aphug
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Globalization
The increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of countries through the flow of goods, services, capital, information, and people.
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
A model that describes population change over time as a country transitions from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system.
Push and Pull Factors
Factors that either induce people to leave their old residence (push factors) or attract them to a new residence (pull factors).
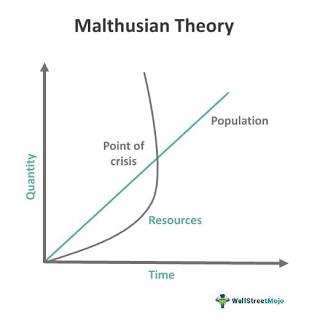
Malthusian Theory
A theory that population growth will always tend to outrun the food supply
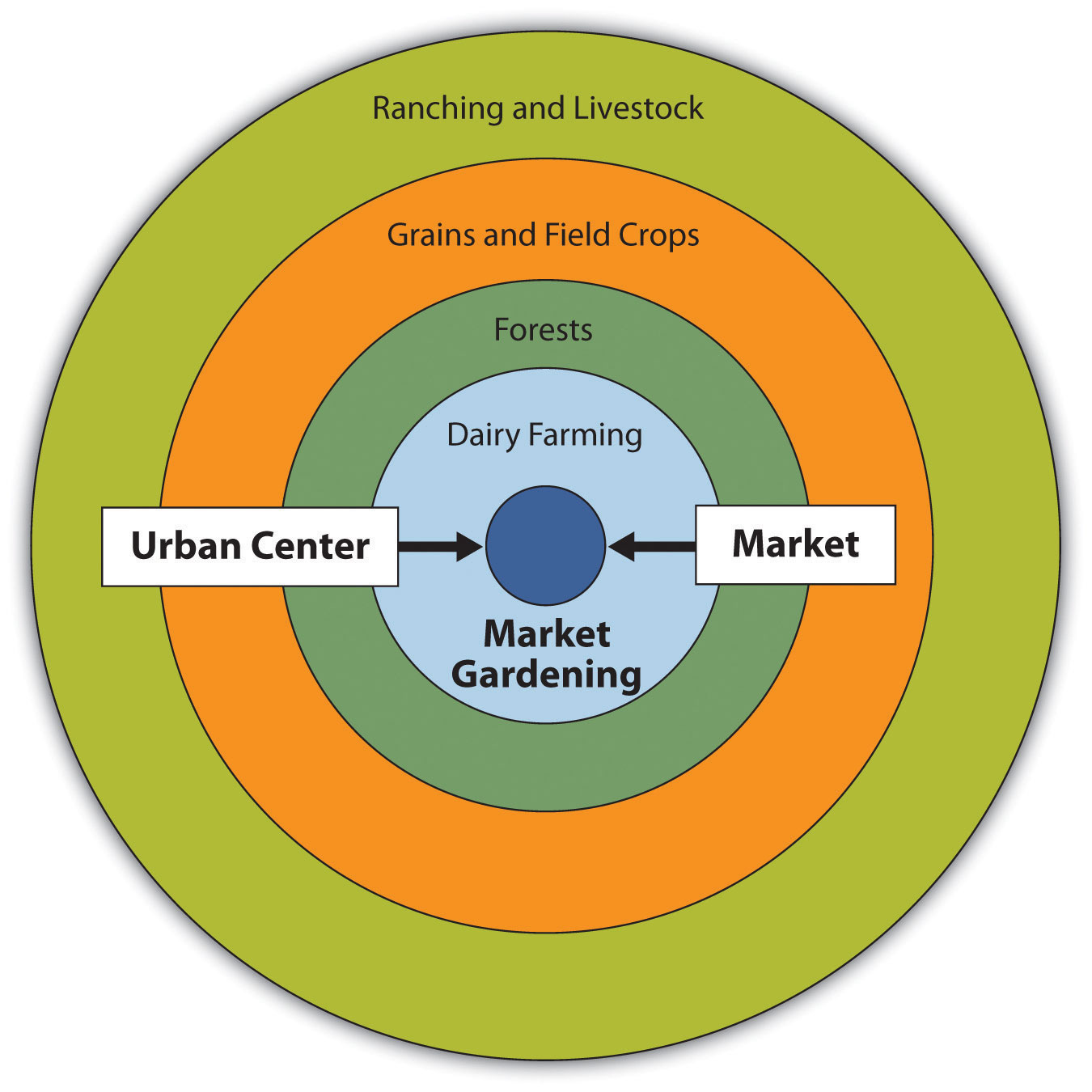
Von Thunen Model
A model of agricultural land use, which illustrates how market processes could determine how land in different locations would be used.
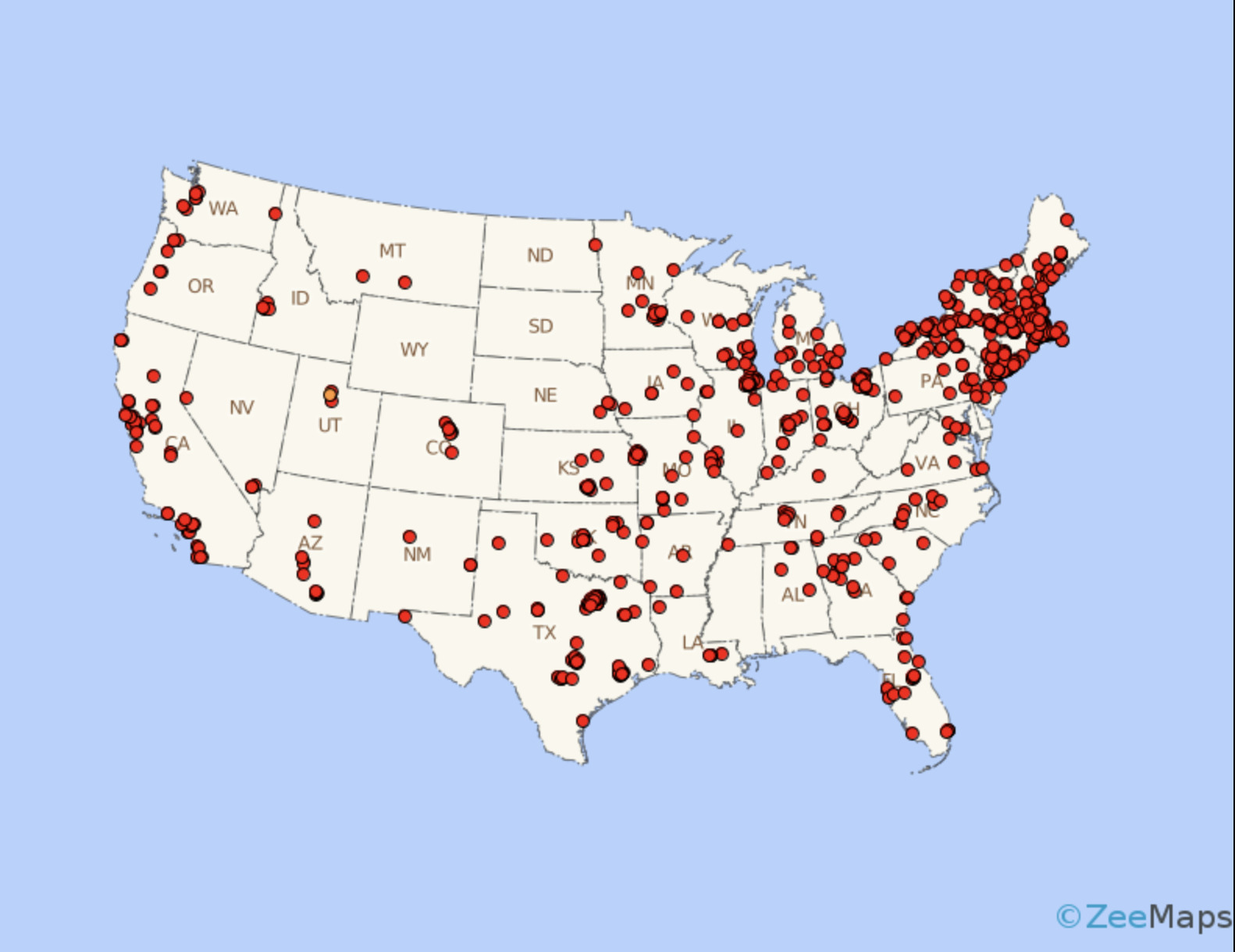
Dot Map
A map that uses dots to represent the occurrence of some phenomenon in order to depict variation in density
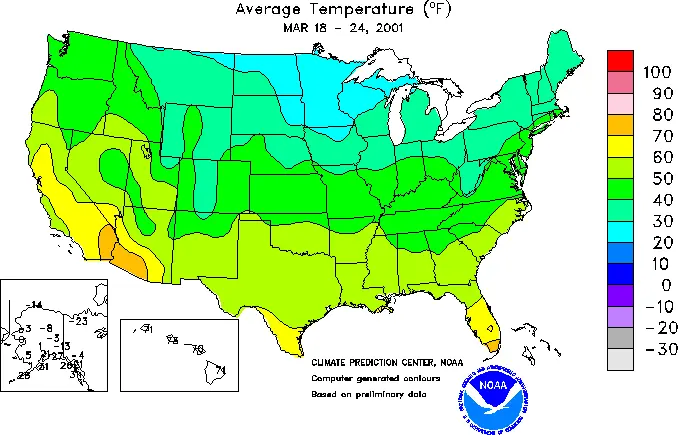
Isoline Map
A map that uses lines to connect points of equal value.
Choropleth Map
A thematic map in which areas are shaded or patterned in proportion to the measurement of the statistical variable being displayed on the map.
Symbol Map
A map that uses various symbols to represent different features, such as cities, roads, or points of interest.
Mercator Map
A map projection that preserves direction and shape, but distorts area and distance.
Thematic Map
A map designed to show a particular theme connected with a specific geographic area.
Territoriality
The attempt by an individual or group to affect, influence, or control people, phenomena, and relationships, by delimiting and asserting control over a geographic area.
State
A politically organized territory with a permanent population, a defined territory, and a government.
Nation
A group of people with a shared culture, history, and often language, who feel a sense of unity.
Sovereignty
The ability of a state to govern its territory free from external control.
Gerrymandering
Redrawing legislative boundaries to benefit the party in power.
Balkanization
The process of a state breaking down due to conflicts or government ineffectiveness.
Shatterbelt
An area of instability located between regions with opposing political and cultural values.
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.
Decolonization
The process of colonies becoming independent.
Centrifugal Forces
Forces that divide a state, such as differing religion or languages.
Centripetal Forces
Forces that unite a state, such as a common language or religion.
Federal State
An internal organization of a state that allocates most powers to units of local government.
Unitary State
An internal organization of a state that places most power in the hands of central government officials.
Supranationalism
A venture involving three or more states involving formal political, economic, and/or cultural cooperation to promote shared objectives
Cultural Hearth
The origin or center of a cultural trend.
Ethnic Enclave
A geographic area with high ethnic concentration, characteristic cultural identity, and economic activity.
Neocolonialism
The use of economic, political, cultural, or other pressures to control or influence other countries, especially former dependencies.
Environmental Geography
The study of the relationships between people and their environment.
Human-Environment Interaction
The relationship between people and their natural environment, including how humans depend on, adapt to, and modify the environment.
Place
A specific point on Earth with human and physical characteristics that distinguish it from other points.
Region
An area of Earth distinguished by a distinctive combination of cultural and physical features.
Scale
The relationship between the portion of Earth being studied and Earth as a whole, specifically concerning the level of detail.
Space
The physical gap or interval between two objects.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
Remote Sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth’s surface from a satellite orbiting Earth or from other long-distance methods.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
Site
Physical characteristics of a place.
Environmental Determinism
the belief that physical geographic factors, such as climate and terrain, have a significant and direct impact on human activities and outcomes.
Possibilism
the theory that while the environment provides constraints and opportunities, human culture and agency are the primary factors shaping human behavior and development
Periphery Country
a nation with low levels of industrial productivity and a low standard of living, often reliant on core countries for capital and raw materials. (For example: Afghanistan, Albania, Bolivia, and many African nations.)
Semi-Periphery Countries
countries that have a standard of living lower than those in the “core,” but much higher than those in the “periphery.” Periphery countries often face challenges like political instability, corruption, and social inequality, which hinder their development. (For example: China, India, Brazil, Mexico, Indonesia, and Russia.)
Core Country
A core country is a highly developed nation with advanced technological infrastructure and strong economic performance, often dominating global trade and investment. For example: United States, Canada, Western European nations (like Germany, France, and the UK), Japan, and Australia.
Dependency Theory
Dependency theory suggests that periphery countries are economically dependent on core countries, leading to a cycle of poverty and underdevelopment due to exploitative relationships
Rank Size Rule
the population of a city in a country or region is inversely proportional to its rank in the city size hierarchy. Essentially, if cities are ranked by size, the second-largest city will have approximately half the population of the largest city, the third-largest will have about one-third the population of the largest, and so on
Population Pyramid
visual representation of age and sex distribution.
Cultural Landscape
human imprint on the physical environment.
Nation-State
A state whose political boundaries align with a single nation (almost everyone belongs to the same culture or ethnicity).
Example: Japan or Iceland—both are culturally and politically unified.
Multinational State
A state that includes more than one nation within its borders.
Example: Canada (includes English-speaking and French-speaking nations).
Stateless Nation
A nation without a sovereign state of its own, often spread across multiple countries.
Example: The Kurds (spread across Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Syria), Palestinians.
Multistate Nation
A nation that is spread across multiple states.
Example: Koreans in North and South Korea—same ethnic group in two different states.
Whats the difference between centripetal forces and centrifugal?
Centripetal Forces unify a state, Centrifugal divides a state.
Supranational Organizations
entities where three or more countries come together to work on shared goals, often giving up some sovereignty to cooperate politically, economically, or militarily.
European Union (EU)
Type: Economic and political union
Main Roles:
Free trade and movement (goods, services, people)
Common currency (Euro)
Regional development and cooperation
Shared laws in certain policy areas (e.g. agriculture, environment)
United Nations (UN)
Type: Global diplomatic and peacekeeping organization
Main Roles:
Prevent conflict, promote peace (UN peacekeepers)
Address global issues (climate change, hunger, education)
Protect human rights
Support development (UNDP, WHO)
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
Type: Military alliance
Main Roles:
Collective defense (attack on one = attack on all)
Promote military cooperation among members
Respond to global security threats (e.g. terrorism, cyber attacks)
Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
Type: Regional political and economic organization
Main Roles:
Promote economic growth and regional stability in Southeast Asia
Reduce tariffs and encourage trade
Foster diplomatic relations
African Union (AU)
Type: Political and economic organization for African states
Main Roles:
Promote unity and solidarity among African countries
Defend sovereignty and independence
Support sustainable development
United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA)
(formerly NAFTA)
Type: Economic/trade agreement
Main Roles:
Promote free trade across North America
Encourage investment and reduce tariffs
Boost economic cooperation
Devolution
power shifting from central to regional governments.
Benefit: Increased local control
Allows regions to govern themselves in ways that better reflect their culture, language, or needs.
Cons: Risk of fragmentation or separatism
Can lead to calls for full independence, weakening the unity of the state
Neolithic Revolution (1st Agricultural Revolution)
Key Feature: Transition from hunting and gathering to settled farming.
Technologies Used:
Domestication of plants and animals (e.g., wheat, rice, goats, and cows).
Simple tools: hoes, digging sticks, and stone tools to clear land and plant crops.
Irrigation systems (early methods to water crops).
Impact: Enabled people to settle in one place and form civilizations.
Industrial Revolution (2nd Agricultural Revolution)
Key Feature: Mechanization and improved farming techniques.
Technologies Used:
Crop rotation (e.g., the four-field system) to maintain soil fertility.
Selective breeding of livestock to improve quality and productivity.
New tools: seed drills, mechanized plows, and threshers.
Increased use of fertilizers and pesticides to boost yields.
Improved transportation: Railroads and canals to move goods.
Impact: Boosted food production, supported urbanization, and began the shift toward commercial farming.
Green Revolution (3rd Agricultural Revolution)
Key Feature: Technological advances in food production to address global hunger.
Technologies Used:
High-yield variety seeds (e.g., “miracle” wheat and rice) to increase crop production.
Chemical fertilizers and pesticides to enhance crop growth and reduce losses from pests.
Mechanized farming equipment: Tractors, combine harvesters, and irrigation systems.
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for increased pest resistance and drought tolerance.
Advanced irrigation systems: Drip irrigation and sprinkler systems.
Impact: Dramatically increased food production worldwide, particularly in developing countries, but also led to environmental issues (e.g., soil depletion, water overuse).
Urbanization
Movement from rural areas to cities due to economic opportunities and better living conditions.
Urban Models
Urban Models: Theories explaining city growth, like Concentric Zone Model (city grows in rings) and Multiple Nuclei Model (cities have multiple centers).
Edge Cities/Suburbs
Development of commercial areas and residential suburbs outside traditional city centers
Sustainable Cities
Focus on eco-friendly infrastructure, public transportation, and reducing urban sprawl.
Heartland Theory
suggests that whoever controls the central Eurasian region (the "Heartland") would control the "World Island" (Europe, Asia, and Africa), and ultimately, the world
Ecotourism
as a form of tourism that focuses on nature-based experiences while promoting conservation and benefiting local communities