Morphology of Flowering Plants, morphology, Morphology of flowering plants- Flowers
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
Gynoecium
Collection of all carpels: ovary, style and stigma
Androecium
Collection of all stamens: anther, filament and pollen grain
Morphology
External Structure
Primary root
The structure that is formed due to elongation of the radicle
Secondary and Tertiary root
Lateral roots coming out from the primary root
Tap Root System
Primary root and its branches example:mustard
Fibrous Root System
Primary root short lived and replaced with large number of roots arising from the base of the stem. Example: wheat
Adventitious Roots
Roots arising from the parts of the plant other than the radicle
Root Cap
Thimble-like structure that covers the root at the apex
Prop Roots
Supporting roots example: banyan tree
Stilt Roots
Supporting roots coming out of the lower nodes of the stem example : sugarcane and maize
Pneumatophores
In swampy areas, roots come of the ground and grow vertically upwards to get oxygen. Example: Rhizophora
Nodes
Region of the stem where leaves are born
Internodes
Portion between 2 nodes
Axillary Bud
Develops into a branch
Leaf Base
The structure through which the leaf is attached to the stem
Pulvinous
Swollen leaf base example: in some leguminous plants
Petiole
Helps hold the blade to light
Lamina/Leaf Blade
Green expanded part of the leaf with veins and veinlets
Venation
Arrangement of veins and veinlets in the leaf blade
Reticulate Venation
When the veins form a network
Parallel Venation
When the veins are parallel to each other
Simple leaf
When the leaf is incised/entire, the incision doesn't reach the midrib
Compound leaf
When the incisions of a lamina reach the midrib breaking it in into a number of leaflets
Pinnately compound leaf
The leaflets are present on a common axis,called rachis, representing the midrib
ex. neem
Palmately compound leaf
Leaflets are attached to a common point (i.e tip of petiole)
ex. silk cotton
Phyllotaxy
Pattern of arrangement of leaves on the stem or branch
Alternate Phyllotaxy
A single leaf arises at each node in an alternate manner. example:China rose, Mustard, Sun Flower
Opposite Phyllotaxy
A pair of leaf arise at each node and lie opposite to each other. Example:Guava
Whorled
More than 2 leaves arises at a node and form a whorl. Example: Alstonia
Inflorescence
The arrangement of flowers on the floral axis
Racemose Inflorescence
The main axis continues to grow, the flowers are borne laterally
Cymose Inflorescence
The main axis terminates in a flower
Thalamus/Receptacle
Swollen end of the stalk on which the flower is arranged
Bisexual
The flower has both Androecium and Gynoecium
Unisexual
The flower has either Androecium or Gynoecium
Actinomorphic
Radial Symmetry example: mustard, chilli
Zygomorphic
Bilateral Symmetry example: pea,bean
Asymmetric
Cannot be divide into 2 equal halves through any plane example: canna
Trimerous
Floral appendages present in multiples of 3
Tetramerous
Floral appendages present in multiples of 4
Pentamerous
Floral appendages present in multiples of 5
Bracts
Reduced leaves
Bracteate
Flowers with reduced leaves at the base of the pedicel
Ebracteate
Flowers with no reduced leaves at the base of the pedicel
Hypogynous
Gynoecium occupies the Highest position while the others lie below it, the ovary is said to be superior example: mustard, China rose, brinjal
Perigynous
The Gynoecium situated at the centre the other parts located on the rim of the thalamus, almost at the same level as that of the ovary, the ovary is said to be half-inferior. Example: plum, rose, peach
Epigynous
The margin of the thalamus grows upward enclosing the ovary completely and the other parts are situated above the ovary. The ovary is said to be inferior. Example: guava, cucumber
Gamosepalous
Sepals are united
Polysepalous
Sepals free
Gamopetalous
Petals united
Polypetalous
Petals free
Aestivation
The mode of arrangement of sepals or petals in floral bud with respect to the other members at the same level.
Valvate Aestivation
Sepals or petals in a whorl just touch one another at the margin without overlapping example: calotropis
Twisted Aestivation
Sepals or Petals overlap one another in a pattern/a particular direction example: China rose, cotton, lady's finger
Imbricate Aestivation
Sepals or Petals overlap one another in any particular direction example: cassia, Gulmohar
Vexillary Aestivation
The largest, standard, overlap the 2 lateral ones, wings, which in turn overlap the 2 anterior ones, keels
Staminode
Sterile stamen
Epipetalous
Stamens attached to petals example: brinjal
Epiphyllous
Stamens attached to the base of the receptacle (perianth) example:Lily
Polyandrous
Stamens remain free
Monoadelphous
Stamens united in one bundle example: China rose
Diadelphous
Stamens United into 2 bundles example : pea
Polyadelphous
Stamens United into 2 or more bundles example: citrus
Perianth
When the calyx and Corolla aren't distinct
Apocarpous
Carpels free example :lotus
Syncarpous
Carpels are fused example :mustard
Placentation
Arrangement of ovules in an ovary
Marginal Placentation
The ovules are present at one common margin eg:pea
Axile Placentation
Ovules are present on the central axis and the ovary is divided into 3 locules eg: China rose
Parietal Placentation
Ovules are present at the perimeter of the ovary eg: mustard
Free Central Placentation
The ovules are present at the central axis but this time the ovary isn't divided into locules eg:primrose
Basal Placentation
Single ovule attached to the base of the ovary eg: sunflower
Parthenocarpic fruit
Fruit formed with the fertilisation of the ovary
Region of Meristematic Activity
place where thin walled cells with dense protoplasm that divide repeatedly (meristems) are created.... cells mature and become specialized in function
Region of Elongation
Where cells produced by mitosis undergo a period of elongation in the direction of the axis of the root.
Region of Maturation
Root hairs are produced in the...
Assimilatory Roots
Roots modified to perform photosynthesis
Ex. Tinospora
Tendrils (Stem Modification)
Thin spirally coiled, develop from axillary bud, and help plants grow.
ex. gourds (cucumber, pumpkins, watermelon)
Thorns
Woody, straight, pointed.
Protect plants from browsing animals
ex. Citrus Bougainvillea
flattened- Opuntia
cylindrical- Euphorbia
Tendrils (Leaf Modification)
modified for climbing
ex. peas
Spines
Modified as a defense mechanism
ex. cacti
Calyx
sepals
Corolla
Petals
Endosperm
a tissue produced inside the seeds of most flowering plants around the time of fertilization.
surrounds embryo
bulky and stores food
Testa
outer layer of seed coat
Tegmen
inner layer of seed coat
Hilum
scar on seed coat through which the developing seeds were attached to the fruit
Micropyle
small pore above hilum through which pollen tube can enter
Aleurone Layer
outermost proteinaceous layer of endosperm
Scutellum
large and shield shaped cotyledon in embryo
Coleoptile
Sheath enclosing plumule
Coleorhiza
sheath enclosing radicle
phylloclade
stem performing photosynthesis
example - opuntia(flattened),
euphorbia(cylindrical)
cladode
internode modificn
pinnate
neem(rachis)
palmate
silk cotton
pulvinus
Swollen leaf base in leguminous plants
hypogynous
Mustard, china rose, brinjal
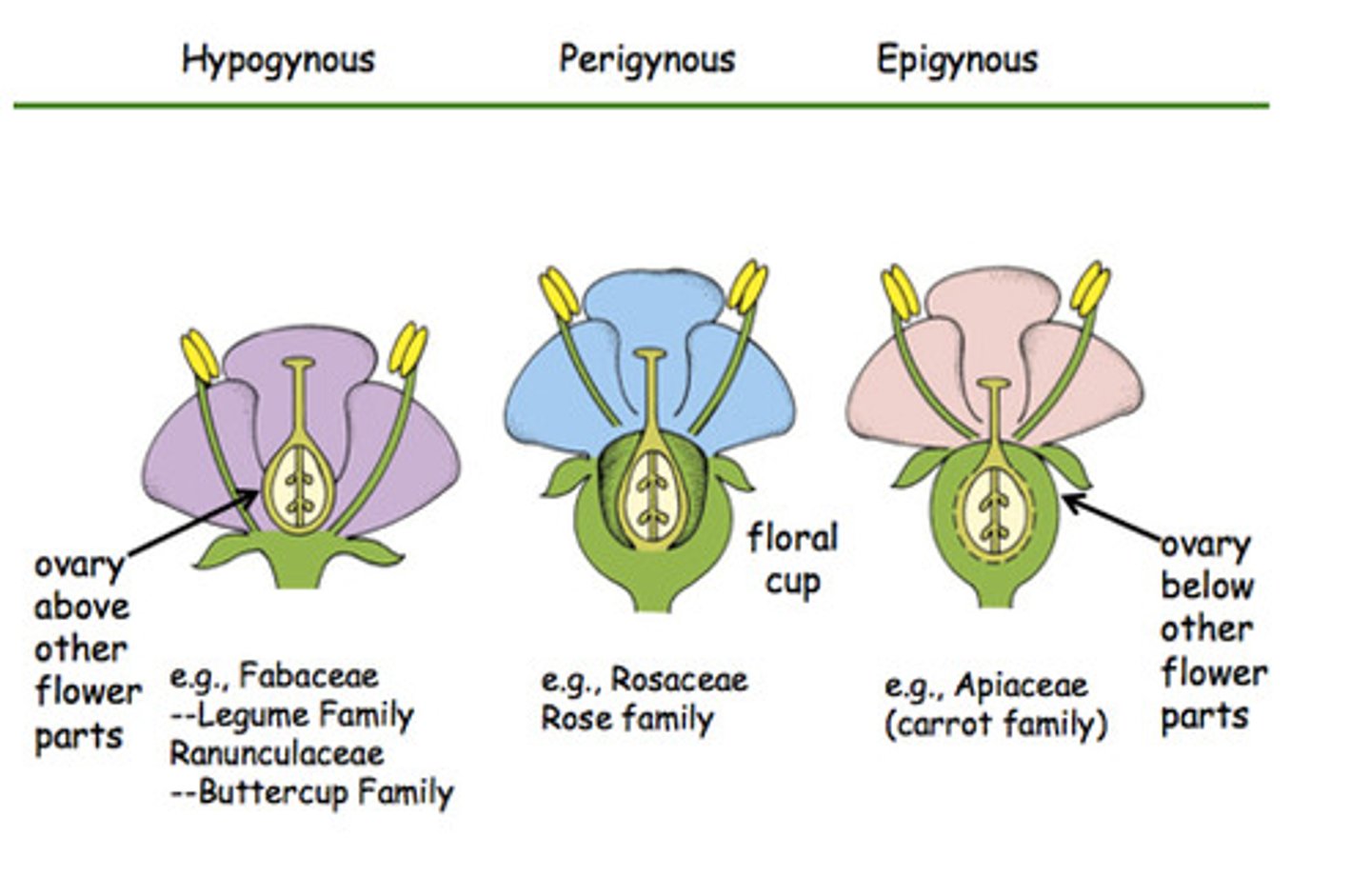
perigynous
plum
rose
peach