anatomy exam 1
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
mizzou prof. hill
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Integumentary system
Consists of Skin, hair, nails. Protects against outside environment and maintains water balance.
Skeletal system
Consists of Bones and cartilage. Supports body and stores minerals.
Muscular system
Facilitates movement, pumps blood, moves materials, controls entrance and exit, generates heat. Consists of Skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle.
Nervous system
Transmits signals. Consists of Brain, Spinal cord, nerves
Endocrine system
Produces hormones to regulate metabolism, growth, reproduction, etc. Consists of Glands
Cardiovascular system
Carries nutrients and oxygen, removes wastes, consists of heart and blood vessels.
Lymphatic (immune) system
Guards against infection, consists of lymph vessels and glands, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, cells.
Respiratory system
Brings in oxygen, eliminates carbon dioxide, consists of nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, lungs
Digestive system
Food intake, water and nutrient absorption, elimination of wastes. consists of oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum
Urinary system
Filters blood, removes waste, consists of kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
Reproductive system
Females: mammary glands, ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, vagina. Males: testes, penis, glands, vas deferens.
Standard anatomical position
standing upright, head facing forward, arms at sides, palms forward, thumbs outward, feet flat, toes forward.
Anterior
Towards the front (ventral)
Posterior
Towards the back (dorsal)
Superior (cranial)
Toward the head
Inferior (caudal)
Toward the feet
Medial
Toward the midline of the body
Lateral
Away from the midline
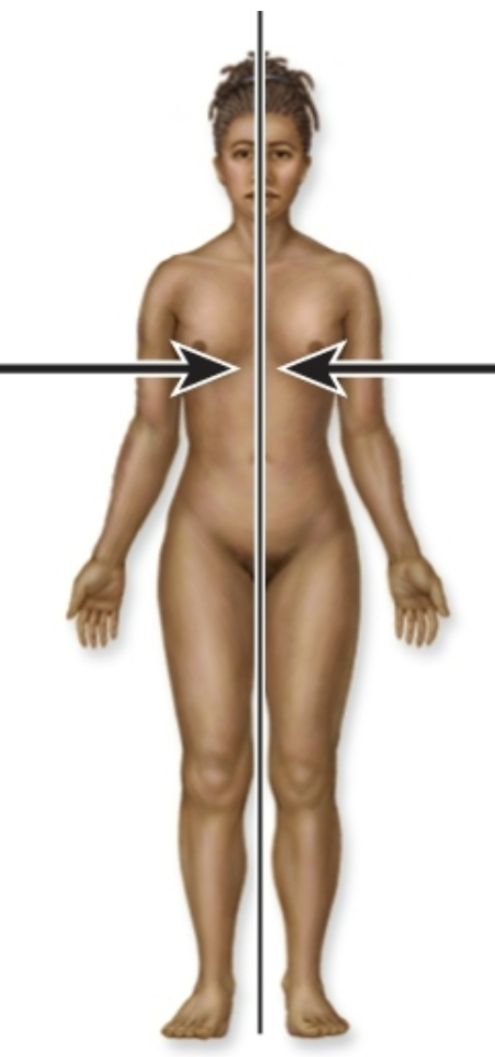
Is this medial or lateral?
medial
what is adipose tissue?
fat storage tissue
what is loose connective tissue?
flexible tissue
what is the integumentary system?
hair, skin, and nails. protect from outside environment
what does pollex mean?
thumb
what does manus mean?
hand
what does carpal mean?
wrist
what does antebrachial mean?
forearm
what does brachial mean?
arm
what does popliteal mean?
back of knee
what does femoral region mean?
thigh
what does crural mean?
leg
what does pes mean?
foot
what does sural region mean?
calf
what does hallux mean?
big toe
what are connective tissues?
tissue that fills internal spaces, provide structural support for other tissues, transport materials like blood, store energy
types of muscle tissue?
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
different shape names for epithelial tissue?
squamous (flat), cuboidal, columnar
where is simple squamous epithelium?
lungs, capillary beds, heart lining, blood vessel lining
where is simple cuboidal epithelium?
kidney tubules, ovary surface, glands
where is simple columnar epithelium?
stomach, intestines, uterine tubes
where is stratified squamous epithelium?
skin surface, mouth, vagina, anus, esophagus
where is stratified cuboidal epithelium?
glands
where is stratified columnar epithelium?
male urethra
where is ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
respiratory tract, trachea, bronchi
what types are loose connective tissue?
areolar, adipose, reticular
what is areolar tissue?
most widespread of loose connective tissue, in dermis and around organs
what is reticular loose connective tissue?
rare, in bone marrow, stroma of spleen, in lymph nodes
what are types of dense connective tissue?
regular, tendons, ligaments
what is regular dense connective tissue?
aligned, in tendons and ligaments
what is dermis dense connective tissue?
different planes in dermis, perissteum, perichondrium
what is elastic tissue?
stretchy, in arteries, trachea, and vocal cords
what are functions of the skin?
prevent h2o loss, homeostasis, vitamin d, sensory, excretion, damage
what are parts of the skin?
dermis, epidermis, hypodermis
what is the epidermis?
surface level, 4-5 layers
what is dermis?
strong and flexible, 2 layers, middle layer
what is hypodermis?
supports skin, stores fat and insulation, allows movement, areolar and adipose
what are eccrine glands?
main sweat glands that cool you down
what are apocrine glands?
glands that make odor sweat and ear wax
what are ceruminous glands?
apocrine specialized sweat glands that make ear wax
what are mammary glands?
glands in breasts that make milk and help with hormonal balance
What are the functions of the circulatory system?
transport, protection, regulation
what does transport mean in relation to the circulatory system?
It moves important substances all around the body: Oxygen from the lungs to cells, Nutrients from the digestive system to tissues, Hormones from glands to target organs, Wastes (like carbon dioxide and urea) to the lungs and kidneys for removal
what does protection mean in relation to the circulatory system?
It helps keep you healthy by: Carrying white blood cells to fight infection, Using antibodies to target germs, Using platelets and clotting factors to stop bleeding
what does regulation mean in relation to the circulatory system?
It helps maintain homeostasis by: Regulating body temperature, Maintaining pH levels, Controlling fluid balance in tissues
what are the four valves?
tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, aortic
what does the tricuspid valve do?
Prevents backward flow of blood from the right ventricle to the right atrium and allows blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle
what does the pulmonary valve do?
Prevents backward flow of blood from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery and allows blood to flow from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation
what does the mitral valve do?
Prevents backward flow of blood from the left ventricle to the left atrium and allows blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
what does the aortic valve do?
Prevents backward flow of blood from the left ventricle to the aorta and allows blood to flow from the left ventricle to the aorta and out to the body
What is the main function of the valves?
ensure that blood flows in the correct direction, preventing backflow and maintaining the heart's efficiency in pumping blood throughout the body.
what are the chordae tendineae?
tough, fibrous cords that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid and mitral valves, preventing valve prolapse during heart contraction
what are the papillary muscles?
cone-shaped extensions of the ventricular walls that attach to the chordae tendineae and help support and stabilize the heart valves.
what are the three steps of the cardiac cycle?
Ventricular Filling (Diastole), Atrial Systole, Ventricular Systole
what is Ventricular Filling (Diastole)?
The heart muscle is relaxed, Blood flows from the atria into the ventricles, AV valves (mitral & tricuspid) are open, Semilunar valves (aortic & pulmonary) are closed, Most of the ventricular filling happens passively during this phase.
Atrial Systole
The atria contract, They push the last bit of blood into the ventricles, AV valves are still open, Semilunar valves remain closed, This “tops off” the ventricles before they contract.
what is Ventricular Systole?
The ventricles contract, AV valves close (this produces the “lub” sound), Blood is pushed into the: Pulmonary trunk (right ventricle → lungs), Aorta (left ventricle → body), Semilunar valves open during ejection.
what is part of the Right Coronary Artery?
Artery branches: Right coronary artery (RCA), Right marginal artery, Posterior interventricular artery (posterior descending artery). Veins that accompany them: Small cardiac vein → runs with RCA/right marginal, Middle cardiac vein → runs with posterior interventricular artery
what is part of the Left Coronary Artery (LCA)?
Artery branches: Left coronary artery (LCA) splits into: Anterior interventricular artery (LAD), Circumflex artery. Veins that accompany them: Great cardiac vein → runs with LAD (anterior interventricular artery), Great cardiac vein continues along with the circumflex
what does the coronary circulation do?
supplies blood to the heart muscle itself
Identify the three layers of the blood vessels.
Tunica Intima, Tunica Media, Tunica Externa
what is the tunica intima?
Innermost layer, Made of endothelium (simple squamous epithelium) + thin connective tissue, In arteries, it may have an internal elastic membrane
what is the Tunica Media?
Middle layer, Made of smooth muscle + elastic fibers, Responsible for vasoconstriction and vasodilation, Usually the thickest layer in arteries
what is the Tunica Externa?
Outermost layer, Made of connective tissue, Protects and anchors the vessel
What are arteries?
Carry blood away from the heart, Thick tunica media, Smaller round lumen, No valves (except at heart exit), Withstand high pressure
what are veins?
Carry blood toward the heart, Thinner walls, Larger irregular lumen, Have valves (prevent backflow), Operate under low pressure
What are the functions of the lymphatic system?
fluid balance, immunity, fat absorption
what is lymph?
interstitial fluid that has entered lymphatic vessels (water, protein, white blood cells, lipids)- pretty much recycled fluid
what are the major lymphatic organs and structures?
red bone marrow, thymus, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils
what is red bone marrow?
produces all blood cells, b cells mature here
what is the thymus?
t cells mature here, most active in childhood
what is the function of lymph nodes?
filter lymph, contain immune cells, swell during infection
what is the spleen?
filters blood (not lymph), remove old red blood cells, stores platelets, immune surveillance
what do the tonsils do?
Trap pathogens entering through mouth/nose
where does lymph drain?
Right Lymphatic Duct or Thoracic Duct (Left Lymphatic Duct)
what does the Thoracic Duct (Left Lymphatic Duct) drain?
Left arm, Left head/neck, Left thorax, All regions below the diaphragm (both legs, abdomen). Empties into Left subclavian vein
what does the Right Lymphatic Duct drain?
Right arm, Right side of head/neck, Right thorax. Empties into: Right subclavian vein
what are the functions of the respiratory system?
Gas exchange (O₂ in, CO₂ out), Regulates blood pH, Voice production, Olfaction, Filters, warms, moistens air
what is the pleural cavity?
Space between visceral and parietal pleura, Contains pleural fluid, Reduces friction & maintains lung expansion
what are the features of the right lung?
3 lobes (superior, middle, inferior), Wider and shorter, Horizontal fissure present
what are the features of the left lung?
2 lobes, Cardiac notch, Lingula
what are the steps of ventilation?
inspiration and expiration