Understanding Heart Function and Blood Circulation
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
Heart
Muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
Excitation
Initial electrical impulse triggering heart muscle contraction.
Contraction
Shortening of cardiac muscle cells to pump blood.

Pressure
Force generated by heart contractions driving blood flow.
Flow
Movement of blood through the circulatory system.
Sinoatrial node
Heart's natural pacemaker initiating electrical impulses.
Action potential
Electrical signal causing muscle contraction in the heart.
Atria
Upper chambers of the heart receiving blood.
Atrioventricular node
Node relaying signals from atria to ventricles.
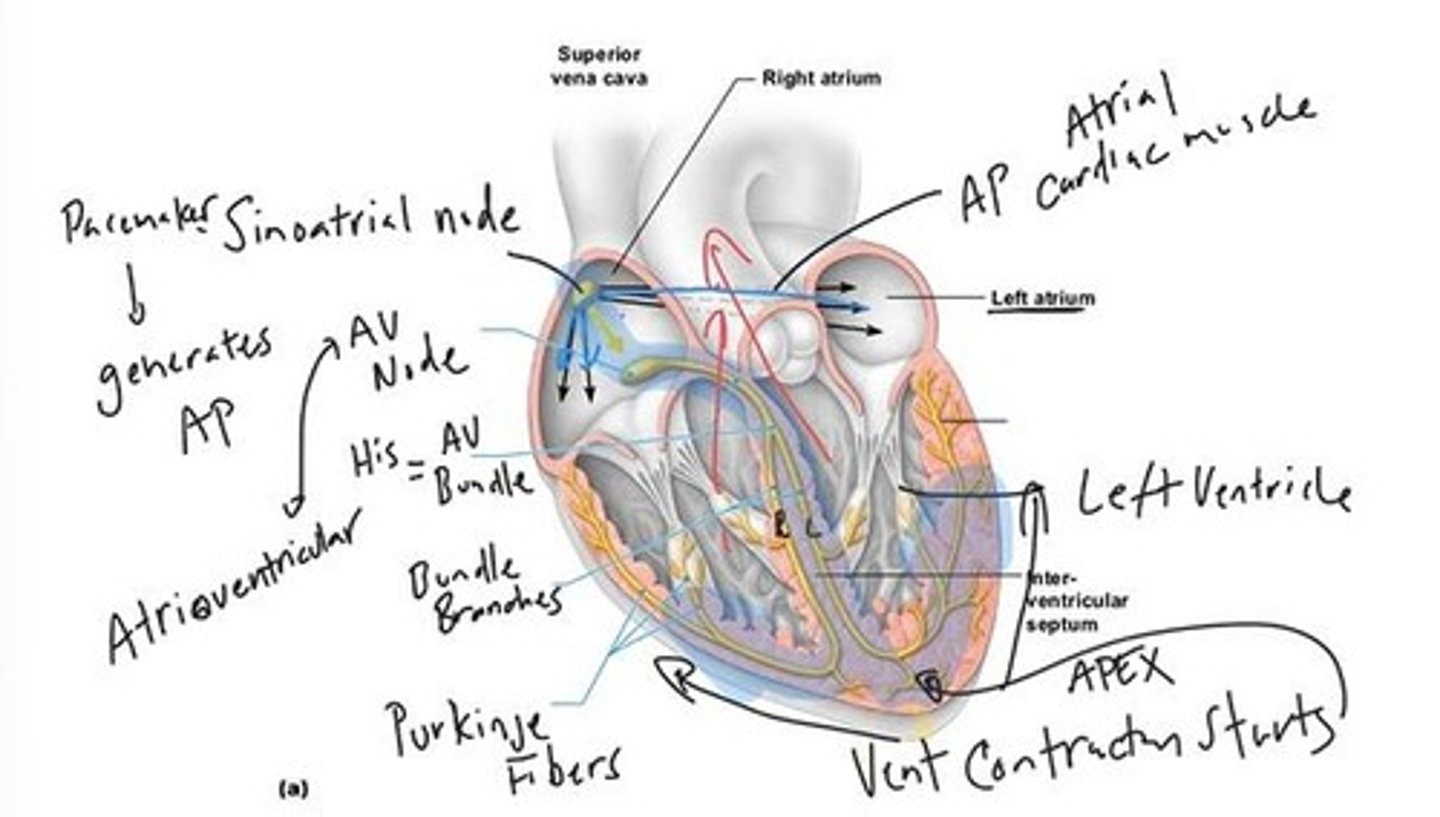
Bundle of His
Pathway for electrical signals from AV node.
Purkinje Fibers
Fibers spreading electrical impulses throughout ventricles.
Apex
Lowest point of the heart where contraction begins.
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Recording of heart's electrical activity over time.
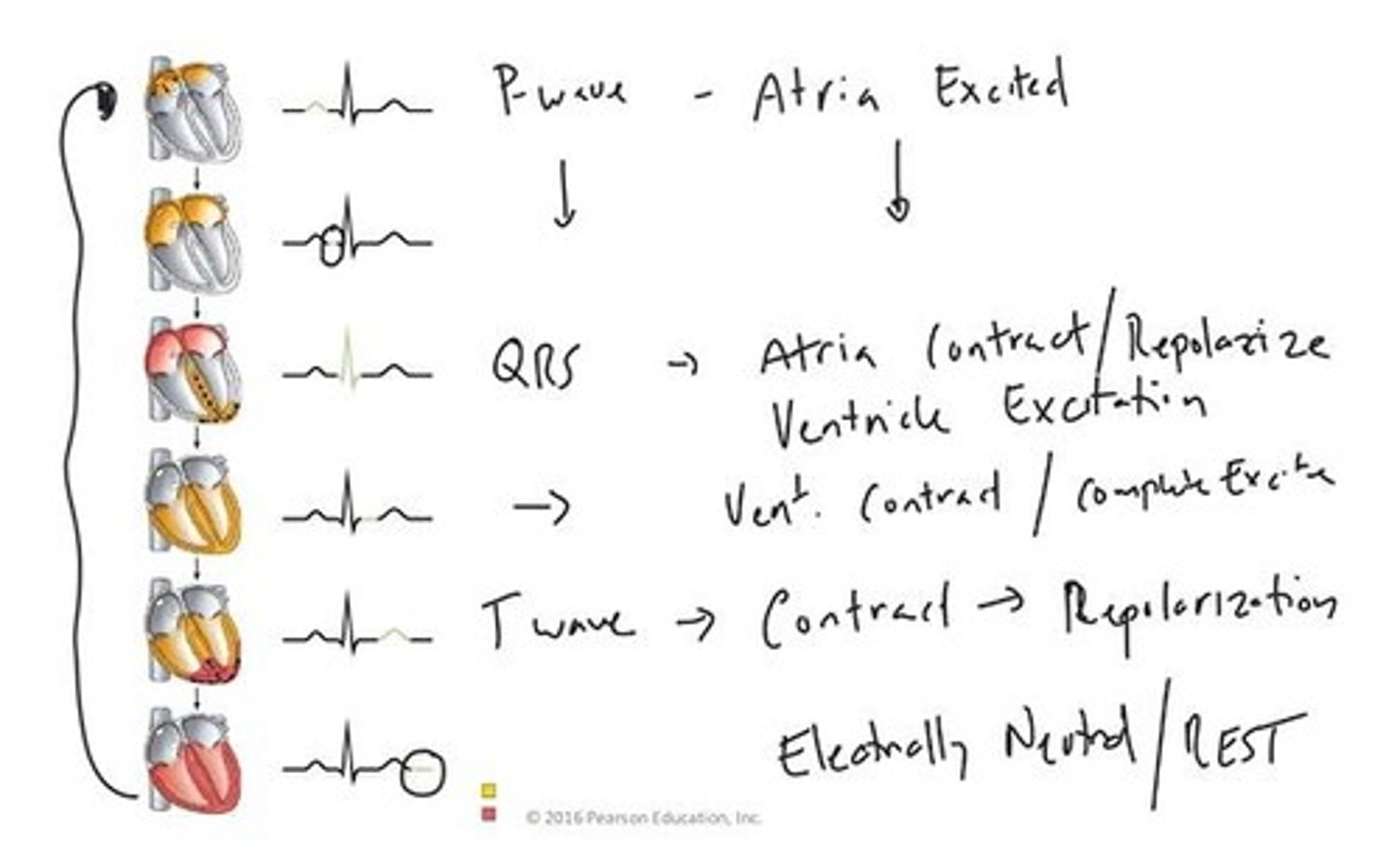
P-wave
Represents atrial contraction in ECG readings.
QRS complex
Indicates ventricular contraction and atrial relaxation.
T-wave
Shows ventricular relaxation and return to rest.
Isoelectric line
Represents heart's electrical inactivity or relaxation.
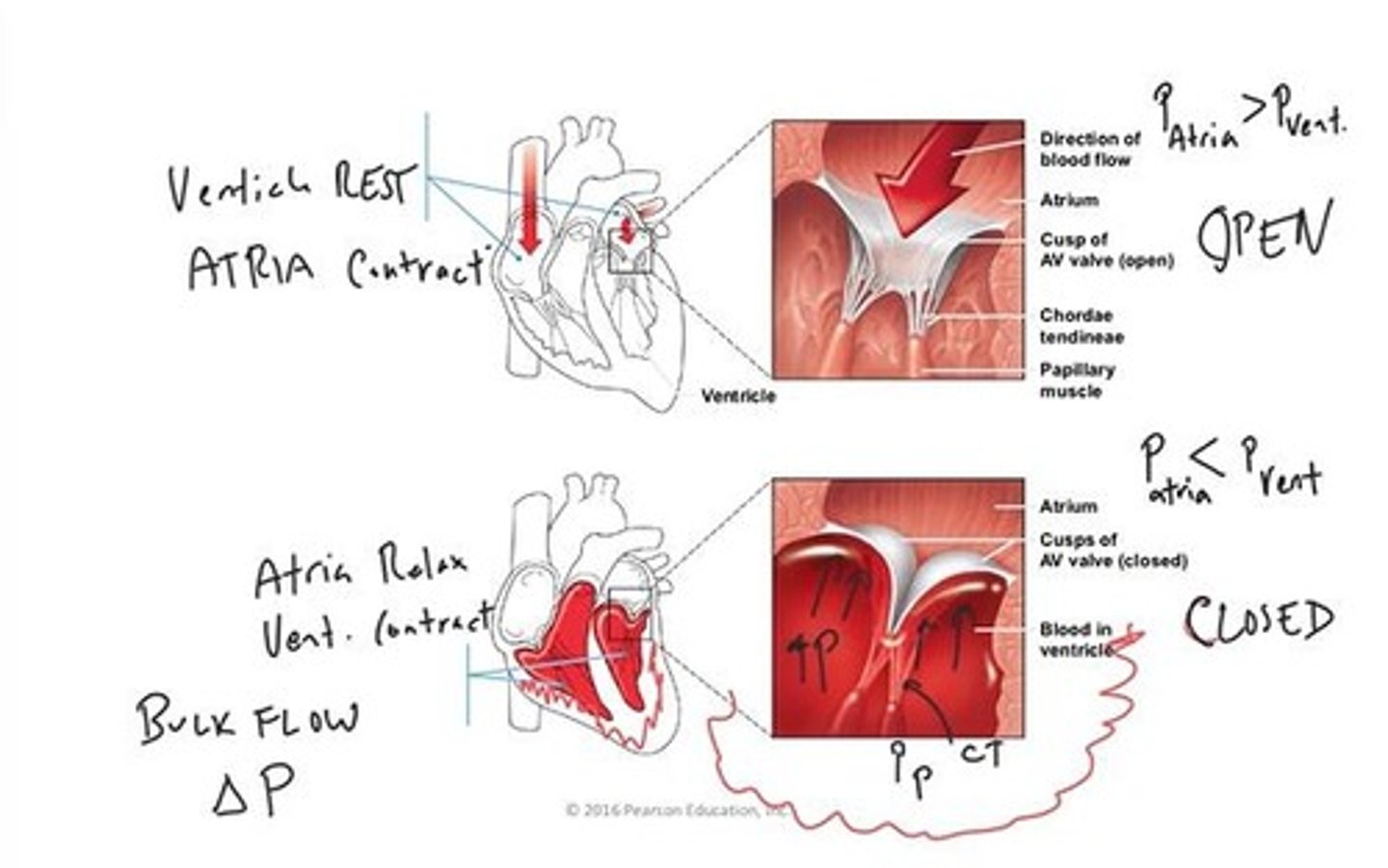
Right Atrioventricular valve
Valve allowing blood flow from right atrium to ventricle.
Pulmonary valve
Valve directing blood from right ventricle to lungs.
Coronary circulation
Blood supply specifically for heart muscle tissue.
Systemic circuit
Pathway delivering oxygenated blood to body tissues.
Unidirectional blood flow
Blood moves in one direction due to valves.
Semilunar valves
Valves preventing backflow from arteries to ventricles.
Atrioventricular valves
Valves separating atria from ventricles, ensuring flow.
Chordae Tendineae
Connective cords linking heart valve flaps to muscles.
Papillary Muscle
Cardiac muscle projections stabilizing heart valve flaps.
Atria
Upper heart chambers that receive blood.
Ventricles
Lower heart chambers that pump blood out.
AV Valves
Valves between atria and ventricles, controlling blood flow.
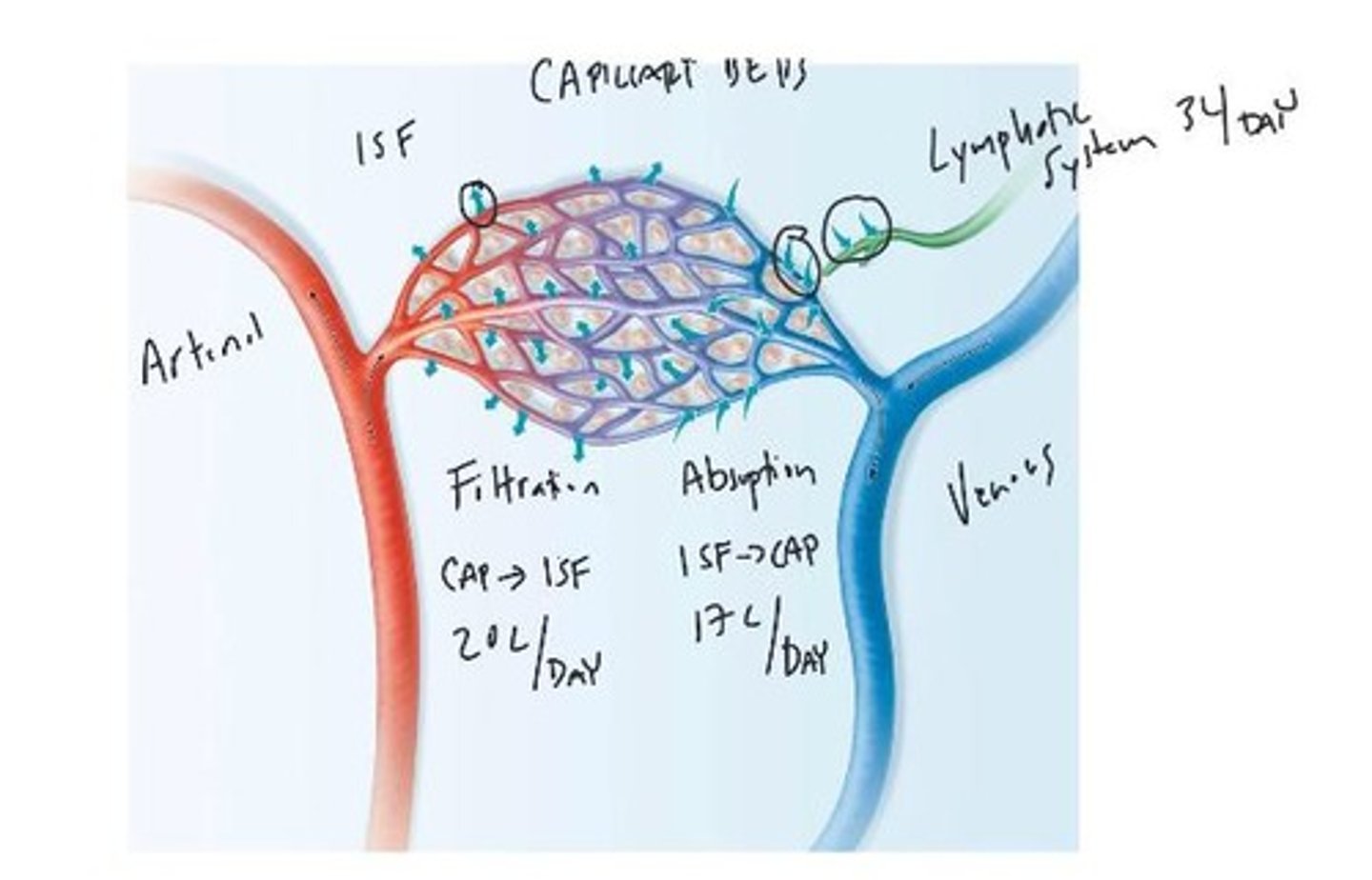
Pressure Gradient
Difference in pressure driving fluid movement.
Bulk Flow
Fluid movement driven by pressure differences.
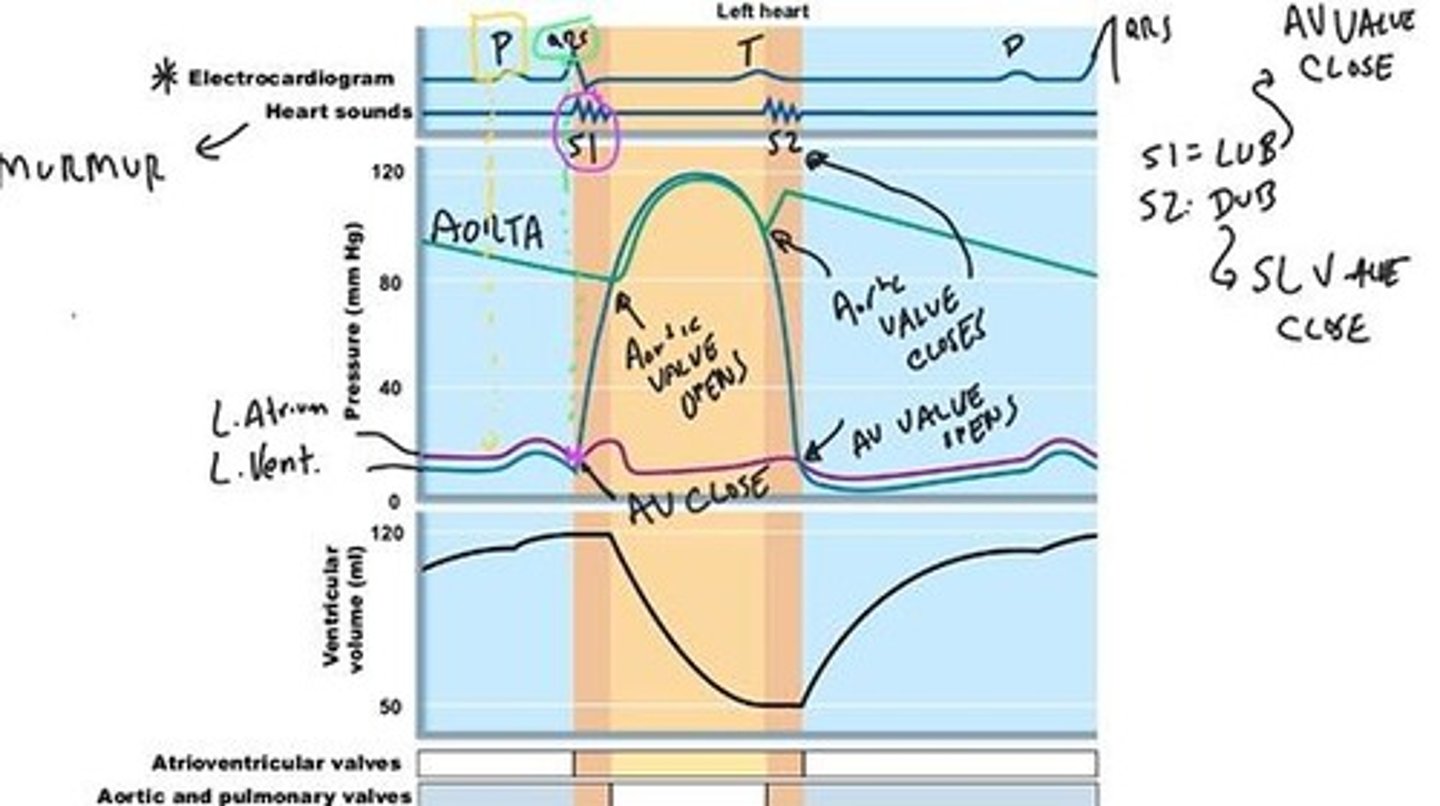
Heart Sounds
Sounds produced by closing heart valves.
S1 Sound
First heart sound, occurs when AV valves close.
S2 Sound
Second heart sound, occurs when aortic valve closes.
Heart Murmur
Abnormal heart sound indicating potential issues.
Ventricular Pressure
Pressure within ventricles during contraction.
Aortic Pressure
Pressure in the aorta during heart cycles.
Atrial Pressure
Pressure within atria during heart cycles.
Ejection Fraction
Percentage of blood ejected from ventricles.
Cardiac Cycle
Sequence of events in one heartbeat.
QRS Complex
ECG representation of ventricular depolarization.
Isoelectric Line
Period of no electrical activity in heart.
Ventricular Filling
Phase where blood fills ventricles from atria.
Turbulence
Disordered flow causing sound around valve rims.
Connective Tissue Skeleton
Structural support for semilunar valves.
Vena Cava
Large veins returning blood to the heart.
Lumen
Inside space of a hollow organ.
Endocardium
Thin tissue layer separating lumen from myocardium.
Myocardium
Cardiac muscle layer responsible for heart contraction.
Serous cavity
Fluid-filled space allowing heart movement.
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding and protecting the heart.
Coronary circulation
Blood supply circuit for the myocardium.
Coronary vessels
Blood vessels supplying myocardium externally.
Acute myocardial infarction
Rapid tissue death in myocardium due to blood flow loss.
EKG
Electrocardiogram measuring heart's electrical activity.
Junctional Rhythm
Heart rhythm from AV node when SA node fails.
Second-degree heart block
AV node partially blocks SA node impulses.
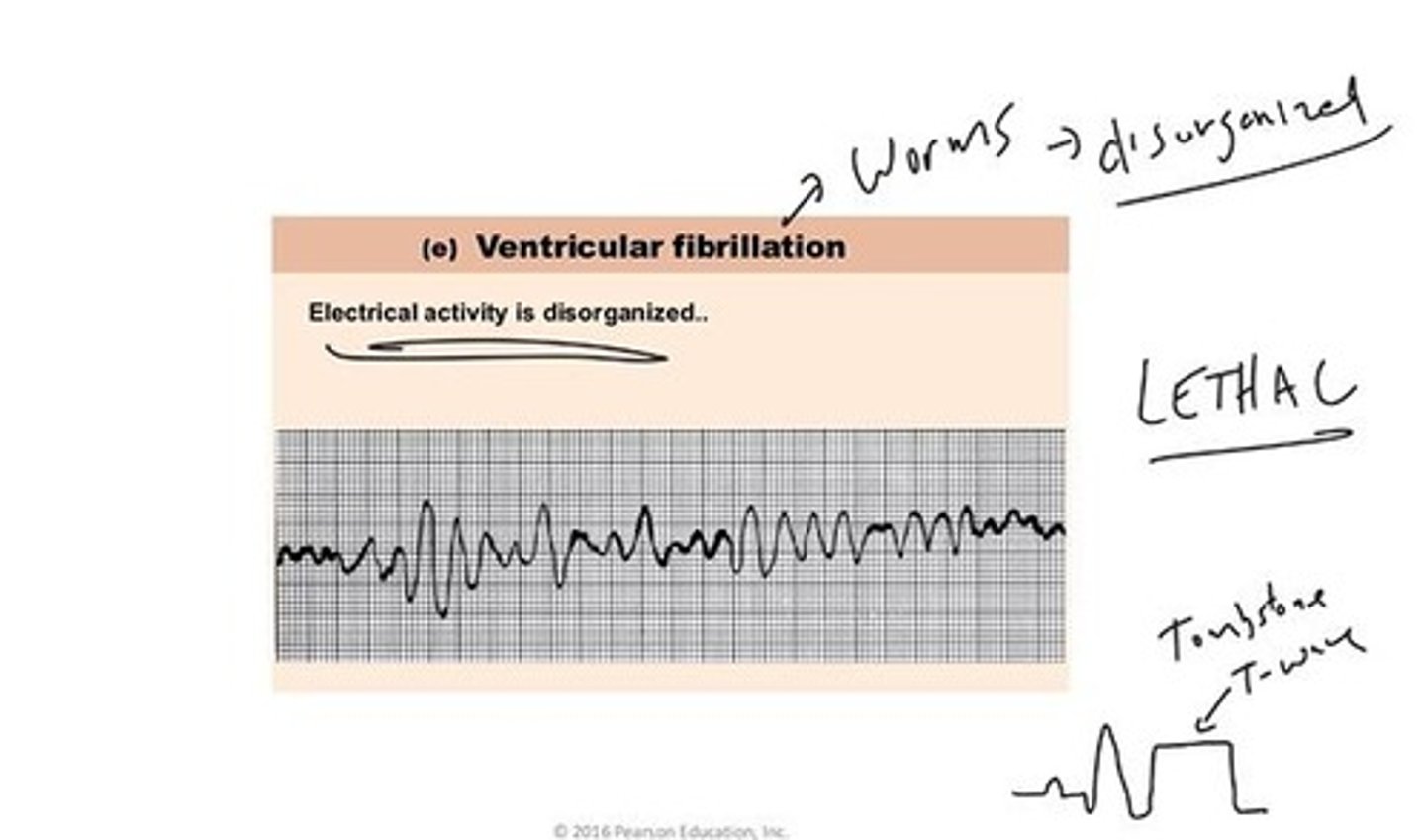
Ventricular fibrillation
Disorganized electrical activity in ventricles.
Cardiac Output
Volume of blood heart pumps per minute.
Heart rate
Number of heartbeats per minute.
Stroke volume
Volume of blood ejected per heartbeat.
End Diastolic Volume
Blood volume in heart at relaxation's end.
End Systolic Volume
Minimum blood volume in heart after contraction.
Ejection Fraction
Stroke volume divided by end diastolic volume.
Single cardiac cycle
One complete heartbeat or stroke.
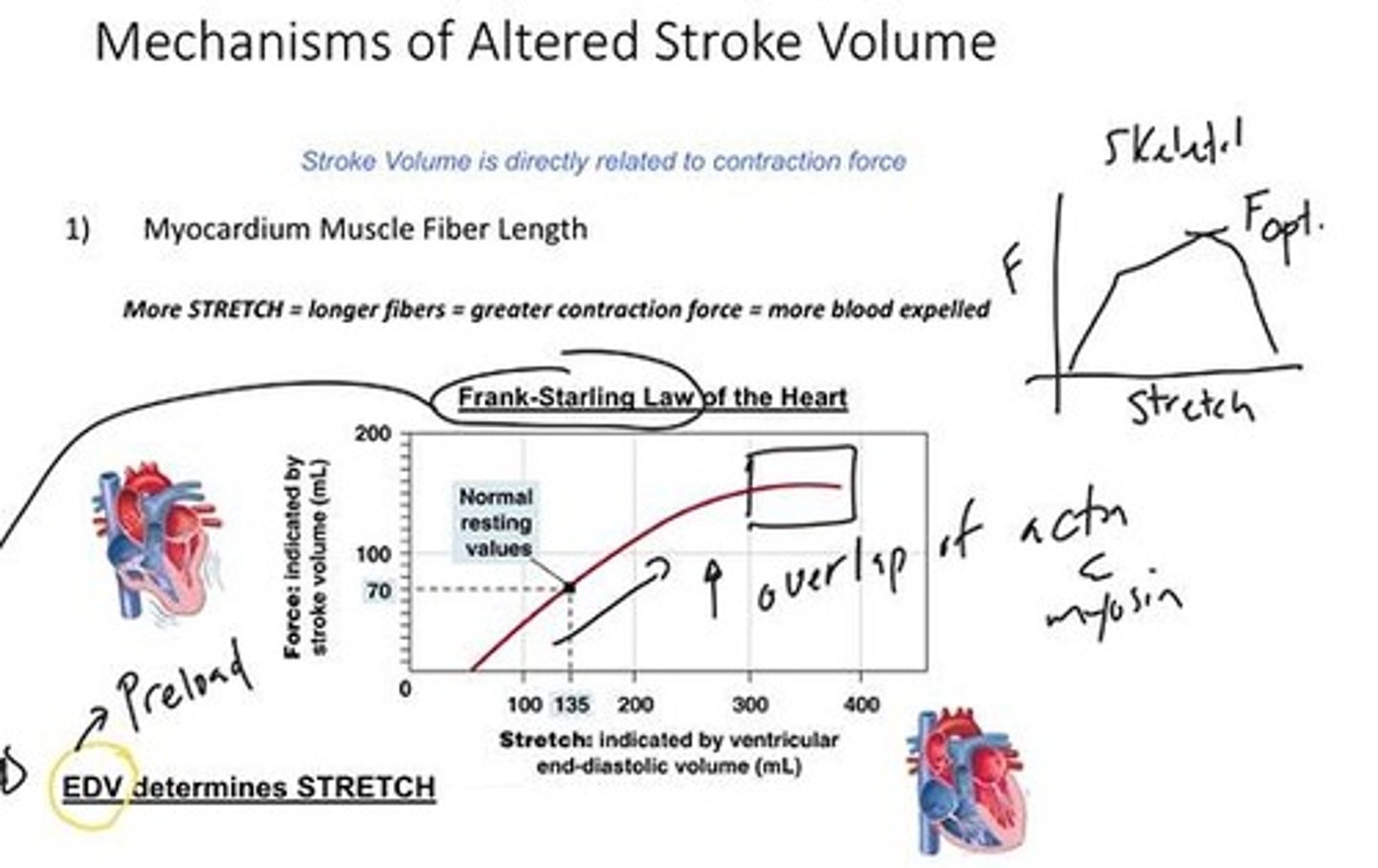
Preload
Volume of blood filling heart before contraction.
Sympathetic influence
Increases heart rate and stroke volume.
Diastolic phase
Heart muscle relaxation phase.
Contraction force
Strength of heart muscle contraction.
End Diastolic Volume (EDV)
Volume of blood in heart before contraction.
Frank-Starling Law
EDV determines heart muscle stretch and contraction.
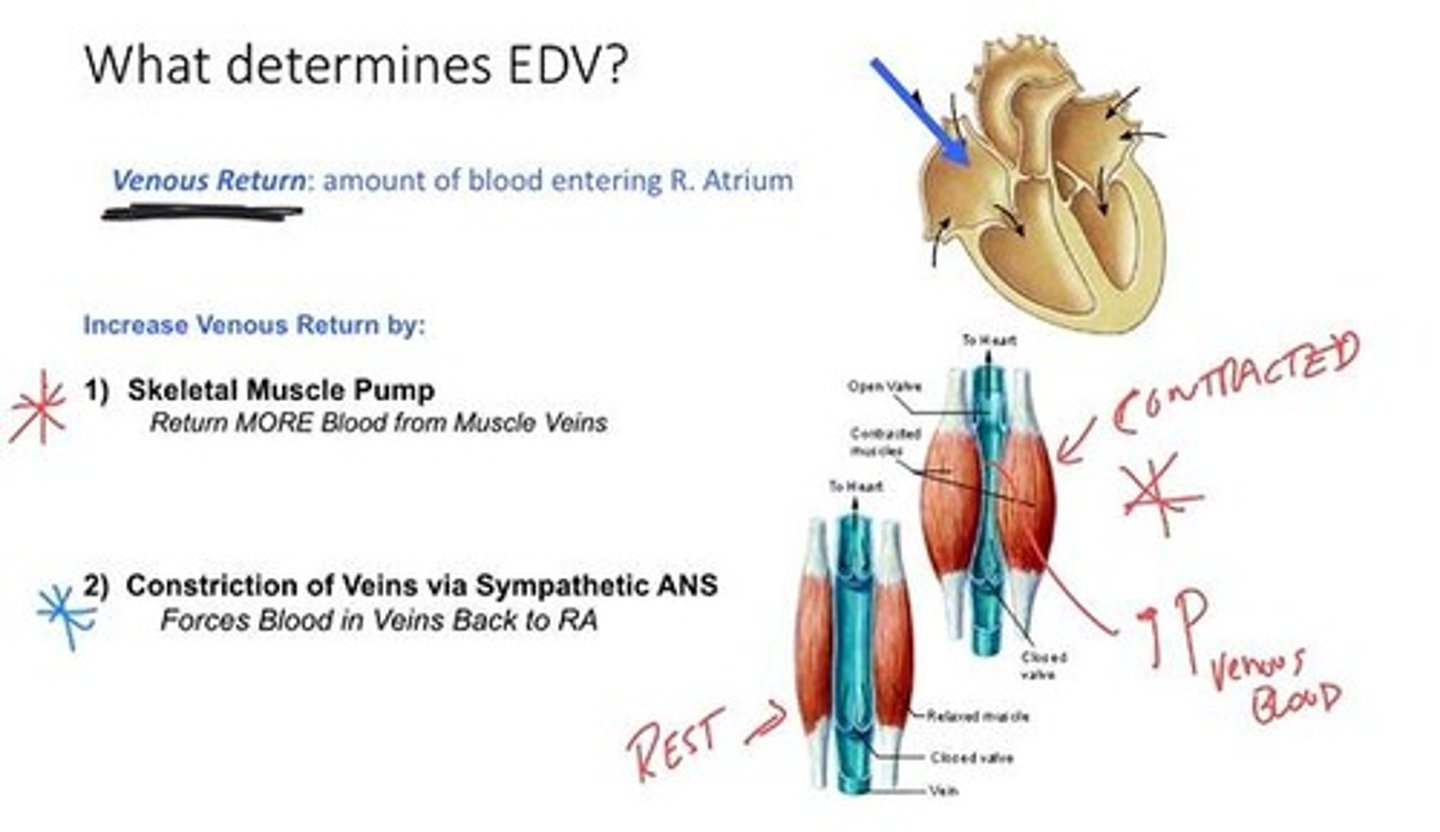
Venous Return
Amount of blood entering the right atrium.
Skeletal Muscle Pump
Muscle contractions increase venous pressure, aiding return.
Constriction of Veins
Sympathetic ANS activation increases venous return.
Respiratory Pump
Pressure changes during breathing enhance venous return.
Ejection Fraction
Percentage of blood ejected during heart contraction.
Contractility
Force of heart contraction independent of stretch.
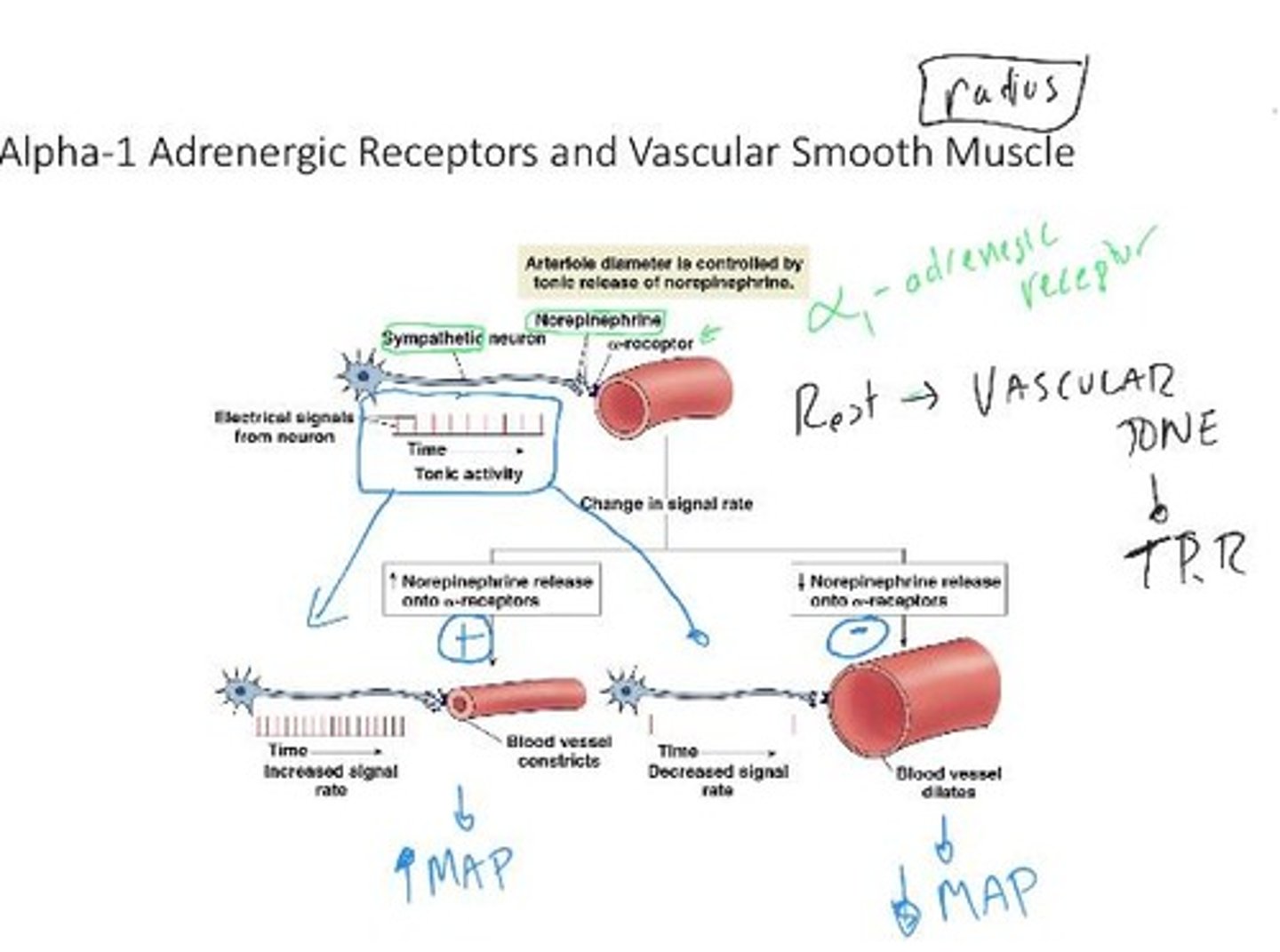
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter increasing heart muscle contraction force.
Epinephrine
Hormone enhancing heart muscle contraction strength.
G-Protein
Mediates neurotransmitter signals in heart muscle.
Calcium Concentration
Increased calcium enhances crossbridge formation in myocardium.
Elastic Arteries
Expand to absorb pressure from heart's output.
Muscular Arteries
Contain smooth muscle to regulate blood flow.
Arterioles
Connect larger arteries to capillary networks.
Crossbridge Formation
Interaction between actin and myosin for contraction.
Pressure Gradient
Difference in pressure driving blood flow.
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Stores calcium for muscle contraction in myocardium.
Inspiration
Breathing in creates lower pressure aiding venous return.
Blood Flow Patterns
Arterioles influence flow into specific capillary beds.
Muscle Veins
Return more blood to heart during contraction.
Sympathetic Nervous System
Regulates heart contractility and blood vessel constriction.
Volume of Blood
Total blood in heart influences stroke volume.
Venules
Small vessels that collect blood from capillaries.
Veins
Blood vessels returning blood to the heart.
Inferior Vena Cava
Vein carrying blood from lower body to heart.
Superior Vena Cava
Vein carrying blood from upper body to heart.
Capillaries
Tiny vessels where exchange of substances occurs.
Blood Volume in Veins
60% of total blood volume resides in veins.
Valves in Veins
Prevent backflow of blood towards the heart.
Pressure Generation by Heart
Heart creates pressure to move blood through arteries.