Proteomics Lecture 2- How does this affect bioinformatics?
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are 4 batch effects?
Calibration
Protein digestion
Peptide clean-up
Buffer change.
3 ways in which batch effects are dealt with?
Retention time confirmation
Experimental procedures (random samples, single-run sample analysis).
Software correction.
Name 3 examples of software packages that handle shotgun proteomics data.
Proteome discoverer
Pekas
MaxQuant
Name 4 types of user-defined thresholds.
MS1/2 data quality
Probability (p value or FDR)
Annotation (database choice)
Intensity thresholds
What are batch effects in data identified by?
PCA
What deals with batch effects in data? (2)
ComBat or BMC
What types of MS proteomic information do we require (4)?
What the protein is.
Level of expression (abundance).
Post-translational modifications.
Which proteins interact.
Role of label-free shotgun proteomics?
Identifies what is in my sample and how much is there.
Role of targeted proteomics?
Directs the mass spectrometer to scan the precursor peptides until it sees once of a specified mass. Increases sensetivity but reduces coverage.
What is used for Metabolic Isobaric labelling?
SILAC.
What does SILAC do?
Stable isotope labelling of amino acids in cell culture. Cells are labelled with heavy amino acid, so the precursor peptide has 2 (heavy and light) peaks which can be quantified and compared.
What is used for Chemical Isobaric labelling?
iTRAQ/ TMT.
What does iTRAQ/TMT do?
Isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantification. Multiplexed isobaric chemical tagging reagent. Proteins are digested and peptides are chemically labelled with isobaric tags.
What does quantifying using a label-free method to measure protein abundance entail?
Spectral counting the total number of MS/MS spectra identified from a particular protein.
How does iTRAQ work? (3)
Up to 8 samples are digested and labelled.
They are mised and seperated by HPLC
They are then put in a mass spectrometer.
What are the challenges of shotgun proteomics? (6)
Usually comparative nowadays
Lots of samples
Lots of missing values
Significant batch effects
Deciding where to put thresholds on e.g., significance (p value or FDR).
How to quantitate- label free? Reference?
What are 2 methods of detecting PTMs?
Phosphopeptide enrichment by IMAC
Glycoprotein enrichment by LAC
Process of Tandem affinity purification to find interacting proteins.
Cell lysis by non- ionic denaturant
Incubation of cell lysate with antibody
Removal of unbounded proteins
Western blot/mass spectrometry analysis
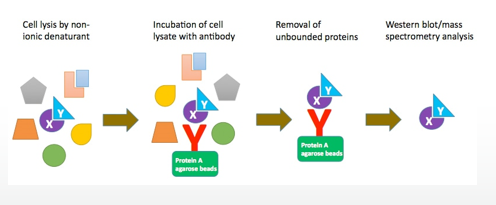
What are X and Y in the Tandem affinity purification? How do they interact?
X= bait protein
Y= prey protein
They interact at a low affinity and may be disrupted by the lysis method.
What is the interactome? This can inform you on likely protein function.
The sum of known interactions, which can inform about likely protein function.
What is pathway analysis?
Can examine the relationship between differentially expressed proteins in the same way as differentially expressed genes.
What does pathway analysis raise questions about?
Which samples need to be tested orthogonally.
How are protein modifications detected (PMTs)?
Phosphoproteomics and glycomics.
What method can be used to locate the location of proteins?
Isolation of organelles or other cell fractions.
What does immunoprecipitation of a target protein do? Why is this useful?
Will brind others along that bind to it. Can be useful to determine binding partners, e.g., receptors/ligands, or other members of protein assemblies, e.g., proteasome.
Name a diagnostic tool for clinical analysis.
MS