MIL Q2L1 (Q3L6 Module)
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Legal, Ethical and Societal Issues in Media and Information
With the growing online community in this new information age, people must know and understand their rights and responsibilities as media and information providers and consumers in order to become digital citizens.
Intellectual Property
Fair Use
Netiquette
Internet Addiction
Cyberbullying.
Significantly encompassing these rights and responsibilities are the issues of ______, ______, ______, ______, and _______
Intellectual Property
World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), the global forum for intellectual property services, policy, information, and cooperation, defined ______
Intellectual Property
referring to the “creations of the mind, such as inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names, and images used in commerce” (World Intellectual Property Organization, 2016).
Industrial Property
Copyright
It can be classified into two categories
Industrial Property
includes patents, trademarks, industrial designs and geographical indications and appellations of origin
Copyright
covers literary works (such as novels, poems, and plays), films, music, artistic works (e.g. drawings, paintings, photographs, and sculptures) and architectural design.
Intellectual Property Code (RA 8293)
Cybercrime Prevention Act (RA 10175)
In the Philippines, IP is protected under two laws
Intellectual Property Code (RA 8293)
Cybercrime Prevention Act (RA 10175)
Both laws protect intellectual property rights, allowing the rightful creators or owners of patents, trademarks, or copyrighted works to benefit from their own work or creation – may it be of moral or material interests.
Infringement
Violation of this law or one of the rights is called ___
Copyright
Patent
Trademark
Industrial Design
Geographical Indications and Appellations of Origin
Types of Intellectual Property
Copyright
It is a legal term used to describe the rights that creators have over their literary and artistic works.
Copyright
This covers works ranging from books, music, paintings, sculpture and films, to computer programs, databases, advertisements, maps and technical drawings (WIPO, 2016).
Copyright
Registration of copyrighted work or displaying of the copyright symbol may not be mandatory but it is recommended to emphasize that the author is claiming copyright protection in the work.
Copyright law
protects the creator’s work from the moment of creation and the owners do not lose this protection.
Patent
It is an exclusive right granted for an invention. It provides the patent owner with the right to consent on the invention or a way for others to use it.
Patent
In return, the patent owner is responsible for making technical information about the invention available in the published patent document or in public (WIPO, 2016)
Trademark
It is a distinguished sign of goods or services of one enterprise from those of other enterprises.
Trademark
It can be compared to what craftsmen used in ancient times as “signature mark” on their product (WIPO, 2016).
Trademark
TM denotes that the owner of the mark is in the process of registration to indicate a claim of ownership, while ® is only used for marks that have been granted registration
Industrial Design
WIPO (2016) defines this as an ornamental or aesthetic aspect of an item.
Industrial Design
A design may consist of three dimensional features such as the shape or surface of an article, or of two-dimensional features such as patterns, lines, or color
Industrial Design Right
protects only the appearance or aesthetic features of a product, whereas a patent protects an invention that offers a new technical solution to a problem.
Geographical Indications and Appellations of Origin
These are signs used on products possessing qualities, a status, or characteristics that are essentially attributable to that location of origin.
Geographical Indications
Generally, this includes the name of the place of origin of the goods (WIPO, 2016).
Intellectual Property Code of the Philippines (RA8293)
The copyrighted works are under this Term of Protection (Source: Official Gazette, 2012, section 213)
Literary works
Validity period is During the lifetime of the author plus 50 years after death
Arts
Validity period is 25 years from the date of creation
Photographic Work
Validity period is 50 years from publication
Audio-Visual Work
Validity period is 50 yearss from publication
Sound Recording
Validity period is 50 years from year recording took place
Broadcast Recording
Validity period is 20 years from date of broadcast
Trademark
Valid for 10 years and may be renewed for a periods of 10 years
Invention Patent
Valid for 20 years from filing date application
Intellectual Property
is essential in creating a culture of creativity, progress, and innovations as any content creator’s exclusive rights to their own creation are secured and protected through the IP law.
Intellectual Property
This means one’s original work cannot be legally copied or used for profit
Copyright law
allows the owner to control access to his or her own work and consequently provides strong penalties for infringement of owners’ rights.
Copyright law
However, the law also includes certain exemptions to the rule and considerations in the use of the copyrighted materials from the owner’s control, which are under the doctrine of Fair Use.
Fair use
is a legal principle stating that one can use a copyrighted work without a license for the following purposes: commentary, criticism, reporting, research, and teaching.
amount and substantiality of the portion taken
purpose and character of one’s use
nature of the copyrighted work
potential market effect (Stim, 2016)
the copyrighted material must observe conditions such as
Fair use
In general, one must own the majority of the new content, give full credit to the original source, and use the content for non-profit purposes to consider it fair use
License
In order to clarify the terms and conditions in control of the creative work between the author and the general public, one needs permission from the copyright holder which is called a ____.
Creative Commons license
Some content creators choose to license their work more freely by giving their work a _______ or even putting their work in Public Domain.
Creative Commons license
These are copyright licenses providing a simple and standardized way to give the public permission to share and use the creative work.
Creative Commons license
This is easier for both the author and the public compared to an agreement in traditional licenses which are more restricting.
Creative Commons
American non-commercial organization that aims to expand the range of creative works available for others to build upon and to share legally.
Creative Commons
The organization has released several copyright-licenses known as Creative Commons licenses free of charge to the public
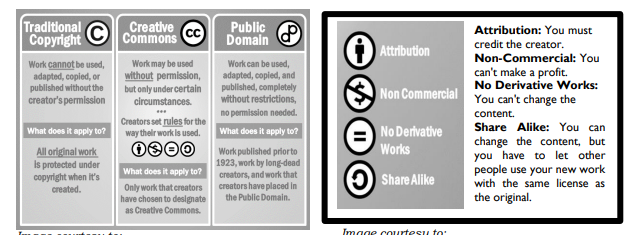
Infographic 1: Copyright, Fair Use, and Public Domain
- Traditional Copyright
- Creative Commons
- Public DomainInfographic 2: Using Creative Commons Content
- Attribution
- Non-Commercial
- No Derivative Works
- Share Works
Below are infographics about copyright, fair use, and creative commons.
Traditional Copyright
Work cannot be used, adapted, copied, or published without the creator’s permission
Creative Commons
Work may be used without permission, but only under certain circumstances. Creators set rules for the way their work is used.
Public Domain
Work can be used adapted, copied, and published, completely without restrictions, no permission needed.
Netiquette
is a set of rules for behaving properly online (Shea, 1997 as cited in E-Learning Guide on Media and Information Literacy, 2017).
Remember the Human
Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life
Know where you are in cyberspace
Respect other people’s time and bandwidth
Make yourself look good online
Share expert knowledge
Keep flame wars under control
Respect other people’s privacy
Don’t abuse your power
Be forgiving of other people’s mistakes
Here are the Ten Core Rules of Netiquette by Virginia Shea
Remember the Human
Your written words are read by real people, all deserving of respectful communication.
Adhere to the same standards of behavior online that you follow in real life
Be ethical and do not break the law.
Know where you are in cyberspace
"Netiquette varies from domain to domain." Get a sense of how the people who are already there appropriately and properly act.
Respect other people's time and bandwidth
You are not the center of cyberspace. Be mindful of other’s time
Make yourself look good online
You will be judged by the quality of your writing thus be cautious of your language. Don’t flame-bait nor swear. Make sense with what you’re talking about.
Share expert knowledge
Courteously sharing your knowledge is fun.
Keep flame wars under control
"Flaming is what people do when they express a strongly held opinion without holding back any emotion." Don't feed the flames; extinguish them by guiding the discussion back to a more productive direction.
Don't abuse your power
Do not take advantage of anyone.
Be forgiving of other people's mistakes
No one is perfect so be kind. If needed, be polite in correcting others.
Netiquette
reminds you to respect and protect your own privacy, as well as others’. You must “self-reflect before you self-reveal” (Common Sense Education).
Virtual Self
is how you present yourself on online platforms.
Virtual Self
Whatever you say or do on the Internet can be viewed and others can easily pass judgment without even knowing who you are outside the virtual environment.
Digital footprint
is any data record of the things you do online.
Digital footprint
Anything on the Internet with your name creates a trail of data about you. This could be information in your personal website, any activity in social media, your browsing history, online subscription, and the like.
Data privacy
Not only virtual self and digital footprint are incorporated in netiquette.
Data privacy
Respecting and managing data privacy is also a responsible behavior on the Internet. The respect should be mutual between the media user and the producer.
Data privacy
the fundamental right of an individual to protect private information from disclosure to information and communication systems is under Republic Act No. 10173 or the Data Privacy Act of 2012. If precautionary measures are not observed in sharing personal information, your online security can be compromised.
Digital Divide
As part of being mannerly towards others online, it is also helpful to know that not everyone has the same access to high-speed internet, or even so, regular digital access, or advanced digital knowledge so we are called to be understanding, helpful, and polite to the digitally disadvantaged.
Digital Divide
This digital inequality or gap between groups in terms of knowledge, usage, and access to ICT due to circumstances like location, income, and age
Computer Addiction
is the “overdependence or a damaging need to do something on computer or internet” (E-Learning Guide on Media and Information Literacy).
Computer Addiction
Its impact could be linked to sleep deprivation, anxiety and even depression. Setting a limit and immersing yourself with outside activity can obviate addiction
Cyberbullying
is the use of digital means of communication that could hurt or harass a person.
Cyberbullying
Examples of this are sending hurtful texts or SNS messages, posting embarrassing photos or videos, and spreading mean or malicious rumors online.