Module 2 : Chromosomes and Cellular Reproduction
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Prokaryote
Unicellular organism with a relatively simple cell structure. Prokaryotes include bacteria (eubacteria) and archaea
Bacteria
One of the three primary divisions of life, consisting of prokaryotic unicellular organisms.
Archaea
One of the three primary divisions of life, consisting of unicellular organisms with prokaryotic cell structure.
Eukaryote
One of the three primary divisions of life; an organism that has a compartmentalized cell structure, including a nuclear envelope and membrane-bounded organelles. Eukaryotes may be unicellular or multicellular.
Nucleus
Compartment in eukaryotic cells that is enclosed by the nuclear membrane and contains the genetic material.
Histone
Low-molecular-weight protein found in eukaryotes that associates closely with DNA to form chromosomes.
Chromatin
Material found in the eukaryotic nucleus; consists of DNA and histone proteins.
What are the 3 major types of cells?
Eukaryote, Archaea, Bacteria
Here we learn that most eukaryotes are diploid; that is, they…..
have two sets of homologous chromosomes.
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 chromosomes, which is made up of 23 sets of homologous chromosomes (or 23 pairs of chromosomes).
Does the number of chromosomes show how complex the organism is?
There does not appear to be a correlation between the complexity of an organism and the number of chromosomes that it has.
If we scroll down to humans, we see that humans have a 2n chromosome number of 46.
This means that humans have ____ sets of homologous chromosomes.
23
ach eukaryotic chromosome is made up of a…..
single, tightly coiled strand of DNA.
chromosome has three important structural features:
a centromere
a pair of telomeres
origins of replication
Centromere
constricted region on a chromosome that serves as the attachment point for spindle microtubules
Telomeres
stable ends of a eukaryotic chromosome that prevent the chromosome from progressive degradation and helps to maintain its integrity.
Origin of Replication
The site were DNA replication is initiated
centromere
(the constricted area of a chromosome)
telomeres
(each arrow is pointing to the ends of the chromosome which are called telomeres)
sister chromatids
(because we see an "X" we have a pair of chromatids which are called sister chromatids; i.e., a single chromatid has been copied/duplicated during S phase)
A single chromosome may exist as a single _____ or it may consist of two….
chromatid, sister chromatids
A sister chromatid refers to either of the two…
identical copies (chromatids) formed by the replication of a single chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere.
its important to distinguish between sister chromatids, which are…… and…
two identical DNA molecules joined together at the centromere of a single chromosome, separate but homologous chromosomes.
When you want to count the number of chromosomes (with one or more chromatids), the easiest way is to count the number of….
centromeres.
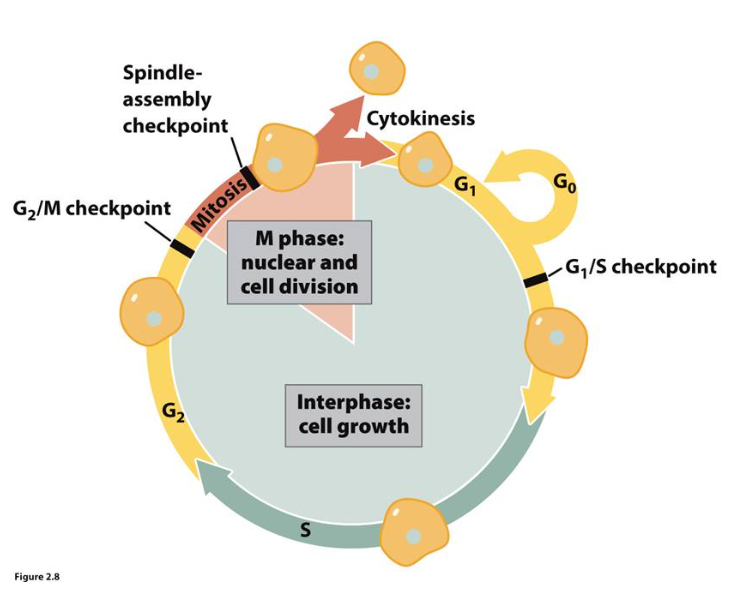
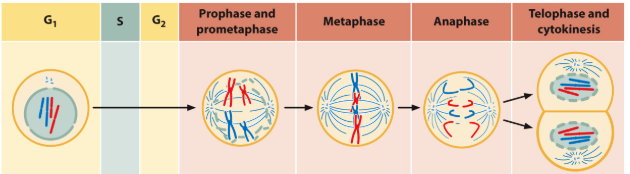
G1, S, and G2 are part of…..
Interphase
Mitosis and Cytokinesis are part of the….
M phase
G1 and G2 are…
Growth phases
n G1, cells are…..
preparing to replicate their DNA,
Cells in G2 are preparing for…
cellular division
In the S phase, the DNA is…
replicated or synthesized
What are the 4 phases of the cell cycle?
G1, S, G2, Mitosis
G0 stage is sometimes called the…
"resting stage" when the cell "steps out" of the cycle.
G0 Cells can exist in this state for…
minutes to decades. These cells are not actively dividing nor are they preparing to divide.
Draw the cell cycle
cell cycle
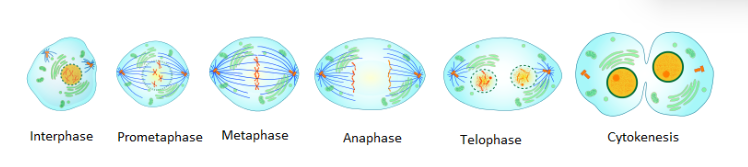
What are the 6 steps of mitosis?
Interphase - Prophase - Prometaphase - Metaphase - Anaphase - Telophase
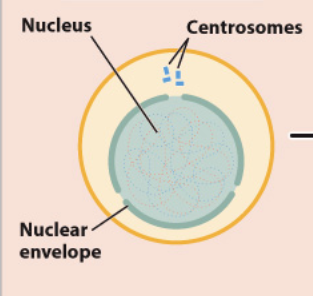
draw Interphase
interphase
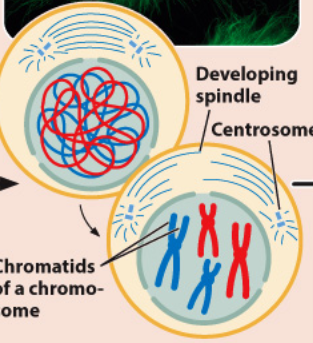
Draw Prophase
prophase
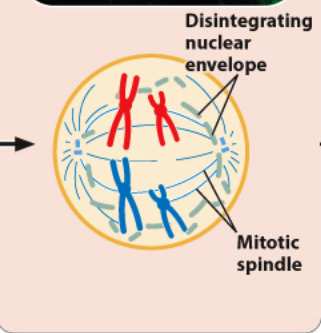
Draw Prometaphase
prometaphase
Draw metaphase
metaphase
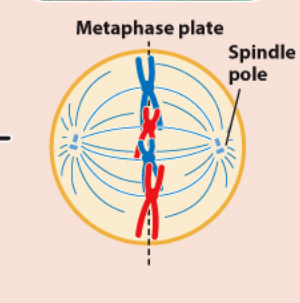
draw anaphase
anaphase
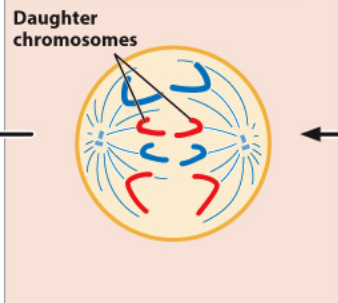
draw telophase
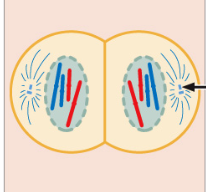
telophase
Fill out this forrm for 2n (Considering # of chromosomes + # of DNA molecules per cell)
chromosome
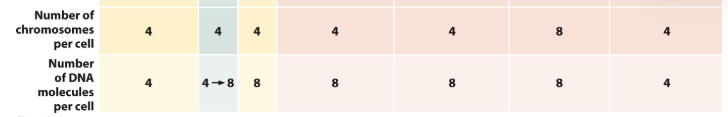
The cell starts in…
interphase.
In interphase, the DNA is referred to as….
chromatin as the strands of DNA are NOT in a condensed state (therefore, we do not see the discreet chromatids; it better resembles a jumbled ball of yarn).
Draw mitosis
mitosis
During the S phase, the DNA is…..
replicated or SYNTHESIZED
In S phase, how many DNA molecules?
We doubled the number of DNA molecules, however, we will still only have 4 chromosomes because these are connected via the centromere.
What comes after S phase?
Now we leave interphase and enter into mitosis!
In prophase, the DNA condenses and forms…
4 (visible) chromosomes, each with 2 sister chromatids (note there are 4 centromeres in the cell, meaning there are four chromosomes).
In anaphase the pairs of sister chromatids that make up each chromosome…
separate and for a brief period of time, there will be 8 chromosomes in the cell (8 centromeres = 8 chromosomes).
After cytokinesis, there will be _____ chromosomes per cell.
4
The 2n chromosome number of a chicken is 78. How many DNA molecules are present during each of the following phases of the cell cycle? (G1-G0)
78, 156, 156, 156, 156,156, 78 in one cell 78 in the other, 78 in one cell 78 in the other, 78 DNA molecules
Meiosis leads to the production of….
gametes in which the number of chromosomes in the cell is reduced by half.
In other words, meiosis is a special type of cell division whereby the chromosomes duplicate….
only once, but the cell divides twice.
Meiosis: One parental (original) cell produces….
4 daughter cells, each having half the chromosome number than the original parental cell.
There are two cell divisions in meiosis, termed, ….
meiosis I and meiosis II.
Draw meiosis generally
meiosis
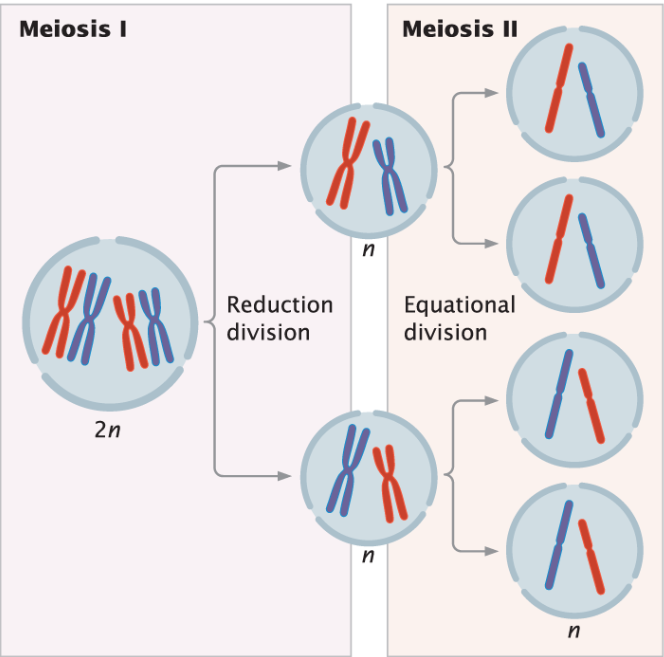
Meiosis I: Often called….
"Reduction Division"
Meiosis I: The purpose is to…
segregate homologous chromosomes into separate cells.
In metaphase I, homologous pairs of chromosomes….
line up along the metaphase plate.
In metaphase I, homologous pairs of chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate. This is a major difference from what we see in mitosis, during which….
single chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate.
During the remainder of meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are….
pulled apart and the cytoplasm divides to separate them into different cells.
At the end of meiosis I, the resulting cells with have….
HALF the number of chromosomes (i.e. they become haploid).
Meiosis II
Often referred to as the….
"Equational Division"
Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, in that….
individual chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate, and sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles.
Draw Meiosis I and II cellular reproduction
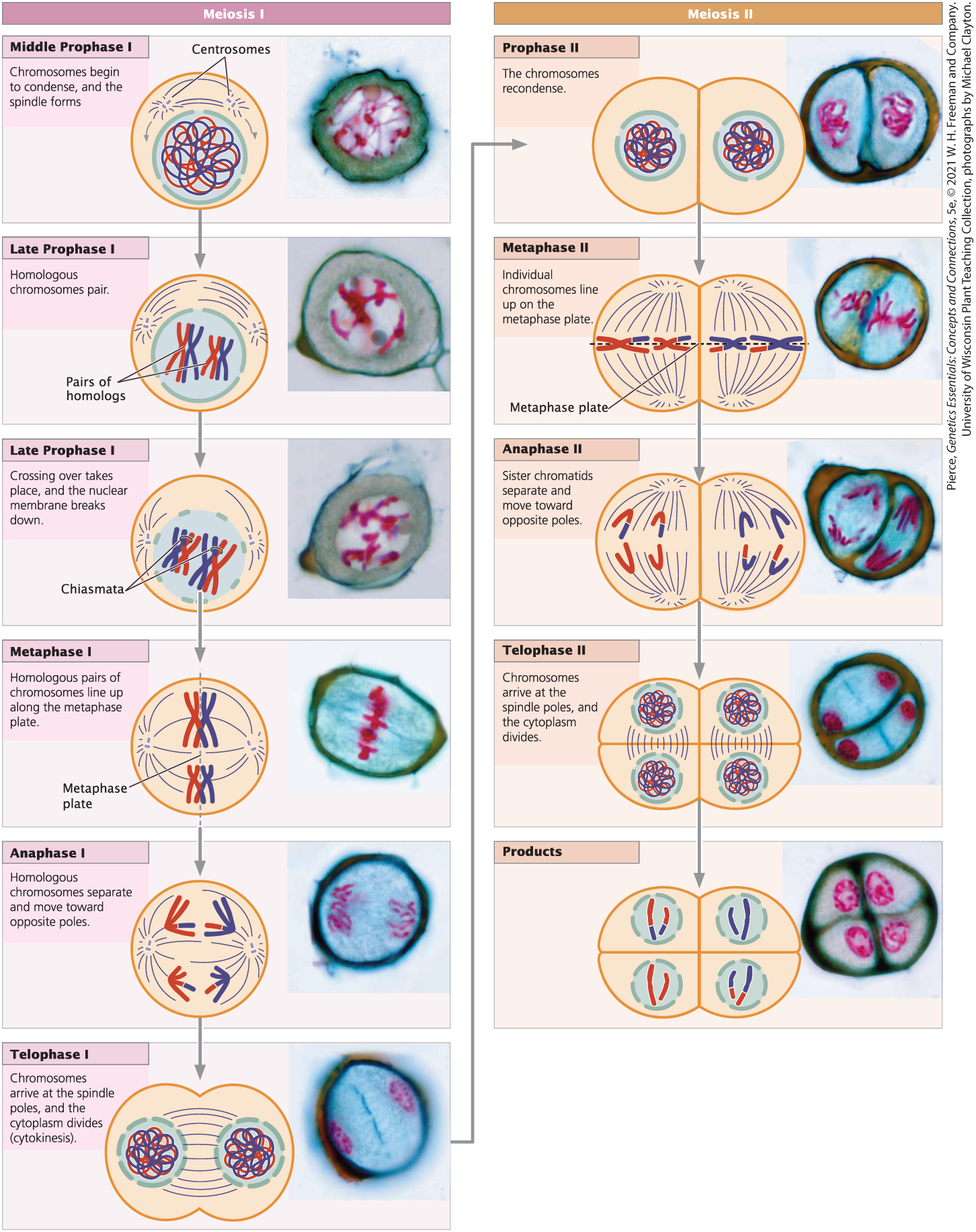
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis: divisions
1, 2
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis: daughter cells
2 per cycle, 4 per cycle
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis: daughter cells details
genetically identical - Chromosome number of daughter cells same as that of parent cell (2n), genetically different - Chromosome number of daughter cells half that of parent cell (1n)
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis: Occurs in…
Occurs in somatic cells vs germline cells
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis: Occurs throughout….
Occurs throughout life cycle, In humans, completes after sexual maturity
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis: used for…
growth, repair, and asexual reporduction,
Used for sexual reproduction, producing new gene combination |
ach cell that undergoes meiosis produces …
four daughter cells (compared to the two produced by mitosis).
In meiosis : Each of these daughter cells has,,,,
half the number chromosomes that the original parent cell contained.
In other words, when a diploid cell undergoes meiosis, it produces…
four haploid daughter cells.
Meiosis generates…
genetic diversity among the daughter cells
No two daughter cells that result from meiosis are…
identical.
There are two ways in which meiosis can generate genetic diversity.
A. Independent assortment, B. Crossing over
A. Independent assortment
Refers to the random separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I.
B. Crossing over
Refers to the exchange of genetic data between homologous chromosomes, which occurs during prophase I.