Unit 1 Junior Year Biology (Macromolecules, Water, Biochemistry)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
1
New cards
what type of bond is between one molecule of water
polar covalent
2
New cards
what type of bond is between two molecules of water
hydrogen bonds
3
New cards
properties of water
versatile solvent, cohesion/adhesion, heat of vaporization (latent heat), high specific heat, less dense as a solid
4
New cards
versatile solvent
Water's ability to dissolve more solutes than any other solvent due to polarity
5
New cards
cohesion/adhesion
cohesion: water bonds to water
adhesion: water bonds to anything else
adhesion: water bonds to anything else
6
New cards
heat of vaporization
The amount of energy required for the liquid at its boiling point to become a gas/ latent heat/ ability to turn into a gas
7
New cards
high specific heat
ability to regulate temperature
8
New cards
less dense as a solid
ice floats
9
New cards
nonpolar hydrophobic does what with water
repels it
10
New cards
monomer
building blocks of polymers
11
New cards
polymer
three or more monomers covalently bonded
12
New cards
anabolic/synthesis reactions
building
stores energy by making bonds
enzyme is needed
water is removed
DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS/CONDENSATION REACTION
stores energy by making bonds
enzyme is needed
water is removed
DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS/CONDENSATION REACTION
13
New cards
dehydration synthesis
water is removed to bond molecules
14
New cards
catabolic/digestion reactions
releases energy
enzyme needed
water is added
HYDROLYSIS
enzyme needed
water is added
HYDROLYSIS
15
New cards
hydrolysis
adding water to break bonds
16
New cards
catabolic feeds...
anabolic
17
New cards
carbohydrates functions
immediate energy/raw materials
18
New cards
carbohydrates components
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
19
New cards
carbohydrates formula
ch2o bc 1:2:1 ratio of c:h:o
20
New cards
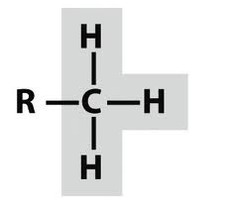
what is every point on a carbon hexagon
every point is a carbon unless labelled otherwise
21
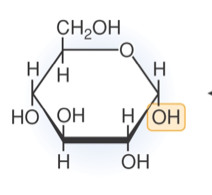
New cards
GLUCOSE STRUCTURE
C6 H12 O6 hexagon
22
New cards
carbohydrate monomer
monosaccharide
23
New cards
polymers of carbs
cellulose, chitin, starch, glycogen
24
New cards
polymers of carbs that give structure
animal chitin
plant cellulose
plant cellulose
25
New cards
polymer carbs storage
plant starch
animal glycogen
animal glycogen
26
New cards
how to build a sugar
hydroxyl groups connect
27
New cards
glycosidic linkage
2 sugars bonded covalently (by dehydration synthesis?)
28
New cards
a standalone 5 or 6 sided ring is usually a
sugar
29
New cards
alpha glucose
hydroxyl on bottom
30
New cards
beta glucose
hydroxyl on top
31
New cards
cellulose
cell walls of plants and fungi
32
New cards
chitin
exoskeleton of insects
33
New cards
lipid components
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
34
New cards
lipids functions
long term energy storage
insulation and protection
cell membrane
insulation and protection
cell membrane
35
New cards
why are lipids so energetic
have a lot of hydrogen and hydrogen has energy
36
New cards
monomers of lipids
no true monomers bc no repeating subunits
37
New cards
monomers of lipids if we are being lax about it
glycerol and fatty acids
38
New cards
classes of lipids
fats, oils, waxes, steroid hormones
39
New cards
GLYCEROL STRUCTURE
3 carbons attached to 3 OH
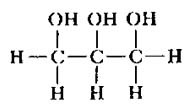
40
New cards
ester linkage
bond between hydroxyl of glycerol and carboxyl of fatty acid
41
New cards
saturated fats
carbon to carbon bonds are single covalent bonds
solid at room temperature
animal fats
solid at room temperature
animal fats
42
New cards
unsaturated fats
carbon to carbon bonds have at least one double bond
liquid at room temperature
plant fats
liquid at room temperature
plant fats
43
New cards
phospholipid structure
hydrophilic head
two hydrophobic fatty acid tails; one saturated, one unsaturated
two hydrophobic fatty acid tails; one saturated, one unsaturated
44
New cards
phoshpolipid where
cell membrane
45
New cards
head of a phospholipid composition
choline
phosphate
glycerol
hydrophilic
phosphate
glycerol
hydrophilic
46
New cards
protein components
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur
47
New cards
protein monomer
amino acid
48
New cards
How many amino acids are there?
20
49
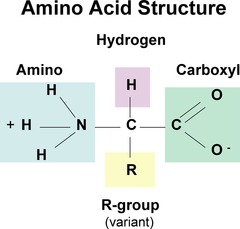
New cards
amino acid structure
Central carbon atom
Amino group
Carboxyl group
Single hydrogen
Variable R group
Amino group
Carboxyl group
Single hydrogen
Variable R group
50
New cards
protein polymer
polypeptide
51
New cards
protein function
enzymes but also EVERYTHING EXCEPT ENERGY, NEVER ENERGY BUT EVERYTHING ELSE
52
New cards
protein bond name
peptide bond
53
New cards
peptide bond
between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
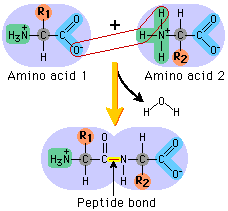
54
New cards
terminuses of a polypeptide chain
N terminus and C terminus
55
New cards
n terminus
exposed amino
56
New cards
c terminus
exposed carboxyl
57
New cards
primary structure of protein
single polypeptide chain
nonfunctional protein
nonfunctional protein
58
New cards
secondary structure of protein
single polypeptide chain
nonfunctional protein
local folding- alpha helices/beta pleated sheets bc of hydrogen bonds between amino and carboxyl groups
nonfunctional protein
local folding- alpha helices/beta pleated sheets bc of hydrogen bonds between amino and carboxyl groups
59
New cards
tertiary structure of protein
single polypeptide chain
nonfunctional protein
whole molecule folding bc of more hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, van der waals interactions
hydrophobic interior folds
nonfunctional protein
whole molecule folding bc of more hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges, van der waals interactions
hydrophobic interior folds
60
New cards
quaternary structure
three or more polypeptides bonded together
fully functional protein
fully functional protein
61
New cards
valence electrons are involved in-?
chemical reactions
62
New cards
most/96% of living matter is
c h o n
63
New cards
Most of the remaining 4% consists of
calcium, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur
64
New cards
ionic bonds
salts and transfer of electrons with charges
65
New cards
covalent bonds
sharing of electrons
66
New cards
polar covalent
unequal sharing of electrons
67
New cards
nonpolar covalent
equal sharing of electrons
68
New cards
How many bonds can carbon make?
4 covalent bonds
69
New cards
carbon is the
backbone of life
70
New cards
carbon shapes
linear, branched, rings
71
New cards
glucose chemical formula
C6H12O6
72
New cards
hydrocarbons
only contain carbon and hydrogen
nonpolar
nonpolar
73
New cards
functional groups
directly involved in chemical reactions
gives organic molecules their unique properties
gives organic molecules their unique properties
74
New cards
hydroxyl
alcohol, -OH
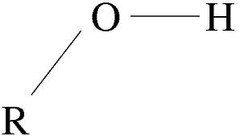
75
New cards
ribose structure
five carbon ring with surrounding Os and Hs
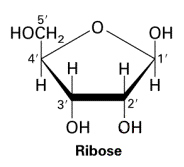
76
New cards
carbonyl locations
at end OR within organic molecule
end is aldehyde
within is ketone
end is aldehyde
within is ketone
77
New cards
carbonyl ketone
within carbon skeleton
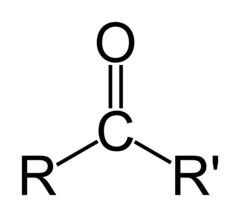
78
New cards
carbonyl aldehyde
end of carbon skeleton
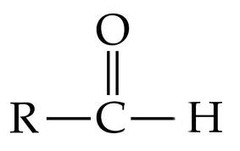
79
New cards
carboxyl
carboxylic acid
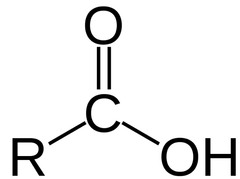
80
New cards
amino group
amines
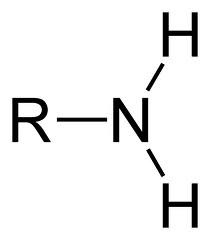
81
New cards
sulfhydryl
Thiols (R-SH)
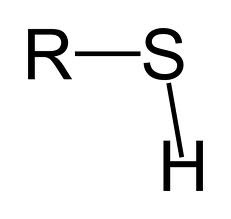
82
New cards
phosphate
organic phosphates
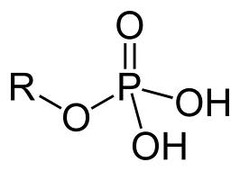
83
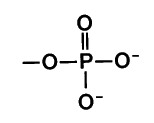
New cards
ionized phosphate form
no hydrogen it seems
84
New cards
methyl
alkanes r-ch3