AP Psych Vocab Quiz 4.1-4.3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Actor Observer Bias:
The tendency for those acting in a situation to attribute their behavior to external causes, but for observers to attribute others’ behavior to internal causes. This contributes to the fundamental Attribution Error.
Example: A student justified his poor performance with external obstacles like family issues. However, his advisor overestimated the importance of internal factors, such as the student’s laziness or lack of knowledge.
Prejudice:
It is an unjustifiable attitude filled with negative emotions, stereotyped beliefs, and an inclination to discriminatory action.
Stereotypes:
A generalized (sometimes accurate but overgeneralized) belief about a group of people.
Ex: Boys are better at math than girls
Dscrimination:
Unjustifiable negative actions toward a group or its members.
Social Identity:
The “we” aspect of our self concept; the part of our answer to “Who am I?” that comes from our group memberships.
Ex: A person strongly identifying as a Debate Team Member or Mexican.
Ingroup:
“Us”— People with whom we share a common identity.
Outgroup:
“Them”— those perceived as different or apart from our ingroup.
Ingroup Bias:
The tendency to favor our own group.
-This is different than mirror image perceptions because it is not a mutual view that is held by conflicting parties.
Scapegoat Theory:
The theory that when things go wrong, finding someone to blame is a target for our negative emotions.
Ex: White government officials referred to Covid as the “Chinese” Virus.
Other Race Effect:
People are generally able to recall faces of their own race more accurately than faces of other races. It emerges during infancy, and is also called the cross-race effect.
Role:
A set of expectations/ norms about a social position, defining how those in the position ought to behave.
Norms:
A society’s understood rules for accepted behavior. Norms prescribe “proper” behavior in social situations.
Normative Social Influence:
Motivated by a person’s desire to gain approval and fit in a group. This is common in collectivist cultures.
Example: NYC girls wearing flared jeans since the other girls are wearing them and they want to fit in.
Informational Social Influence:
Influence resulting from a person’s willingness to accept other’s opinions about reality, such as when reading online product and movie reviews.
EX: People follow health practices that are recommended by health experts because they are uncertain. They assume the professionals are right.
Culture:
The behaviors, ideas, and values shared by a group of people and transmitted from generations.
Tight Cultures:
A place with clearly defined and reliably imposed norms.
Loose Cultures:
A place with flexible and informal norms.
Ex: Western cultures
Frustration Aggression Principle:
The principle that frustration— the blocking of an attempt to achieve some goal— creates anger, which can generate aggression.
EX: People who are overheated have overheated tempers. Hungry people are more angry.
Social Scripts:
A culturally modeled guide for how to act in certain situations.
EX: Girls who watch actors drink and hookup at parties in movies copy that behavior in real life.
Passionate Love:
An aroused state of intense positive absorption in another, usually in the honeymoon phase of a relationship (Empire Times).
Companionate Love:
The deep affectionate attachment we feel for those with whom our lives are intertwined. Feelings of calmness and trust label companionate love.
Ex: Grandparents (Bc they don’t have a lot of passion anymore).
Self-Disclosure:
The act of revealing our intimate aspects and secrets to others.
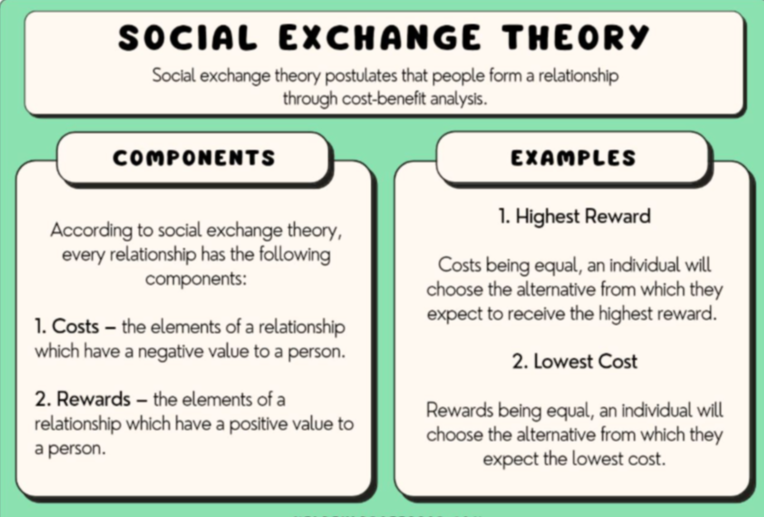
Social Exchange Theory:
The theory that our social behavior is an exchange process, where we maximize the benefits and minimize the costs.
Example: If someone is donating blood, they may weigh the costs of doing it (Anxiety and discomfort) against the beliefs (social approval, good feelings). If the rewards outweigh the costs, they will help.
Altruism:
The selflessness concern for the welfare of those in dire need.
Example: Noah wants to travel the world and help people in the most dire need.
Social Responsibility Norm:
An expectation that people will help those needing their help.
Example: Hope enjoys walking around her local park picking up litter. She is doing it so everyone has a clean environment to enjoy (Social Responsibility Norm).
Mirror Image Perceptions:
Mutual views that are often held by conflicting parties. When each side sees itself as ethical and peaceful, and sees the other side as evil and aggressive.
Example: Americans during the Cold War assumed that America represented the side of good and the Soviet Union represented evil.
Reciprocity Norm:
An expectation that people will help, not hurt, those who have helped them. Those for whom we do favors for will most likely return the favor.
Superordinate Goals:
Shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation.
Example: Two friends are currently in a fight, but they cooperate in order to finish a group project.
GRIT:
Graduated and Reciprocated Intiatives in Tension Reduction; a strategy designed to decrease international tensions with a few conciliatory acts.
Small gestures: Smiling, touches, and a word of apology.