Congenital Anomalies of Female Reproductive Tract
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Are congenital anomalies common or rare?
RARE
When are uterine anomalies usually seen?
usually not seen at birth
generally diagnosed
at puberty (symptoms or menstrual difficulties arise)
in infertility clinic (problems getting pregnant/ carrying pregnancy to term)
what are the three etiologies of congenital anomalies?
disruption in development of paramesonephric ducts
failure of fusion of paramesonephric ducts
failure of reabsorption of median septum of fused paramesonephric ducts
know this image!
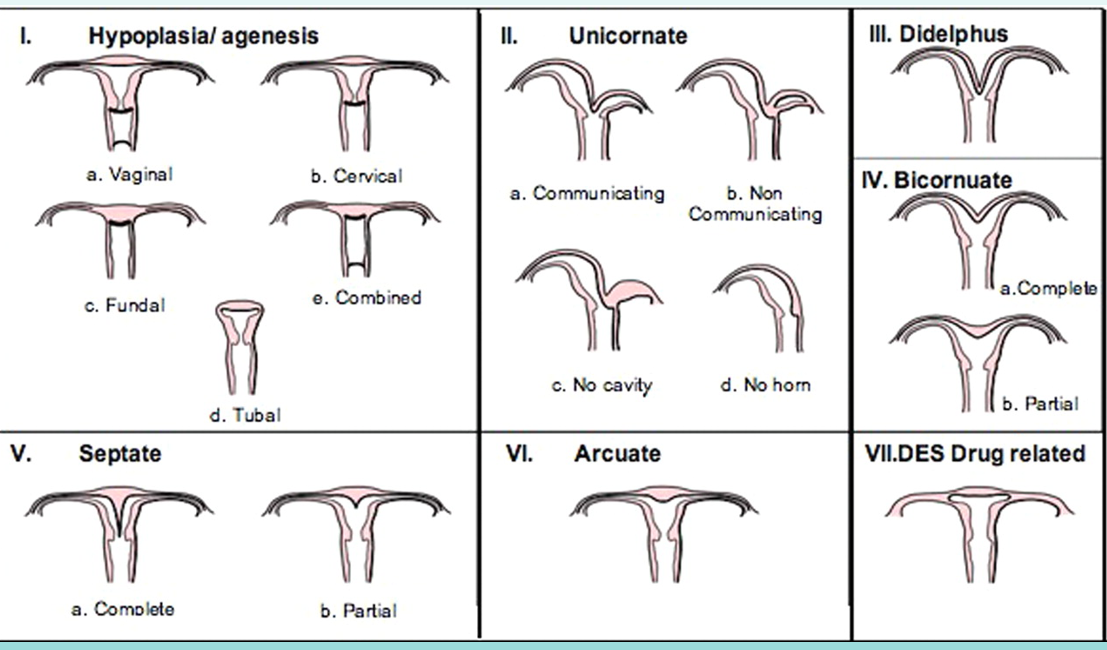
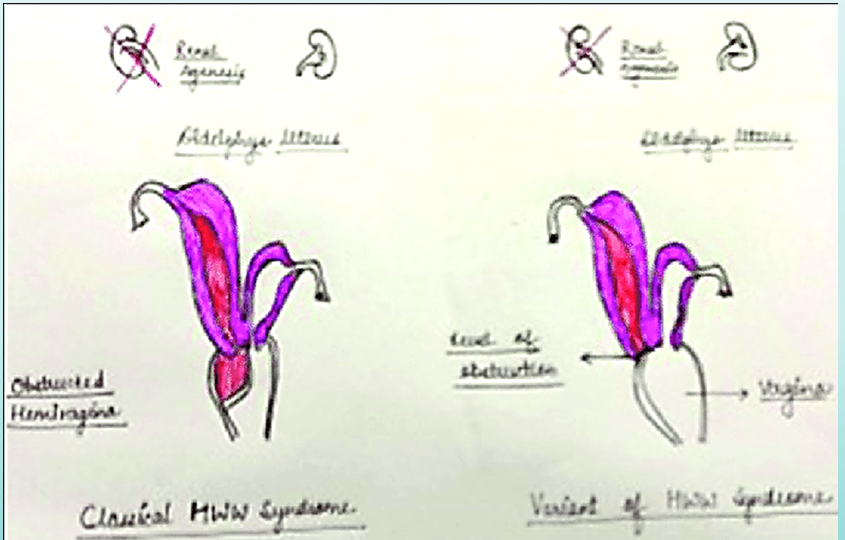
what is Mayer-Rotikansky Kuster-Hauser Syndrome
complete agenesis of uterus and vagina
agenesis/ hypoplasia of uterus and/or vagina
can have agenesis of only vagina with normal uterus
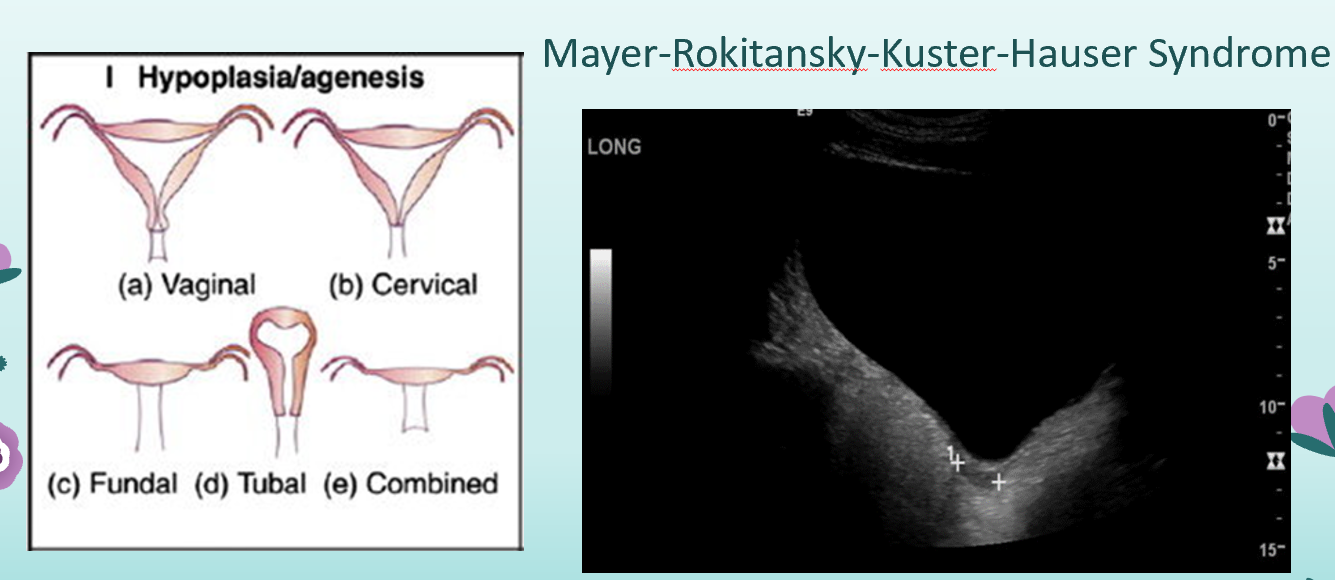
what is incomplete recanalization?
normal uterus but small vaginal pouch?
what is the main modality for evaluating Class 1 Mullerian anomalies? what is the best approach?
Ultrasound
transabdominal approach with a full bladder
what other imaging modality has an important role in analyzing mullerian anomalies (class 1)?
MRI— 3D reconstruction is very useful
Fertility prognosis for Class 1 Mullerian Anomalies?
agenesis generally incompatible with successful pregnancy
hypoplasia can be surgically corrected
vaginal hypoplasia- can have successful pregnancy
uterine hypoplasia- depends on amount of endometrial tissue and degree of hypoplasia
what is hypoplasia?
incomplete development or underdevelopment of an organ or tissue
what is an alternative for pregnancy with agenesis of uterus and vagina?
normal ovaries, so can harvest oocytes for surrogate carrier
what is a unicornuate uterus (uterus unicornis)?
developmental failure of one paramesonephric duct while the other develops normally
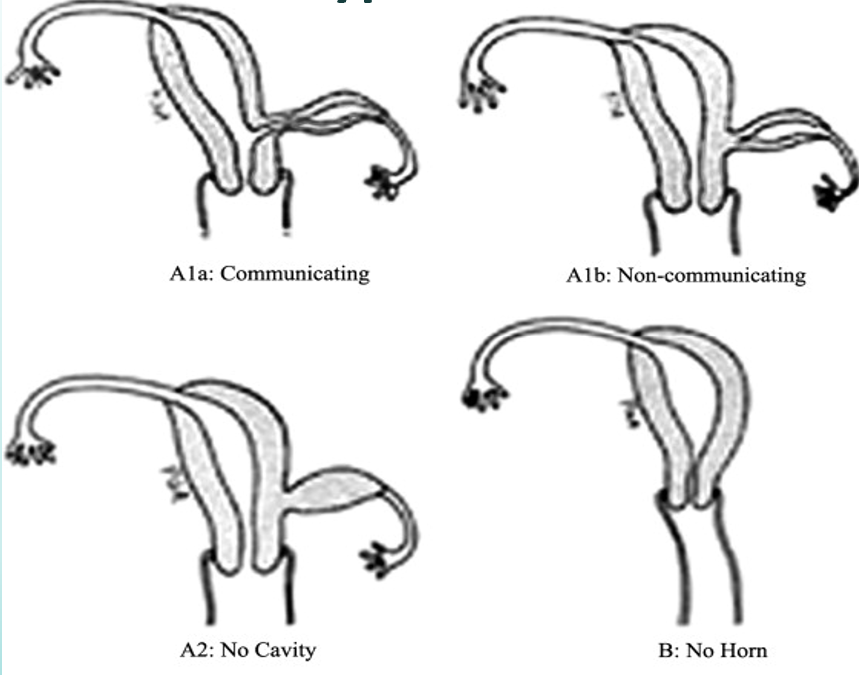
which horn is most often absent in a Unicornuate Uterus?
left horn most often absent
what often occurs in someone with a unicornuate uterus?
agenesis of ovary on same side as absent horn (ipsilateral)
if you see a uterine anomaly and the patient did not know, what should they have looked at and why?
their kidneys because they form at the same time?
associated renal anomalies (with unicornuate uterus):
renal agenesis (on same side as missing horn)
horseshoe kidney
pelvic kidney (on same side as missing horn)
In a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn, is the rudimentary horn always present?
no
what two things can a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn be?
communicating or noncommunicating
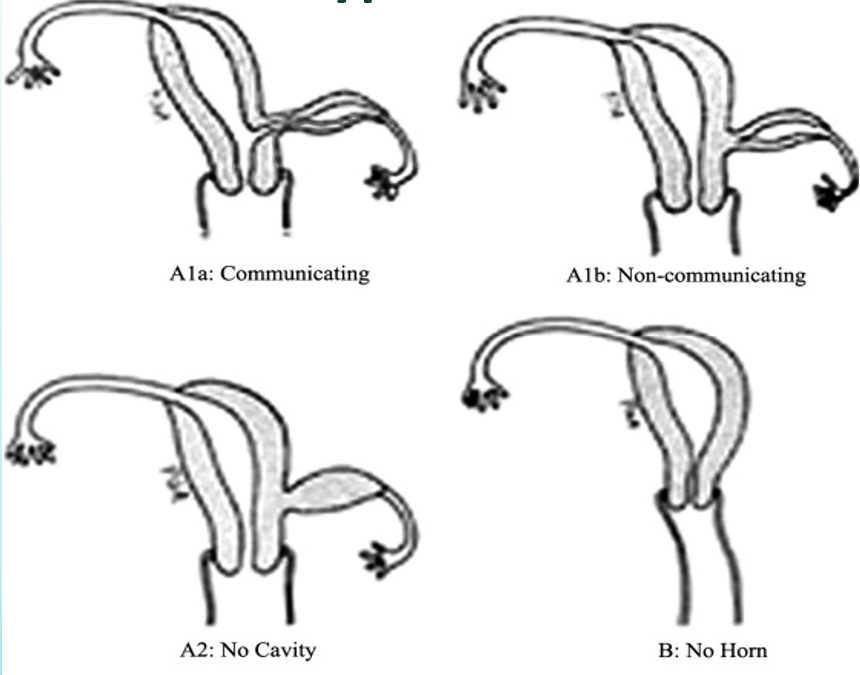
what is a communicating unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn?
endometrial tissue communicates with endometrial canal of “normal” horn
can be site of ectopic pregnancy
what is a noncommunicating unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn?
two types:
functioning endometrial tissue present:
Retrograde menses through rudimentary tube—> Endometriosis
No communication available at superior end—> Hematometra in non-communicating horn
If have superior opening (rudimentary tube), can be site of ectopic pregnancy due to transperitoneal migration of sperm.
no functioning endometrial tissue present:
hypoechoic mass adjacent to “normal” horn.
What is the treatment for unicornuate uterus?
resection recommended, regardless of whether communicating or non communicating
why are there poor pregnancy outcomes for unicornuate uterus?
lack of uterine muscle mass— can’t carry to term
abnormal vasculature— inhibits fetal nourishment
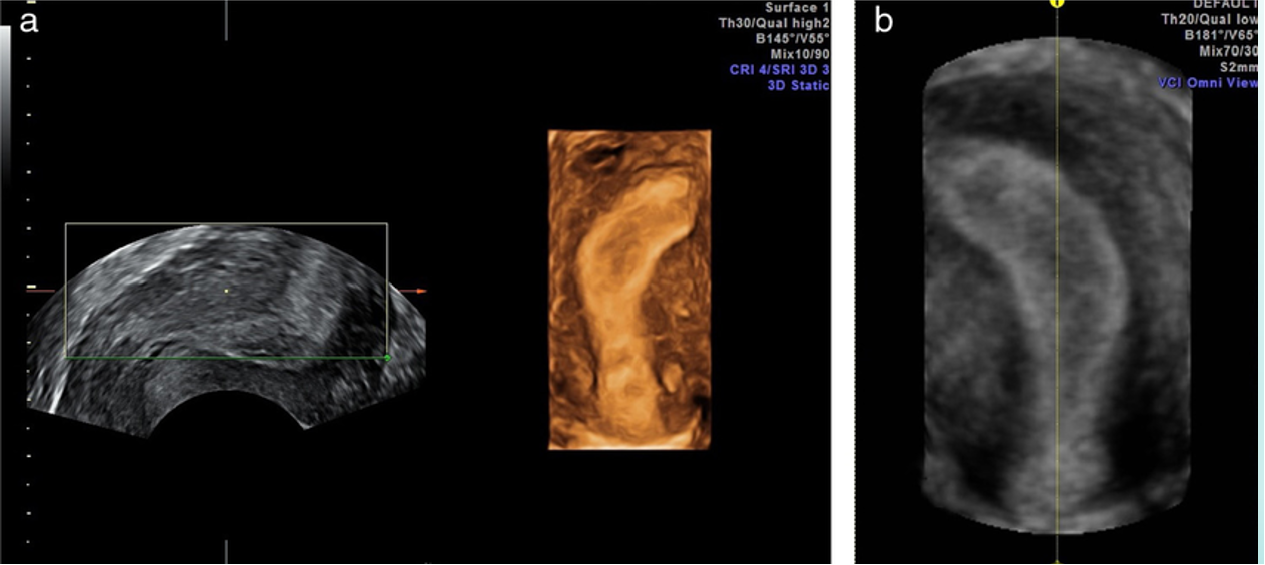
what anomaly is depicted?
unicornuate uterus (transvaginal US)
what is uterus didelphys?
two uterine horns
two cervices
two vaginas
complete midline failure of mullerian duct fusion
is there communication between the two uterine horns in uterus didelphys?
NO communication between the two horns because they are two completely separate things
which Mullerian Anomaly has the strongest association with renal agenesis?
Uterus Didelphys
what occurs when one vagina is obstructed in uterus didelphys? (sometimes on vagina can be obstructed)
hematometrocolpos
accumulation of blood in the vagina and uterine cavity due to intra-uterine hemorrhage.
What is Wunderlich-Herlyn-Werner Syndrome?
uterus didelphys with obstructed unilateral vagina
agenesis of kidney and ureter on same side as obstruction
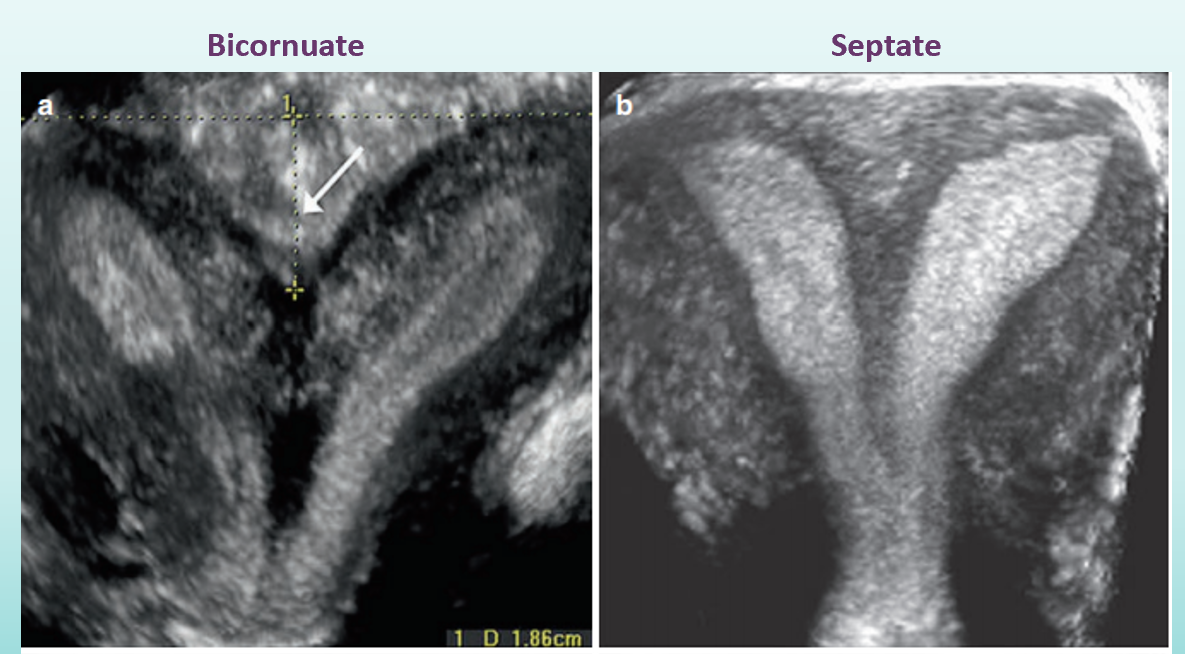
How do you distinguish a bicornuate uterus from a septate uterus?
evaluate fundal notch— outer contour (this is what is heart shaped in a bicornuate uterus)
no notch is seen with septate uterus!
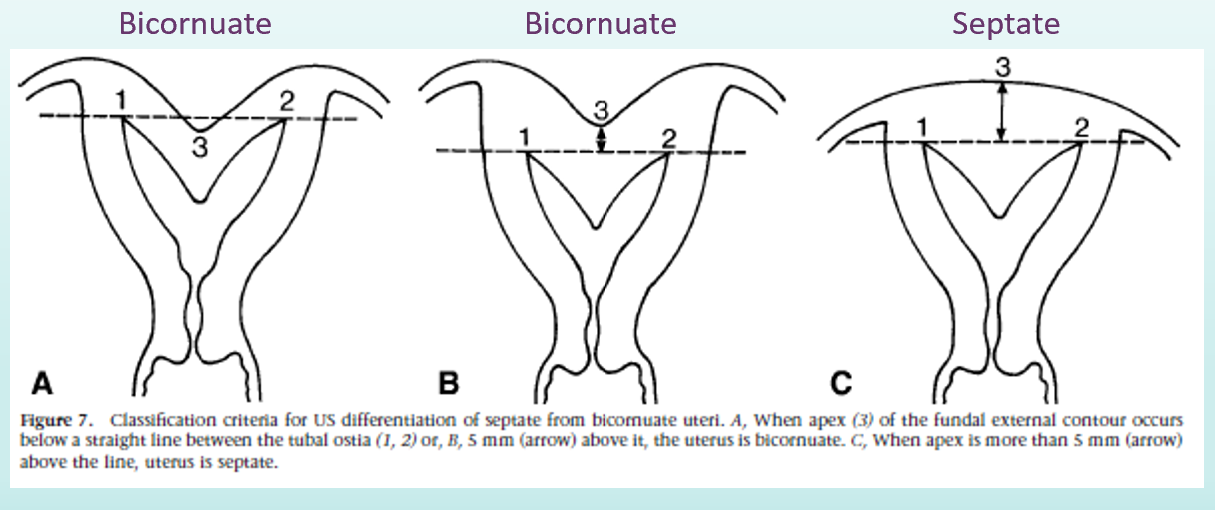
cleft depth for:
bicornuate uterus
septate uterus

why is differentiation of bicornuate uterus and septate uterus important?
treatment and fertility prognosis are very different for the two conditions
if evaluating for a uterine anomaly, what must you do?
transvaginal
what is transvaginal technique for bicornuate vs septate uterus?
must have 3D reconstruction of true coronal plane of uterus
evaluate outer uterine fundal contour
make straight line across superior margin of horns
measure depth of cleft
if greater than 10 mm (1cm) = bicornuate
if less than 10 mm with separation of endometrial cavities reaching to cervix= septate
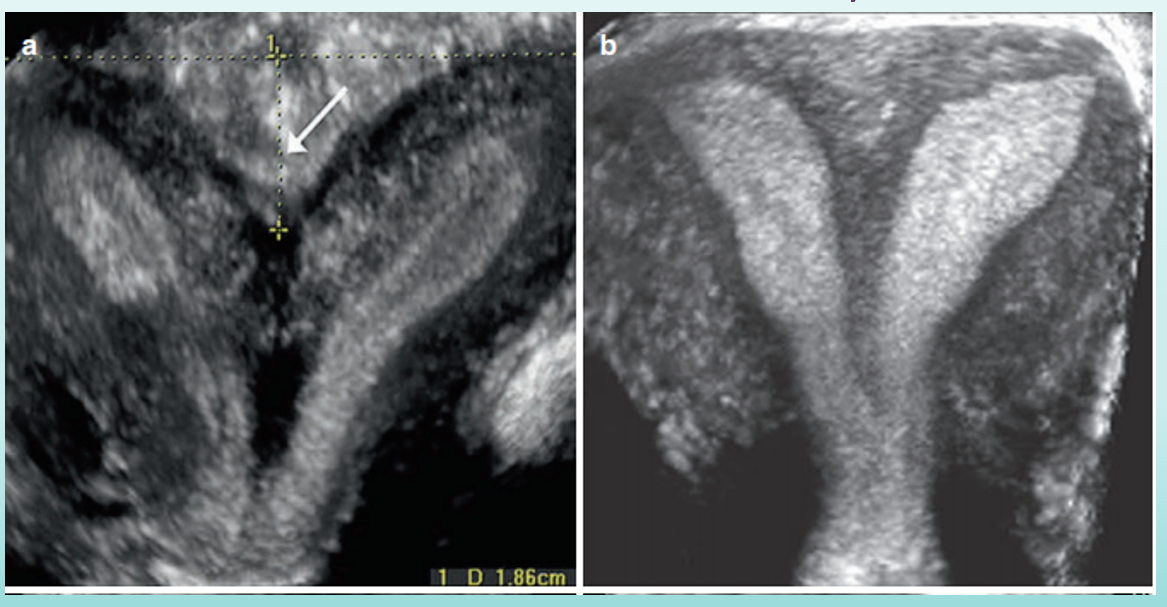
which is bicornuate, which is septate?
there is usually no issue getting pregnant with a bicornuate uterus, but what are the pregnancy outcomes?
spontaneous abortion (before 20 wks)
premature births (before 38 wks)
live birth
cervical incompetence
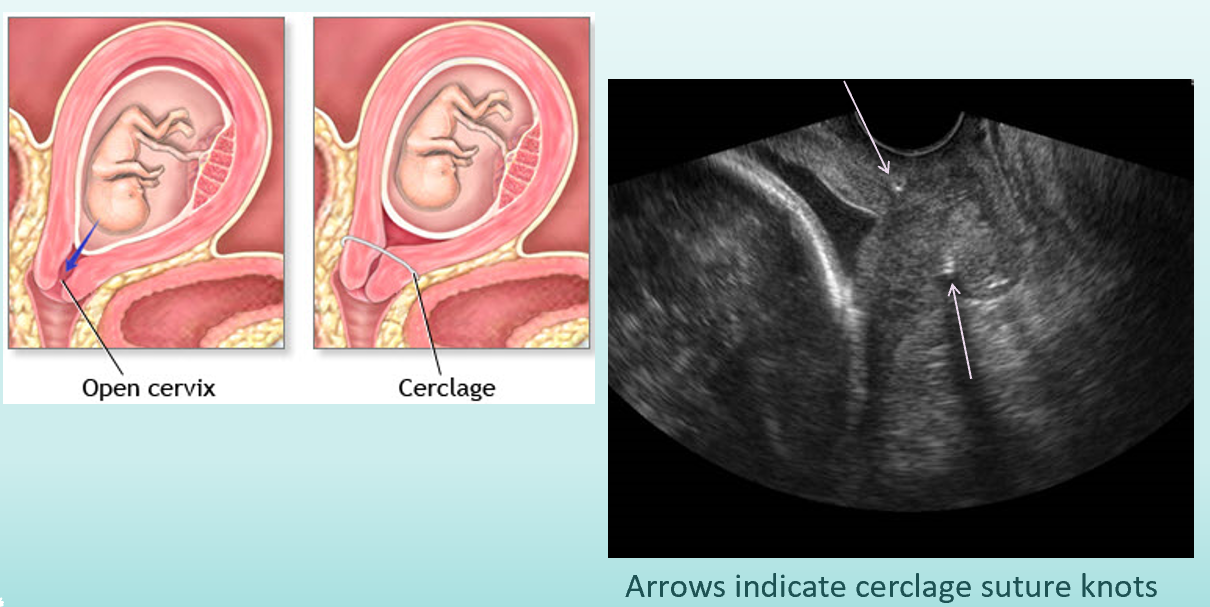
what is cervical cerclage? what does cervical cerclage prevent?
ring or sutures that hold cervix closed.
cervical incompetence in bicornuate uterus
what is the most common form of congenital uterine anomaly?
septate & subseptate (55%)
what does the top part of the septum (in septate/ subseptate) contain?
myometrium
also is vascular
difference between complete septate vs subseptate septum?
subseptate: entire septum has myometrium
complete septate: inferior septum has more fibrous connective tissue
septate and subseptate uterus have a strong associate with…
infertility:
myometrial tissue makes septum more contractile
abnormal endometrium resists successful implantation
division of endometrial cavity into smaller space increase premature birth risk
what is a septate uterus?
complete failure of uterine septum to reabsorb
complete duplication of uterine cavities but not duplication of uterine horns! (aka single uterine cavity divided by septum)
where does the septation extend to in a septate uterus?
external os of cervix
what does a perforated/ interrupted septum allow?
communication between the two sides of the uterine cavity
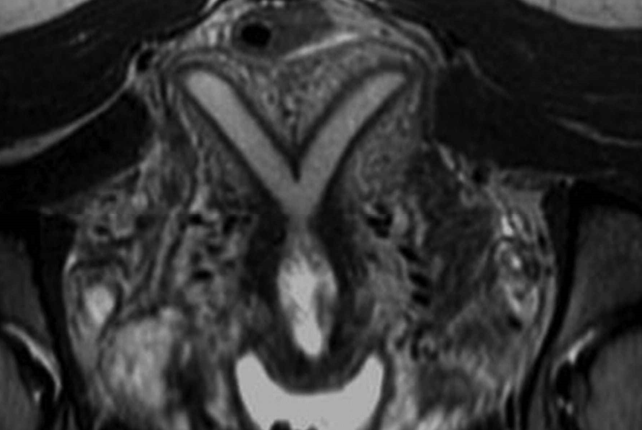
what uterine anomaly is this?
septate uterus
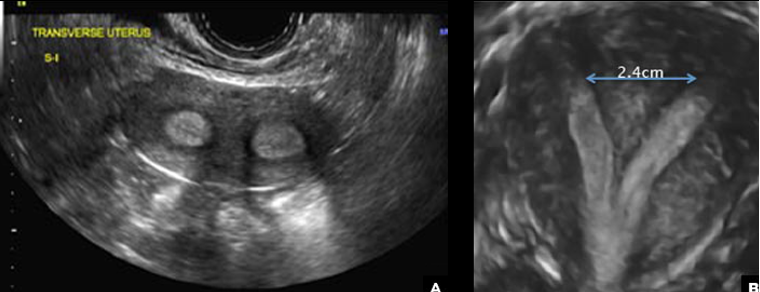
what uterine anomaly is this?
septate uterus
what is a subseptate uterus?
partial septum that does not extend to external os of cervix
what is the key to recognizing septate uterus?
evaluation of external uterine contour
may be normal (convex)
may be flat
may be slightly concave
what is it very important to differentiate a septate uterus from?
bicornuate uterus
what improves the obstetric outcomes of septate (class V) anomaly?
hysteroscopic removal of septum
what is an arcuate uterus?
considered to be a normal variant
mildest form of defect that causes bicornuate uterus
mild indentation of fundus into endometrial cavity
what may the external contour of an arcuate uterus look like?
may be:
convex (normal)
slightly concave (saddle shaped)
what is the ultrasound method for differentiating between septate and arcuate?
•Must use transvaginal approach
•Obtain 3D reconstruction of coronal plane
•Measure angle of cleft into endometrial canal
•Obtuse angle= arcuate uterus
•Acute angle= subseptate/septate uterus
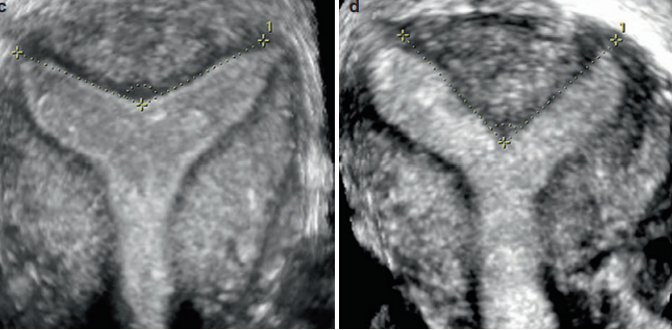
which is arcuate and which is septate?
left is arcuate, right is septate
What is DES?
Diethylstibestrol: synthetic estrogen used 1948-1971
what did DES do?
doubled risk of breast cancer
caused DES daughters: developmental anomalies of uterus, endometrial cavities and cervix
increased risk of developing female reproductive cancers
what is a T-shaped endometrial cavity?
result of DES
hypoplastic uterus
constriction of bands
widening of lower uterine segment
narrowing of fundal segment of endometrial canal
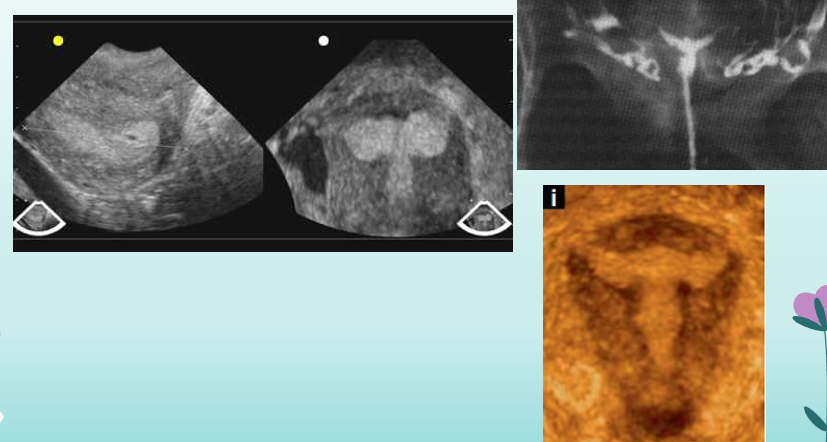
what uterine anomaly is this?
DES uterus