4051 Adolescent Development and Emerging Adulthood Final Exam
1/168
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 8-13 and Coming of Age in America with Dr. Plauche at LSU
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
peers
What is the main socializer in developed countries during adolescence?
time with family decreases
time with same-sex friends remains stable from childhood
time with other-sex friends increases
main people adolescents hang out with is same-gender friends
shifts to romantic partners in emerging adulthood
boys; girls
In traditional culture, adolescent ____ spend more time with friends than adolescent ___ do.
more time with families than in the West
educational orientation, media and leisure preferences, participation in risk behavior, and support and nurturance
What are some of the areas that friends tend to influence in adolescence?
influence is interesting because adolescents tend to associate with people who are similar to themselves → selective association
discourage
Peer influence was found to _____ risky behavior through people they associate with.
informational, instrumental, companionship, and esteem
What are the four types of support friends provide to one another during adolescence as described by Thomas Berndt’s theory on support?
informational support
________ occurs when advice and guidance in solving personal problems is given between friends.
ex. I need some advice on what to do.
instrumental support
_______ occurs when friends help with tasks of various kinds.
ex. giving someone a ride
companionship support
______ occurs when friends rely on each other as companions in social activities.
ex. join student government club because your friend asked
esteem support
______ occurs when friends provide each other congratulations for success and encouragement or consolation for failure.
ex. your presentation was so great or I am sorry that interview did not go well
cliques
What do you call small groups of friend who know each other well, do things together, and form a regular social group?
crowds
What do you call large, reputation-based groups of adolescents that help adolescents locate themselves within the social structure?
Elites, Athletes, Academics, Deviants, etc.
aid in identity formation
help make sense of social contexts
most influential during mid-adolescence
relational aggression
_________________ is a form of nonphysical aggression that harms others by damaging their relationships?
more common among girls because they are socialized to not use physical aggression
often they are not even allowed to say they are upset
has negative outcomes for both the target and the aggressor
ex. excluding someone socially, spreading rumors, or silent treatment
fewer
American minority cultures have the same types of crowds as White adolescents, but perceive ___ crowd distinctions in other ethnic groups than they do in their own.
one adolescent peer crowd, dormitory for relaxing, and men’s house for adolescent boys and widowed or divorced men
What are some different types of crowds across cultures?
bullying
________ is the aggressive assertion of power by one person over another in peer relations, and it is common in many countries in adolescence.
components: aggression, repetition, result of a power imbalance
negative effects: physical and psychological symptoms
¼ of perpetrators are also victims
trust and loyalty
The difference between friends and peers is friendships require ______ and _____ in adolescence and emerging adulthood.
passion, intimacy, and commitment
What at the three fundamental qualities of Sternberg’s Theory of Love?
intimacy :: commitment :: passion
_____ : involves feelings of closeness and emotional attachment :: ______ : is the pledge to love someone over the long run, through the ups and downs that are often part of love :: _____ : involves physical attraction and sexual desire
infatuation and romantic love
What are the most common types of love in adolescence?
hint: long-term commitment is absent at this time
liking, infatuation, empty love, romantic love, companionate love, fatuous love, and consummate love
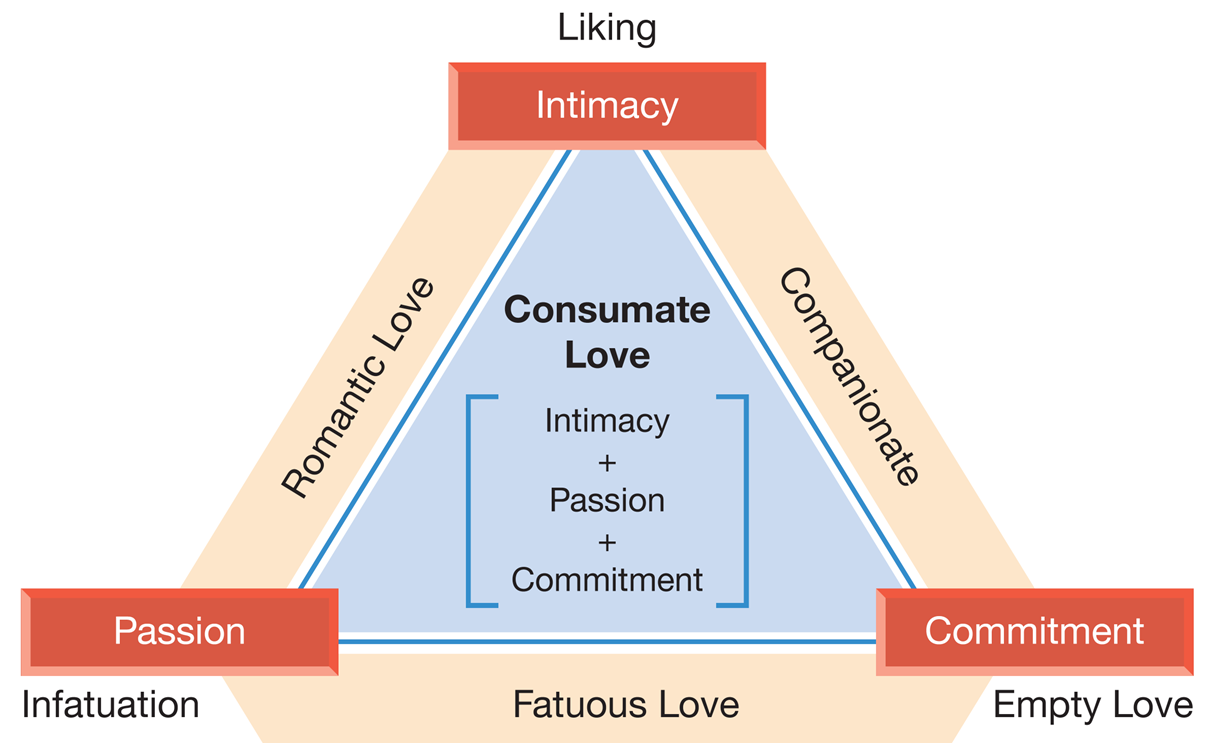
What are the forms of love described by Sternberg’s theory of love?
liking
What form of love is based on intimacy alone without passion or commitment?
infatuation
What form of love is based on passion alone without intimacy or commitment?
empty love
What form of love is base on commitment alone without passion or intimacy?
romantic love
What form of love combine passion and intimacy but lacks commitment?
companionate love
What form of love combines intimacy and commitment but lacks passion?
fatuous love
What form of love combines passion and commitment without intimacy?
consummate love
What form of love integrates all three fundamental qualities of love: passion, commitment, and intimacy?
dating; going with; hanging out with; seeing
Prior to the 1970s, adolescent love looked like ____ and currently it is _____, ______, and _____.
more informal
often they are friends first
recreation, learning, status, companionship, intimacy, and courtship
What are the reasons adolescents’ form love relationships?
proactive script; reactive script
Dating scripts are the cognitive models that guide romantic interactions. _____ is a relationship script more common among males and includes initiating the relationship, deciding where to go, controlling the public domain, and initiating sexual contact. While _____ is a romantic script more common for females that focuses on the private domain, responding to partner’s gestures in the public domain, and responding to his sexual initiatives.
high ranking of mutual attraction and dependable character
What are the cross-cultural similarities of choosing a marriage partner?
female chastity
What is important when choosing a marriage partner in Eastern and Middle Eastern cultures that is not important in Western cultures?
arranged marriages are also more common
commitment first
passion if it develops
intimacy is modesty
marriage is seen as uniting two families based on status, religion, and wealth
sexual harassment
_______: A wide range of threatening or aggressive behaviors related to sexuality, from mild harassment such as name-calling, jokes, and leering looks to severe harassment involving unwanted touching or sexual contact
High in adolescence
LGBT and early maturing girls targeted at higher rates
Sexual and romantic joking and teasing common
Difficult to identify border between harmless and harassment
sexual coercion
________: An act of sexual aggression in which a person, usually a woman, is forced by a romantic partner, date, or acquaintance to have sexual relations against her will.
Due to verbal pressure, alcohol or drugs, or physical force
Different views between males and females
permissive views or adamantly forbid it
What views regarding adolescent sex do countries that have low rates of teen pregnancy have?
do to the mixed messages about sexuality, the US has high rates of teen pregnancy
ex. Scandinavian countries
1890 to 1920
When did the United states pass laws requiring school attendance through early teenage years?
now, more than 90% of 14- to 17-year-olds are in school
different from developing countries
education is for urban middle class past childhood
comprehensive high school
School curriculum went from broad liberal arts education to ___________________ which is a form of the American high school that arose in the 1920s and is still the main form today, which encompasses a wide range of functions and includes classes in general education, college preparation, and vocational training.
allows for more flexibility and delays in career decisions
secondary school
______ are the schools attended by adolescents, usually including a lower and an upper school.
college-preparatory, vocational, and professional school
What are the three secondary schools that are common in most European countries?
college-preparatory school
One type is a ________________ that is similar in many ways to the American high school in that it offers a variety of academic courses and the goal is general education rather than education for any specific profession. However, in Europe these schools do not include classes in recreational subjects such as music and physical education. In most European countries, about one-half of adolescents attend this type of school.
vocational school
A second type of secondary school is the ___________, where adolescents learn the skills involved in a specific occupation such as plumbing or auto mechanics. Usually, about one-fourth of adolescents in European countries attend this type of school.
about 1/3 of adolescents in Europe attend this type of school
professional school
Some European countries also have a third type of secondary school, a ____________ devoted to teacher training, the arts, or some other specific purpose. About one-fourth of European adolescents usually attend this type of school.
gender gap (favors boys), poorly funded, overcrowded, insufficiently trained teachers, exclusive private schools, well-funded universities for elite, and inferior education for all else
What are the similarities in education in all developing countries?
their economic development
What is the key influence on a country’s academic performance?
500 to 1,000 students, supportive and involved teachers, firm discipline when needed, favorable school climate, and promotes engagement
What are the characteristics of effective schools?
False
The family environment impacts the adolescent’s engagement and achievement through high school especially regarding their expectations for achievement. Authoritative has the least favorable associations with involvement while neglectful has the most favorable associations. T/F
friends; peers
_____ help school engagement more than parents and provide support and encouragement for doing well, while _____ create a “big fish in a little pond effect” and adolescents tend to hide achievement from them.
10 hours
How many hours of work has been found to not have an effect on academic achievement and engagement in high schools but more than this will have a negative effect?
it is more than just a self-selection effect
socializing; organized activities
The amount of time spent on ____________ is negatively associated with grades, while ____________ are positively associated with grades.
True
High school education is not as highly values by America as other developed countries because they want children to be “well-rounded”. T/F
Asian cultures
What culture highly values high school education?
positive
there is a _____ association between SES and grades, test scores, and highest level of education completed.
immigrant paradox
The research finding that the more generations an immigrant family has been in the United States, the worse the children do in school is called the ___________.
Asian American, White, and African American and Latino
What are the performance rankings of different ethnicities in the US from the highest to the lowest?
the top is because:
strong emphasis on educational achievement
believe success is due to effort
more likely to have academically oriented friends
the bottom is because:
more likely to live in poverty
believe can succeed in career without academic achievement
girls
What gender of adolescents is more likely to achieve higher grades and are less likely to drop out because they enjoy the school environment more and have more supportive relationships?
tend to perform better academically at all levels
precocity, independence, drive for mastery, and excellence in information processing
Gifted students are students who have unusually high abilities in academics, art, or music. What are the four characteristics of gifted students?
hint: evident at an early age
hint: need less instruction and support and work alone
hint: focusing for long periods on topic or challenge before them
hint: understand information quickly, learn faster, fewer reasoning errors, and more effective learning strategies → may develop themselves
these students are placed in AP classes to provide a more challenging curriculum
learning disabilities
________ is a diagnosis made when a child or adolescent has normal intelligence but has difficulty in one or more academic areas and the difficulty cannot be attributed to any other disorder.
difficulty can be in reading, written language, and math
often correlates with social and emotional difficulties
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
_______ is a disorder characterized by difficulty in maintaining attention on a task along with a high activity level that makes self-control problematic.
more common in boys → possibly not more common just more often diagnosed
usually prescribed medication
70%
What percentage of US high school graduates attend college?
females more likely than males
Asian Americans most likely ethnic group to attend
Gender differences in chosen major
proportion of women in fields like medicine and law have been increasing dramatically since 1970.
current takes 5-6 years to obtain “4-year” degree
50%
Nearly ____ of all college students drop out. Some factors related to retention are:
previous academic performance
ethnic background
family SES is the number 1 reason for dropping out
Programs to enhance retention rates:
peer mentoring
special programs for first-year students
collegiate, vocational, academic, and rebel
What are the four types of student subcultures in college?
most students blend the four subcultural types
main purpose of each
fellowship and partying
gain skills to get a job
drawn to ideas and knowledge
engaged with ideas but critically detached
hunting, fishing, and gathering, farming and care of domestic animals, and childcare and household work
What are some types of adolescent work in traditional cultures?
adolescent boys in traditional cultures learn the work of adult men
adolescent girls in traditional cultures typically have responsibility for household work such as food preparation
industrial work
______ started in traditional cultures due to globalization.
gain skills and contacts that could lead to better jobs
brutal work, miserable pay, and long hours
adolescents earn 1/3 to ½ the pay of adults
Two issues started after globalization
Debt bondage: Arrangement in which a person who is in debt pledges his labor or the labor of his children as payment.
Commercial sexual exploitation: The practice of coerced or forced sex work for purposes of economic gain.
many adolescent girls have been forced into prostitution
Number of child and adolescent laborers fell during first decade of 21st century
17th to 18th
In the ________ centuries in the West, adolescent boys worked on farm and adolescent girls cared for domestic animals and did household work.
18th to 19th
In the ________ centuries in the West, industrialization occurred. Working in factories, coal mines, and processing plants became more common. Farming declined to less than 40%. This lead to long hours, dangerous conditions, and health hazards. Before, most adolescents in the West grew up on a family farm.
20th
In the _______ century, a number of adolescents in school through mid-teens rose. After WWII, combined school with part-time work as cooks, servers, and clerks. Towards the end, about 80% of high school students were
baby-sitting; yard work
Typical first jobs for adolescent girls are ____ and _____ for boys.
restaurant or retail, 15-20 hours per week, repetitive and monotonous, part-time, and few see it as a basis for future career
What are the typical characteristics of high school employment workplaces?
disrupts sleep, eating, and exercise
What are the effects of working more than 10 hours a week on psychological functioning? Prior to that, there are no increased psychological symptoms.
occupational deviance
______ are deviant acts committed in relation to the workplace, such as stealing supplies.
more than 60% of adolescents
possible causes: boredom, no personal investment, little supervision
adolescents who work are more likely to us alcohol, cigarettes, or other drugs
scholars disagree if this is causation or correlation
gain responsibility, develop new occupational skills, and beneficial relationships with adults in workplace
What are some of the benefits of adolescent work?
the forgotten half
_____ is the nearly half of young Americans who enter the workplace following high school rather than attending college.
loss of high-wage sectors caused decline in income
the new basic skills
_____ are skills identified by Murnane and Levy that are required for high school graduates who wish to be able to obtain the best jobs available in the new information-based economy.
these skills are
reading and doing math at ninth-grade level or higher
solving semi structured problems
communicating effectively orally and in writing
using a computer for word processing and other tasks
collaborating in diverse groups
teaching skills to adolescents directly in the workplace tends to be effective
crystallization, specification, implementation, stabilization, and consolidation
Donald Super’s theory of the development of occupation goals has 5 stages. What are the 5 stages?
Most people change their career at least once
crystallization
What is the stage in the development of occupational goals that occurs at ages 14-18 where they learn about interesting occupational fields?
specification
What is the stage in the development of occupational goals that occurs at ages 18 to 24 where people focus on specific occupations and begin to pursue education?
implementation
What is the stage in the development of occupational goals that occurs at ages 21-24 where people enter the job itself?
stabilization
What is the stage in the development of occupational goals that occurs at ages 25-35 where people establish self in career?
consolidation
What is the stage in the development of occupational goals that occurs at ages 35 and up where people seek advancement?
personality characteristics and gender
What are the different influences of occupational goals?
realistic, investigative, social, conventional, enterprising, and artistic
What are the six categories of personality characteristics?
there are a variety of personalities in one occupation
realistic
What personality characteristic is this?
High physical strength, practical approach to problem solving, and low social understanding.
Best occupations: those that involve physical activity and practical application of knowledge, such as farming, truck driving, and construction.
investigative
What personality characteristic is this?
High on conceptual and theoretical thinking.
Preference for thinking problems through rather than applying knowledge.
Low on social skills.
Best occupations: scholarly fields such as math and science.
social
What personality characteristic is this?
High in verbal skills and social skills.
Best professions: those that involve working with people, such as teaching, social work, and counseling.
conventional
What personality characteristic is this?
High on following directions carefully, dislike of unstructured activities.
Best occupations: those that involve clear responsibilities but require little leadership, such as bank teller or secretary.
enterprising
What personality characteristic is this?
High in verbal abilities, social skills, and leadership skills.
Best occupations: sales, politics, management, running a business.
artistic
What personality characteristics are this?
Introspective, imaginative, sensitive, unconventional.
Best occupations: artistic occupations such as painting or writing fiction.
gender socialization, women anticipate difficulties balancing work and family (the second shift)
Women tend to have jobs in the service sector, which are low paying and low status. Men tend to hold jobs like engineer, chemist, surgeon, and computer software designer, which tend to be high paying and high status. What causes the gender differences in occupational goals?
10; explore; meander
In emerging adulthood, an average American holds ___ jobs between ages of 18-30. At this time emerging adults either _______ (sort out what kind of work is desired) or ______ (find any job to pay bills until something better comes along). Most seek identity-based work but majority never find the work they seek.
Black; latino
Unemployed is the status of persons who are not in school, not working, and who are looking for a job. Unemployment is concentrated among ____ and ____ adolescents due to obtaining less education and decline in high-paying, low-skilled manufacturing jobs.
upgrade education, improve school-to-work programs, improve access to employment, and provide government-funded public service jobs
What are some ways to fix the unemployment trend?
community service
____ in adolescence has positive effects on academic, personal, social, and civic development. It is motivated by individualistic and collectivistic values, and they are more likely to be involved in political activities and volunteer organizations as adults.
peace corps; AmeriCorps
In emerging adulthood, they can join the ____, an international service program in which Americans provide service to a community in a foreign country for two years.
95% have undergraduate degrees
serve in education, environment, business, agriculture, health
receive monthly living allowance
most would repeat experience
There is also the ____ which sponsors volunteers to work in local community organizations. The national service program in the United States in which young people serve in a community organization for up to two years for minimal pay. The volunteers receive living allowances, health insurance, and education award. Encourages higher civic engagement and overall life satisfaction.
self-confidence, self-discipline, leadership skills, and educational and occupational opportunities
Emerging adults who enter military service are more likely to come from low-SES family backgrounds. What are the positive effects of adolescents and emerging adults in the military?
anxiety, depression, aggression, loss of parenting, and girls experience rape
Developing countries commonly have mandatory ____ which are children and adolescents forced to become soldiers. What are some of the negative consequences?
exposed to traumatic experiences and redefine self as leader if in service long enough
Cultivation theory
What media theory proposes that TV consumption shapes people’s worldviews to resemble what is depicted on TV?
ex. mean world syndrome
mean world syndrome
What theory says that the more people watch television, the more likely they are to believe that the world is dangerous and that they are at risk for being a crime victim?
social learning theory
What theory proposed that people tend to imitate behaviors they see rewarded when performed by others in media?
uses and gratifications approach
What is the approach to understanding media that emphasizes that people differ in numerous ways that lead them to make different choices about which media to consume and that even people consuming the same media product will respond to it in a variety of ways depending on their individual characteristics?
media practice model is an example of this approach
media practice model
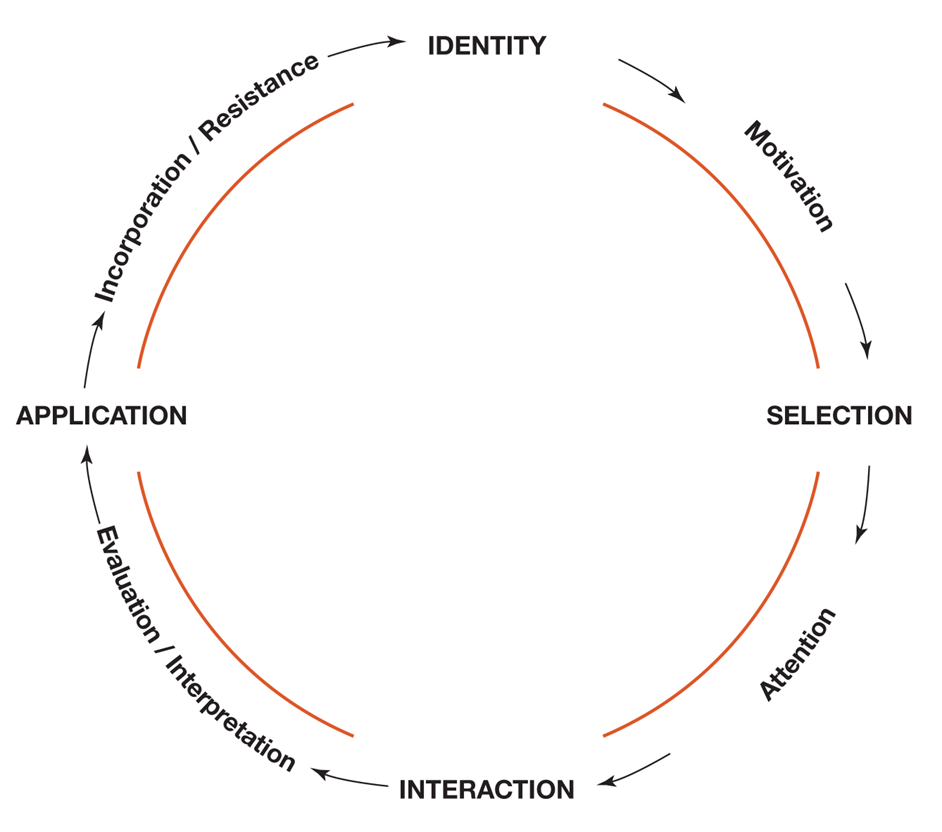
What theory proposing that media use begins with identity, then proceeds to selection, attention, interaction, application, and back to identity?
our preferences motivate us to select media that gets our attention then we interact with it and evaluate/interpret it, apply it to our life and incorporate or resist it