Chapter 9- Adaptive immune response BOOK
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Naive T cells
Have not yet encountered a specific antigen
Effector T cells
Some effector T cells are directed to the sites of pathogen entry while others are directed to interact with B cells to produce antibodies
Primary immune response vs secondary
primary: initial antigenic response=primary
Subsequent reencounter with the same pathogen in a secondary immune response
CD4 T cells
Naive Cd4 t cells can differentiate into different types of efefctor T cells such as T helper 1 and 2, 17, FH and reg
TFH
T Follicular helper
Activate MHC class II bearing target cells, such as macrophages, mucosal epthelial cells and B cells
Treg
Regulatory T cells
Inhibit initiation and extent of immune activation
Memory T cells
Can retain effector functions and persist for months to years at substantially higher numbers than their naive clonal precursors
Where are the adaptive immune responses initiated?
Secondary lymphoid organs- lymph nodes, spleen, mucosa associated lymphoid tissue MALT- ex Payers Patches
Consists of different parts where B and T cells are concentrated
Contain macrophages, dendritic cells, stromal cells
Marginal zone B cells
Do not recirculate
a region located at the interface between the red and white pulp. They serve as a first line of defense against blood-borne pathogens, particularly encapsulated bacteria.
Germinal center
B cells are proliferating and undergoing somatic hypermutation
Follicular dendritic cells
Not from bone marrow
Specialized stromal cells that are limited to B cell zones
Produce chemokine CXCL13 which acts on the receptor CXCR5 on B cells to attract the to follicles
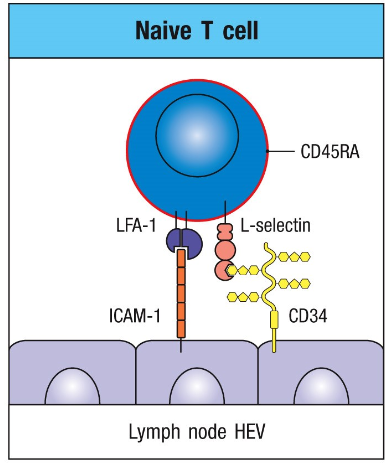
HEV
High enothelial venules
Found in T cell zones→ thick endothelial cell lining → specialized for the recruitment of lymphocytes into lymph nodes
Peyers patches
Lymph node like structures interspersed at intervals beneath gut epithelium of the small intestine
Sample antigens from intestinal lumen→ provides sites for B cells to synthesize IgA
How do B and T cells enter sec lymphoid organs?
Enter via blood→ directed via chemokines to B and T cells (secreted by stromal cells)
Enter via HEV→ cell cell interaction→ NOT antigen specific but governed by cell adhesion molecules
(Except the spleen→ enter via marginal sinus)
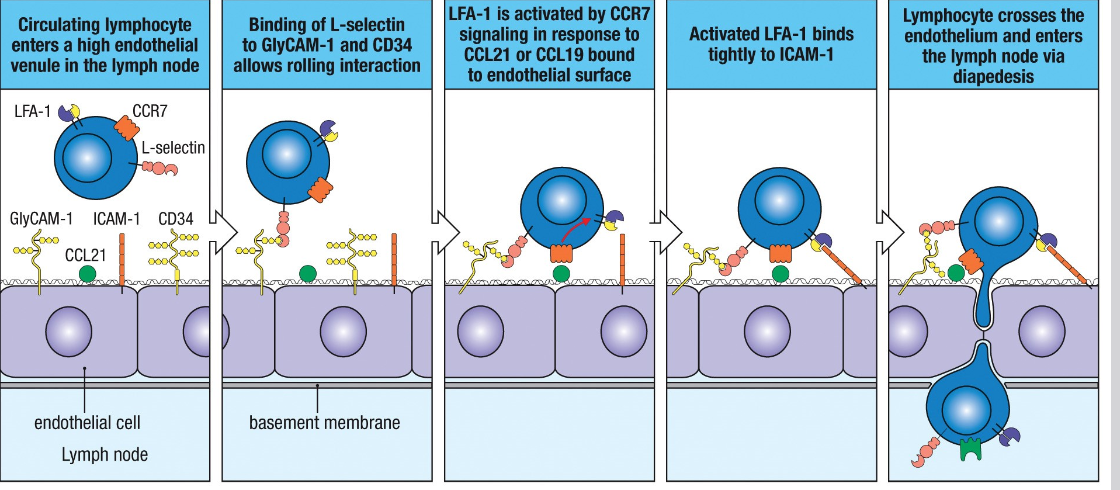
HEV interaction: Selectin interaction → activation of integrins by chemokines
Selectins
Important for guiding lymphocytes to particular tissues → called homing
Naive T cells→ mediated by L-selectin → marker for these cells in T cell zones
Cell surface molecules→ bind carbohydrates on endothelial cells
CCR7
Chemokine receptor expressed by naive T cells, regulatory T cells
CCR7 + chemokines→ activates LFA-1→ increasing affinity to ICAM→ higher avidity→ arrestthe T cell on the surface→ enables crossing of HEV and enter lymphoid tissue
FRCs
Fibroblast reticular cells
Creates a 3D network → fascilitates interactions of naive T and dendritic cells
T cell in lymph node
T cells enter lymph node cortex from blood via HEV
T cells not activated leave via cortical sinuses
T cells activated by APC dendritic cells → cant leave T cell zone→ proliferation
Differentiation to effector cells→ T cells exit via cortical sinsues
Dendritic cells
Central players between innate and adaptive immunity
They sense pathogens- innateimmunity
They activate naive T cell responses→ adaptive immunity
Antigen presenting cells
All express MHC class 2 + present peptides
Dendritic cells→ activates naive T cells for diff
Macrophages→ to receive help from effector and memory T cells like cytokines or surface molecules→ to kill microbe
B cells→ present to T FH cells to GC responses
Dendritic cells
Express 2 main co stimulatory molecules glycoprotreins B7.1 and B7.2 (CD80/CD86)
They deliver signals to naive T cells expressed CD28
Can also present self peptides
Very important with co stimulatory activity→ if no→ no immune response→ use adjuvants (with ex bacteria)
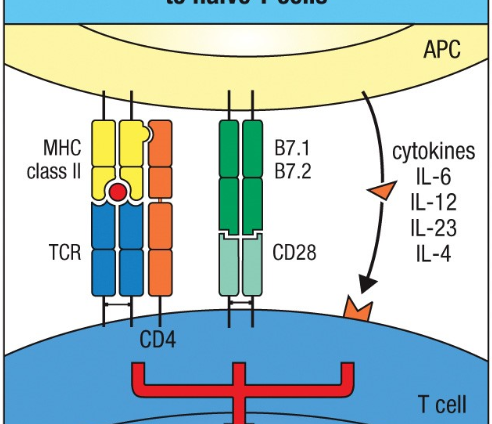
3 kinds of signals involved in activation of naive T cells by APCs
MHC+ antigen peptide recognized by TCR and CD4
C28 on T cell bind B7 molecules on APC→ proliferation+survival
Cytokines activate cytokine R→ differentiation
ALL 3 signals are NEEDED for expansion + differentiation of naive T cell→ effector cell
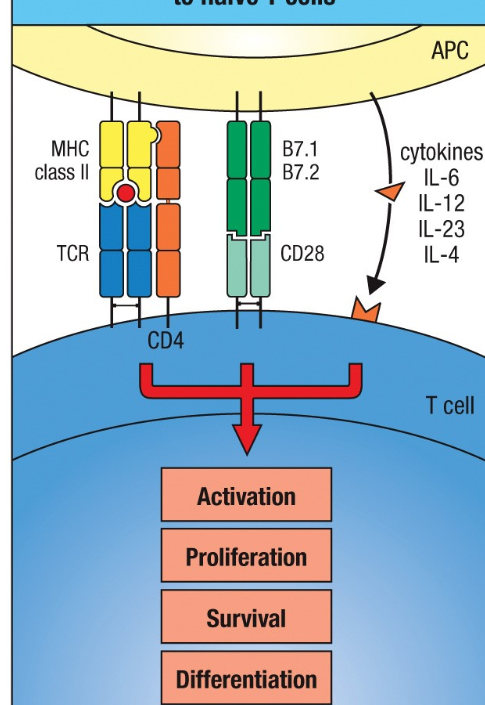
Activation of T cells to effector cells
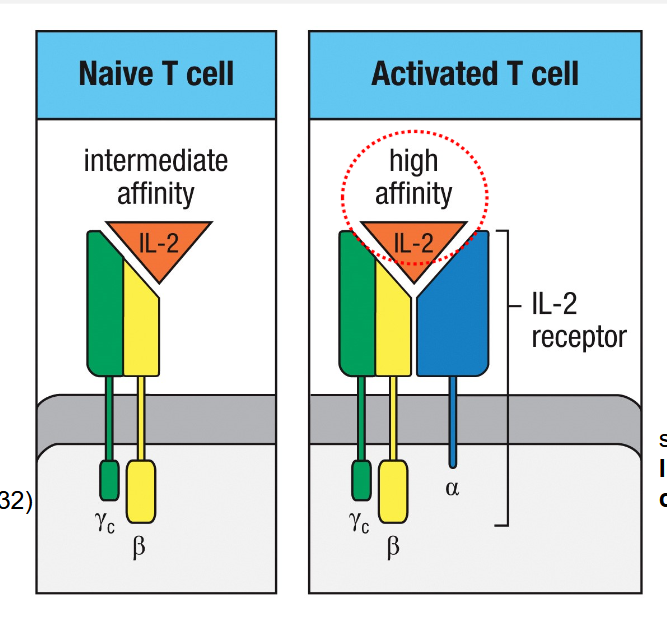
Leads to the expression of alfa chain of IL-2R/CD25
Production and response of IL-2 is important whenT cells become activated
Gamma and beta chains are already expressed
T Reg cells already express IL-2Ralfa→ can outcompete naive T cells→ act as a sink for IL-2 by limiting its availability to other cells→ when T cells have IL2Ralfa→ competition
CTLA-4
B7 can bind → Inhibits and dampen of immune response→ no T cell activation or clonal expansion
CTLA-4 inhibits activation by outcompeteting CD28 → higher affinity
Are expressed AFTER activation of T cells
CD40L
TNF family
Expressed on the surface of T cell after initial activation
Signals via CD40 on APCs to upregulate B7→ clonal expansion
CD4 and CD8 cells can be activated BY SAME APC
Lead to licensing
CD4 cell bind to same cell bound to CD8→ further activation of the APC=licensing
CD4 cell produce CD40L which induced the APC to produce B7 + CD70→ which bind CD8 cell→ AMPLIFYING CD8 response
Also produces IL-2→ enhance memory
CD4 t cells can differentiate into
Several distinct subsets
Helper or regulatory cells
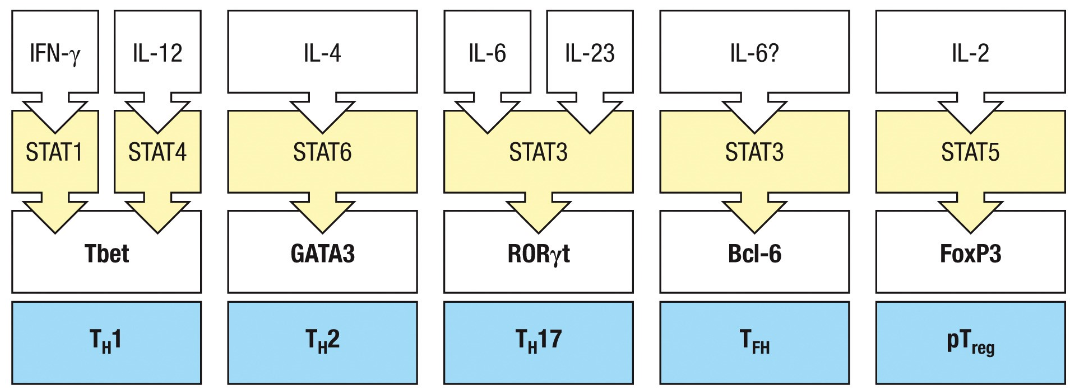
TH1,Th2,Th17, T follicular helper, regulatory cells
TH 1,2, 17 are defined by the combinations of cytokines they produce
TH1
Produce IFN gamma
Intracellular microbes→ mostly mycobacteria
Th1 recognize microbial antigen on macrophage→ activation of macrophage further by IFN-gamma
TFH develop in concert with TH1→ promote B cell class switching that favors opsonizing IgG antibodies
TH2
Produce IL4,5 and 13
Control infections by parasites, helminths→ promoting eosinophils, basophils and mast cells
TFH develping in concert promotes class switching of B cells to produce Ig E.
TH17
Produce Il-17A and IL-17F, IL-22
Extracellular bacteria and fungi and amplify neutrophilic and monocytic responses
Cytokines activate barrier epithelial cells→ producing antimicrobial peptides
TFH developing in concert promote class switching to opsonizing IgG2 and IgG3
TFH
Develop in concert with TH1 and TH2 or TH17
Produce some cytokines the same as above
Influences the class switching of B cells to generate immunoglobulin isotypes
Also produce Il-21→ B cell maturation and support of germinal center response
Helps to produce high affinity anitibodies
T Reg
Promote tolerance to antigens→ produce TGF-beta + IL-10
TFH + T reg development favor production of IgA
Prevents T cell mediated immune response
2 ways of development:
During positive selections Treg is developed, in thymus→ natural T reg
Naive CD4 T cells develop into T reg, in secondary lymphoid organs→ called induced T reg
STAT
Family of Transcription factors
Cytokines direct the development of effector cells by activating different member of the STAT family
T reg cells
pTreg vs tTreg cells
PTreg→ in secondary, express FoxP3, need RA for development
tTreg→ develop upon antigen recognition in thymus, express Fox P3
Cytokines suppression
The subsets of CD4 cells can produce cytokines that can negatively regulate the development of effector activity of other subsets
T reg function
Preventing autoreactive immune responses
tTreg→ develop during + selection in thymus→ constitutive expression of IL-2Ralfa. L selectin, CRR7 and CTLA-4
pTreg→ arise in periphery from CD4 cells, express SAME as tTreg
FoxP3→ important transcription factor prevents production of IL-2, cannot produce it themself→ need other cells to do it
CTLA-4 remove B7 on APC cells
Effector T reg
eTreg
Produce IL-10→ inhibits expression of MHC molecules and co-stimulatory molecules
Also inhibits cytokine production of APC
Effector molecules of T cells
Cytotoxin→ stored in granules in cytotoxic cells, need regulation due to not specific→ trigger apoptosis in any cell
Cytokines or membrane associated proteins→ synthesized by all effector T cells, ex CD4 cells→ restriced to MHC bearing cells class 2. Auto or paracrine or long distance
Polarization
Immunological synapse ensures polarized release of cytokines so that they are concentrated at the site of contact with the target cell
What cell surface molecules do most effector T cells express?
Members of the TNF family
Ex: TnF-alfa, lymphotoxins (LTs), Fas ligand (CD178), CD40 ligand
Fas
Contains a death domain
FasL+ Fas (CD95)→ induces death by apoptosis of Fas bearing cell
Cytotoxic T cells
Kills target through apoptosis induced by extracellular signals or by the lack of signals for survival
2 pathways for apoptosis: Activation of proteases
-extrinsic pathway→ death receptors→ death inducing signaling complex (DISC)
-intrinsic pathway→ induced through noxious stimuli or lack of growth factors
Proteases involved in apoptosis
Specialized→ called caspases
Synthesized as pro-caspases→ catalytic domain is inhibited→ activated by other caspases→ cleavage
2 types: initiator caspases cleaves other
Effector caspases initiates cellularchangesassociated with apoptosis
Intrinsic pathway
Triggered by the release of cytochrome c from mitochondira→ triggers the activation of caspases→ forms a apoptosome
Cytotoxic effector cells
Calcium dependent release of cytotoxic granules upon recognition of antigen on the surface if target cell
Granules= modified lysosomes containing 3 classes of cytotoxic effector proteins: perforin, granzymes, granulysin
These proteins are stored in cytotoxic granules in a active form→ but no actions in granules.
Perforin
Forms pores which both causes direct damage and forms a conduit → contents of granules can be released here to the target cell
Granzymes
Activate apoptosis once delivered to target cell cytosol via pores formed by perforin
Granulysin
ANtimicrobial activity, at high C is able to induce apoptosis
Serglycin
Cytotoxic granules also contain serglycin
Proteoglycan which acts as a scaffold, forms a complex with perforin and granzymes
Cytotoxic T cells are…
Serial killers
Kill one cell at a time
Reorient their golgi + microtubule organization center to focus secretion to one point of contact with target cell