Orgo Exam 3 Memorizations
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
SN1 Reaction (1 pi bond to 2 sigma bond)
unimolecular substitution, 2 steps, retention AND inversion, 1 intermediate
SN2 Reaction (1 pi bond to 2 sigma bond)
bimolecular substitution, 1 step, inversion, no intermediate
E1 Reaction (2 sigma bonds to 1 pi bond)
unimolecular elimination, 2 steps, E OR Z, 1 intermediate
E2 Reaction (2 sigma bonds to 1 pi bond)
bimolecular elimination, 1 step, beta-hydrogen and leaving group are anti
Good E Donor Nucleophiles
Anions, uncharged N,P,S, and big bulky bases
Poor E Donor Nucleophiles
H2O, alcohols, uncharged carboxylic acids
Electrophile Hinderance (Primary to Tertiary)
Less hindered = substitution, More hindered = elimination
SN2/E2 Rate
Single step = RDS
SN1/E1 Rate
2nd step is RDS
5 Rate and Reactivity Influences
Nucleophilicity, Leaving Group Ability, Crowding at Electrophile, Solvent Effects, and Hinderance of Nucleophile
Rate: Nucleophilicity
OH- is a better donor than OH2
Rate: Leaving Group Ability
Sulfonate esters = fastest LG’s:
Triflate > tosylate = mesylate
Halogens are slower:
I- > Br- > Cl -
Rate: Crowding
More crowded at electrophile = slower
Less crowded at electrophile = faster
Rate: Solvent Effects
Aprotic solvents = faster
Hydrogen bonds = slower (solvent cage)
Rate: Nucleophile Hinderance
Less hindered = faster
Hydroboration Oxidation
Reagents: 1. BH3 or BH2 2. H2OH and NaOH
Products: Addition of H/OH
Anti-Markovnikov, Syn
Hydroboration Oxidation Steps
Boron reagent is added to less hindered carbon
H2O is eventually added
Syn addition
Halogenation
Reagents: Halogen source + extra nucleophile
Products: Addition of halogen/nucleophile
Markovnikov, Anti
Halogenation Steps
2 arrows connect to halogen simultaneously to avoid carbocation intermediate
Triangle ring forms
Nucleophile comes in and connects to other carbon
Anti addition
EpOxidation
Reagents: Some sort of peroxyacid + alkene
Products: Syn addition of an “O”, creates pair of diastereomers
Epoxidation Steps
5 total arrows
Epoxidation occurs at most substituted alkene
Syn addition of oxygen to form triangle ring
Dihydroxylation Oxidation
Reagents: KMnO4 or OSO4 (ionic compounds)
Products: Syn addition of 2 OH’s
Workup step, don’t need to know
Dihydroxylation Steps
3 total arrows
Syn addition of OH/OH
Ozonolysis Oxidation
Reagents: O3, and Zn if reductive and H2O2 if oxidative
Products: Double bond is cleaved in half and H is added if reductive and OH is added if oxidative
Hydrogenation Reduction
Reagents: H2 with aid of metal catalyst (Pd/C)
Products: Alkene turns to alkane with addition of H/H
Syn addition of H/H
Alkyne will react until completely saturated
Hydrogenation Reduction with a Poisoned Catalyst
Reagents: Alkyne and H2 with some sort of metal (Pd) + solid support (CaCO3) + Poison (PbO or quiroline)
Products: Forms an alkene and tops after 1 addition of H/H
Syn, Z alkene only
Hydrogenation Reduction with a Dissolving Metal
Reagents: Li or Na metal + NH3 (l) as catalyst
Products: Alkyne converts to a E alkene
Anti only
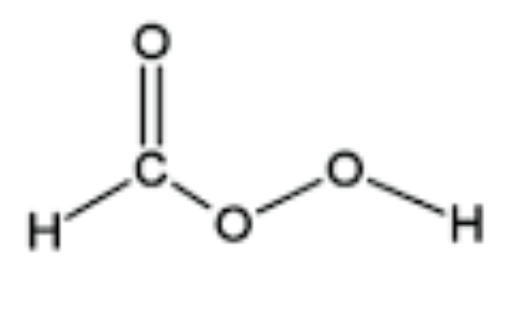
Peroxyformic Acid
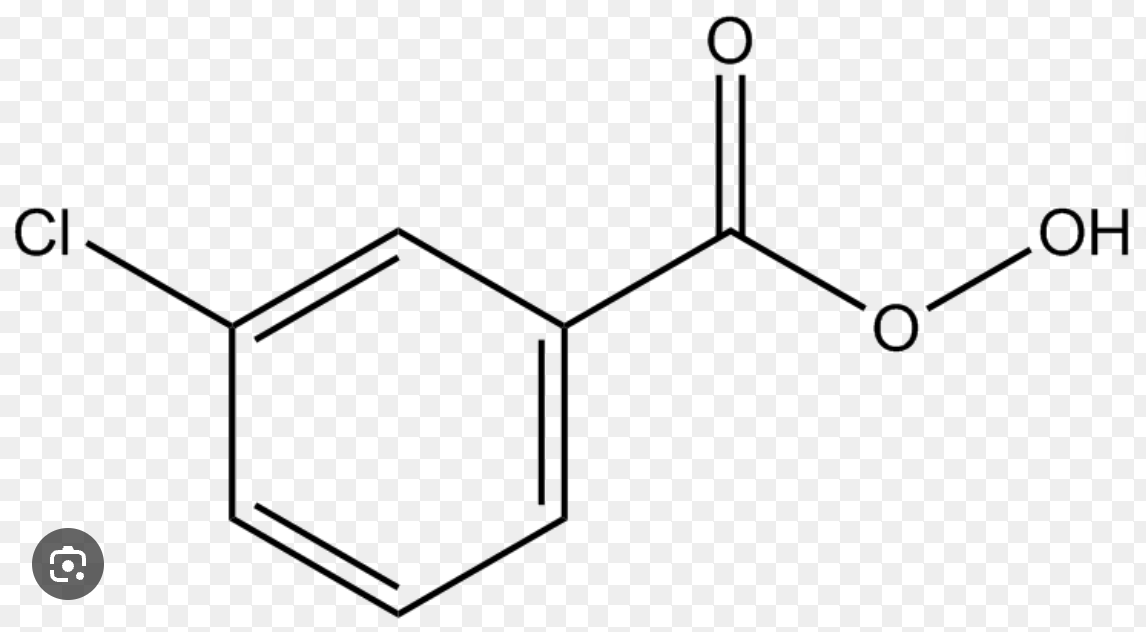
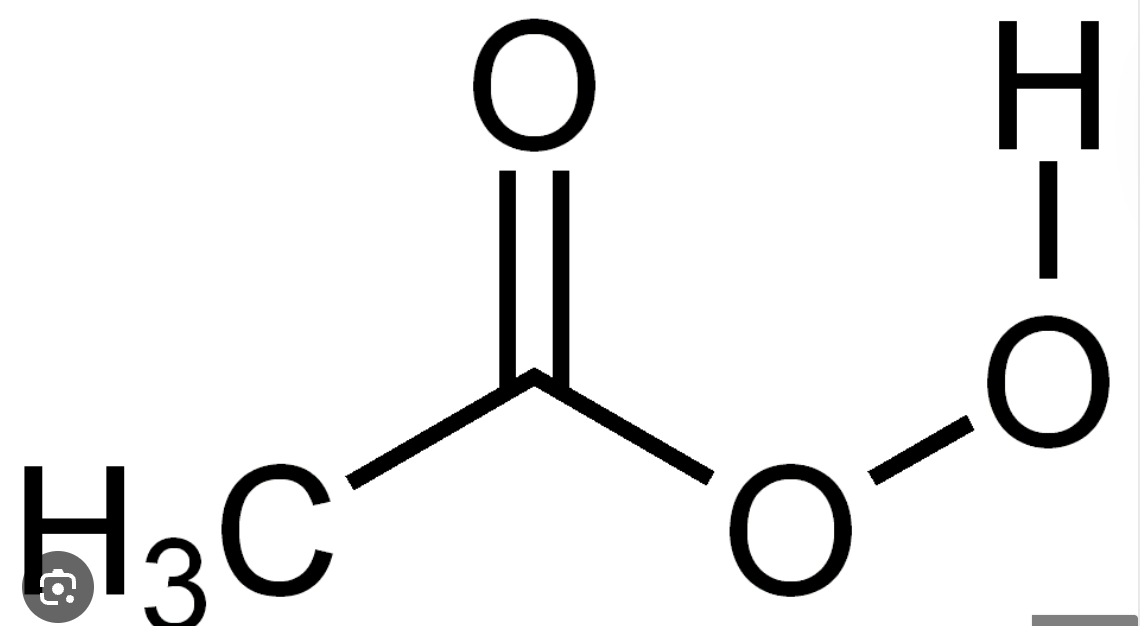
Peroxyacetic Acid
MCPBA