Biodiversity Bio
1/77
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Describe variation
No 2 species are the same
Variation exists between all organisms
Without variation there is no life
Who created the Morphological Concept
Carl Linnaeus
What is the Morphological Concept?
A classification of species based on look
How is binomial nomenclature formatted?
Genus the Species. 1st letter of genus is capitalized, species name italicized
What is the biological species concept?
Defines a species as a population whose members can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
Pros of BSC
simple, widely accepted definition
focus on reproductive isolation
Cons of BSC
cannot be applied to asexual organisms, extict species,
Species definition
A group of organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring
Speciation definition
formation of a new species from the splitting of one pre-existing species into two or more new species.
Possible causes of speciation
sympatric
allopatric
sudden event
Cause of speciation: Sympatric definition
Reproductive barrier preventing/limiting interbreeding between two pop.
Cause of speciation: allopatric definition
physical barrier that might exist between two pop
Peripatric
Small population of a species colonizes somewhere new and become isolated
Parapatric
Different environmental factors lead to a new species
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46
How many chromosomes do chimps have?
48
Karyogram?
Image of a karyotype
Karyotype?
Appearance and # of chromosomes in cell from tallest to smallest, with gender chromosomes at bottom.
When are karyograms taken?
metaphase of mitosis
Why are chimps and humans related?
Common ancestor
Genome?
all genetic material of an organism
What is single nucleotide polymorphism?
a variation in a single DNA building block, or nucleotide, found in at least 1% of the population
What can genome mapping be used for.
help us reclassify certain species into genuses and families they are more closely related to. AKA phylogenetics
E coli genome size
5 million
yeast genome size
12 million
fruit fly genome size
140 million genome size
frog genome size
??
People gene size
3 billion
What is evolution?
Change in heritable traits over time
What can evolution result in?
speciation
What is some evidence of evolution?
study of fossils
selective breeding
comparative anatomy
nucleotide and amino acid sequences
What is the use and disuse theory?
structures used to strengthen, develop and enlarge, while ones that are not used weaken.
Charles Darwin’s idea of evolution?
Comes from natural selection
certain traits are heritable and if they increase ability to survive they will be passed down to next generation
Cons of Darwin’s evolution?
likey to never be falsified
molecular phylogeny
comparative analysis of the sequences of the bases in DNA and RNA, and the amino acids in proteins to infer evolutionary history.
What is a mutation?
change in base sequence of DNA
Harmful vs helpful mutations?
harmful — not passed on , helpful passed on AKA natural selection
Selective breeding
Deciding favorable variations and reproducing them, selectively
Artificial Selection
choosing what organisms will reproduce together
What did Darwin theorize?
Since all the structures are the same, we must come from a common ancestor
What are homologous structures
structures derived from the same body part of a common ancestor
What is an piece of evidnece of divergent evolution?
homologous structures
When does divergent evolution occur?
when organisms arising from the same ancestral species adapt to different environmental conditions according to the pressures of natural selection.
What are analogous structures?
same function but do not necessarily come from the same body part and do not indicate a common ancestor
What is convergent evolution?
evolution that has happened from the pressures of environment not common ancestor
Analogous vs homologous structures
Homologous structures share a common evolutionary ancestor and may have different functions (e.g., a human arm and a bat wing), while analogous structures have similar functions but different evolutionary origins, evolving independently to solve a similar environmental challenge
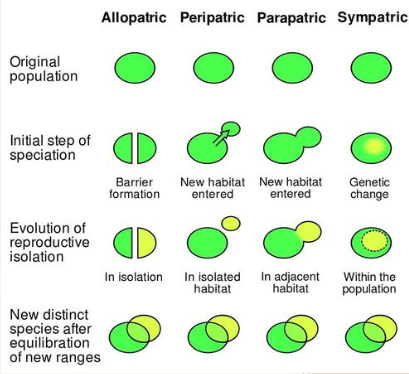
Reproductive Isolation
ue to one reason or another, part of a species becomes reproductively isolated from another
Examples of reprodcutive isolation
bonobos and chimpanzees
Two effects of reproductive isolation
no gene flow
two seperate gene pools
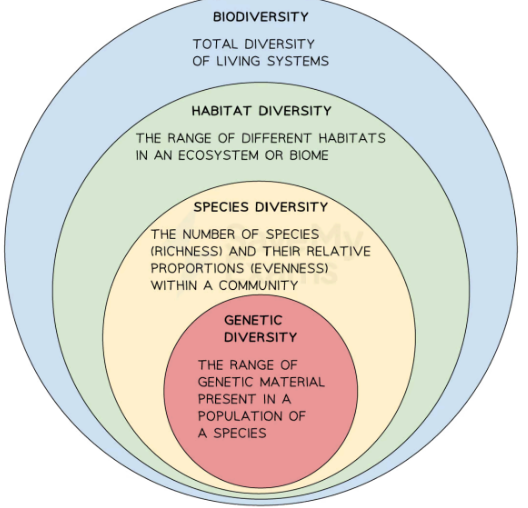
Definition of biodiveristy
variety of life in an area
what are the levels of biodiversity
ecosystem, species, and genetics
What is the highest level of biodiversity
ecosystem biodiversity
Species biodiversity?
richness and eveness/ number of species in a community
What is the lowest level of diversity
Genetic Diversity
Talk about the north island giant moa
hunted to extinction
anthropogenic extintion
what are in situ efforts
Protecting a species in its native habitat.
Ex Situ
Conserving species outside of their natural habita
examples of in situ efforts
establishing natural parks
rewiliding areas
examples of ex situ efforts
zoos
seed banks
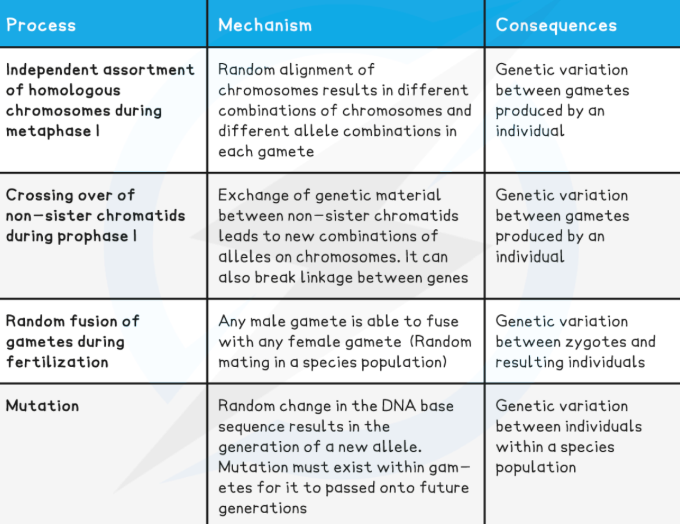
three main sources of variation
ranfom mutation, meiosis, sexual reproduction
what does meiosis enable in mutations
the production of haploid cells to make gametes
Variation exists fue to what process
random orientation during metaphase I
hello in asexually reproducing populations all memebrs of population are identical
What does meiosis mean in variation?
offsrpidng are varied in allels and random
How does variation promote survival?
survival of the fittest
variation that decrese survival decrease in number
What is a selective pressure?
external envioronmental factors that influences sucess of individuals in a population
examples of selective pressures
predation
disease
climate
When is it called a sexual dimorphism?
Morphological difference between male and female
Intersexual selection
One biological sex chooses which individual of the other sex to mate with
Intrasexual selection
Competition of members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex
sexual vs natural selection
ss is competition for mates while ns is competition for resources
examples of speciation
darwins finches
grand ranyon squirrels
things that decrease variation in a species
stabalizing selection
genetic drift
non random mating
allopatric speciation is also the same as
geographic isolation