Weekly Quiz Questions
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
A student new to neuroscience research is practicing recording resting membrane potentials from giant squid axons. During one of the trials, the resting membrane potential, which is normally around -60 mV, measured -15 mV. Which statement best describes what might have occurred during the experiment?
1. The student added too much potassium to the extracellular solution.
2. The student added too much sodium to the extracellular solution.
3. The student did not add enough potassium to the extracellular solution.
4. The student did not add enough sodium to the extracellular solution.
5. The student added too little potassium and too much sodium to the extracellular solution.
1. The student added too much potassium to the extracellular solution.
When the extracellular potassium concentration increases, it leads to a higher concentration gradient favoring potassium efflux out of the cell. This efflux of positively charged potassium ions causes the cell to become more positive, leading to depolarization and a shift towards a less negative resting membrane potential.
Studies of the ionic basis of the action potential in squid giant axon found that
1. decreasing sodium outside the cell decreases the size of the action potential.
2. decreasing sodium outside the cell increases the size of the action potential.
3. decreasing potassium outside the cell decreases the size of the action potential.
4. decreasing potassium outside the cell increases the size of the action potential.
5. manipulating sodium has large effects on both the size of the action potential and the resting membrane potential.
1. decreasing sodium outside the cell decreases the size of the action potential.
Hodgkin and Katz proposed that sodium was the predominant ion associated with the firing of an action potential because
1. the membrane potential approaches the Na+ Nernst potential during the rising phase.
2. the membrane potential approaches the Na+ Nernst potential during the falling phase.
3. sodium ions can move more quickly than other ionic species.
4. sodium ions are the only ions that can flow into the nerve cell body.
5. the sodium gradient explains the rising phase, falling phase, and overshoot of the action potential.
1. the membrane potential approaches the Na+ Nernst potential during the rising phase.
Which observation was not observed in Hodgkin and colleagues' voltage-clamp study of squid action potentials?
1. Capacitive currents in response to hyperpolarizing voltage steps
2. Capacitive currents in response to depolarizing voltage steps
3. A transient inward current as a result of depolarization
4. A sustained outward current as a result of hyperpolarization
5. A delayed outward current as a result of depolarization
A sustained outward current as a result of hyperpolarization
A researcher conducts a voltage clamp experiment on a giant squid axon and collects the data shown in the graph. At what membrane potential was the cell clamped?
1. 0 mV
2. Sodium's equilibrium potential
3. -65 mV
4. Potassium's equilibrium potential
5. -110 mV
2. Sodium's equilibrium potential
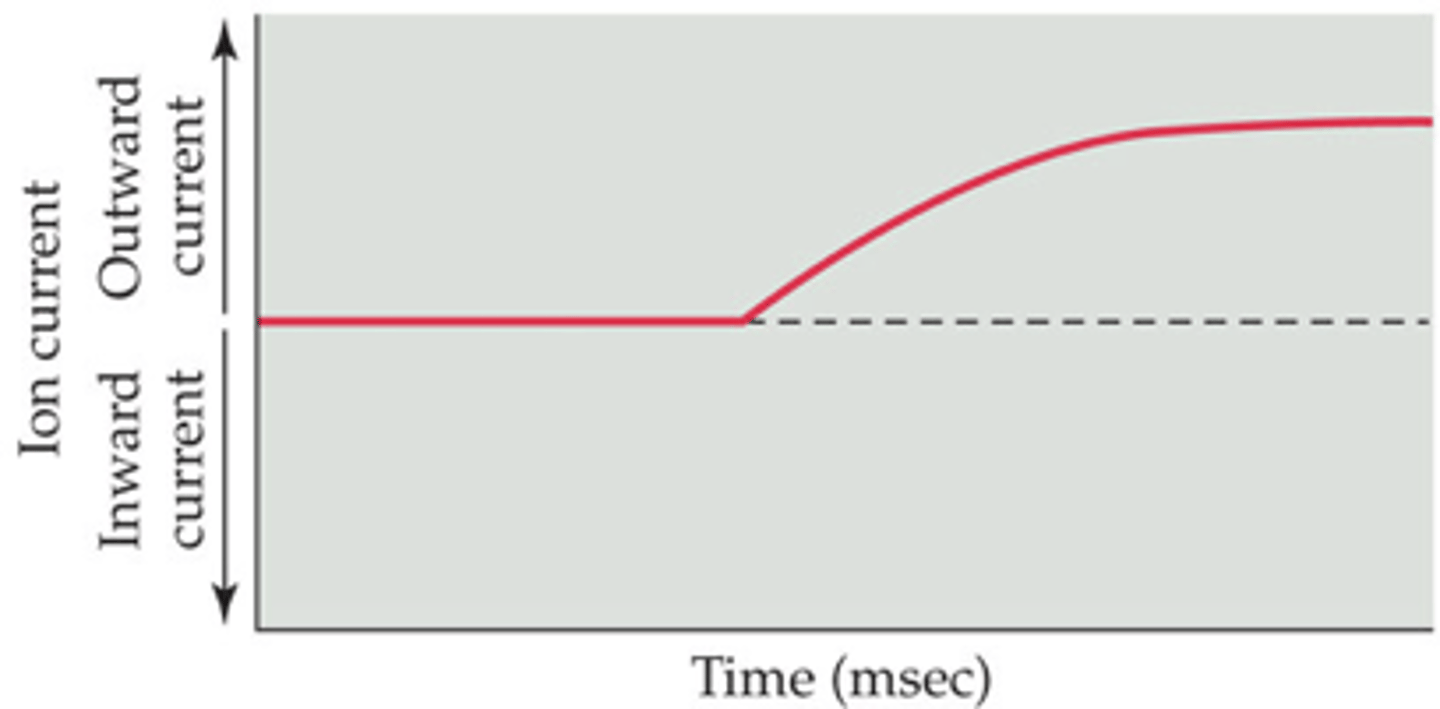
Which observation is not evidence that helped to identify sodium as the early current of the action potential?
1. The current declined when there was decreased driving force on sodium fluxes.
2. The current disappeared near the Nernst potential for sodium.
3. The early current was blocked by tetrodotoxin.
4. The early current was unaffected by tetraethylammonium.
5. When the late current was blocked, the reversal potential of the inward current shifted to a negative membrane potential.
5. When the late current was blocked, the reversal potential of the inward current shifted to a negative membrane potential.
Which of the following is not integral to the action potential waveform?
1. A change in permeability of the membrane to sodium
2. A change in permeability of the membrane to potassium
3. A transient increase in the sodium current
4. An initial decrease in the potassium current
5. A "self-activating" aspect to the rise in the sodium current
4. An initial decrease in the potassium current
Hodgkin and Huxley's mathematical model?
The action potential can be reconstructed based entirely on the time course and amplitudes of the ionic conductances
Which statement on the rising or overshoot phase of the action potential is
:1. The time from threshold to maximum depolarization is essentially instantaneous (i.e., too fast to be measured accurately with current electronics).
2. A negative feedback loop leads to a regenerative depolarization that would increase continuously if unchecked.
3. The degree of depolarization is limited in part by the declining driving force on potassium entry.
4. The degree of depolarization is limited in part by the inactivation time course for the sodium current.
5. The degree of depolarization is limited in part by the inactivation time course of the potassium current.
4. The degree of depolarization is limited in part by the inactivation time course for the sodium current.
Which statement does not stem from the application of Ohm's law to ionic conductances?
1. The driving force on the ionic current is the difference between the membrane potential and the ion's Nernst potential.
2. The conductance for an ion is inversely proportional to the resistance of the membrane to the passage of that ion.
3. All permeant ions experience an identical driving force at each time point during the course of an action potential.
4. The conductance for each ion can be calculated based on the measured ionic currents and the calculated driving force.
5. The calculations stemming from Ohm's law can be used to derive a mathematical description of the action potential.
3. All permeant ions experience an identical driving force at each time point during the course of an action potential.
In the phase labeled D, _______ ions are moving _______ the cell.
1. potassium; into
2. sodium; into
3. potassium; out of
4. sodium; out of
5. both sodium and potassium; out of
3. potassium; out of - electrochemical equilibrium
The squid giant axon is useful in neuronal studies because
1. Its axon is easy to penetrate with recording electrodes because it is so long.
2. The cytoplasm in the axon can be extruded, thus allowing studies of its composition.
3. Multiple synapses between the nerve cells make them easy to study.
4. Its giant ion channels allow insertion of recording electrodes into the channels.
5. The axon has fewer ion channels, which simplifies the analysis of observations.
2. The cytoplasm in the axon can be exposed, thus allowing studies of its composition.
A dull probe stimulates a Pacinian corpuscle. An electrode is placed midway down the axon, and action potentials are recorded. After one second, the probe is pushed with greater force. What change will occur in the recording?
1. The height of action potentials will increase.
2. The frequency of action potentials will increase.
3. The frequency of action potentials will decrease.
4. The resting membrane potential will increase.
5. The threshold potential level will increase.
2. The frequency of action potentials will increase.
Voltage clamp data, in which investigators analyzed membrane conductances during action potentials, showed all of the following except:
1. the sodium current was rapidly activated by depolarization.
2. the potassium current activates on a comparatively slow time scale of a few ms.
3. at certain potentials, there can be zero current even with a large conductance.
4. depolarization leads to a time-dependent inactivation of the sodium current.
5. depolarization leads to a time-dependent inactivation of the potassium current.
5. depolarization leads to a time-dependent inactivation of the potassium current.
Which statement regarding refractory periods is true?
1. They allow neurons to fire an unlimited number of action potentials per unit of time.
2. During the refractory period the cell requires a less intense stimulus to reach the threshold.
3. The refractory period arises in part due to the increase in sodium conductance across the membrane.
4. The refractory period arises in part due to the decrease in potassium conductance across the membrane.
5. The refractory period ends when the sodium channels are no longer inactivated.
5. The refractory period ends when the sodium channels are no longer inactivated.
Which treatment was shown to eliminate the early inward current in squid giant axons?
1. Removal of external sodium
2. Doubling of external sodium
3. Removal of external potassium
4. Doubling of external potassium
5. Removal of all external cations
:1. Removal of external sodium
A surprising result that emerged from the molecular and genetic analysis of ion channels was the
1. size of the individual ion channels.
2. voltage-dependence of the ion channels.
3. time-dependence of the ion channels.
4. discovery of differences in ionic selectivity.
5. sheer number of different ion channels.
5. sheer number of different ion channels.
Which statement regarding the diversity of ion channels is false?
1. With only six different types, potassium channels are the least diverse channel type.
2. There are at least 10 different sodium channels in humans.
3. Sodium channels that do not inactivate have been found.
4. There are least 10 different types of calcium channels.
5. Calcium channels serve diverse functions such as influencing action potential shape and mediating the release of neurotransmitters.
With only six different types, potassium channels are the least diverse channel type.
Which ligand-gated ion channel is regulated primarily by an intracellular signal?
1. Glutamate receptor
2. The potassium-activated calcium channel
3. The glutamate receptor
4. The cAMP- and cGMP-gated ion channels
5. The acid-sensing ion channels
4. The cAMP- and cGMP-gated ion channels
Which of the following was observed in studies measuring the efflux of radioactive sodium from the squid giant axon?
1. Dramatic increase of efflux during a brief train of action potentials
2. Sharp drop in efflux when intracellular potassium was removed
3. Dependence of efflux upon the presence of ATP
4. Decrease of efflux when ATP synthesis was increased
5. No recovery when potassium or ATP was restored.
3. Dependence of efflux upon the presence of ATP
The current flowing through individual ion channels
1. was visualized with the advent of the voltage clamp in 1956.
2. exhibits the same time course across all individual sodium channels.
3. reflects the passage of thousands of ions per millisecond.
4. has a different voltage dependence than the macroscopic ionic current has.
5. has a different reversal potential than the macroscopic ionic current has.
3. reflects the passage of thousands of ions per millisecond.
Which statement is a common, defining feature of membrane-bound active ion transporters?
1. All are electrogenic.
2. All transport two or more different ions.
3. All catalyze the conversion of ATP to ADP.
4. All are able to move at least one ion against its concentration gradient.
5. All move sodium across the membrane.
4. All are able to move at least one ion against its concentration gradient.
The paddle-like, charged transmembrane domains of potassium channels may
1. serve as a plug or inactivation gate.
2. be the primary voltage sensors.
3. confer ion selectivity to the channel.
4. enable the aggregation of channel subunits into functional channels.
5. dehydrate the ions as they cross the membrane.
2. be the primary voltage sensors.
Which statement regarding photoreceptor cells is true?
1. Like typical sensory neurons, they fire action potentials when the cell depolarizes to threshold in response to stimuli.
2. Unlike typical neurons, their resting membrane potential is more negative, usually around -100mV.
3. Unlike typical neurons, cation channels are open at rest, allowing the influx of sodium and calcium.
4. Unlike typical neurons, neurotransmitter release is dependent on an influx of potassium ions.
5. Unlike typical neurons, they hyperpolarize in response to a stimulus due to opening of chloride channels.
3. Unlike typical neurons, cation channels are open at rest, allowing the influx of sodium and calcium.
The death of retinal cells in retinitis pigmentosa is most likely caused by
apoptosis
The main reason that rods are more sensitive to light than cones is that
1. the photopigment of rods is much more sensitive to light than the photopigment used in cones.
2. the eye contains 1000 times as many rods as cones.
3. the rod transduction mechanism provides greater signal amplification.
4. rods are sensitive to a much broader range of wavelengths.
5. rods have many different types of opsin proteins.
the rod transduction mechanism provides greater signal amplification.
By which mechanism are rod signals transmitted in conditions of low light?
Rod bipolar cells synapse on amacrine cells, which in turn synapse on cone bipolar cells.
You measure changes in membrane potential in an ON-center bipolar cell that is exposed to light in the center of its receptive field. What response would you expect to see?
Depolarization due to decreased release of glutamate by the photoreceptor cell
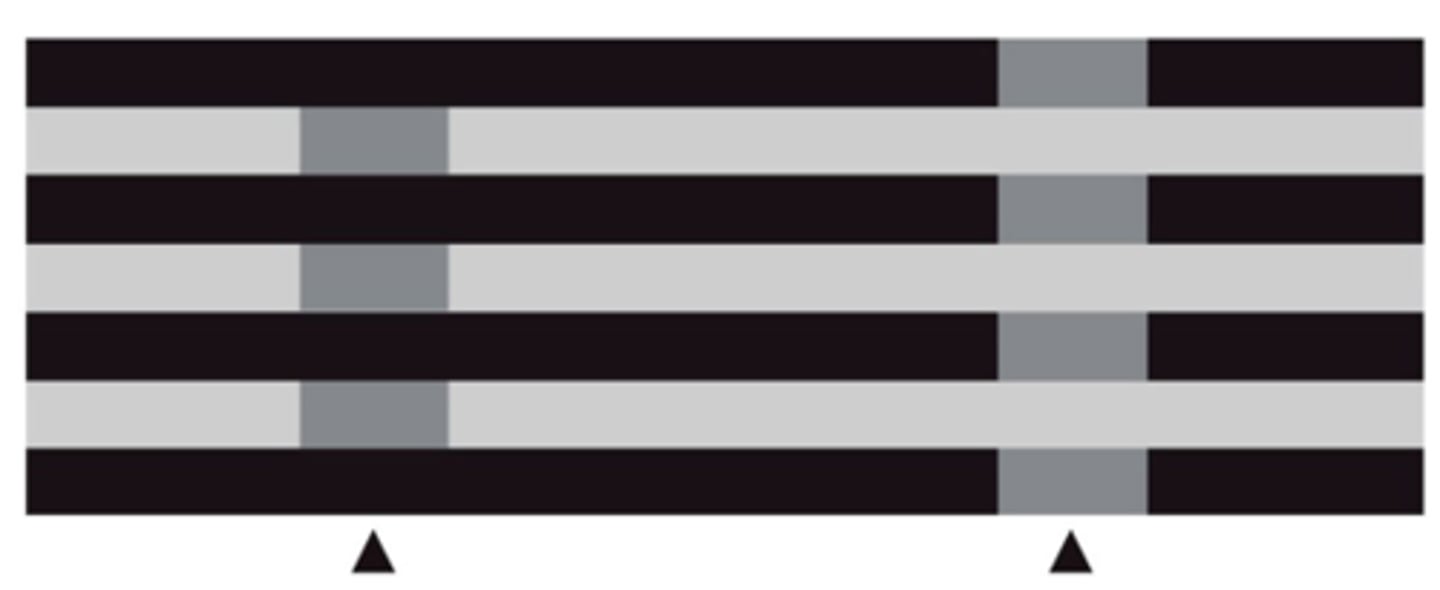
The illusion shown, in which dark rectangles are placed within a pattern of light and dark bars, is best explained by which statement?
1. Light scatters between adjacent photoreceptors.
2. Photoreceptors are unable to spatially resolve the intersections of the white bars.
3. Photic information is conveyed only by graded electrical responses.
4. Brightness percepts are generated on a statistical basis as a means of contending with the inherent ambiguity of luminance.
5. All of the above are equally valid explanations.
Brightness percepts are generated on a statistical basis as a means of contending with the inherent ambiguity of luminance.

The two main functions of the retinal pigment epithelium are _______ and _______.
Question
1. structural support to maintain curvature of the retina; phagocytosis of shed outer segments
2. structural support to maintain curvature of the retina; synthesis of rhodopsin
3. phagocytosis of shed outer segments; synthesis of rhodopsin
4. phagocytosis of shed outer segments; regeneration of the photoreceptor photopigments
5. synthesis of rhodopsin; regeneration of the photoreceptor photopigments
phagocytosis of shed outer segments; regeneration of the photoreceptor photopigments
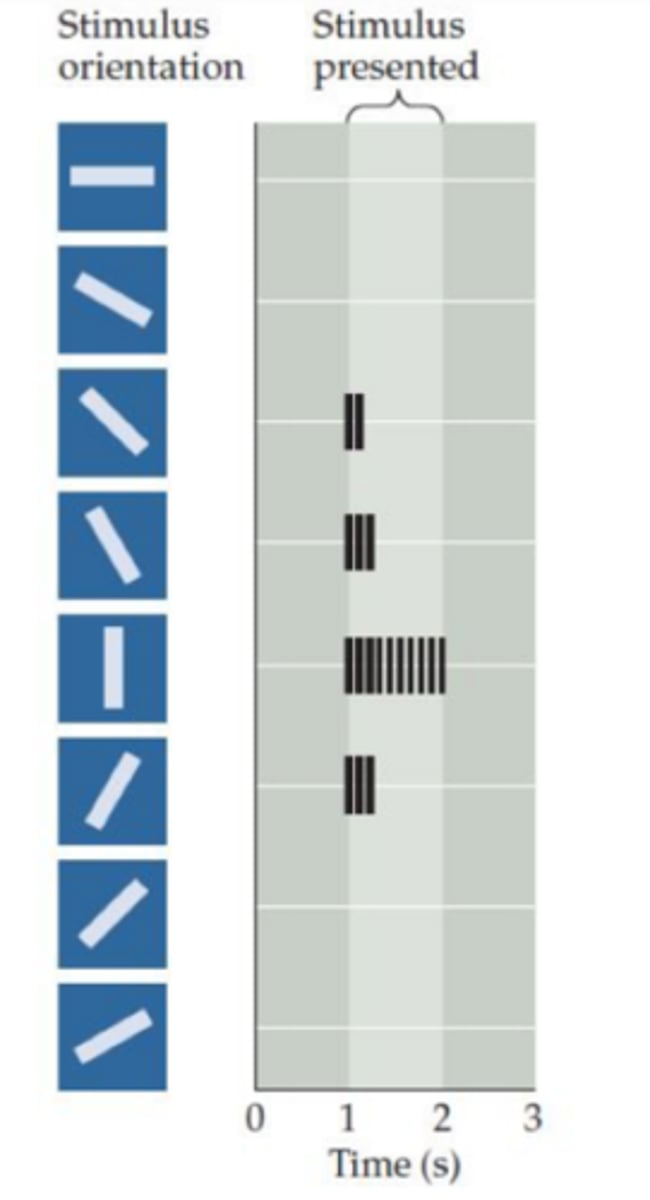
The figure shows the results of an experiment in which an animal is presented with visual stimuli, and recordings are taken simultaneously from the CNS. Given the stimuli and the observed recordings, where must the activated neurons be located?
1. Lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus
2. Optic tract
3. Primary visual cortex
4. Fusiform gyrus
5. Retinal ganglion cell
3. Primary visual cortex
Upper motor neurons
1. control the upper half of the torso.
2. synapse on muscles in the eye, neck, and head.
3. synapse on local circuit neurons and/or lower motor neurons.correct!
4. affect motor patterns only indirectly via their inputs to the basal ganglia.
5. have cell bodies that are located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord.
2. synapse on muscles in the eye, neck, and head.
The patellar tendon (knee-jerk) reflex is
1. mediated by Golgi tendon organs.
2. a monosynaptic reflex arc mediated by Ia afferents.
3. a polysynaptic reflex arc that integrates the input from groups Ia, Ib, and II afferents.
4. mediated by collaterals of somatosensory afferents.
5. a volitional response to the impending impact of an object (i.e., the physician's rubber hammer) directed toward the knee.
2. a monosynaptic reflex arc mediated by Ia afferents.
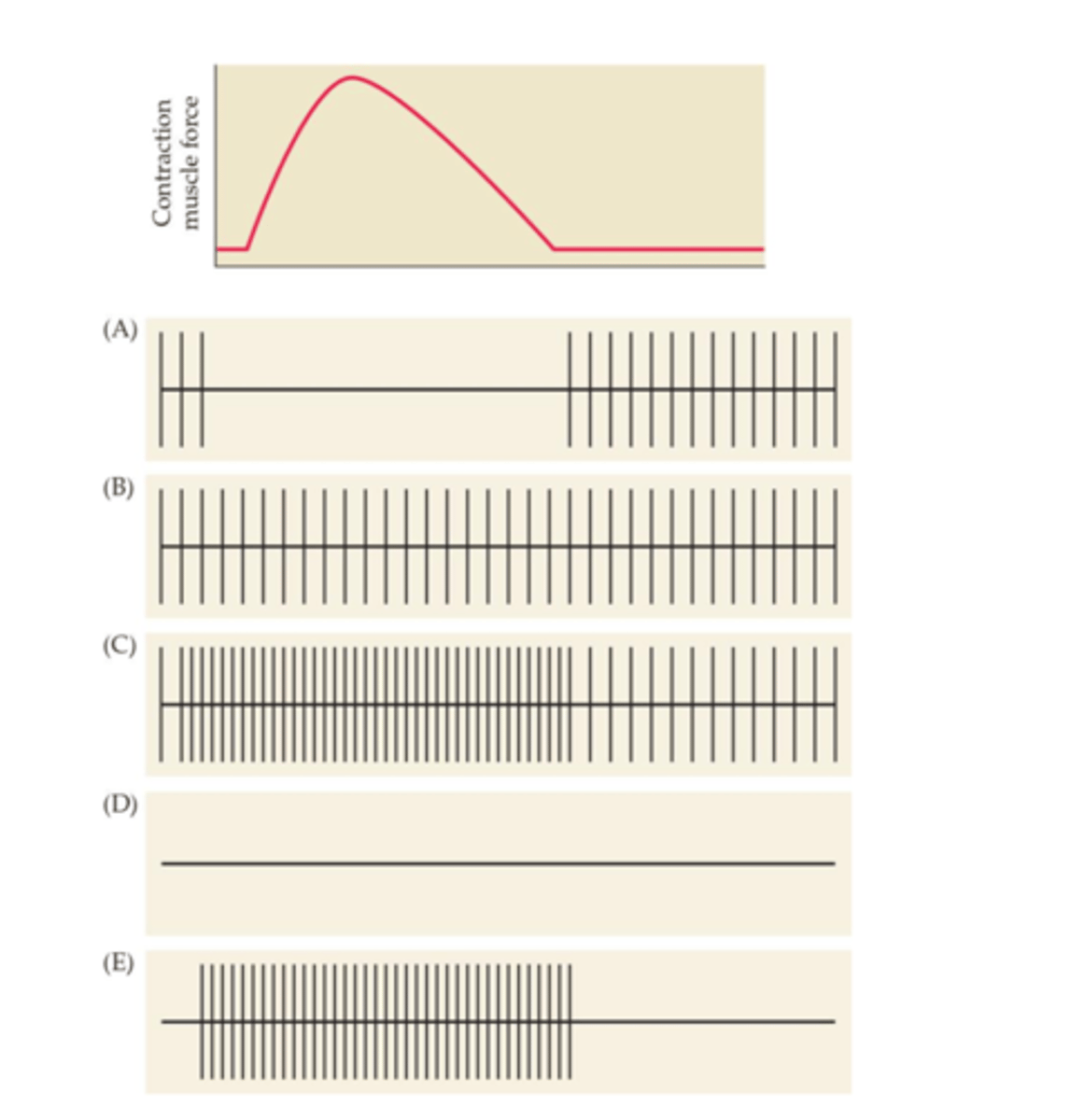
An animal model is developed in which gamma motor neurons are dysfunctional. If you record the activity of the Ia fiber (spindle afferent), which pattern would you expect to see when the innervated muscle contracts?
A
Golgi tendon organs are most sensitive to
1. muscle tension.
2. muscle stretch.
3. absolute joint position.
4. muscle contraction frequency.
5. muscle fatigue.
1. muscle tension
Which statement about the withdrawal reflex is false?
1. It can be initiated by pain- and temperature-sensitive sensory fibers.
2. It has opposing effects within a limb.
3. It has opposing effects in the left and right limbs.
4. It controls muscles by means of polysynaptic pathways.
5. It results in extensor muscle activation within the stimulated limb.
5. It results in extensor muscle activation within the stimulated limb.
Which statement about cat locomotion is false?
1. Flexors play an important role during the swing phase.
2. Extensors play an important role during the stance phase.
3. It is controlled by a single spinal central pattern generator (CPG) that always produces left-right alternation within a segment.
4. Some gaits alternate activity between the left and right legs.
5. Some gaits involve synchronous use of forelimbs and hindlimbs.
3. It is controlled by a single spinal central pattern generator (CPG) that always produces left-right alternation within a segment.
The lamprey central pattern generator (CPG)
1. produces dorsal-ventral flexion waves that run the length of the body.
2. requires sensory feedback in order for the spinal CPG to oscillate.
3. is controlled by a series of segmental ganglia.
4. generates an alternating left-right bending pattern by means of crossed inhibitory fibers.
5. is easy to study because there are only four cells in each hemi-segment of the spinal cord.
4. generates an alternating left-right bending pattern by means of crossed inhibitory fibers.
Proper functioning of the lamprey central pattern generator (CPG) is dependent on which input?
1. Descending inputs from the brainstem or cortex
2. Excitatory interneurons that cross the midline
3. Inhibitory interneurons that cross the midline
4. Inhibitory interneurons that do not cross the midline
5. Motor neurons that cross the midline
3. Inhibitory interneurons that cross the midline
Which symptom would you expect to see in a patient with lower motor neuron damage?
1. Hyperactive deep reflexes
2. Increased muscle tone
3. Babinski's sign
4. No development of atrophy
5. Hypoactive deep reflexes
5. Hypoactive deep reflexes
One candidate hypothesis for the selective degeneration of lower and upper motor neurons in ALS is that
1. these neurons share distinct sets of G-protein-coupled receptors.
2. these neurons exhibit high resting firing rates.
3. motor neurons are used far more intensively than other CNS cell types.
4. these cells are exposed to infectious agents via their peripheral projections.
5. their very long axons make them more vulnerable to defects in axonal transport.
5. their very long axons make them more vulnerable to defects in axonal transport
A motor pool (as opposed to a motor unit) consists of
all of the motor neurons that project to a given muscle
The motor neurons innervating the medial gastrocnemius muscle of the cat are found
spanning several segments of lateral lumbar and sacral spinal cord.
Spinal interneurons that project ipsilaterally between the lumbar and cervical enlargements are most likely involved with
ensuring coordination of the forelimbs and hindlimbs
Asynchronous firing of motor neurons
provides a means by which a population of motor neurons can maintain constant force over a finite time interval.
Upper motor neurons involved in the control of axial muscles would most likely project to the spinal cord in which pattern?
Medial gray matter over many spinal segments
Which statement about directional tuning and population coding by primary motor cortical neurons is true?
The vector summation of population responses of primary motor cortical neurons is important for directional control of motor movements.
Which statement about "mirror" motor neurons is false?
1. They are found in the ventrolateral portion of premotor cortex.
2. They fire in response to a specific motor act, irrespective of there being a behavioral goal associated with the act.
3. They fire in response to observation of a particular motor act being performed by others.
4. They fire most strongly in response to an observed motor act that corresponds to the act that would activate the neuron during self-initiated movements.
5. They encode the intention to make a particular motor act.
2. They fire in response to a specific motor act, irrespective of there being a behavioral goal associated with the act.
The rubrospinal pathway
- Conveys nerve impulses from red nucleus (which receives input from cerebral cortex and cerebellum) to contralateral skeletal muscles that govern precise, voluntary movements of distal parts of upper limbs.
- might not exist in humans
The "indirect pathway" from cortex to spinal cord does not play a role in
1. feed-forward postural adjustments.
2. weight shifts, as when a cat lifts one paw.
3. certain motor functions that are spared after damage to the direct corticospinal pathway.
4. post-injury recovery of fine motor functions such as using two fingers to pick up food.
5. relaying information from cortex to spinal cord via the reticulospinal neurons.
4. post-injury recovery of fine motor functions such as using two fingers to pick up food.
What is not a function of the reticular formation?
1. Modulation of cortical functions via serotonergic, noradrenergic, and cholinergic transmitter systems
2. Modulation of cortico-striatal interactions
3. Descending modulation of spinal reflexes
4. Coordination of gaze centers and branchiomotor functions
5. Transmission of spinal nociceptive and tactile sensory signals to the cerebellum
5. Transmission of spinal nociceptive and tactile sensory signals to the cerebellum
Which statement about the reticular activating system is true?
It supports transitions between sleep and wakefulness.
Upper motor neuron syndrome
weakness, spasticity, increased tone, hyperactive deep reflexes, clonus, babinski's sign, loss of fine voluntary movements, passive leg drop
Babinski sign (plantar reflex)
- The toes flex upward when sole of foot is stimulated, indicating motor nerve damage.
- corticospinal tract.
- changes between infancy and later development.
- upper motor neuron deficit.
- affected by stroke, trauma, and other neurological problems.
A patient is diagnosed with a tumor located in the right internal capsule. Which motor dysfunction would you expect to see in this patient?
Left side paralysis (or severe weakness) of the lower face
Cortical areas that plan and initiate motor sequences
1. all fall within the primary motor cortex.
2. comprise five functionally distinct and anatomically isolated regions.
3. comprise several functionally distinct but highly interconnected regions.
4. all receive direct inputs from the basal ganglia.
5. all show a high threshold for the elicitation of motor behaviors.
3. comprise several functionally distinct but highly interconnected regions.
Although the phenomenon is not well understood, the increased muscle tone and spasticity that develop after an upper motor neuron injury appears to be due, at least in part, to
increased responsiveness of motor neurons to Ia afferent inputs.
corticospinal tract
Lateral: pyramidal motor tract responsible for contralateral voluntary fine movement
Anterior: Descending Pyramidal motor tract responsible for ipsilateral voluntary, discrete, skilled movements
synapse onto spinal local circuit neurons
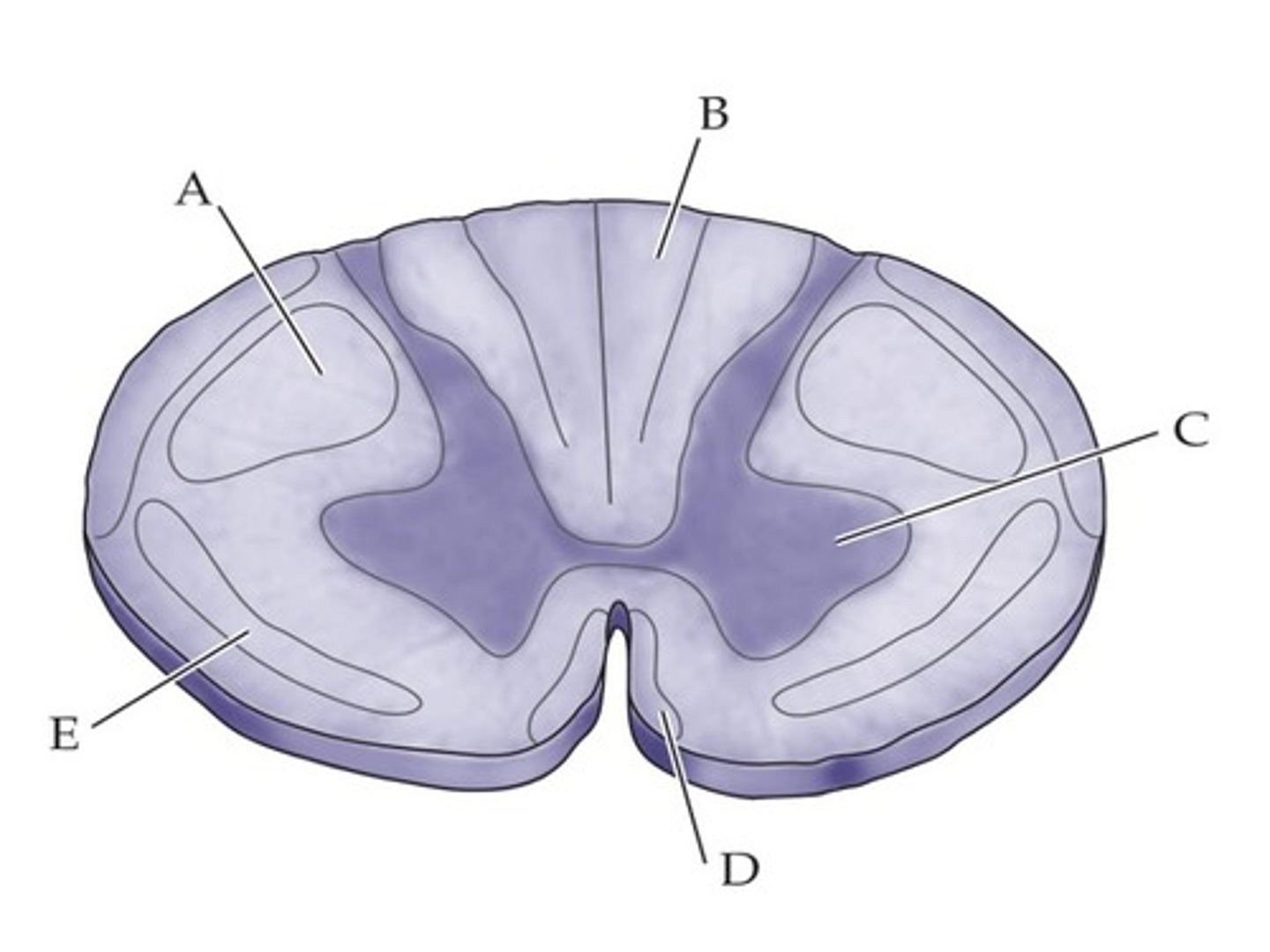
A patient is having difficulty sitting and standing without support. If you know this is due to a spinal cord injury, in which location would you expect the damage to be?
D
Which method helped scientists correct a long-standing misconception about the neurological origins of facial weakness deficits seen in humans?
1. fMRI, or functional magnetic resonance imaging
2. Anatomical tract-tracing in primates
3. High-resolution EEG
4. Optical imaging of neuronal activation patterns in the cortex
5. PET scans
2. Anatomical tract-tracing in primates
A "muscle field"
is the group of muscles whose activity is directly facilitated by a given upper motor neuron.
Which statement about primary motor cortex neurons is false?
1. The firing of primary motor cortical neurons occurs precisely at the onset of a muscle contraction.
2. Primary motor cortical neurons can be directionally selective.
3. The firing rate of a primary motor cortical neuron codes for or contributes to the force of a movement.
4. The directional control of a movement is coded by the activity of a population of primary motor cortical neurons.
5. The directional responses of primary motor cortical pyramidal cells tend to be broadly tuned in that they respond over a somewhat broad range of movement directions.
The firing of primary motor cortical neurons occurs precisely at the onset of a muscle contraction.
When Graziano and colleagues extended cortical microstimulation in monkeys to time epochs approximating those of natural movements, they observed
purposeful movements distributed sequentially across multiple joints.
"Spike-triggered averaging"
is a means of correlating upper motor neuron activity with muscle activation