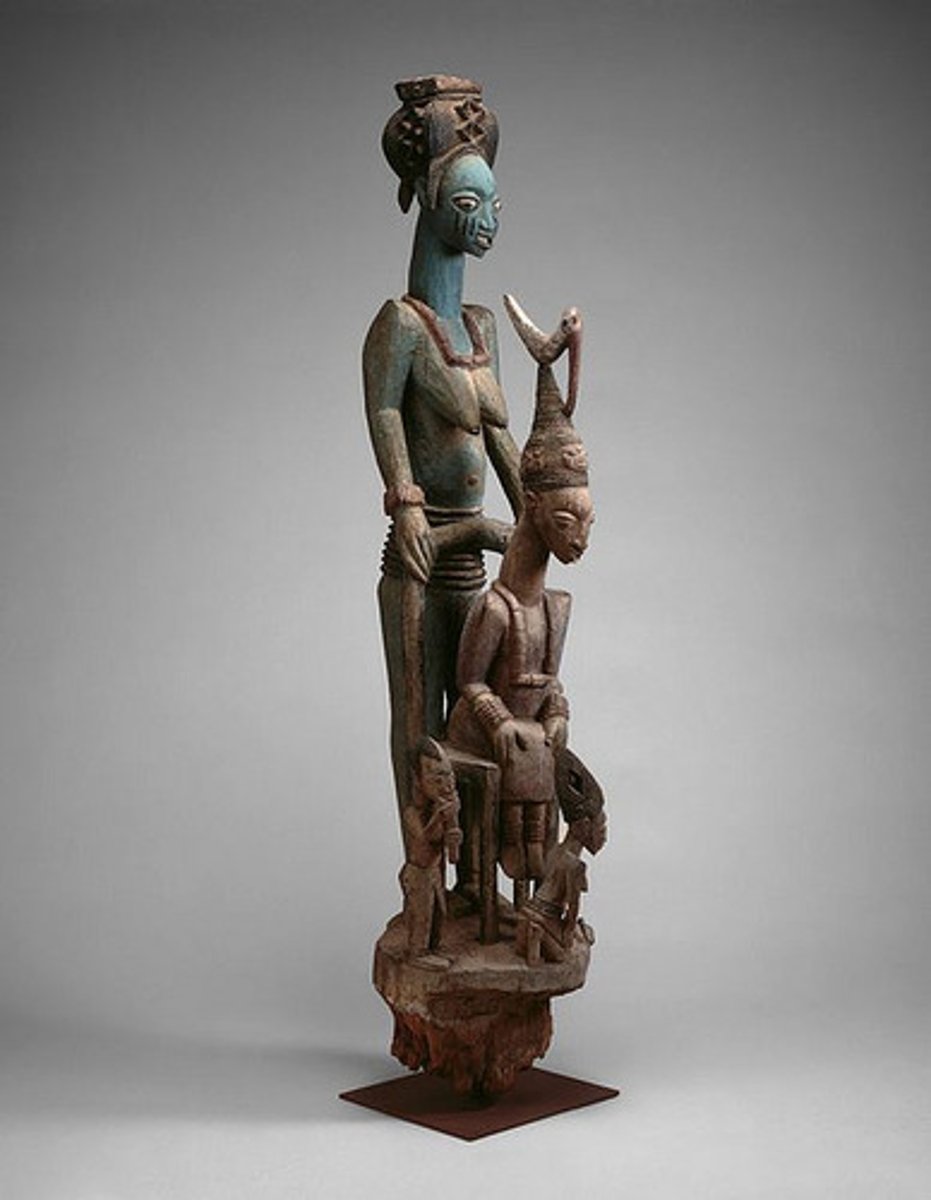
Yoruba Art

Trans-Saharan Trade Route
gold-salt trade; linked North and West Africa; across Sahara Desert; spread Islam; land trade
lineage
A type of clan, typical of W. Africa, in which members claim descent from a single ancestor.
Matrilineal
relating to a social system in which family descent and inheritance rights are traced through the mother
Nzinga Mbemba (Afonso I)
ruler of the Kingdom of Kongo in the first half of the 16th century--> reigned over the Kongo Empire from 1509 to late 1543
nuclear family
Mother, father and children living as a unit
Polygnous Family
A family unit consisting of a man, his wives, and their children.
secret societies
West African societies whose membership is secret or whose rituals are known only to society members. Their most significant function is the initiation of boys and girls into adulthood
Assimilation
the social process of absorbing one cultural group into harmony with another
Polytheistic
Belief in many gods
Animistic
The belief inanimate objects have spiritual attributes.
fetish
a natural object or an artifact believed to have magical power. a charm.
call and response
a song style in which a singer or musician leads with a call and a group responds
Griot
a member of a class of traveling poets, musicians, and storytellers who maintain a tradition of oral history in parts of West Africa.
timeline: separation of hominids from apes
5-10 mya
timeline: emergence of australopithecines
4 mya
timeline: emergence of homo habilis
2.4 mya
timeline: emergence of homo erectus
1.7 mya
timeline: homo erectus beginning spread through Eurasia
1.6 mya
timeline: appearance of modern humans
100,000-200,000 yrs ago
timeline: beginning of Sahara desert formation
6000 BCE
timeline: first agricultural settlements in Egypt
5000 BCE
timeline: pre-dynastic period in Egypt
3800 BCE
timeline: unification of Egypt
c. 3150 BCE
timeline: Egypt's old kingdom
2700-2150 BCE
timeline: Egypt's middle kingdom
2100-1650 BCE
timeline: Egypt's new kingdom
1550-700 BCE
timeline: rule of Kushites over Egypt
750-670 BCE
timeline: Founding of Meroë
540 BCE
timeline: beginning of iron smelting in W. Africa
c. 500 BCE
timeline: destruction of Kush
50 CE
timeline: Islamic conquest of N. Africa
632-750 CE
timeline: Empire of Ghana; Islam begins to take root in W. Africa.
c. 750-1076 CE
timeline: Empire of Mali
1230-1468 CE
timeline: Rise of Yoruba States
c. 1300 CE
timeline: Start of Portuguese exploration and establishment of trading outposts on W. African coast.
1434 CE
timeline: Centralization of power in Benin
c. 1450 CE
timeline: Empire of Songhai
1464-1591 CE
timeline: Rise of Kingdom of Dahomey and the Akan states
c. 1650 CE
the role of Africa in the evolution of modern humanity
The origins of humanity lie in the savanna regions of Africa.
The argument over the race of the the Egyptians began in the __________ century when ____________________ sought to refute____________________________________________________.
19th century; African Americans and white reformers; claims by racist pseudo-scientists that people of African descent were inherently inferior to people of European descent.
What does the controversy surrounding the race of ancient Egyptians reflect and reveal?
It reflects more about the racial politics of recent history than it reveals about the Egyptians themselves, who did not regard themselves in ways related to modern racial terminology.
Describe West African society on the eve of the expansion of the Atlantic slave trade. What were the society's strength and weaknesses?
West African society's strength was its growth in farming, its weakness was that the governments were not powerful enough to stop Portuguese and other Europeans from entering the country and taking control of the slave trade.