1/3 Kaminski In-Class Review
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Eye drops contain how many drops/mL unless otherwise specified?
20 drops/mL
What is the formula for BSA?
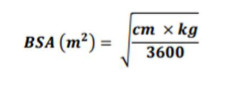
Microbial Contamination
Source-
Consequences-
source: microbes( bacteria, etc.)
consequence: infection
Chemical Contamination
Source-
Consequences-
source- chemicals (or bacteria that produce chemicals)
consequence- immunogenic/ toxic effects
Physical Contamination
Source-
Consequences-
source: rubber from stoppers, glass, particulate matter
consequence- occlusion of blood vessels, thrombosis, death, phlebitis
Personal Preparation for Compounding:
What should be done with jewelry?
Can nail polish or fake nails be worn?
Should you remove your outdoor clothes (Ex: coat)?
Should you remove makeup?
If I have a respiratory infection, is it okay if I compound as long as I’m wearing a face mask?
take it ALL off
NOPE
YEPP
YEPP
NOOOOOOOOOO
What conditions would preclude someone from going in IV room?
rashes
sunburns
weeping sores
respiratory infections
conjunctivitis
What is the order for garbing?
shoes
hair
face mask
wash hands
gown
sanitize hands
glove
disinfect gloves
How do we properly wash our hands?
at least 30 seconds
warm water
clean up to forearms, get under fingernails
dry using lint-free towel
water should run DOWN FINGERS TO ELBOWS
most common product is chlorhexidine gluconate
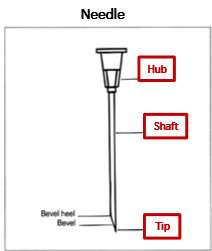
Critical Site(s) of a Needle
hub
tip
shaft
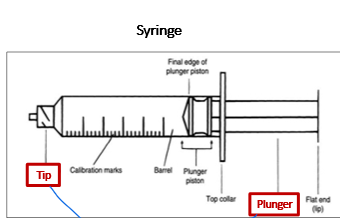
Critical site(s) of a syringe
tip
ribs of plunger
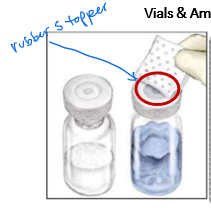
Critical site(s) of a vial
rubber closure
Critical site(s) of a ampule
neck
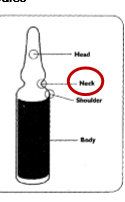
Critical site(s) of a bag
additive/injection port

Quality Assurance is ________________.
a. proactive
b. retroactive
c. reactive
a- proactive
Quality Control is ________________.
a. proactive
b. retroactive
c. reactive
b- retroactive
Quality Assurance includes which of the following?
SATA:
a. policies
b. sampling
c. testing
d. procedures
a, d
Quality Control includes which of the following?
SATA:
a. policies
b. sampling
c. testing
d. procedures
b, c
Personal Training/ Evaluation should be performed every _____________.
a. month
b. 6 month
c. year
c- year (12 months)
A finger-tip test to analyze hand hygiene is performed in what room after what?
Performed in ante room after handwashing
For Initial finger-tip sampling to test hand hygiene, how many samples is/are needed? How many subsequent samples?
Initially- 3
Subsequently-1
All finger-tip tests are performed every ____ months.
6
To pass the finger-tip test for hand hygiene what cfu must you have?
0
To pass the finger-tip test for aseptic technique what cfu must you have?
less than or equal to 3
How many samples do you need to take initially and subsequently for the finger-tip test analyzing aseptic technique?
1
Media fill tests are performed every ____ months.
6
What’s passing and what’s failing for a media fill test?
pass= clear
fail= turbid (growth)
Air sampling tests are done every ____ month(s).
6
What is the frequency for surface sampling tests?
monthly
True/ False: Air sampling and surface sampling tests are performed in all classified areas.
true
Sporicidal cleaning is performed every _____________.
a. 6 months
b. year
c. month
d. day
c- month
What is cleaned daily?
floors!!!!!
PEC
equipment/trays
What is cleaned monthly?
walls
doors
storage shelves/bins
ceilings if necessary
Hypotonic solutions shift water ___________________.
a. into the cell
b. out of the cell
c. not at all
a
Hypertonic solutions shift water ___________________.
a. into the cell
b. out of the cell
c. not at all
b
Isotonic solutions shift water ___________________.
a. into the cell
b. out of the cell
c. not at all
c
Risks of
hypotonic solutions
hypertonic solutions
isotonic solutions
hypo- hypotension, hemolysis, hyponatremia (think anything hypo causes hypo)
hyper- circulatory overload, osmotic demyelination, venous irritation
iso- fluid overload
Examples of
hypotonic solutions
hypertonic solutions
isotonic solutions
hypo- ½ NS, ¼ NS, D2.5W (anything <0.9% Saline or <5% Dextrose in Water)
hyper- D10W, 5% dextrose in Lactated Ringers, 3% saline (anything >0.9% Saline or >5% Dextrose in Water)
iso- NS, Ringer’s Solution, D5W
BWFI and bacteriostatic NS is ONLY used for ______________.
reconstitution
BWFI and bacteriostatic NS should not be used in ______________ or for what kind of administration?
not used in neonates
not for IV administration
Is water (SWFI, BWFI) isotonic?
Should water be used for direct patient administration?
NOT isotonic
NOT for direct patient administration
A Large Vol parental is >______mL.
>100 mL
A Small Vol parental is <______mL.
<100mL
IV pushes, boluses, IV piggybacks, and intermittent infusions are typical administration methods of ___________ volume parentals.
small
Continuous infusions are a typical method of administration for __________ volume parentals.
large
Do NOT use __________ for patients in a diabetic coma.
dextrose
Timing for
IV push
Intermittent Infusions
Continuous Infusions
IV push: seconds-minutes
Intermittent Infusions: minutes-hours
Continuous Infusions: constant
What are the typical diluents for reconstitution?
SWFI
BWFI
NS
Bacteriostatic NaCl 0.9%
What are the typical vehicles small/large volume for administrations?
NS
D5W
Lactated Ringers
Additives are used to do what 4 things?
maintain sterility
maintain solubility
maintain stability
ease administration
“SASS”
True or False: Additives have some therapeutic efficacy.
FALSE- additives must NOT INTERFERE w/ therapeutic efficacy
Pyrogens are any foreign substance to the body that cause _________.
fever
Endotoxins are a type of pyrogen that are found in the walls of gram ______ bacteria.
a. neg
b. pos
a- negative