CH 301 Final Exam
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
224 Terms
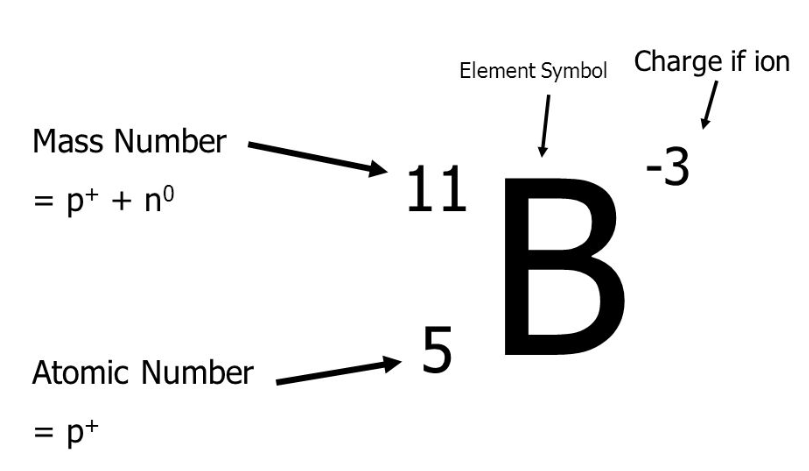
Number of Protons =
Atomic Number (bottom)
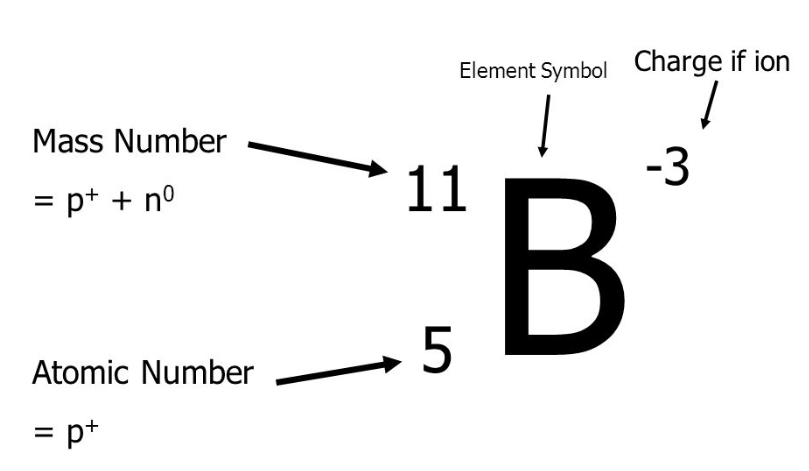
Number of Neutrons =
Mass Number - Atomic Number
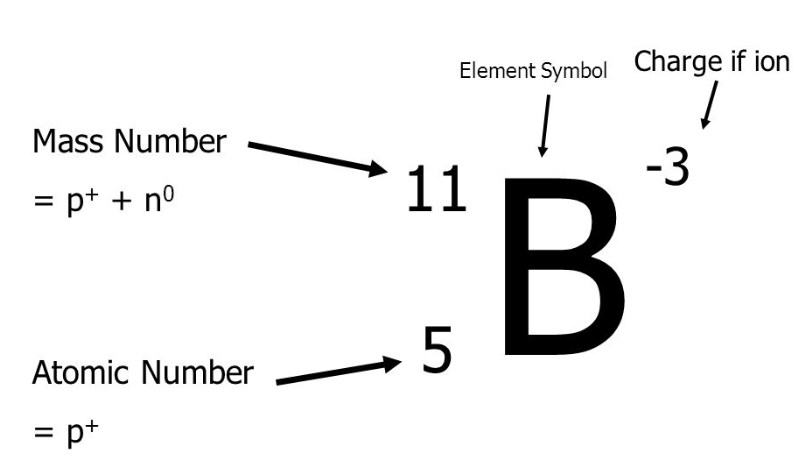
Number of Electrons
Atomic Number - Charge
1
Mono
2
Di
3
Tri
4
Tetra
5
Penta
6
Hexa
7
Hepta
8
Octa
9
Nana
10
Deca
Molecular Compounds =
Nonmetal + Nonmetal
Molecular Compounds
Use Prefixes
Ionic Compounds =
Metal + Nonmetal
Ionic Compounds
Do NOT use prefixes
Ammonium
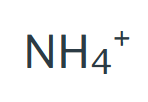
Bicarbonate
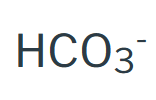
Carbonate
CN - 3
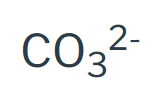
Cyanide

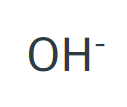
Hydroxide
Nitrate
CN - 3
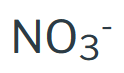
Nitrite
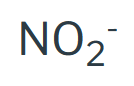
Peroxide
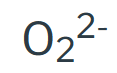
Phosphate
SP - 4

Sulfate
SP - 4

Sulfite
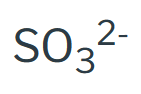
Equation for calculating the percent composition of an element
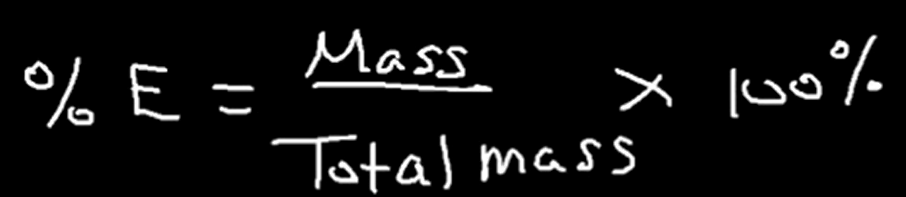
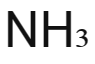
Ammonia
Diatomic Elements
Br I N Cl H O F
1 KJ
1000 J
1 L
1000 mL
What do you use to convert grams of a substance to moles of that substance?
Molar Mass (#g/1mol)
4 Steps for Gram to Gram Conversion
Grams x Molar Mass x Molar Ratio x Molar Mass = Grams
Solute
Thing being dissolved
Molarity (M) =
Moles of Solute/Liters of Solution
Mass =
Moles x Molar Mass
Equation for 2 values of Molarity and 2 values of Volume
M1V1 = M2V2
Sodium Dichromate
Na2Cr2O7
How do you find the oxidation state of an element in a compound?
1) write an equation based on the compound, 2) set the equation equal to the net charge, 3) solve for the unknown value
No net charge in a compound =
zero
What has an oxidation state of zero?
Any element in its pure elemental form (Ex. H2, N2, O2)
Oxidation state of Fluorine
-1
Oxidation state of Oxygen (Oxide)
-2
Oxidation state of Oxygen (peroxide)
-1
Oxidation state of Hydrogen (Bonded to a Nonmetal)
+1
Oxidation of Hydrogen (Bonded to a Metal)
-1
Calcium Hydride
CaH2
Hydrogen Peroxide
H202
Sulfuric Acid
H2SO4
In a M1V1 = M2V2 problem with 2 different solutions (2 different substances)….
take into account the molar ratio found in the balanced reaction of the 2 substances
“Concentration” =
Molarity (M)
What two ions always produce H2O when paired up?
H+ & OH-
Step 1 of writing a balanced reaction:
Write the reactants like R + R —> ?

Step 2 of writing a balanced reaction:
Write down the oxidation states (charges) of each reactant

Step 3 of writing a balanced reaction:
Pair the two inside terms and the two outside terms of the reactants
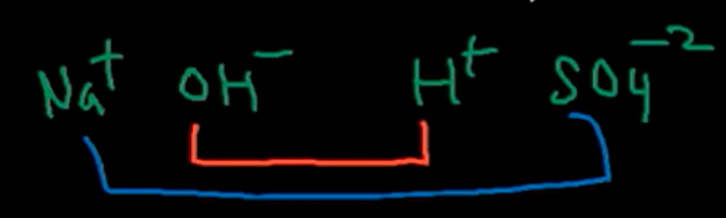
Step 4 of writing a balanced reaction
Use the criss-cross method to determine the products

Step 5 of writing a balanced reaction
Add the products to the equation

Step 6 of writing a balanced reaction
Balance the reaction
SATP =
T = 298 k & P = 1 atm
STP =
T = 273 k, P = 1 atm, & 1 mole of any gas = 22.4 L
Combined Gas Law
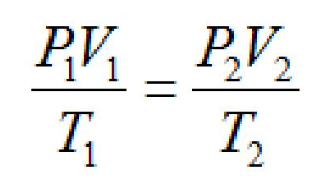
Volume units when using the combined gas law
mL OR L
Pressure units when using the combined gas law
atm OR torr
Temperature units when using the combined gas law
k ONLY
Density =
Mass/Volume
To find the density of a gas at STP…
take the molar mass (g/mol) and multiply it by 1mol/22.4 L
Density also =
(Pressure x Mass)/R x Temperature; R = 0.08206 (L x atm)/mol x k
If pressure is in atm use
0.08206 (L x atm)/mol x k for R
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
When you’re trying to find the identity of an unknown gas…
find the molar mass of each answer choice and compare it with the molar mass of the unknown gas
When you have a “collected over water” problem…
you must consider the partial pressure of water (Ptot = Pgas + PH20)
Units of Molar Mass
#g/1 mol
1 atm =
760 torr
Vapor pressure of water =
partial pressure of water
The average kinetic energy of a sample of gas is dependent on
temperature
For a sample of gas KE =
3/2RT
Temperature and the average kinetic energy of a sample of gas are
Proportional
The average velocity of gas particles is dependent on
temperature
The root mean square velocity of a gas =
M = molar mass (kg/mol); R = 8.314 J/mol x k
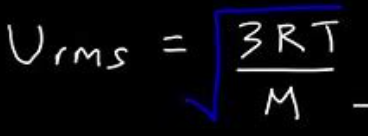
Vrms and Temperature are
proportional (gas particles move faster at a higher temperature)
Pressure =
Force/Area
Heavier gas particles move
slower
If you increase your mass, but decrease your speed, the pressure will
be the same
Force x contact time =
mass x delta velocity
Heavier gas particles
do NOT exert greater pressure
What’s an example of a very light gas?
Hydrogen Gas (H2)
What’s an example of a very heavy gas?
Chlorine Gas (Cl2)
According to the ideal gas law, the pressure must be the same, regardless of whether one gas is light or one is heavy if
the volume, moles, and temperature are the same
The pressure inside a container is dependent on
the total number of moles of gas particles inside the container (bc n is part of the ideal gas law; n inc = P inc)
Under what conditions will a real gas behave like an ideal gas?
High temperature, Low pressure
What kind of pressure favors the formation of liquid
High
The specific heat capacity of water (l) is
4.184 J/g x degrees Celsius
Equation for heat energy (q) with a temperature change =
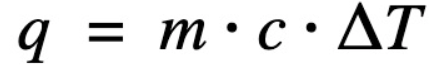
Equation for heat energy (q) with a phase change and units kJ/mol =
q = n x delta H
Equation for heat energy (q) with a phase change and units J/g =
q = m x delta Hfus
Fusion (s —> l) is an
endothermic process so q = +; delt H = +
Freezing (l —> s) is an
exothermic process so q = -; delta H = -
Phase change from gas to solid
deposition (exo)