Lecture 3.2: Brain and Cranial Nerves
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
193 Terms
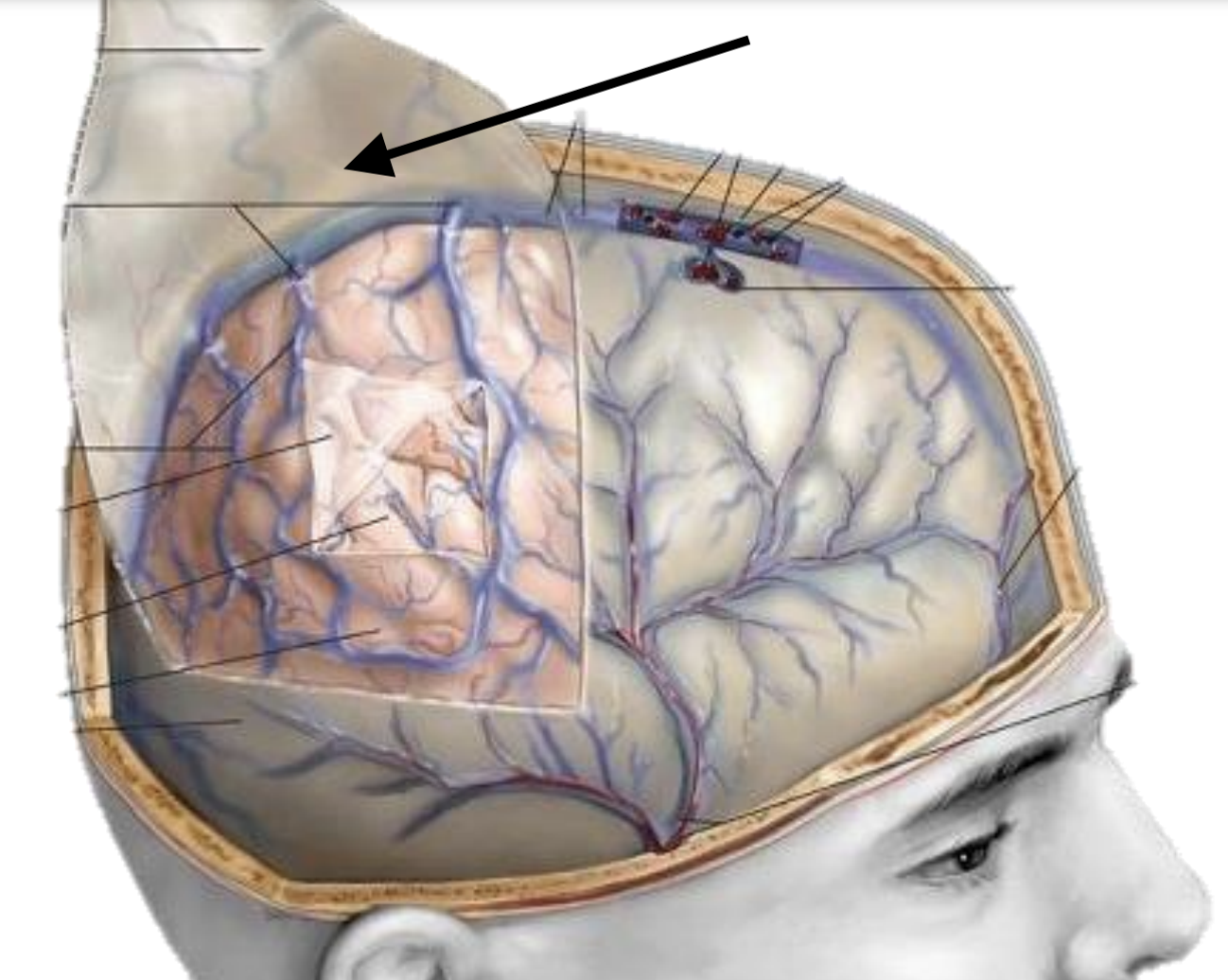
What are the cranial meninges? (deepest to most superficial)
Pia mater, arachnoid mater, dura mater
Name the meninge
Dura mater
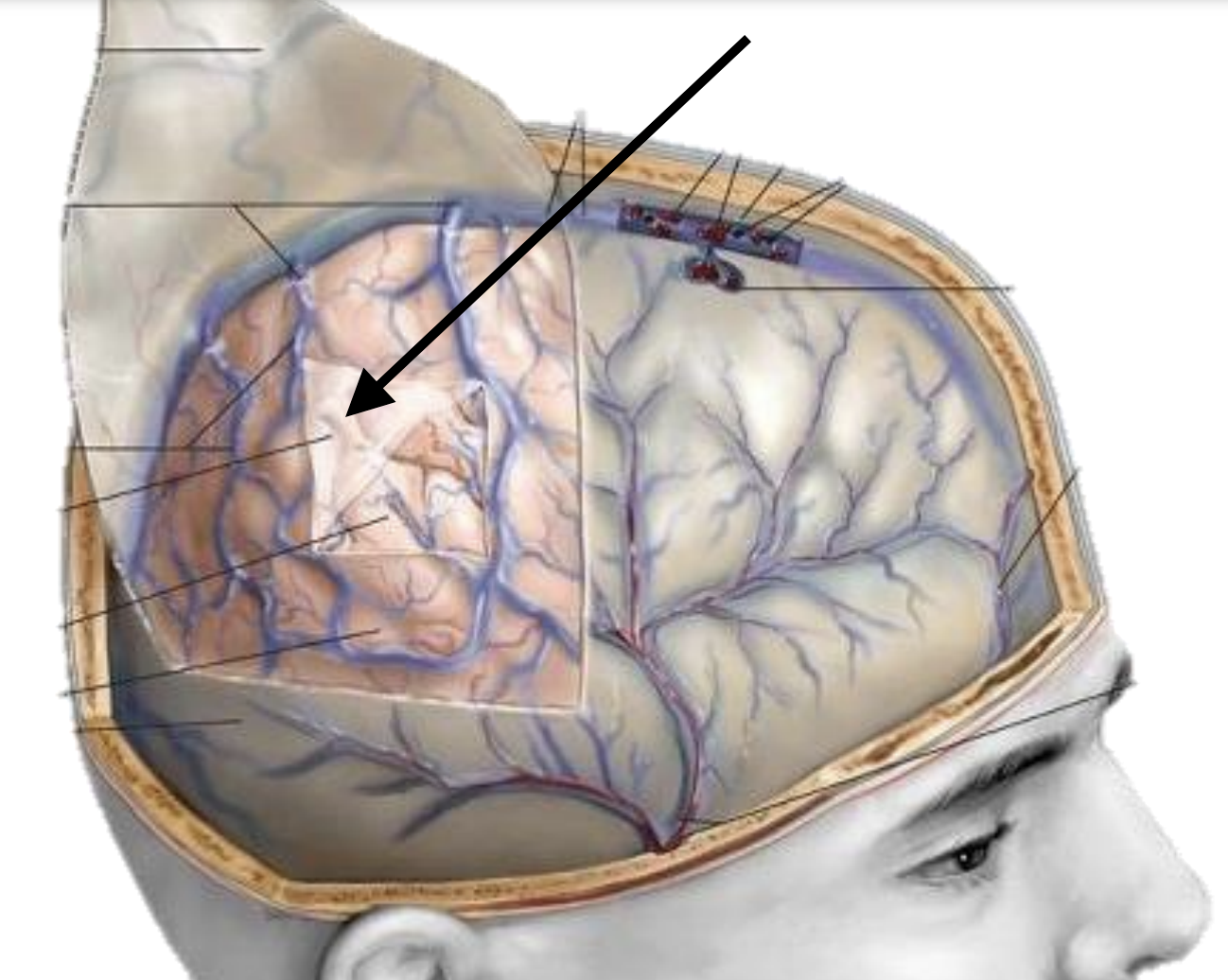
Name the meninge
Arachnoid mater
Name the meninge
Pia mater
What are the dural venous sinuses?
Meningeal layer, periosteal layer
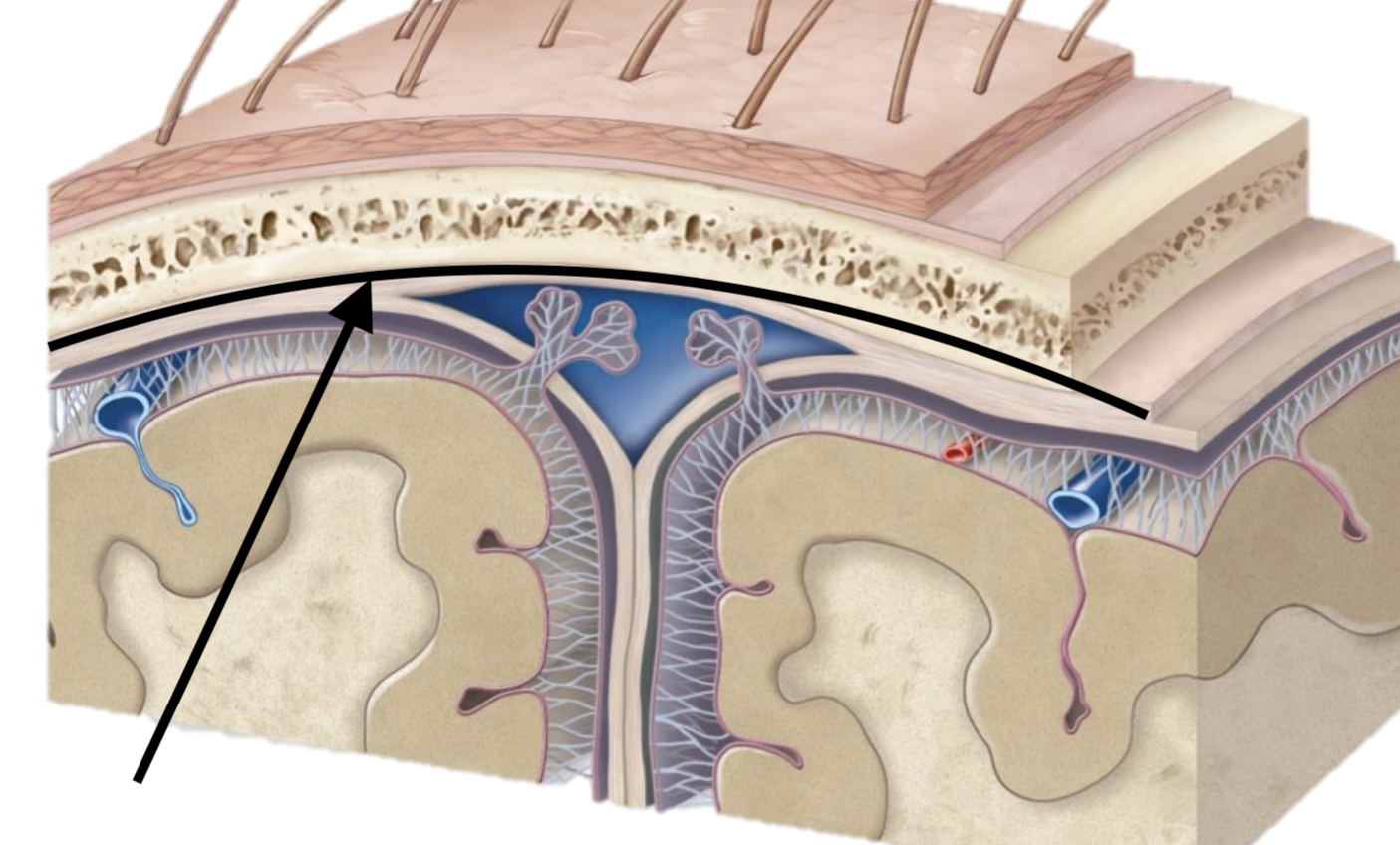
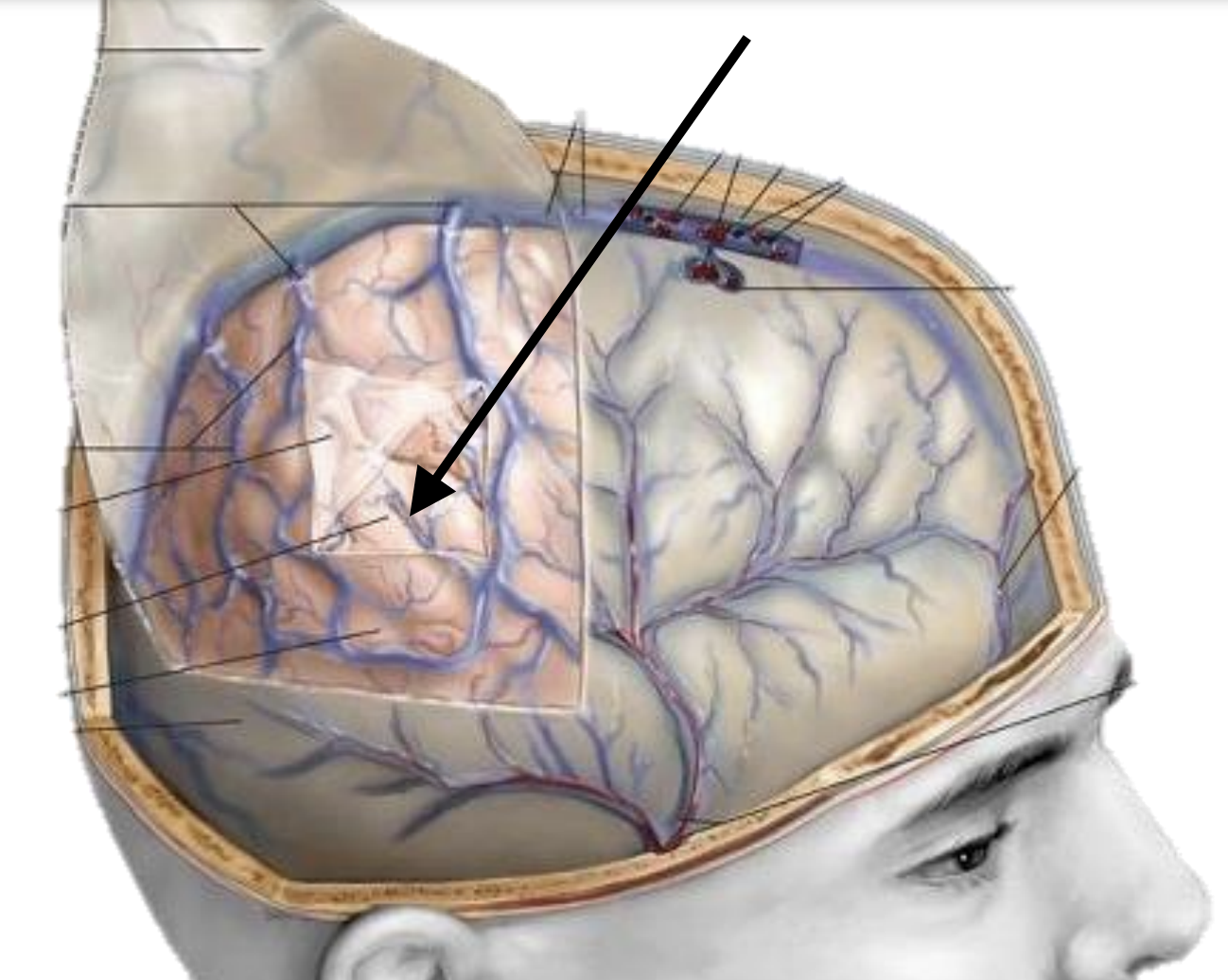
Name the dural mater layer
Periosteal layer
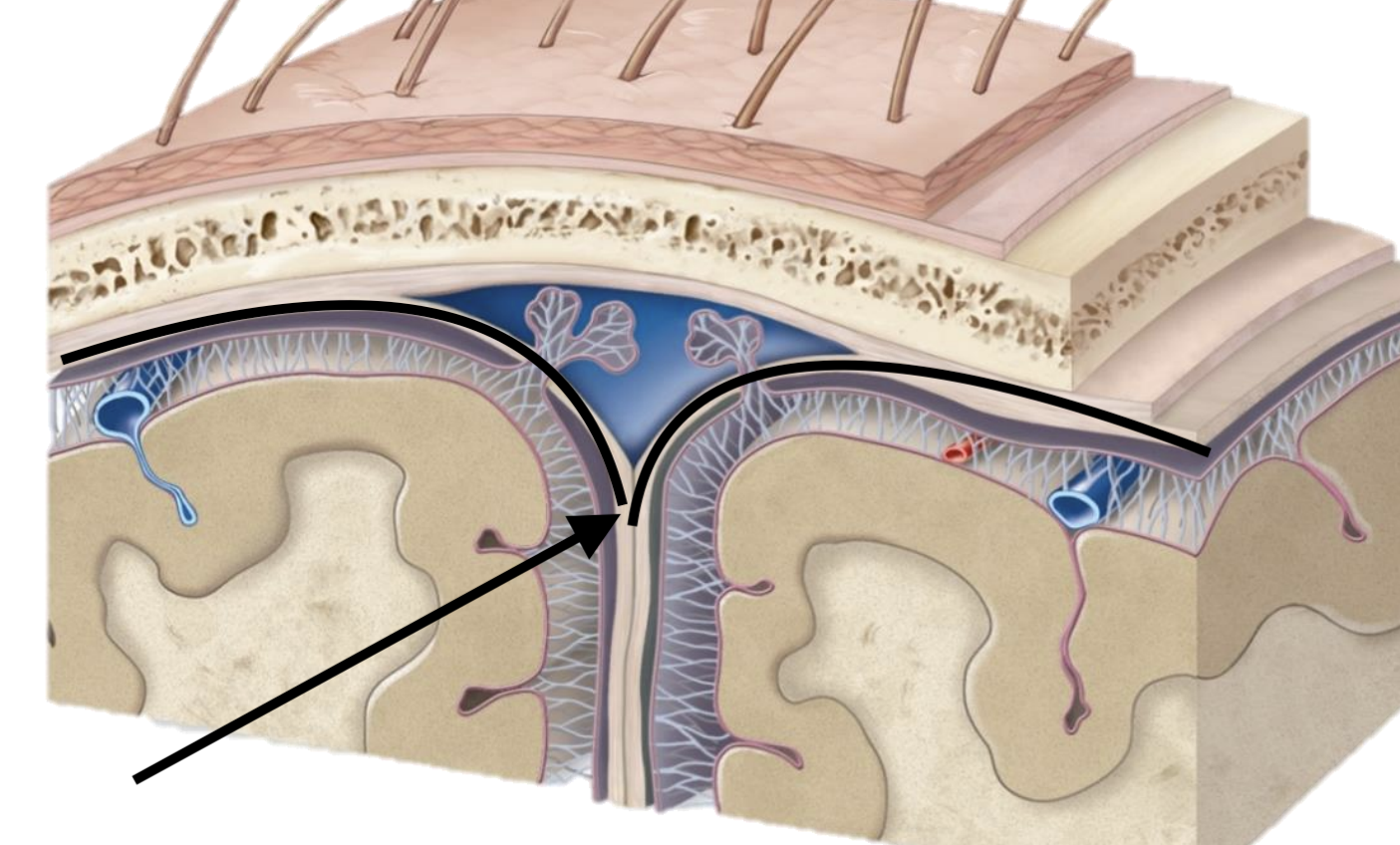
Name the dural mater layer
Meningeal layer
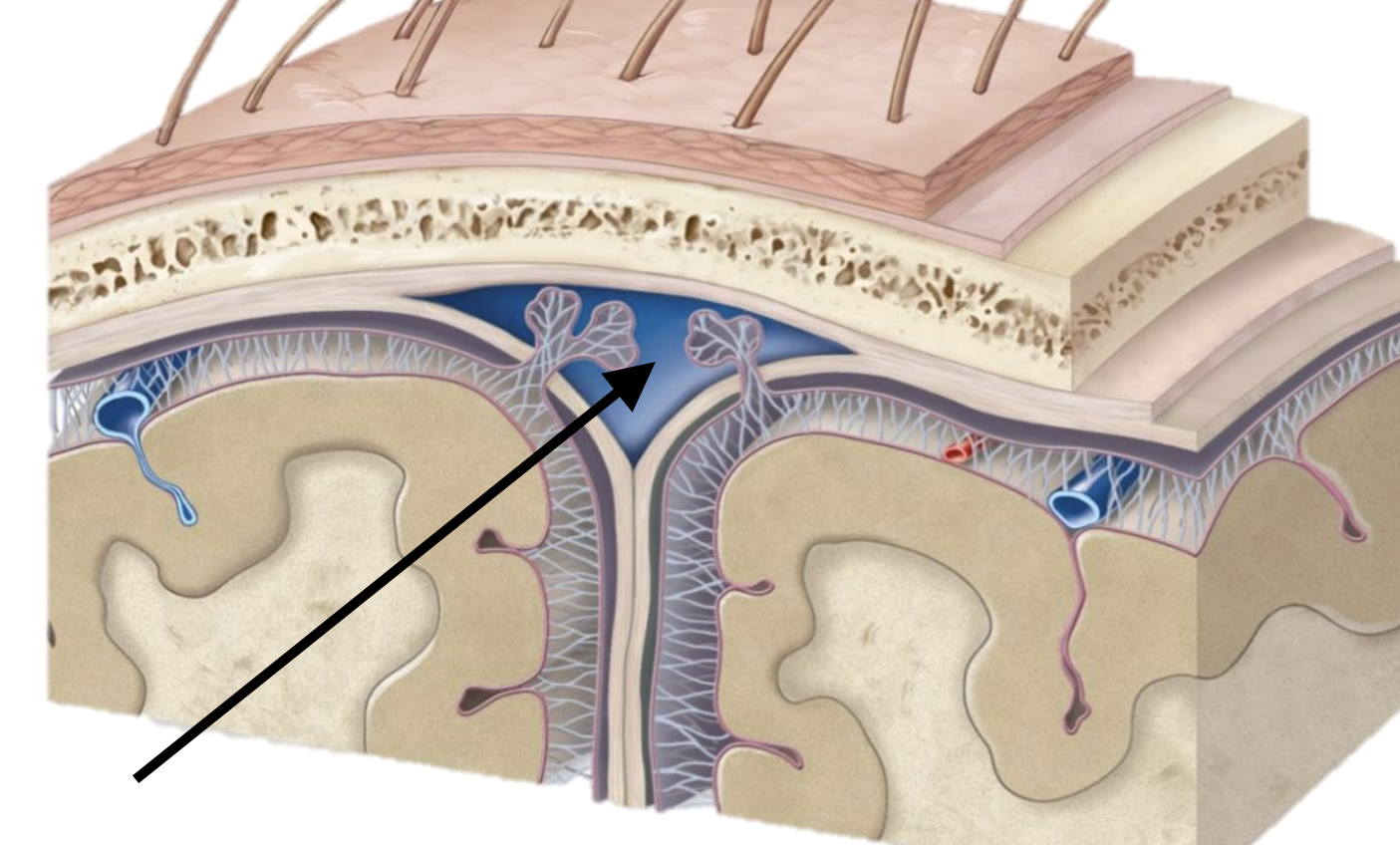
Name the structure
Dural venous sinus
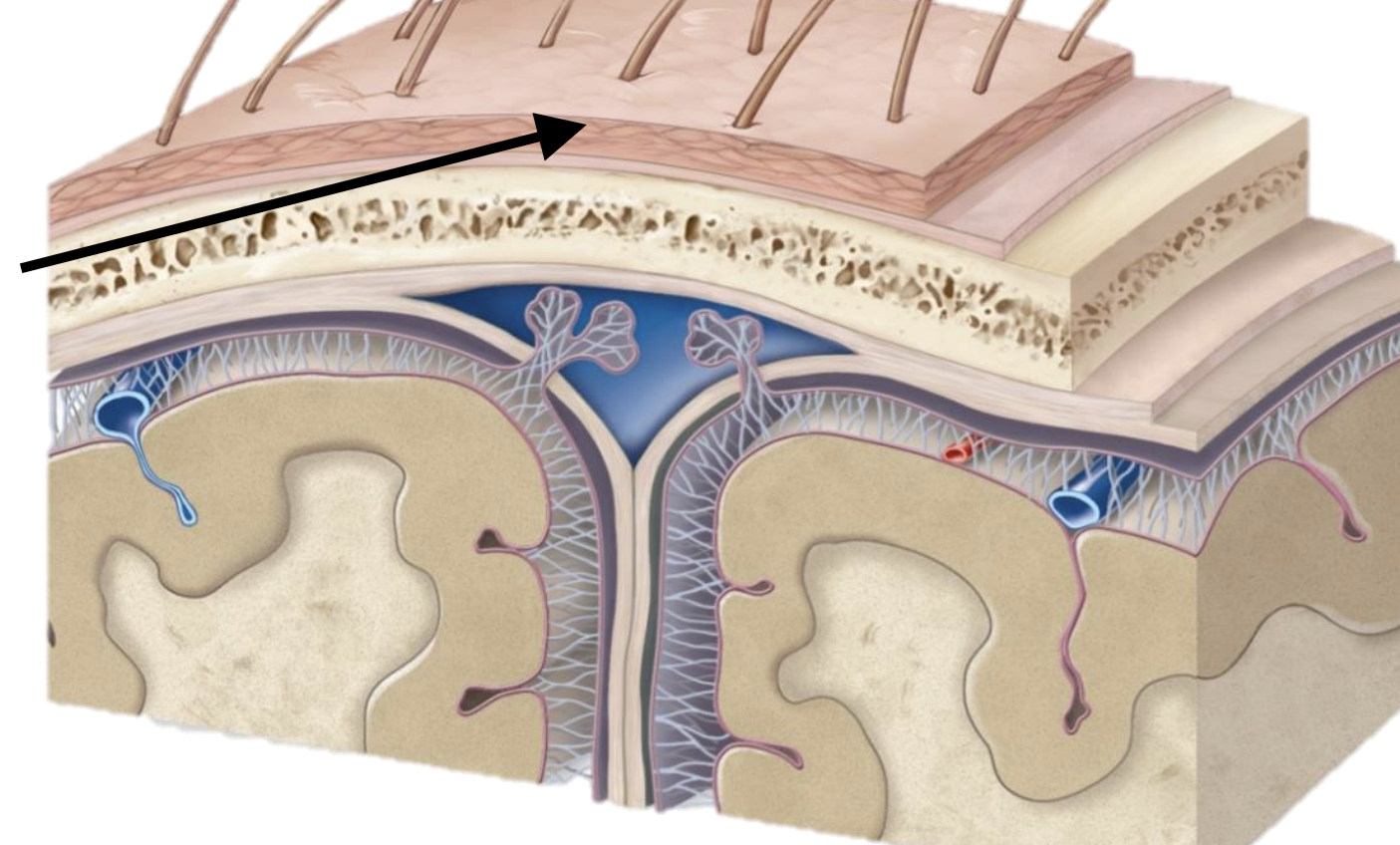
Name the structure
Skin
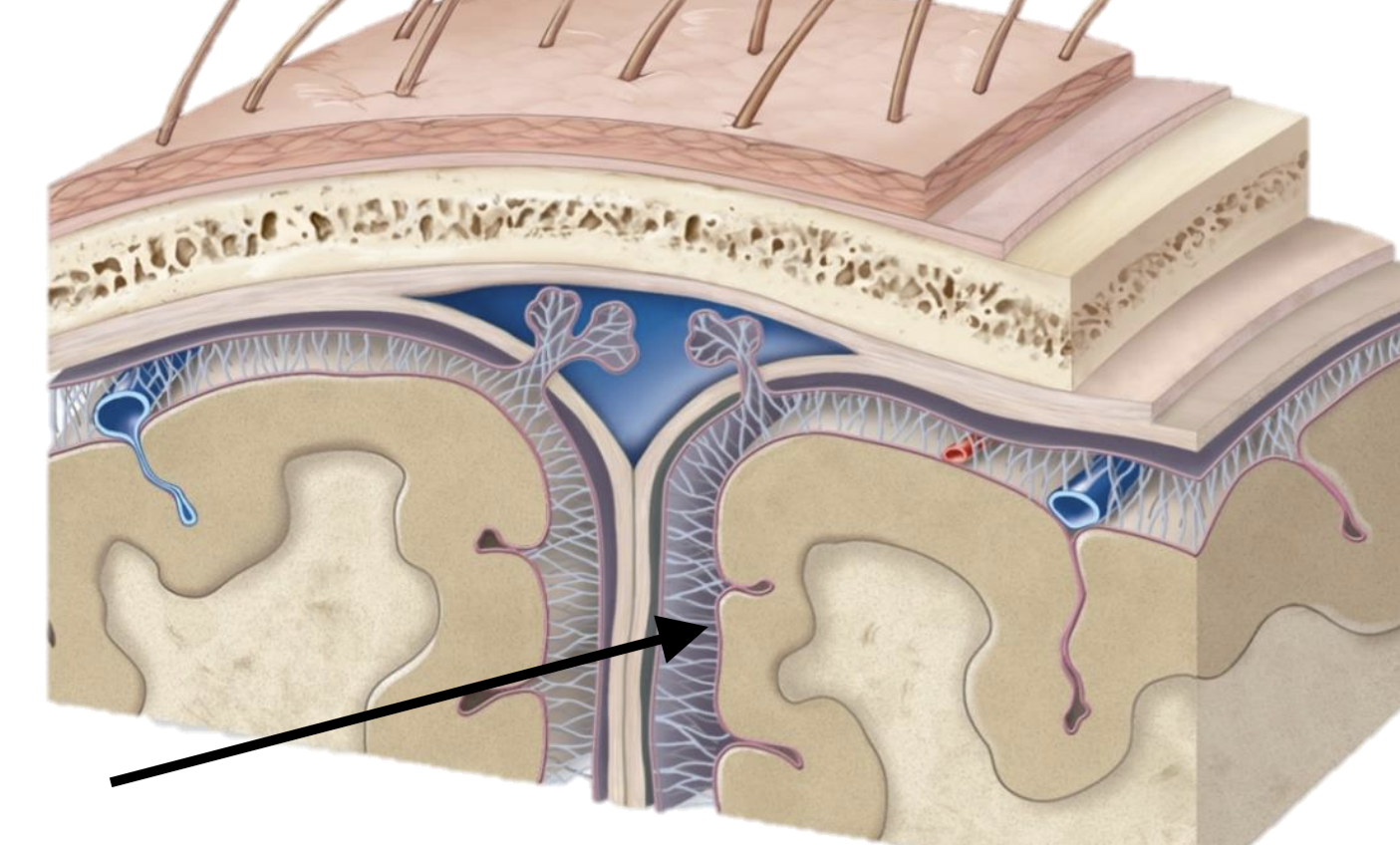
Name the structure
Arachnoid
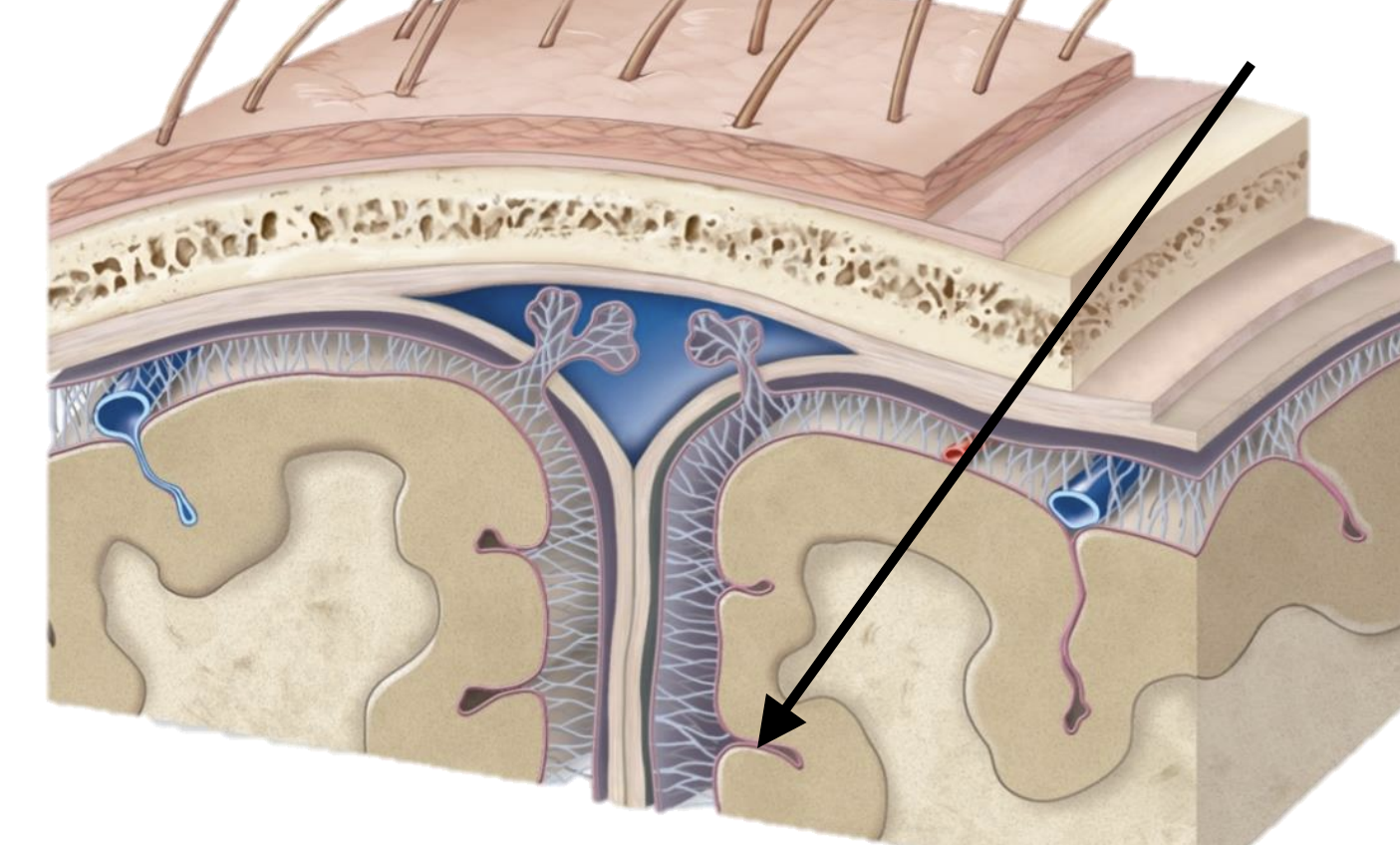
Name the structure
Pia
What structures are included in the dural septa?
Falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli
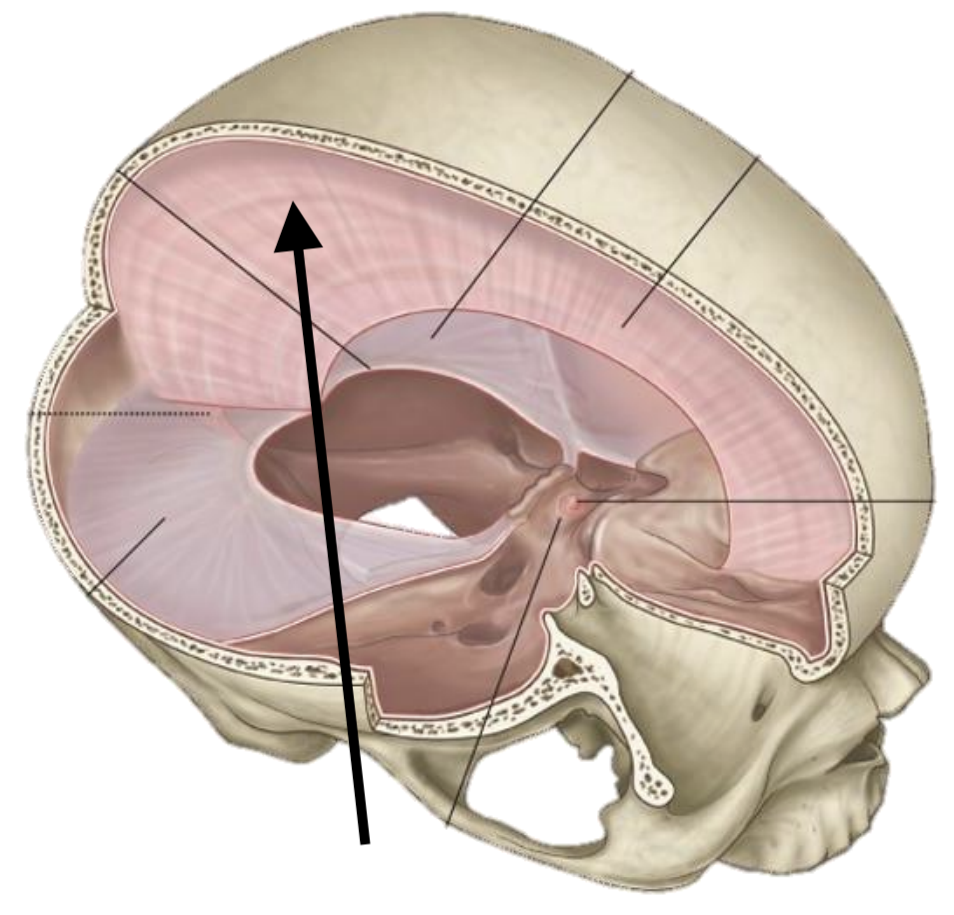
Name the structure
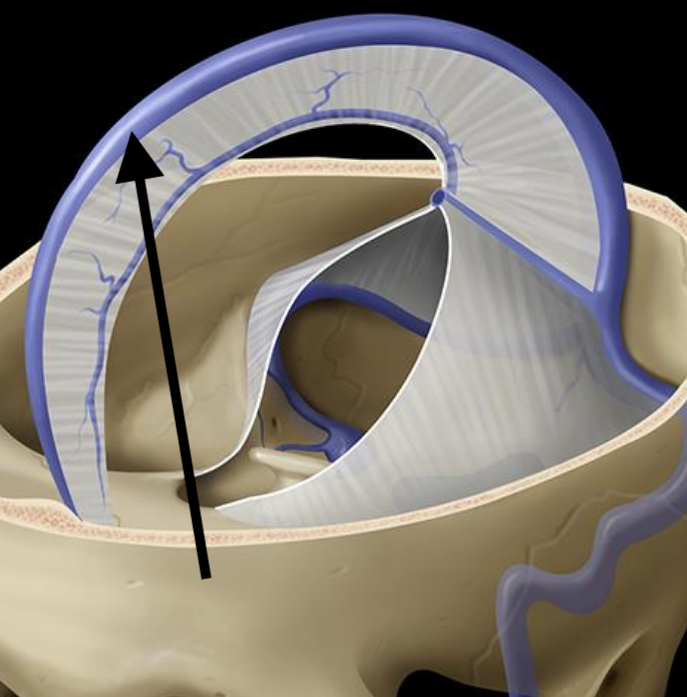
Falx cerebri
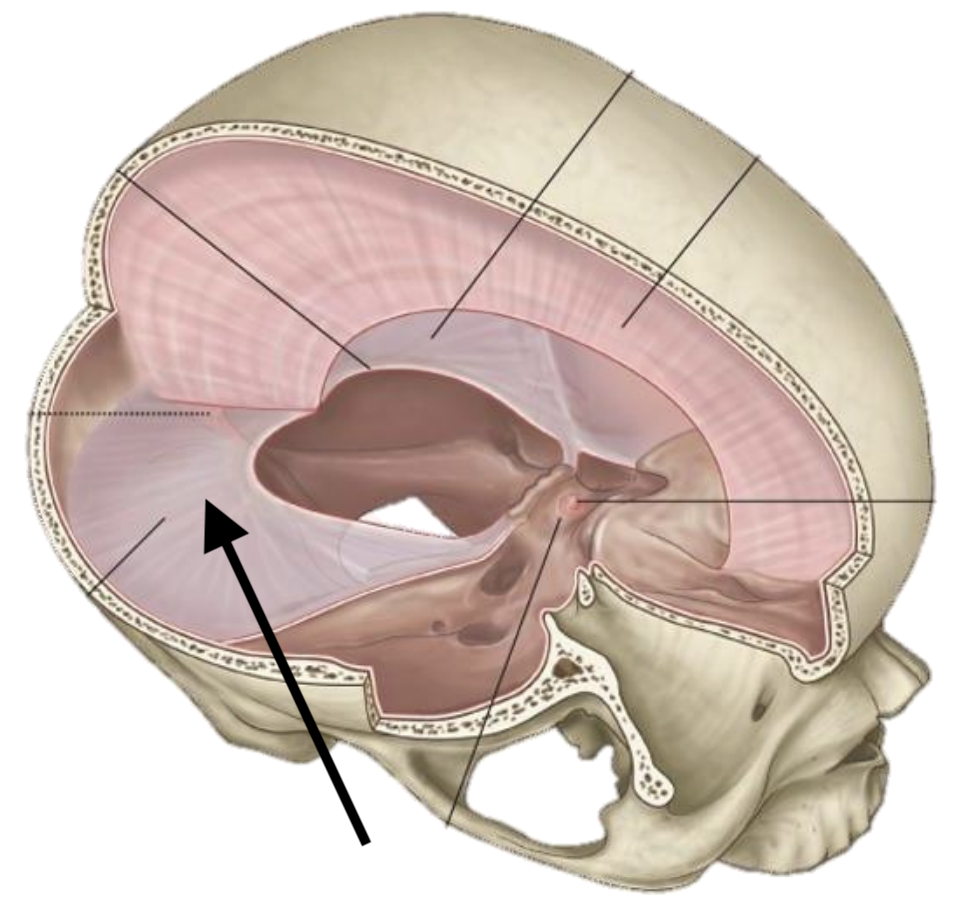
Name the structure
Tentorium cerebelli
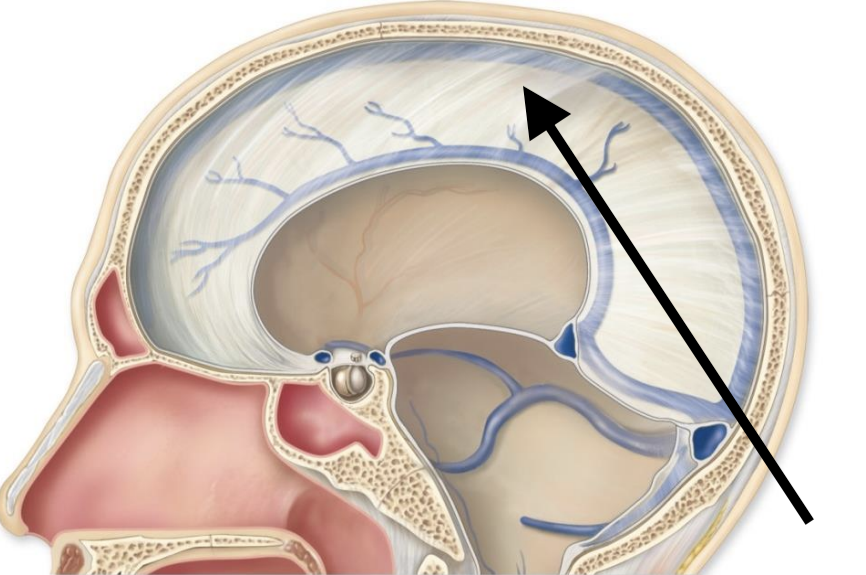
Name the structure
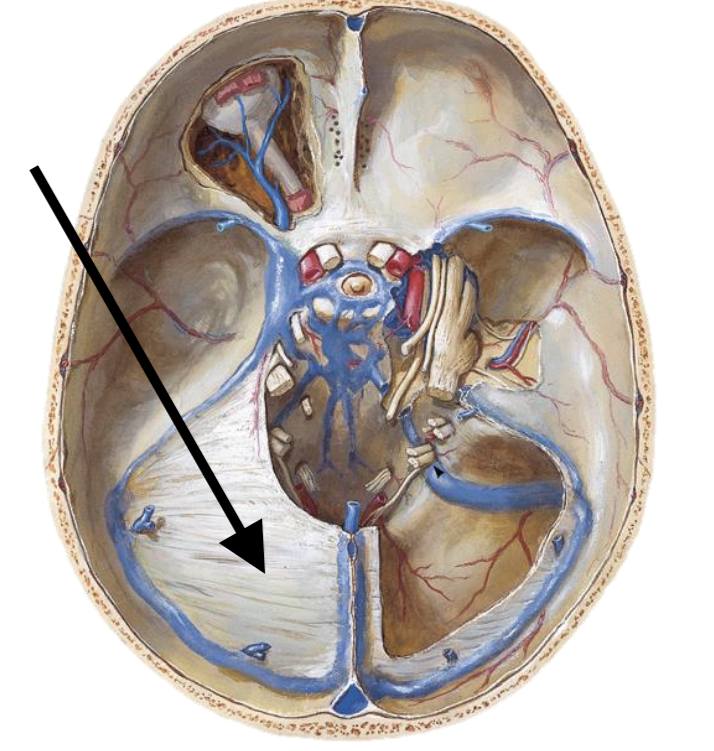
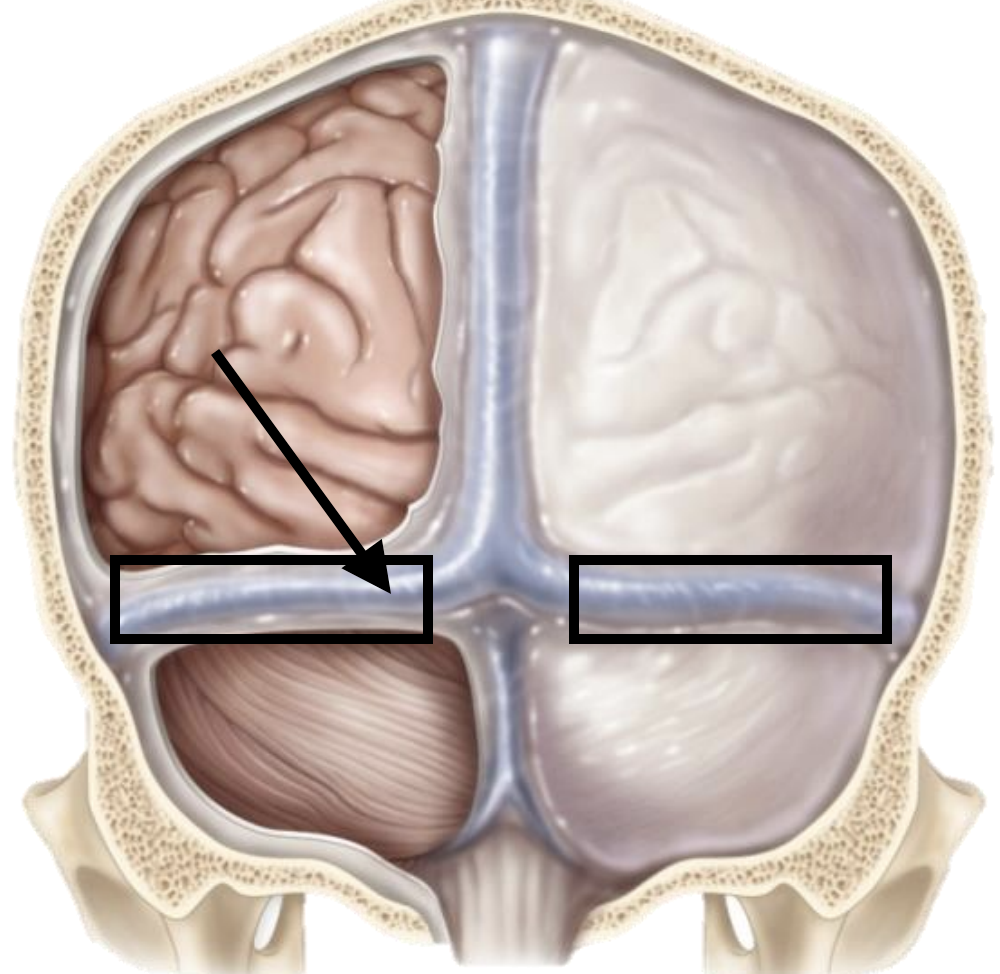
Falx cerebri
Name the structure
Tentorium cerebelli
Name the structure
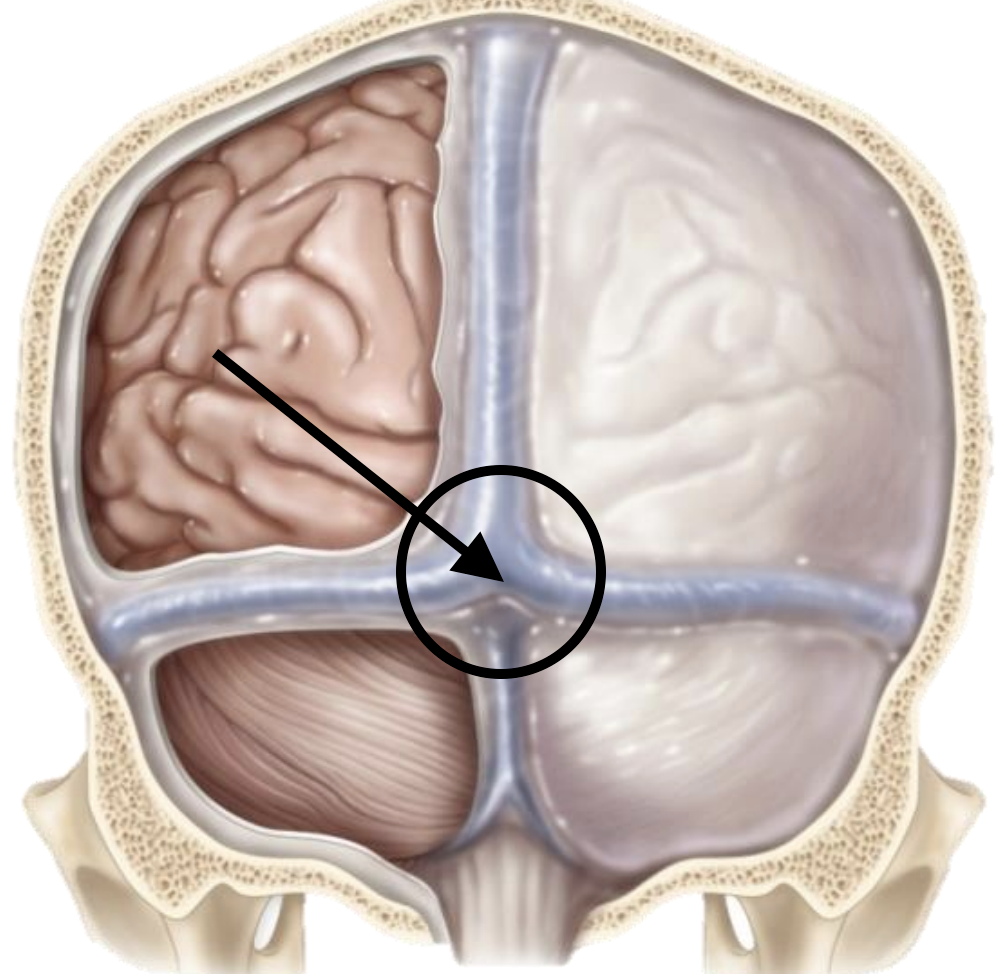
Transverse sinus
Name the structure
Confluence
Name the structure
Superior sagittal sinus
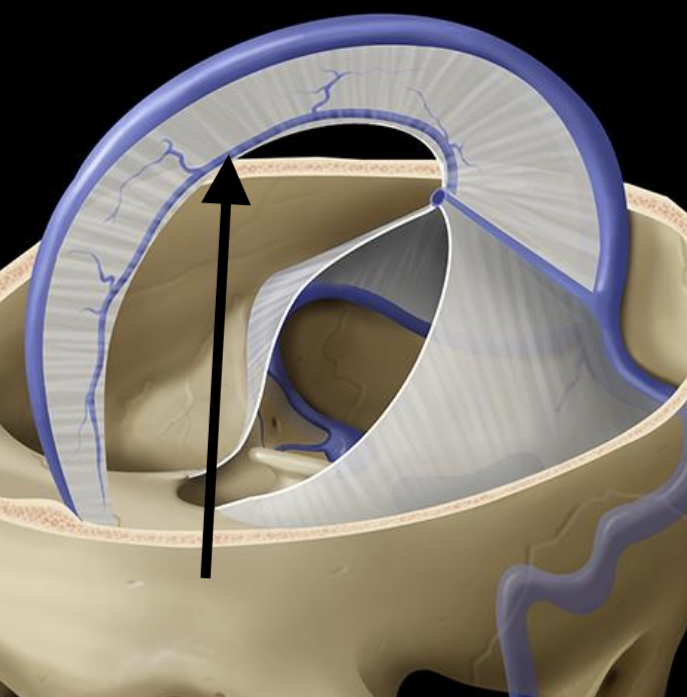
Name the structure
Inferior sagittal sinus
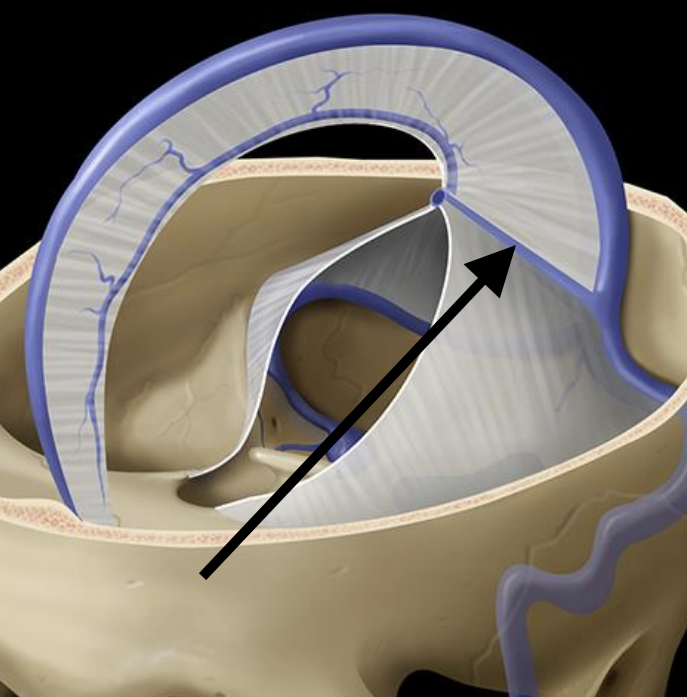
Name the structure
Straight sinus
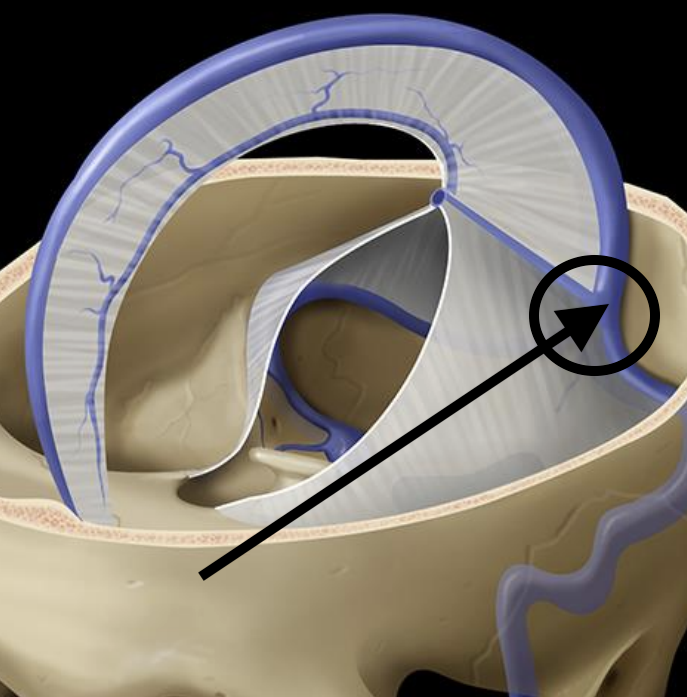
Name the structure
Confluence
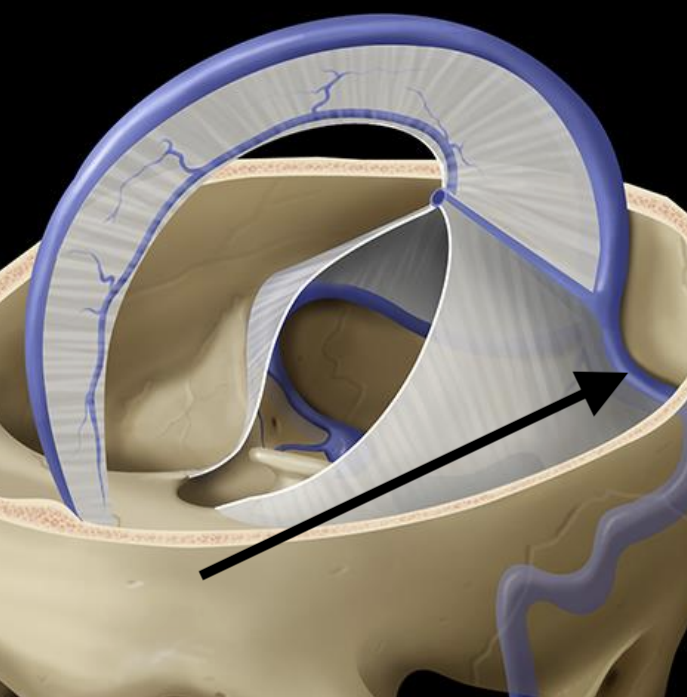
Name the structure
Transverse sinus
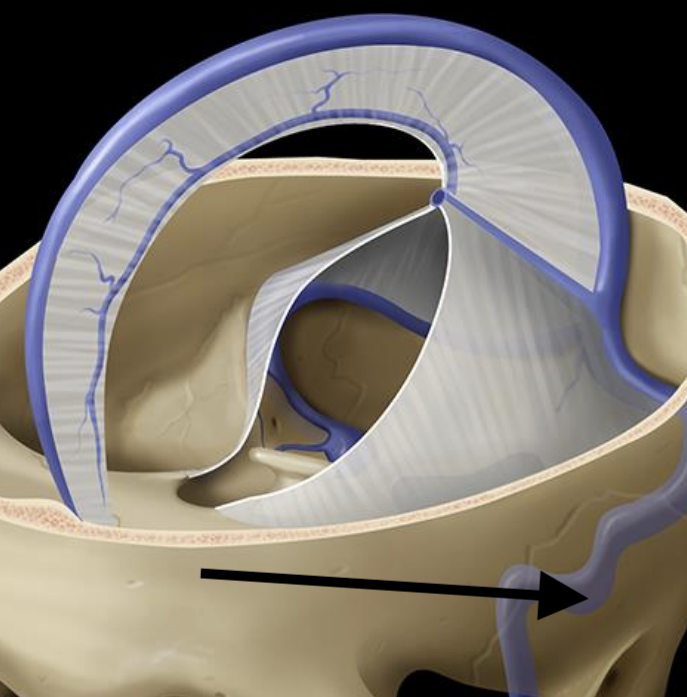
Name the structure
Sigmoid sinus
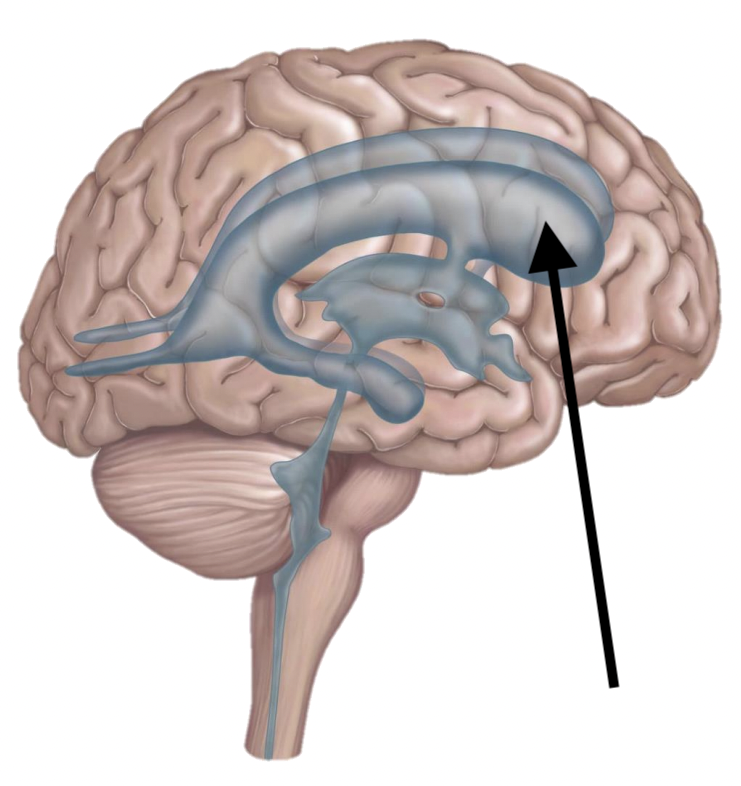
Name the structure
Lateral ventricles (x2)
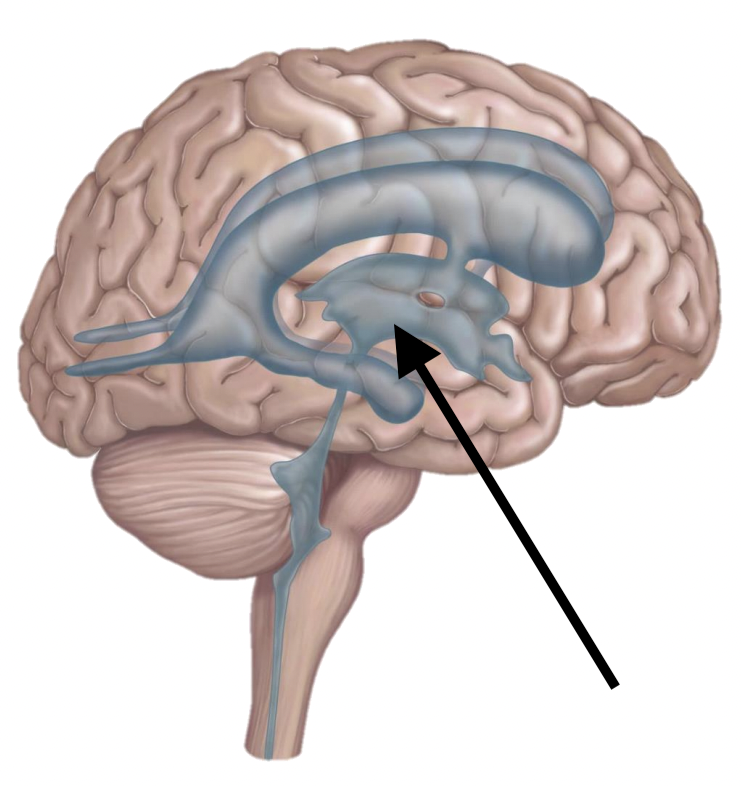
Name the structure
3rd ventricle
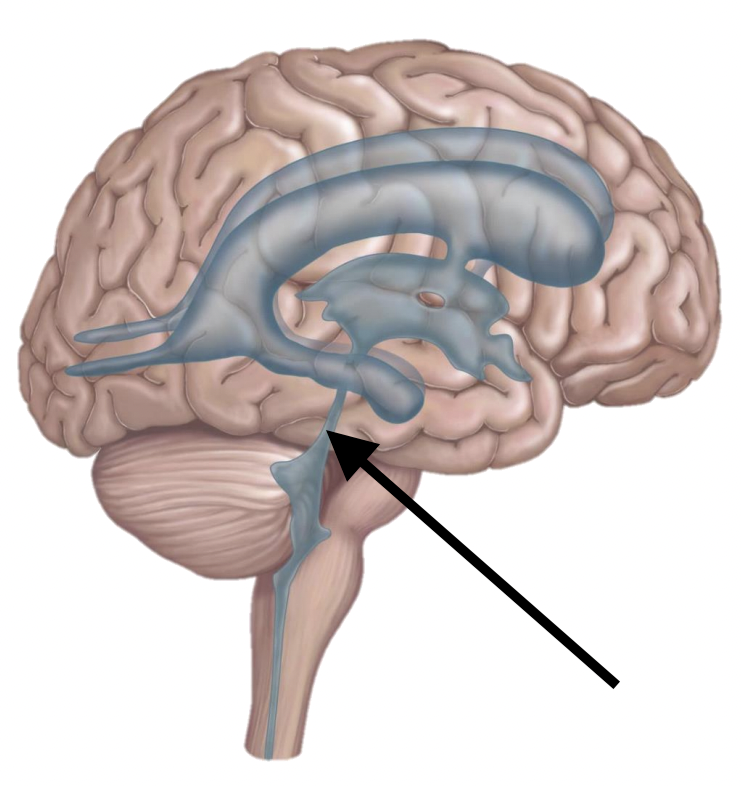
Name the structure
Cerebral aquaduct
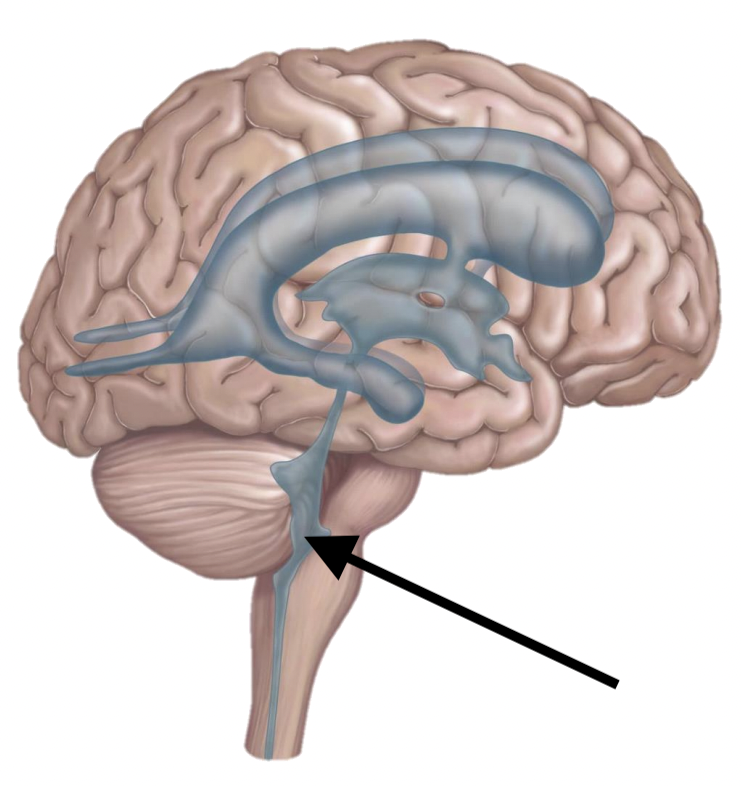
Name the structure
4th ventricle
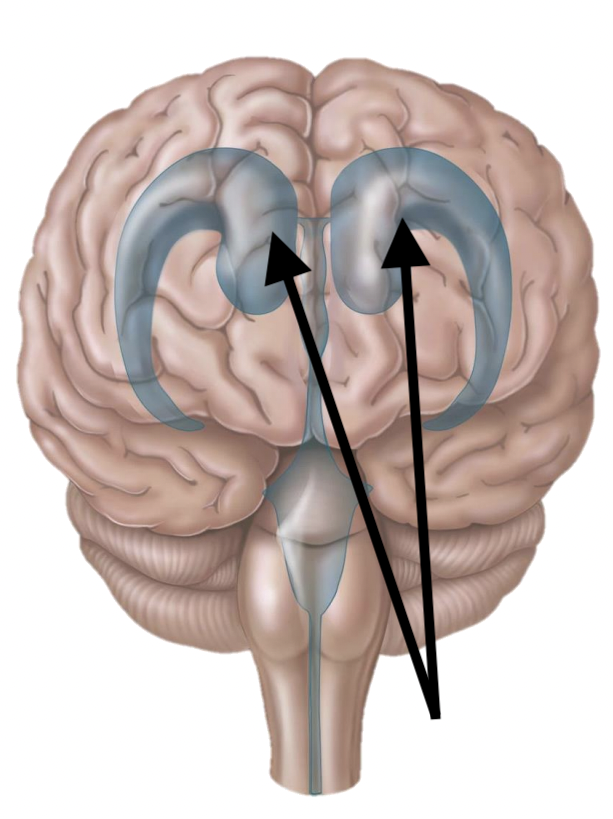
Name the structure
Lateral ventricles (x2)
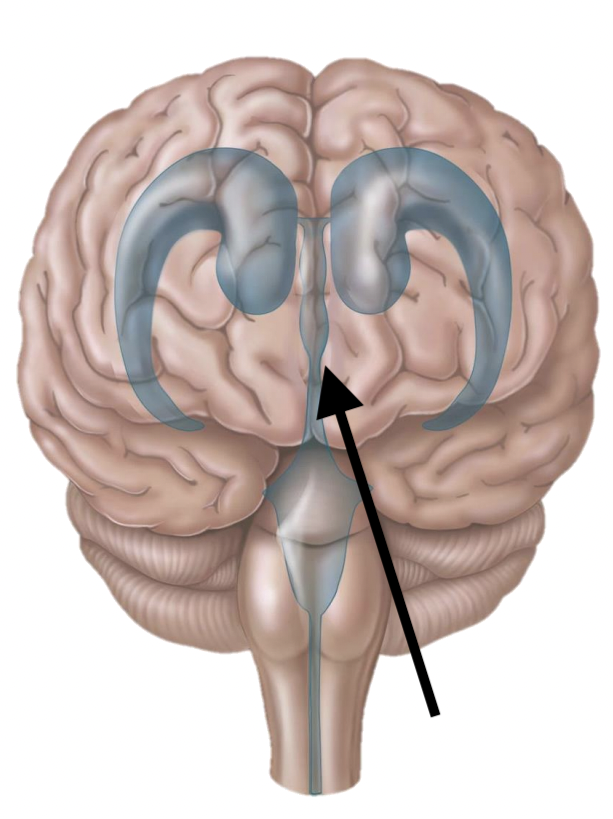
Name the structure
3rd ventricle
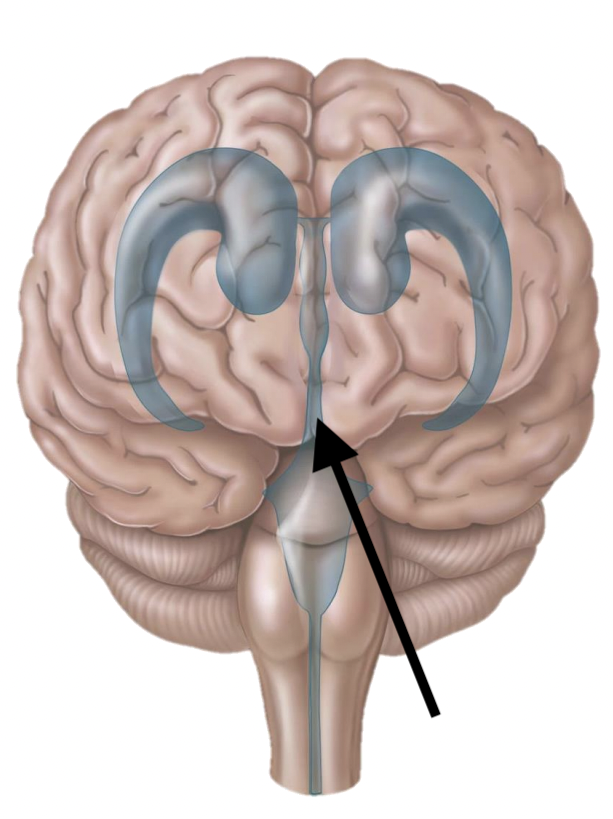
Name the structure
Cerebral aquaduct
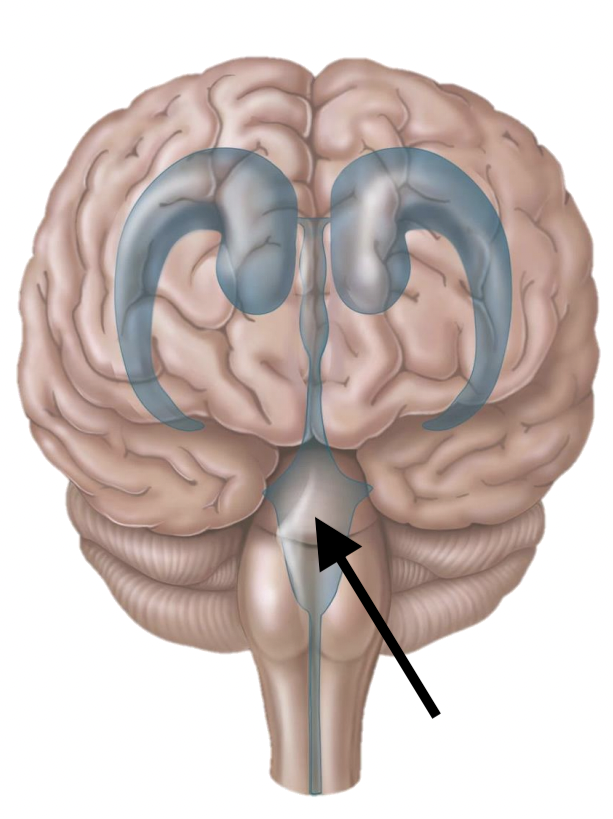
Name the structure
4th ventricle
Define cerebrospinal fluid
A clear liquid that circulates in the ventricles and subarachnoid space
What are the functions of cerebrospinal fluid?
Buoyancy, protection, chemical stability
How is CSF formed?
By the choroid plexuses (ependymal cells + capillaries) within each ventricle
Describe CSF circulation
CSF is produced by the choroid plexus in the ventricles
CSF flows from 3rd ventricle to the cerebral aquaduct to the 4th ventricle
CSF flows from 4th ventricle to the subarachnoid space to the central canal of spinal cord
Excess CSF flows into arachnoid granulations (villi), which drain into the dural venous sinuses
What structures are included in the telecephalon brain region?
Cerebrum
What structures are included in the diecephalon brain region?
Epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
What structures are included in the mesencephalon brain region?
Midbrain
What structures are included in the metencephalon brain region?
Pons, cerebellum
What structures are included in the myelencephalon region?
Medulla oblongata
What brain structures are a part of the brain stem?
Midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
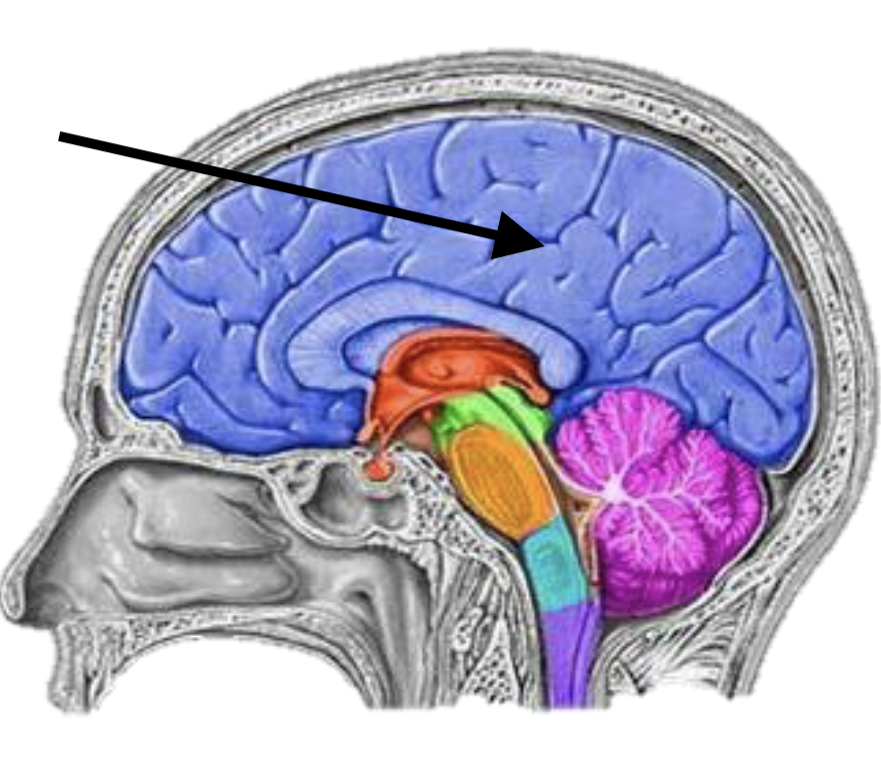
Name the brain structure
Cerebrum
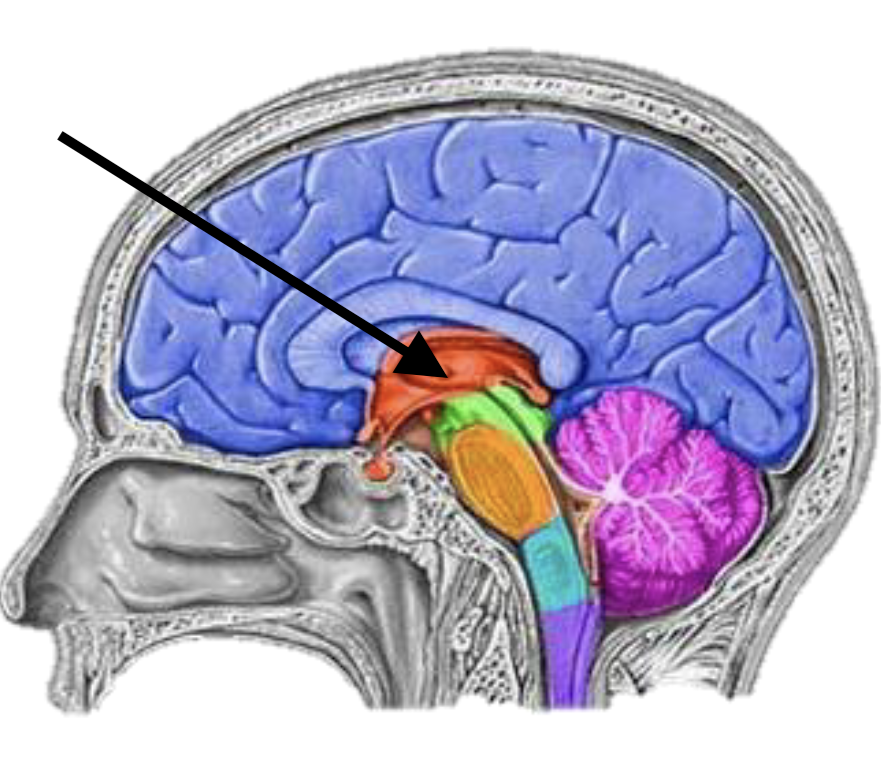
Name the brain structure
Epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
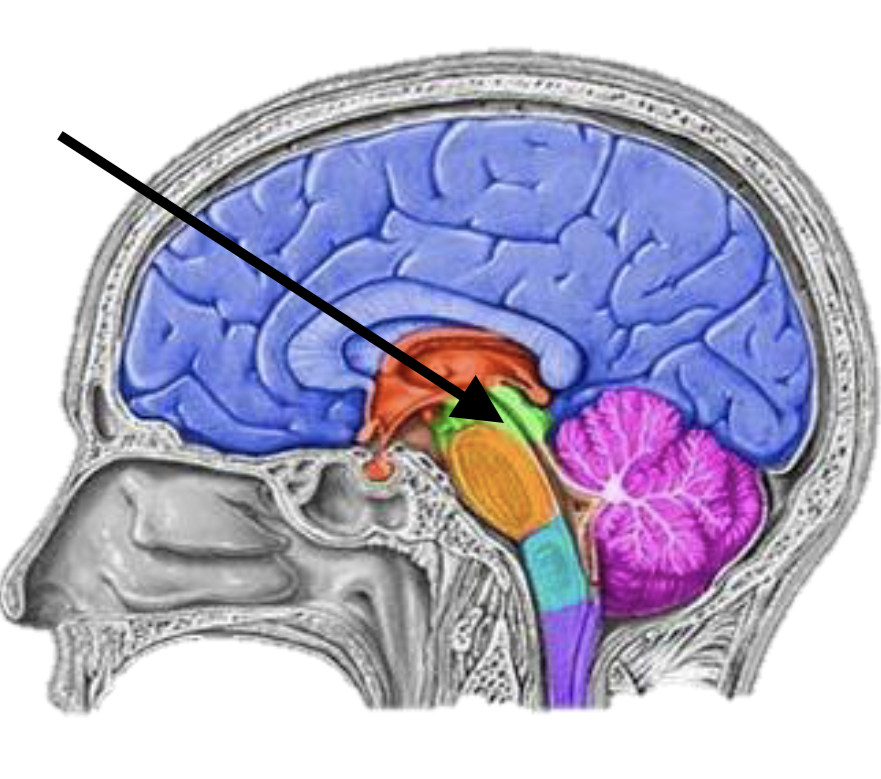
Name the brain structure
Midbrain
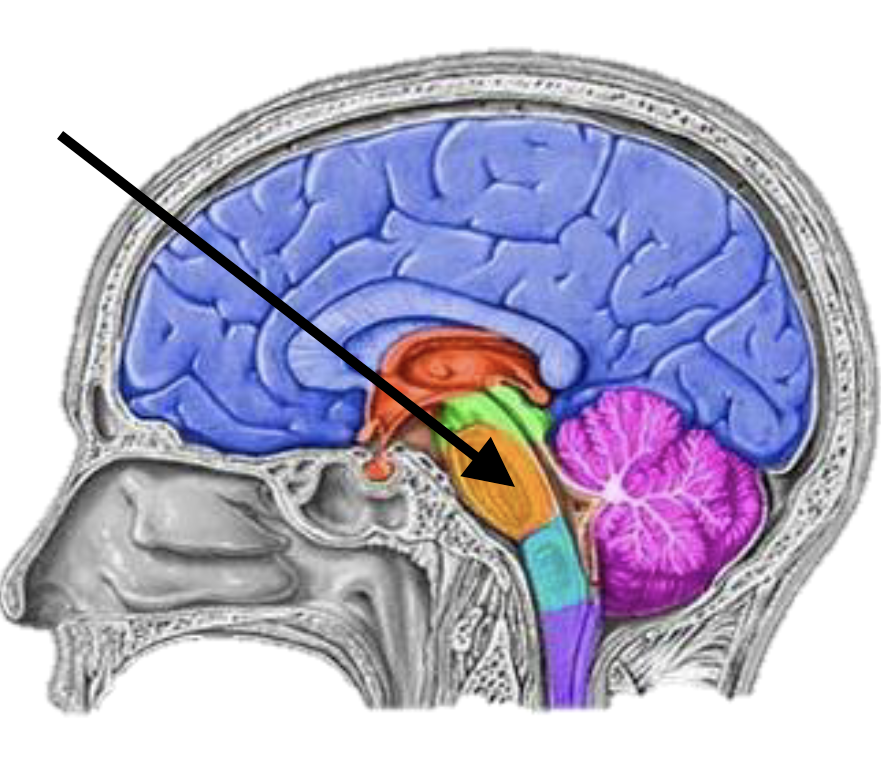
Name the brain structure
Pons
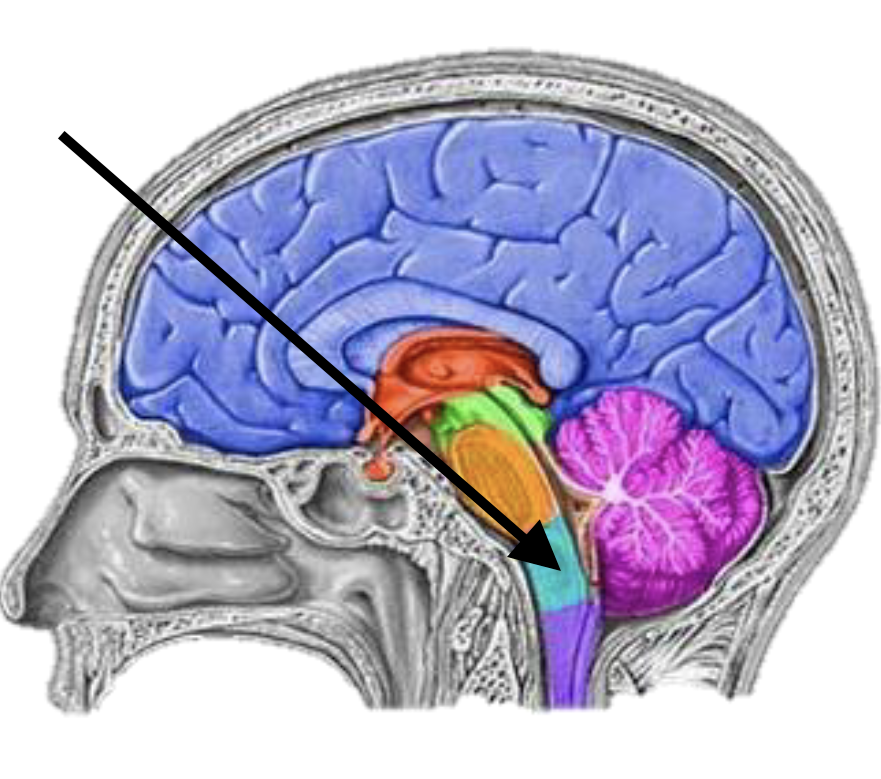
Name the brain structure
Medulla oblongata
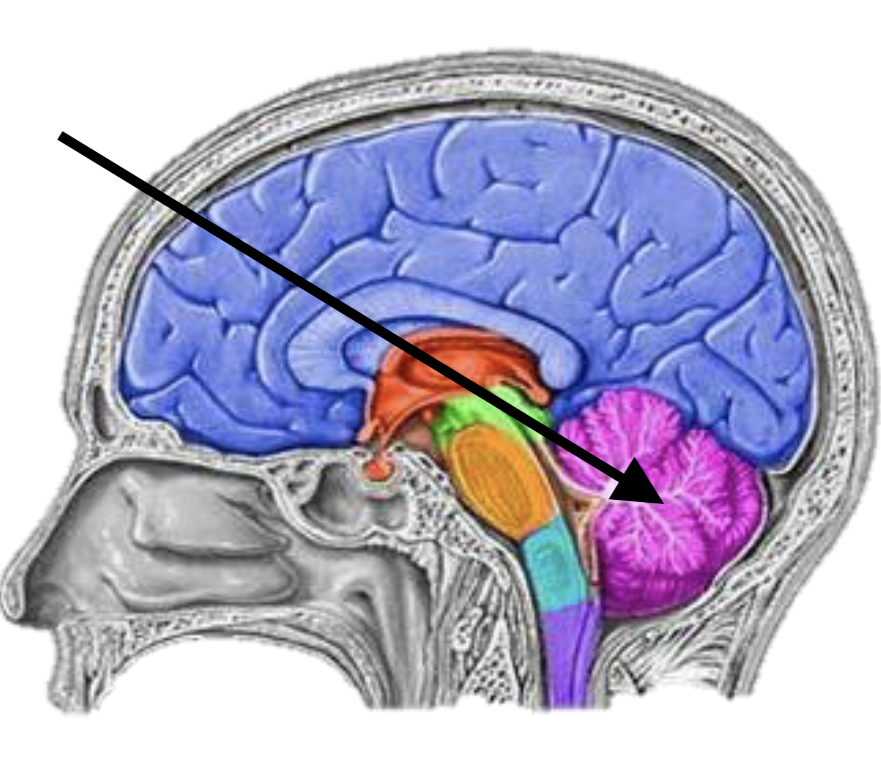
Name the brain structure
Cerebellum
How is the brain organized?
Grey matter and white matter
Describe grey matter
Contains motor neuron and interneuron cell bodies
How is grey matter distributed?
Cerebral cortex, nuclei
Describe white matter
Contains axons
Describe the distribution of white matter
Internal surfaces of the brain
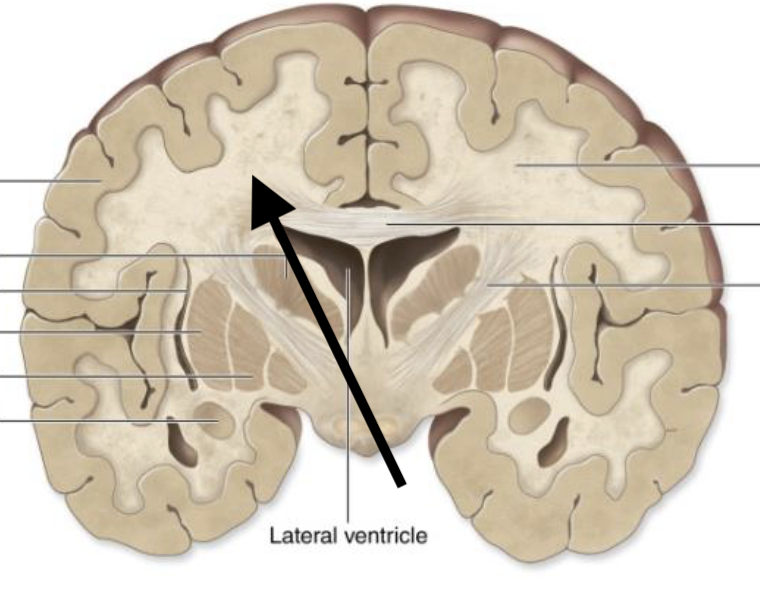
Describe the type of matter
White matter
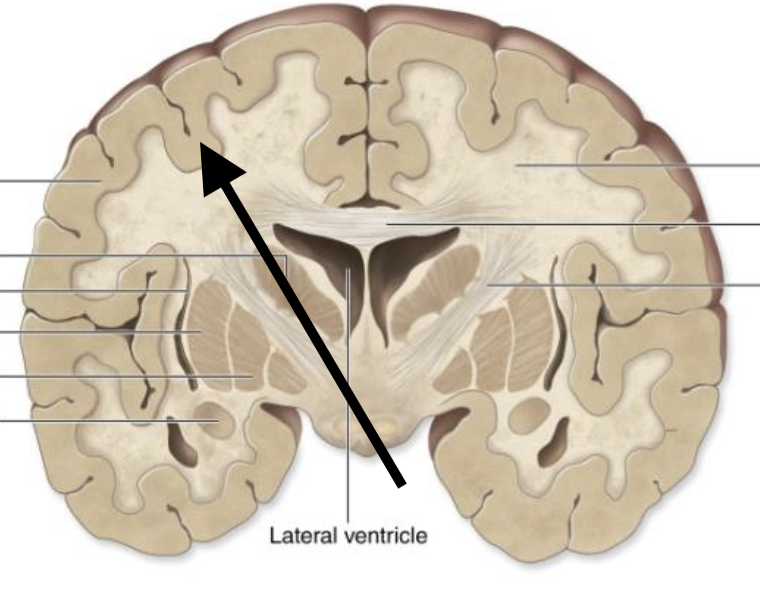
Describe the type of matter
Grey matter
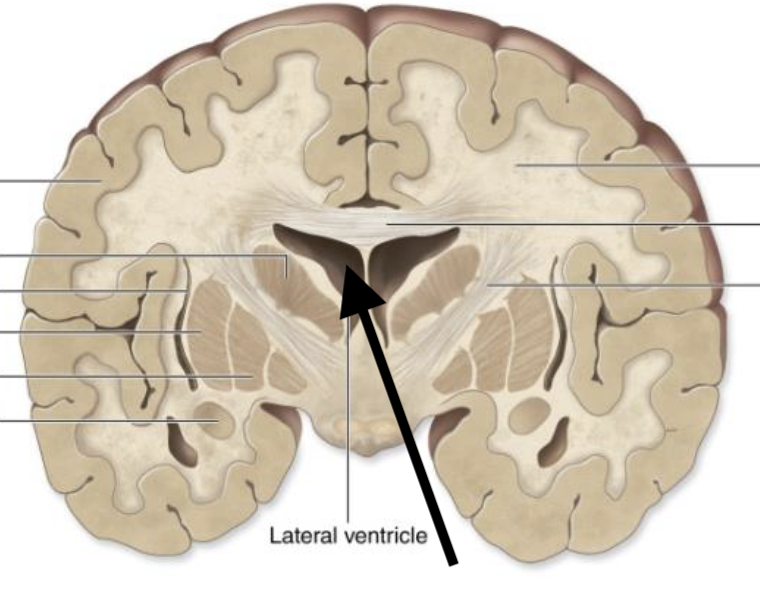
Name the structure
Nuclei
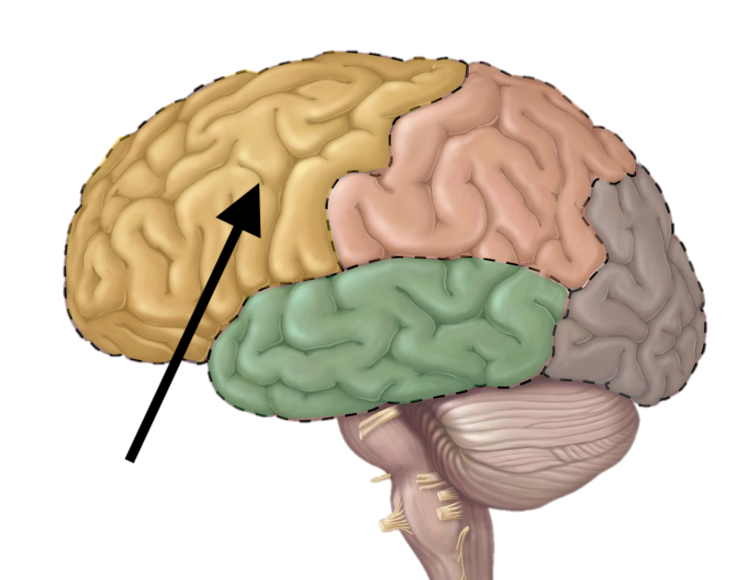
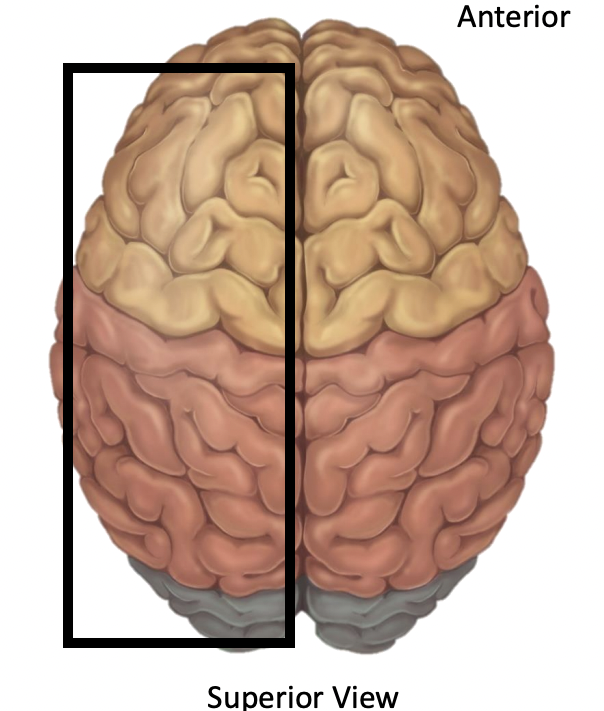
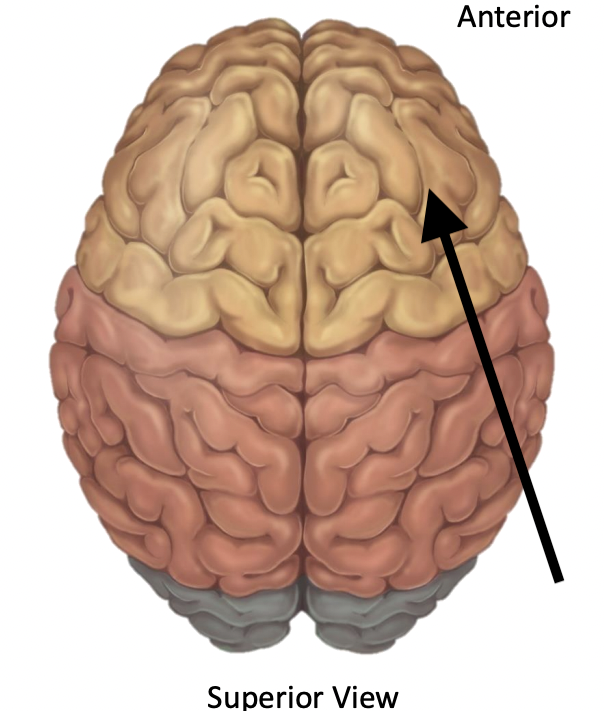
Name the lobe
Frontal
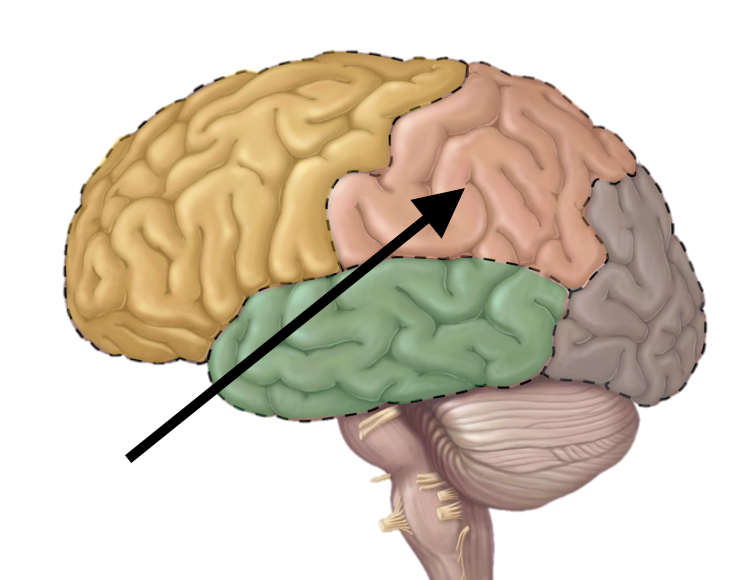
Name the lobe
Parietal
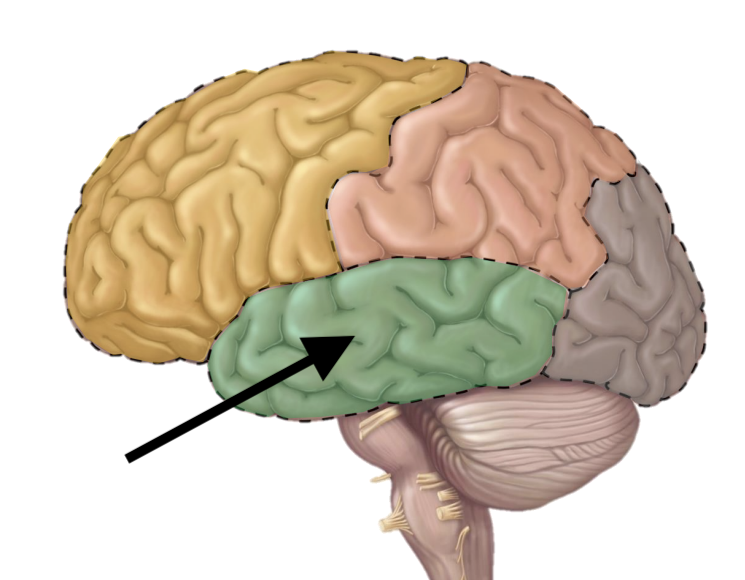
Name the lobe
Temporal
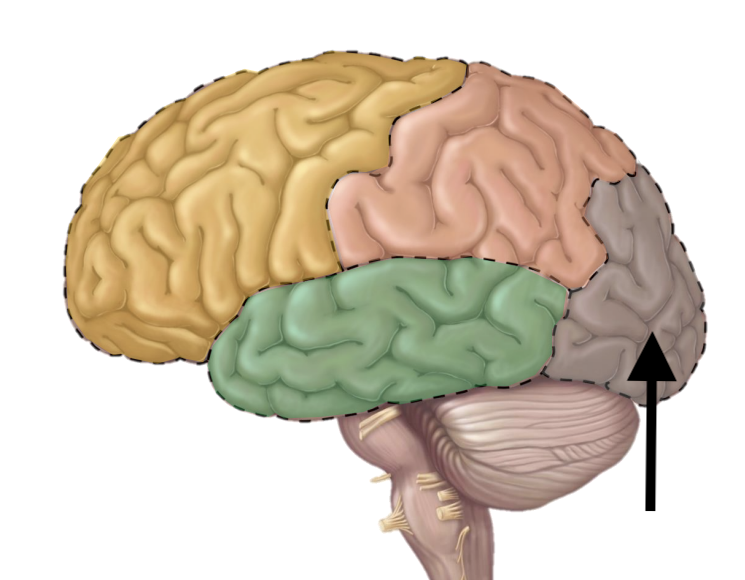
Name the lobe
Occipital
Name the structure
Cerebrum
Name the structure
Cerebellum
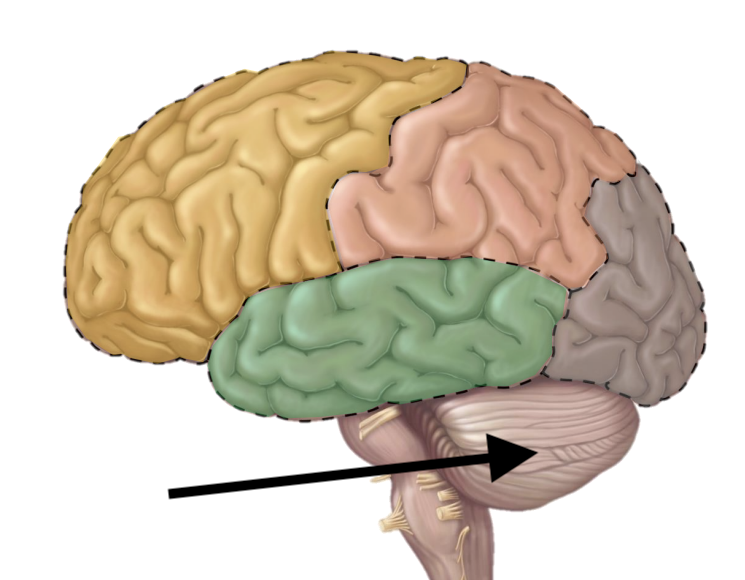
Name the structure
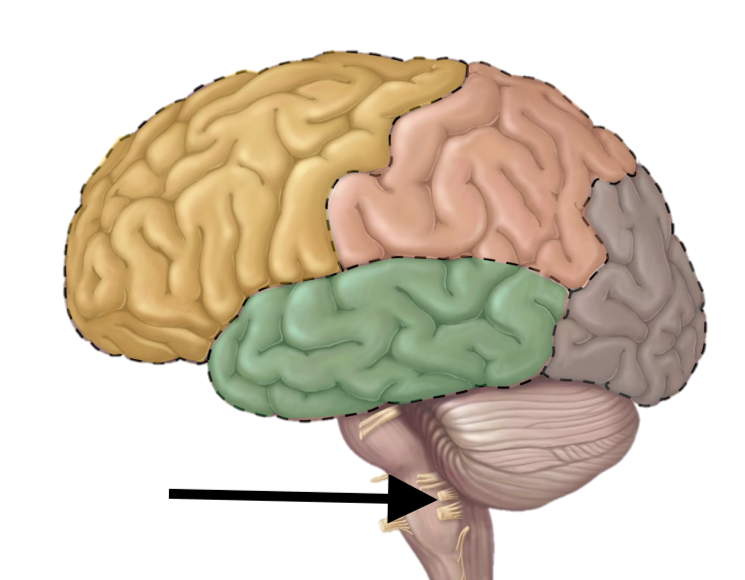
Brain stem
Name the structure
Cerebral hemisphere
Name the structure
Longitudinal fissure
Name the lobe
Frontal
Name the lobe
Parietal
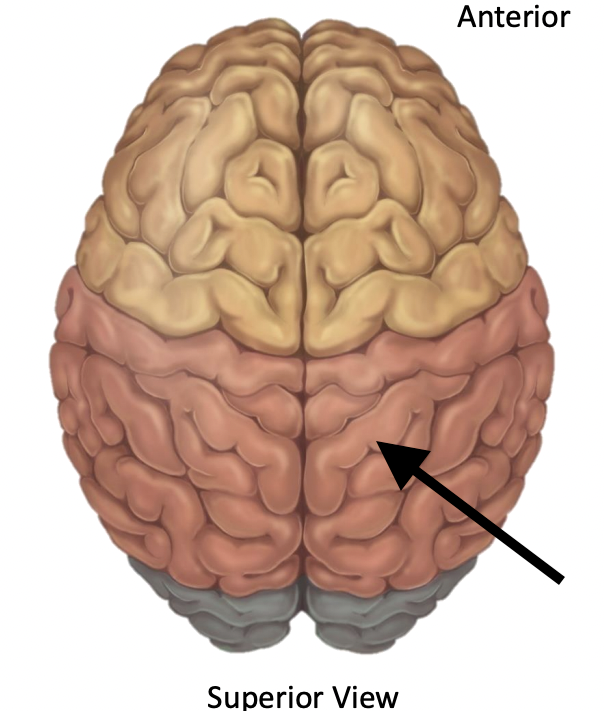
Name the lobe
Occipital
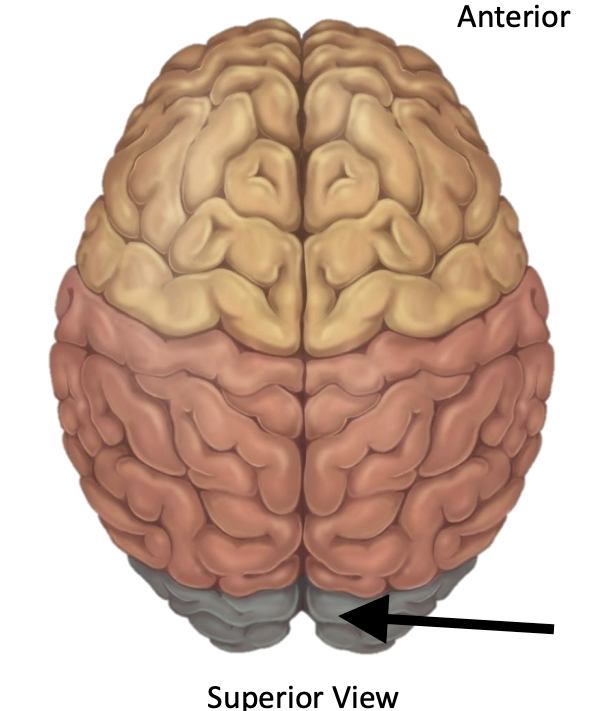
Name the structure
Longitudinal fissure
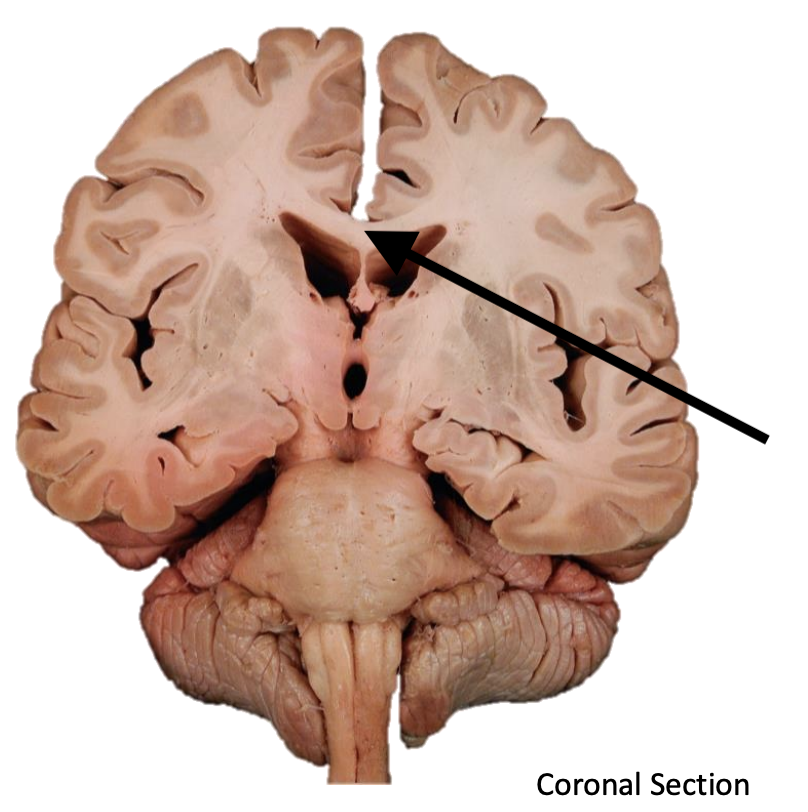
Name the structure
Corpus callosum
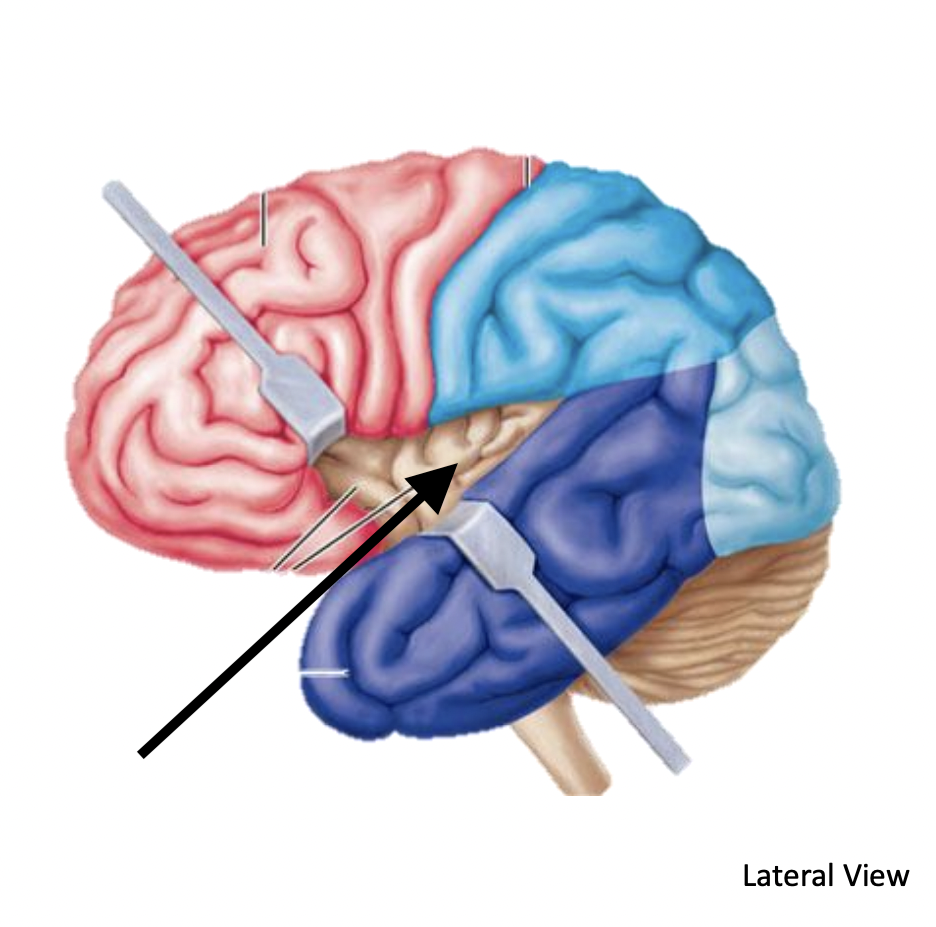
Name the lobe
Insula
Define sulci
Grooves or fissures
Define gyri
Ridges, raised areas
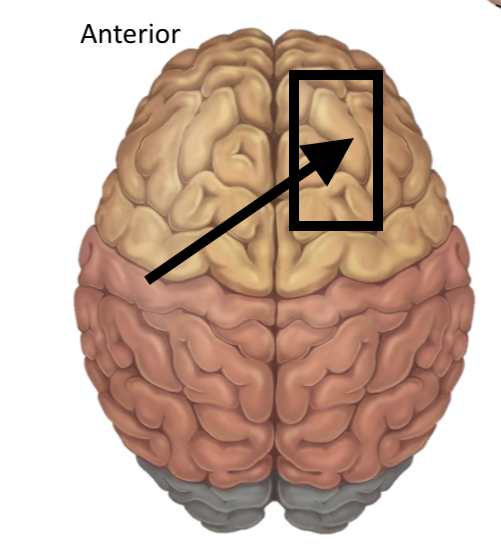
Name the structure
Sulci
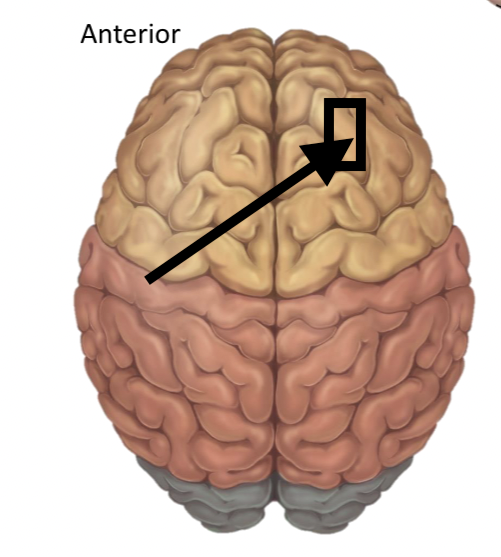
Name the structure
Gyri
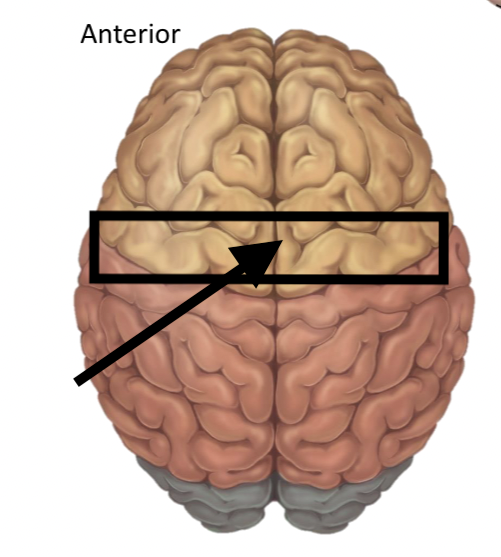
Name the structure
Precentral gyrus
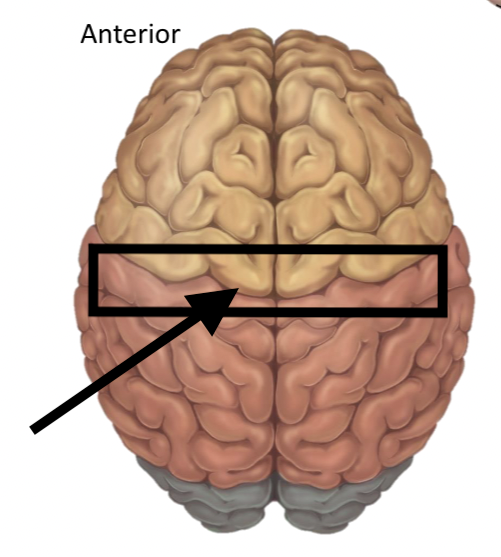
Name the structure
Central gyrus
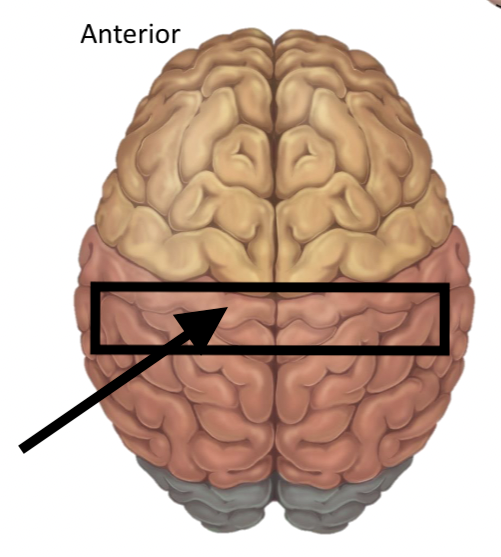
Name the structure
Post-central gyrus
What are the functional areas of the cerebrum (LOBES)?
Frontal lobe, insula, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe
What are the primary structures included in the frontal lobe?
Primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, frontal eye field, motor speech area
What are the primary structures included in the insula?
Primary gustatory cortex
What are the primary structures included in the parietal lobe?
Primary somatosensory cortex, somatosensory association area
What are the primary structures included in the occipital lobe?
Primary visual cortex, visual association area
What are the primary structures included in the temporal lobe?
Primary auditory cortex, auditory association area, primary olfactory area
What are the functional areas of the cerebrum (CORTEXES)?
Primary (SOMATIC) MOTOR cortex, Primary SOMATOSENSORY cortex
Where is the primary (somatic) motor cortex located?
Within precentral gyrus
Where is the primary somatosensory cortex located?
Within postcentral gyrus
Contrast the precentral gyrus with the postcentral gyrus
Precentral gyrus controls voluntary movement and motor function, postcentral gyrus controls sensory perception
Describe cerebral (basal) nuclei of the cerebrum
Gray matter within inner white matter (composed of interneuron and motor neuron cell bodies)
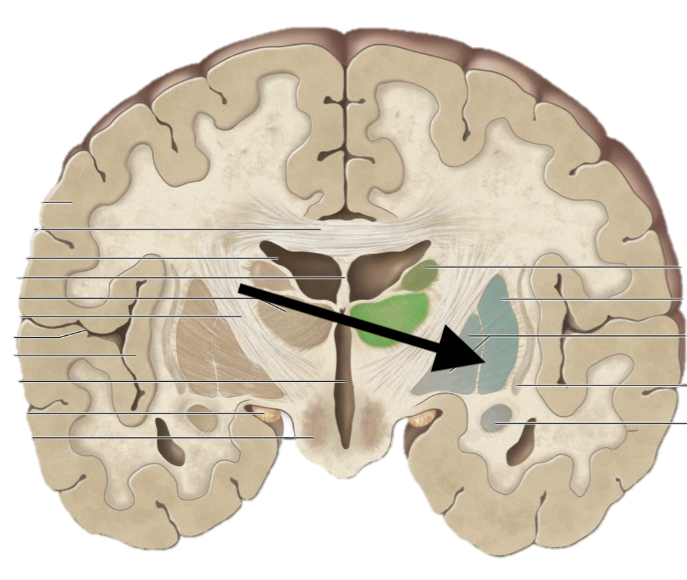
Name the structure
Cerebral (basal) nuclei
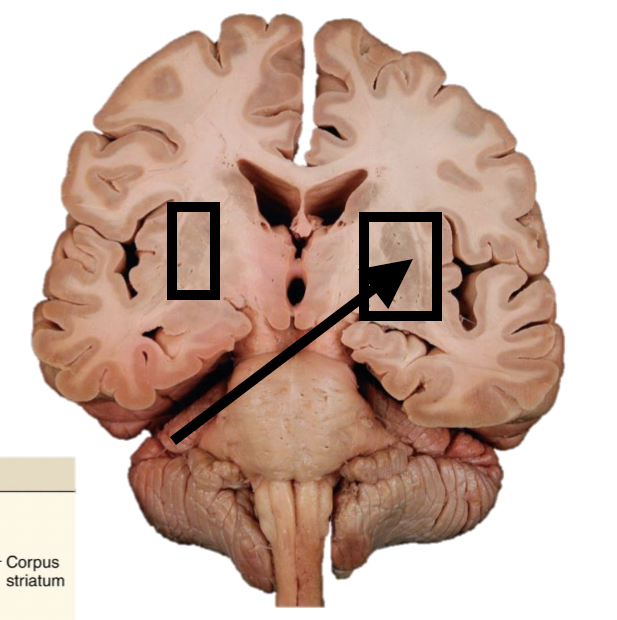
Name the structure
Cerebral (basal) nuclei
Describe white matter tracts of the cerebrum
Bundles of axons that create pathways for neural signals and thus connect parts of the CNS
Describe association tracks of the cerebrum
Connect areas within the same hemisphere
What are the types of association tracks?
Arcuate fibers, longitudinal fasciculi, commissural tracts, projection tracts
Describe the function of arcuate fibers
Connect gyri WITHIN a lobe
Describe the function of longitudinal fasciculi
Connect gyri BETWEEN lobes
Describe the function of commissural tracts
Connect corresponding lobes BETWEEN hemispheres
Describe the function of projection tracts
Connect the cerebral cortex to other parts of the CNS
What do commissural tracts cross?
Corpus callosum
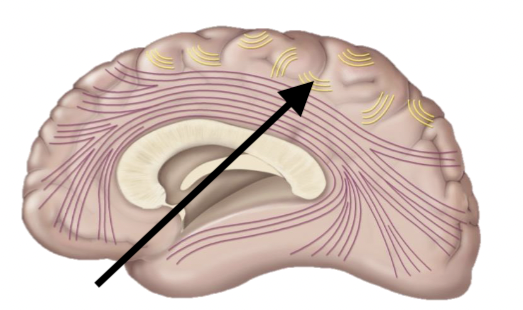
Name the structure
Arcuate fibers