EKG: Intro to Single Lead Interpretations
1/57
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
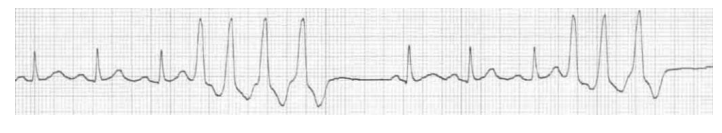
Normal Sinus Rhythm
What does this EKG show?
60-100, normal
Characteristics of Normal Sinus Rhythm EKG:
Rate = __-___ bpm
Rhythm = regular
Axis = -
Interval = ________
Hypertrophy = -
Morphology = -
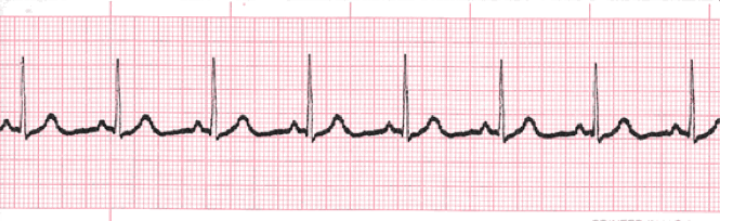
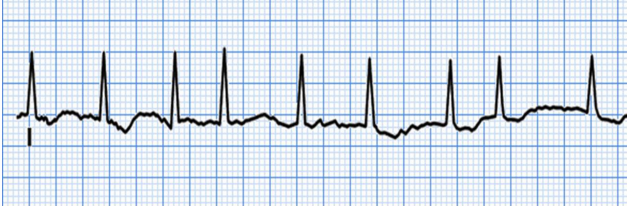
Sinus Bradycardia
What does this EKG show?
60, regular
Characteristics for Sinus Brady EKG:
Rate = < __ bpm
Rhythm = _______
Axis = -
Intervals = normal
Hypertrophy = -
Morphology = -
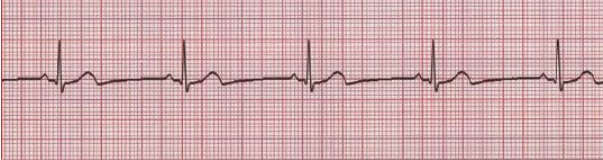
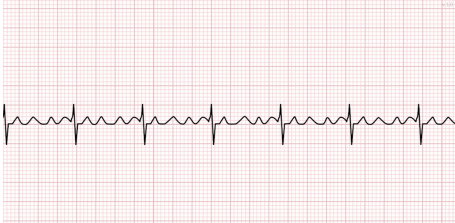
Sinus Tachycardia
What does this EKG show?
100, intervals, morphology
Characteristics of Sinus Tachy EKG:
-Rate is > ___ bpm
-Rhythm, __________, and ___________ are normal
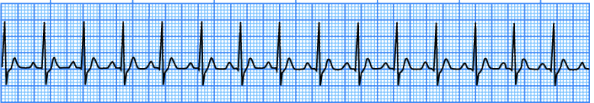
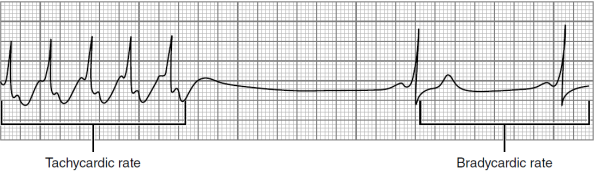
Sinus Arrhythmia/Dysrhythmia
What does this EKG show?
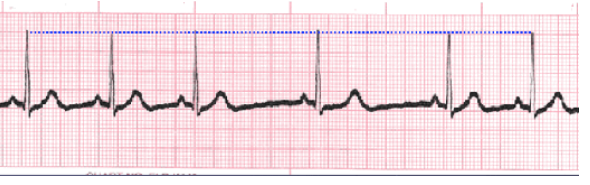
rate, 3, intervals
Characteristics of Sinus Arrhythmia/Dysrhythmia EKG:
-Normal _____, intervals, and morphology
-R-R intervals vary by _ or more _______
-Irregular rhythm
SVT
What does this EKG show?
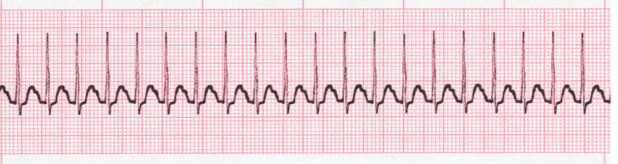
cannot, P, increased, merge
Characteristics of Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) EKG
-________ differentiate between _ and T waves
-Has an _________ heart rate (150-250 bpm)
-Rhythm and morphology are normal
-Intervals are irregular, for the P and T waves ______ together
-3 types: AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT), AV reciprocating tachycardia (AVRT), and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Long QT
What does this EKG show?
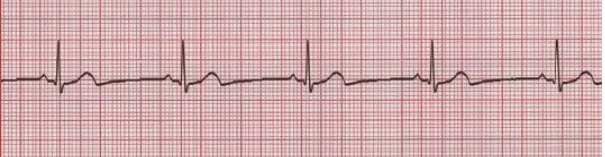
II, 5, 6, U, .44, .46, .5, regular, QT
Characteristics of Long QT
-Measured in lead __, V_, or V_
-Large _ waves should be included (+1mm)
-QTc for males > .__, and > .__ in females. A QTc above ._ greatly increases your risk of torsades
-Rate and rhythm are _______, but the __ interval is irregular
Ventricular Tachycardia
What does this EKG show?
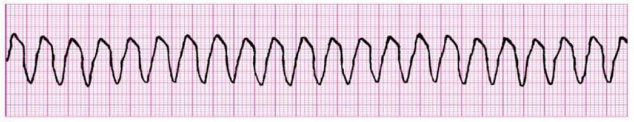
p, QRS, 100, irregular
Characteristics of Ventricular Tachycardia EKG
-No _ wave (atria) and wide ___ (ventricles)
-Rate is usually > ___ bpm
-Rhythm and hypertrophy are regular
-Intervals and morphology are ___________
Torsades De Pointe
What does this EKG show?
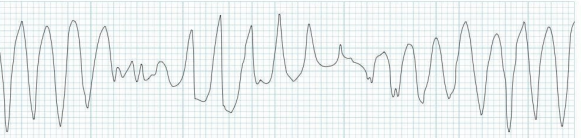
ventricular, QT, QRS, U, 100, intervals
Characteristics of Torsades De Pointe on EKG
-A type of ________ tachycardia associated with long __, twisting of ___ around isoelectric line, and large _ waves may precede TdP
-Rate is > ___ bpm
-Rhythm, ________, and morphology are irregular
Ventricular flutter
What does the EKG show?
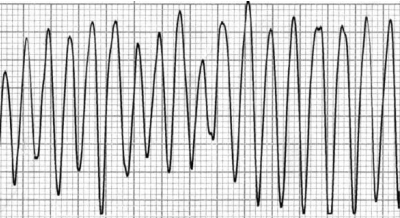
tachycardia, rhythm, 200, intervals
Characteristics of Ventricular Flutter on EKG
-A type of ventricular ___________ characterized by a loss of organization or _______
-Extremely high heart rate (+ ___ bpm)
-Irregular rhythm, __________, and morphology
Ventricular Fibrillation
What does this EKG show?
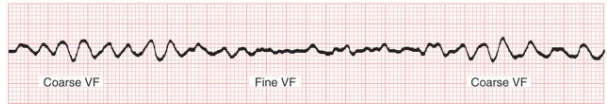
3, beat, irregular
Characteristics of Ventricular Fibrillation
-Coarse V Fib = waveforms > _ mm
-Fine V Fib = waveforms < 3 mm
-Rate = no actual ____
-Rhythm, intervals, and morphology are __________
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW)
What does this EKG show?
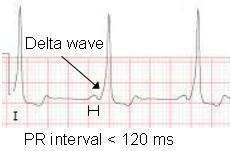
reentrant, delta, morphology
Characteristics of Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) on EKG
-Congenital condition causing a _________ current resulting in a _____ wave, which is a triangle before starting the QRS complex
-Rate, rhythm, and intervals are regular
-____________ is irregular
Atrial Flutter
What does this EKG show?
atrium, 200, saw tooth, irregular
Characteristics of Atrial Flutter on EKG
-A reentry current within the right _______, meaning the current is stuck in the atria
-Atrial rate can be ____+. Typically exhibits a 3:1 or 4:1 ___ ______ pattern, meaning there are 3 or 4 P waves before a QRS complex
-Rate, intervals, and morphology are ________
-Rhythm can be regular or irregular
Atrial Fibrillation
What does this EKG show?
depolarization, 350, irregular
Characteristics of Atrial Fibrillation on EKG
-Uncoordinated ____________ of the atria, where the atrial rate can be +___. Caused by twitching of the atria
-Rate, rhythm, intervals, and morphology are __________. Rhythm could also be regular
Sick Sinus Syndrome
What does this EKG show?
pause, bradycardic, irregular
Characteristics of Sick Sinus Syndrome on EKG
-Sinus _______ followed by __________ response
-Rate, rhythm, and intervals are __________
-Morphology is regular
R, first, drop, Wenkebach, Ps, Mobitz, Ps, third
The Heart Block Poem
-If the _ is far from P, then you have ____ degree
-Longer, longer, longer, _____. Then you have ___________
-If some __ don’t get through, then you have ______ II
-If __ and Qs don’t agree, then you have ____ degree
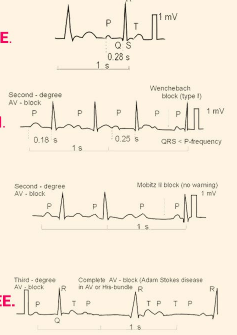
1st Degree AV Block
What does this EKG show?
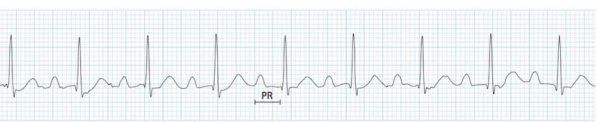
long, consistent
Characteristics of 1st Degree AV Block on EKG
-PRI is > .2 sec, so it’s _____ but ________.
-QRS complex follows every P-wave
-Rate, rhythm, and morphology are regular
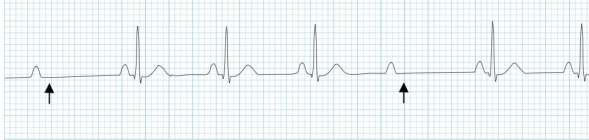
Wenckebach (2nd degree AV block)
What does this EKG show?
increases, P, QRS
Characteristics of Wenckebach (2nd Degree AV Block) on EKG
-PRI _________ in duration until there is a _ wave without a subsequent ___ complex
-Rate and morphology are regular
-Rhythm and intervals are irregular = irregular PRI and dropped QRS
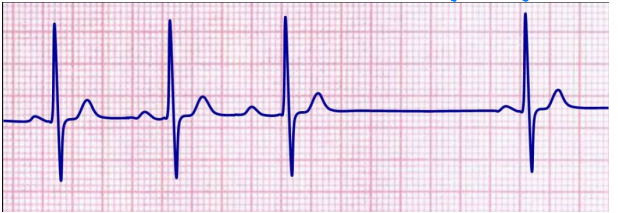
Mobitz Type II (2nd Degree AV Block)
What does this EKG show?
PRI, QRS
Characteristics of Mobitz Type II (2nd Degree AV Block) on EKG
-Normal ___ but dropped ___ complex
-Consistent PRI, but one P wave will be missing its QRS complex
-Irregular rhythm
-Regular rate and morphology
3rd Degree AV Block
What does this EKG show?
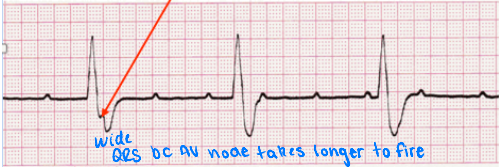
SA, independent, P, buried
Characteristics of 3rd Degree AV Block on EKG
-__ node and AV node are completely ___________ of each other
-It is the only heart block where the _ waves can be _______
-Irregular rate, rhythm, intervals, and morphology
Paced
The small vertical line seen on the EKG is indicative of a _________ heartbeat
-the position of the vertical line speaks to where the pacemaker was placed in the heart
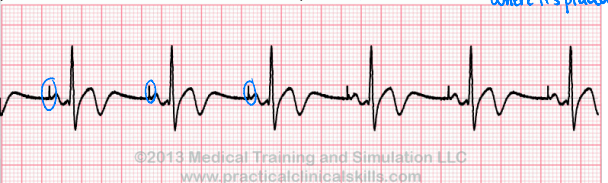
Junctional Escape Rhythm
What does this EKG show?
bradycardic, P, QRS, wide
Characteristics of Junctional Escape Rhythm on EKG
-Rate is ____________
-_ wave is absent, inverted, or may be seen after ___. The QRS complex also has an abnormal interval and is _____
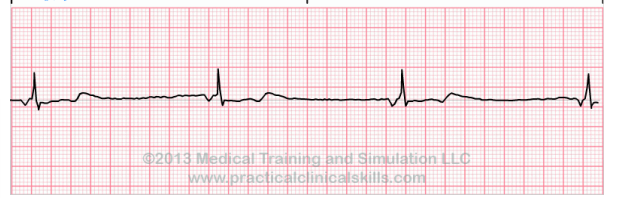
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
What does this EKG show?
absent, QRS, faster
Characteristics of Accelerated Junctional Rhythm on EKG
-P wave is _______, inverted, or may be seen after ___
-The AV node is working _______ than normal, producing a regular heart rate of 60-100 bpm
-QRS interval is irregular, and so is the P wave morphology
R-on-T Phenomenon
What does this EKG show?
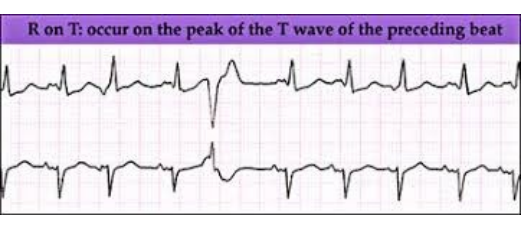
ectopic, T
Characteristics of R on T Phenomenon on EKG
-Superimposed _______ beat on the _ wave
-Regular rate, rhythm, and intervals
-The only abnormality is found within the T wave
Hypokalemia
What does this EKG show?
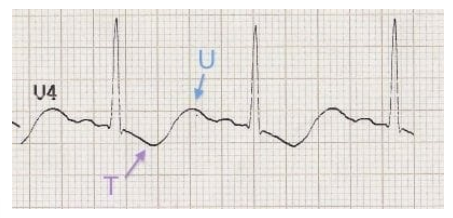
T, U
Characteristics of Hypokalemia on EKG
-Inverted or flat _ wave typically with prominent _ waves
-Regular rate, rhythm, and intervals
-Irregular T wave morphology
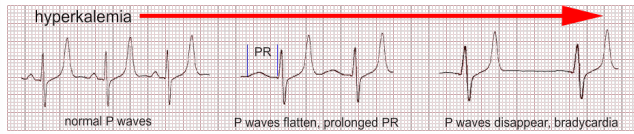
Hyperkalemia
What does this EKG show?
-Peaked T waves
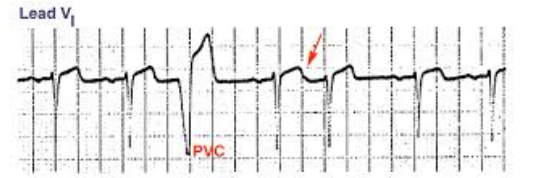
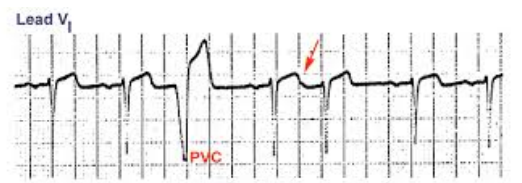
Premature ventricular contractions (PVC)
-Ectopic beat with an abnormally wide and long QRS complex
-Abnormal morphology
-Premature
Extrasystole
A type of ectopic beat characterized by the absence of a beat
Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC)
-Ectopic beats characterized by an extra p wave
-Can be hidden within the waves, making it hard to see
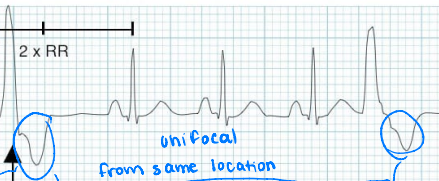
Unifocal
Are these unifocal or multifocal?
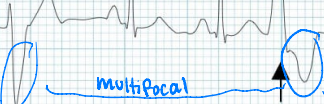
Multifocal
Are these unifocal or multifocal?
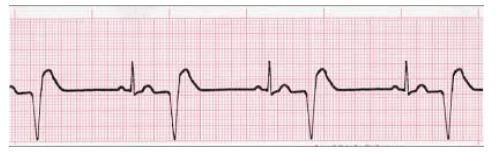
Bigeminy
What can be seen here?
-Refers to the presence of a PVC after each normal beat
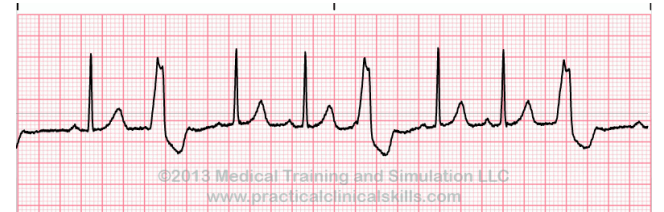
Trigeminy
What can be seen here?
-Refers to the presence of a PVC after 2 normal beats
Quadrieminy
What can be seen here?
-Refers to the presence of one PVC after every 3 normal beats
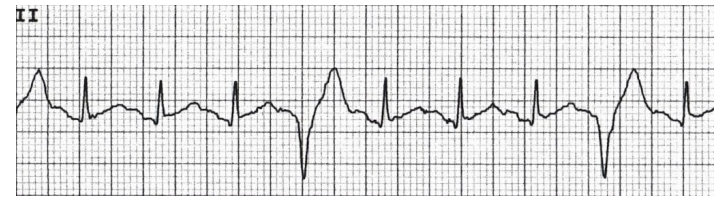
Couplet
When two PVCs are next to each other, this is called a ____________
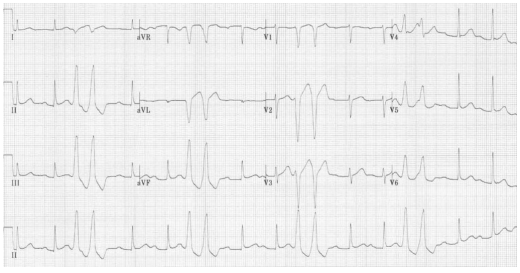
Triplet
When three PVCs are next to each other, this is called a _______
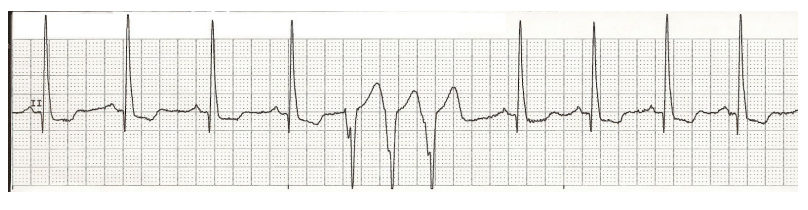
Non-Sustained VT
What can be seen here?