High-Risk Newborns: Classification, Care, and Complications
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Low birth weight (LBW)
Infants weighing less than 2500 g.
Very low birth weight (VLBW)
Infants weighing less than 1500 g.
Extremely low birth weight (ELBW)
Infants weighing less than 1000 g.
Preterm
Infants born before 37 weeks of gestation.
Late Preterm
Infants born between 34-36 6/7 weeks of gestation.
Term
Infants born between 37 and 42 weeks of gestation.
Early Term
Infants born between 37 through 38 6/7 weeks of gestation.
Full Term
Infants born between 39 through 40 6/7 weeks of gestation.
Late Term
Infants born between 41 through 41 6/7 weeks of gestation.
Post term
Infants born after 42 weeks of gestation.
Appropriate for gestational age (AGA)
Infants whose weight is within the 10th to 90th percentile on the intrauterine growth (IUG) curve.
Small for date (SFD)
Infants whose weight is below the 10th percentile on the IUG curve.
Large for gestational age (LGA)
Infants whose weight is above the 90th percentile on the IUG curve.
Symmetric IUGR
Intrauterine growth restriction where weight, height, and head circumference are all affected.
Asymmetric IUGR
Intrauterine growth restriction where head circumference is normal, but weight is below normal.
High-risk infants
Infants classified based on birth weight, gestational age, and predominant pathophysiologic problems.
Potential problems of preterm infants
Differing care needs compared to term, post term, or postmature infants of equal weight.
Preterm Infant
An infant born before 37 weeks of gestation.
Respiratory Function
The ability of the infant to breathe effectively.
Cardiovascular Function
The functioning of the heart and blood vessels in the infant.
Thermoregulation
The process of maintaining an optimal body temperature.
Neutral thermal environment
The goal of providing a temperature range that minimizes heat loss.
Cold stress
A condition where the infant loses body heat and cannot maintain a stable temperature.
Central Nervous System Function
The functioning of the brain and spinal cord in the infant.
Nutrition
The process of providing or obtaining the food necessary for health and growth.
Minimal enteral nutrition (MEN)
A feeding strategy that provides small amounts of nutrients to stimulate the gut.
Renal function
The ability of the kidneys to filter blood and produce urine.
Hematologic status
The condition of the blood and its components.
Immunity
The ability of the body to resist infections.
Corrected age
The age of the preterm infant adjusted for prematurity, calculated by adding gestational age and postnatal age.
Milestones
Developmental achievements that are expected at certain ages.
VLBW survivors
Very low birth weight infants who survive and are at increased risk for neurologic or cognitive disability.
Catch-up body growth
The accelerated growth that occurs in preterm infants during the first 2 years of life.
High-risk infant
An infant who is more susceptible to health complications.
Transepidermal water loss
The loss of water through the skin, which is greater in preterm infants.
Neonatal Resuscitation
The process of providing emergency care to newborns who are not breathing or have inadequate circulation.
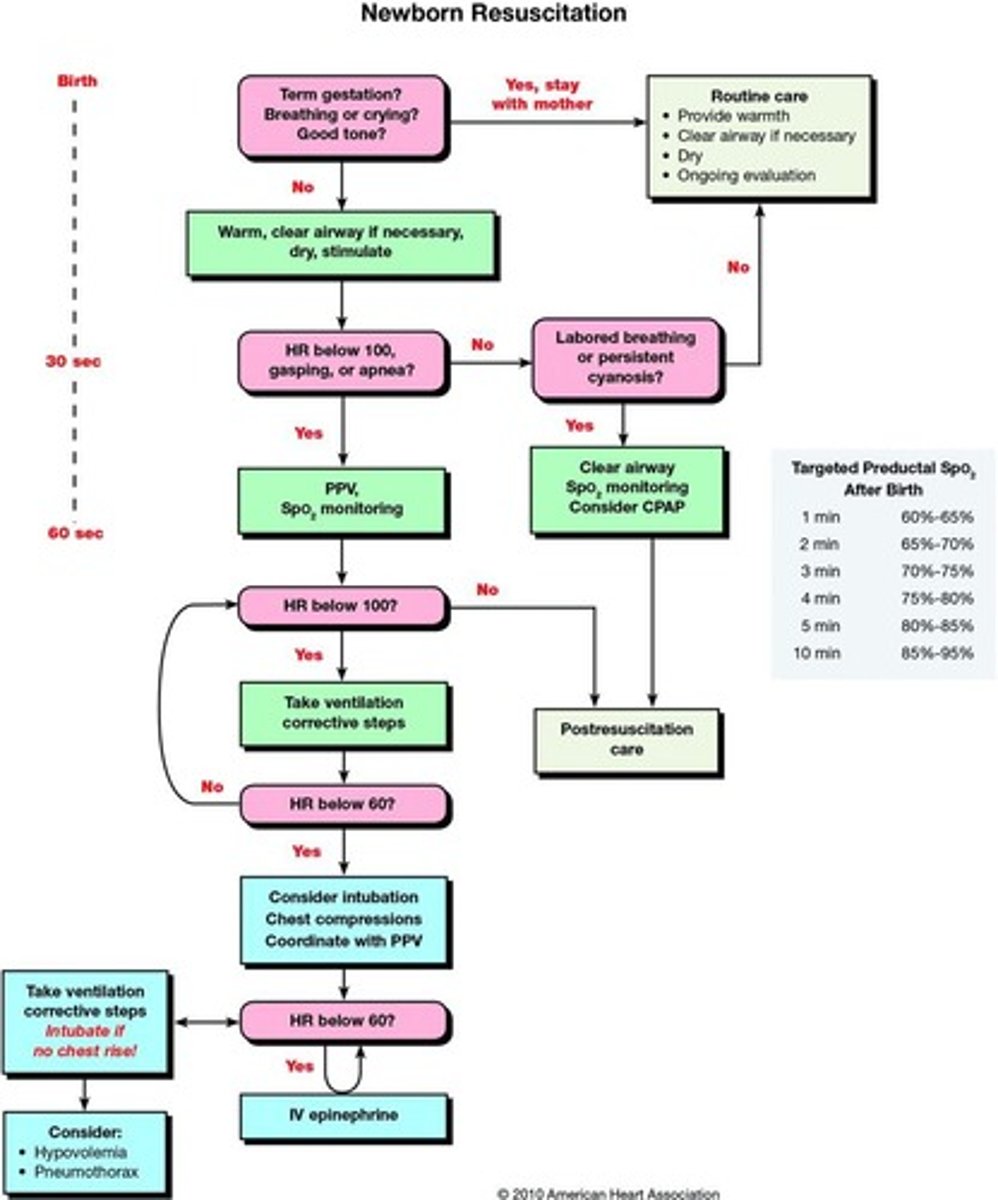
Oxygen Therapy
The administration of oxygen to improve oxygenation.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy
A method to keep the airways open by providing a continuous level of pressure.
Mechanical Ventilation
A method of providing respiratory support using a machine.
Asphyxia
A condition caused by insufficient oxygen reaching the tissues.
Resuscitation Medications
Medications used during resuscitation to support heart and lung function.
Epinephrine
A medication used in resuscitation, administered at a concentration of 1:10,000.
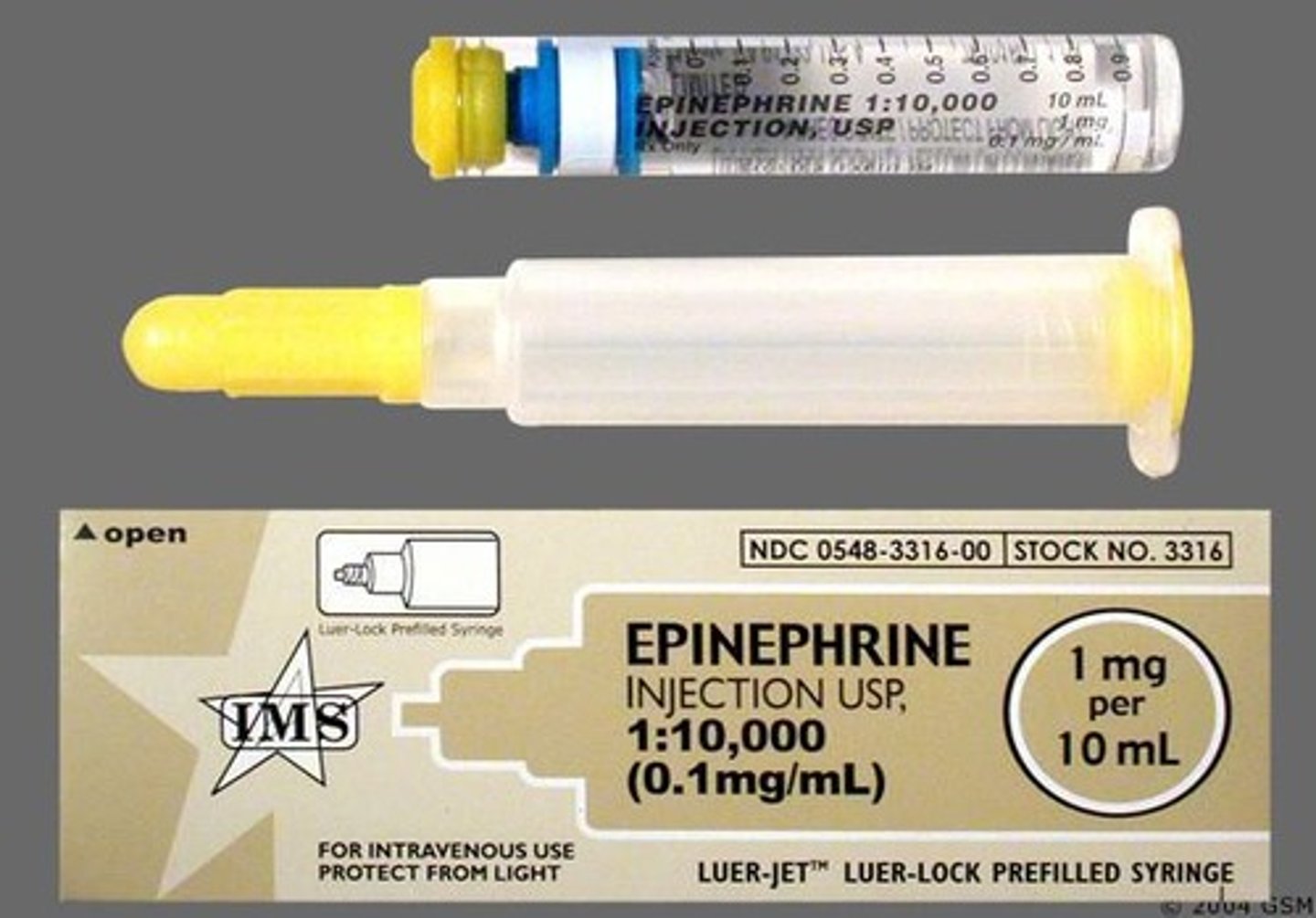
Volume expanders
Fluids used to increase blood volume, such as Normal Saline or Lactated Ringers.
Narcan
A medication used to reverse opioid overdose, administered at a dose of 0.1mg/kg IM or IV.
Sodium Bicarb
A controversial medication used in resuscitation, administered at 2 meq/kg.
Human Milk
Natural milk produced by humans for infant nourishment.
Infant Formula
Commercially prepared substitute for human milk, designed for infant feeding.
Insensible water loss (IWL)
The loss of water from the body that occurs without awareness, often through the skin and respiratory tract.
Oral Feeding
Feeding method where the infant is fed directly from a bottle or breast.
Gavage Feeding
Feeding method where a tube is inserted into the stomach to deliver nutrition.
Gastrostomy Feedings
Nutritional delivery method through a surgically placed tube in the stomach.
Parenteral Nutrition
Nutritional support given intravenously, bypassing the digestive system.
Advancing Infant Feedings
Gradually increasing the amount and variety of feedings for infants.
Nonnutritive Sucking
Sucking behavior that does not involve feeding, often for comfort.
Neonatal Skin Condition Scoring (NSCS)
A daily assessment to minimize skin breakdown in NICU infants.
Kangaroo Care
Skin-to-skin contact between the parent and infant to promote bonding and warmth.
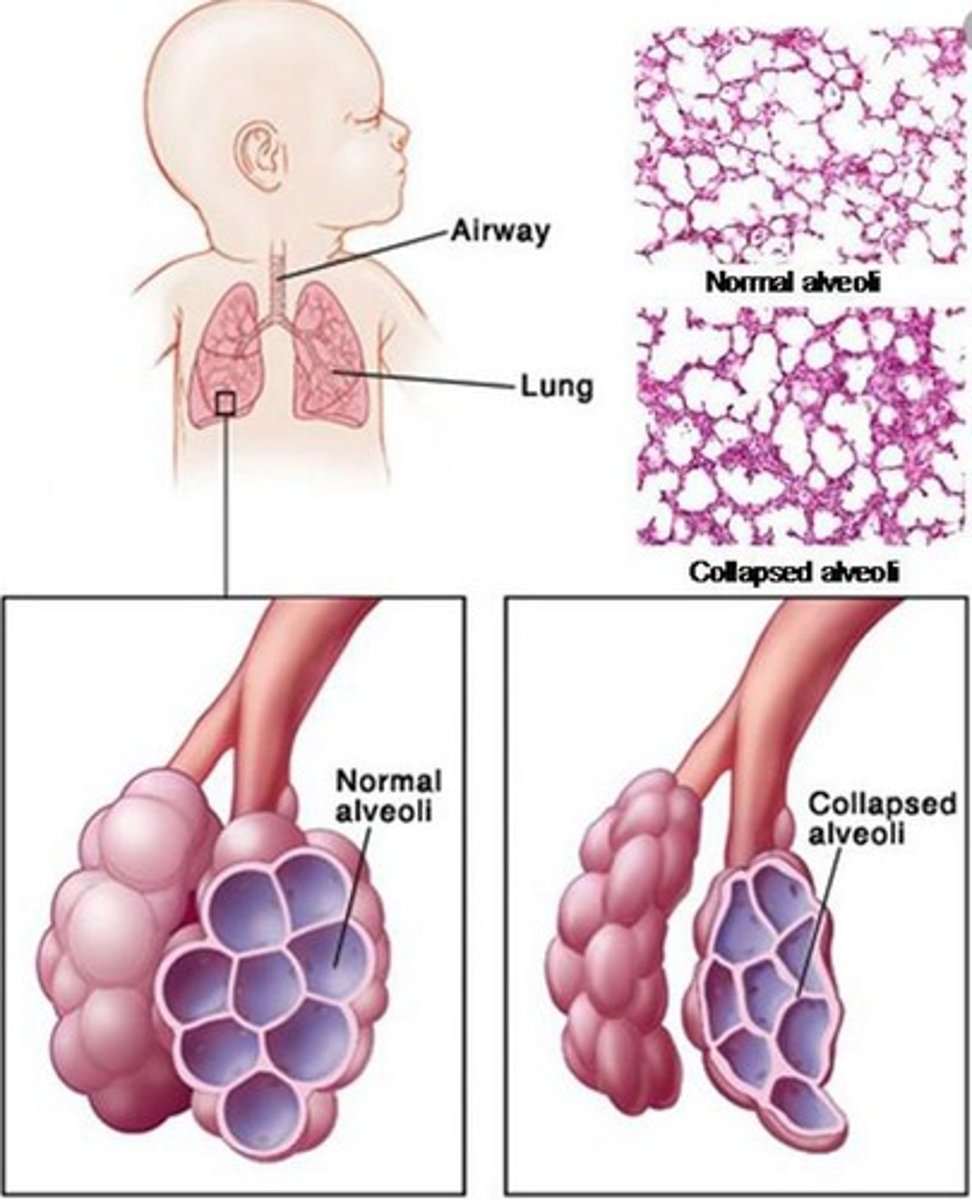
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
A condition caused by a lack of pulmonary surfactant, leading to breathing difficulties in infants.
Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
A disorder affecting the developing retinal vessels of preterm infants.
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD)
A chronic lung condition commonly found in preterm infants requiring mechanical ventilation.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
A condition where the fetal ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth.
Germinal Matrix Hemorrhage
The most common type of intracranial hemorrhage in infants, usually occurring in those less than 34 weeks.
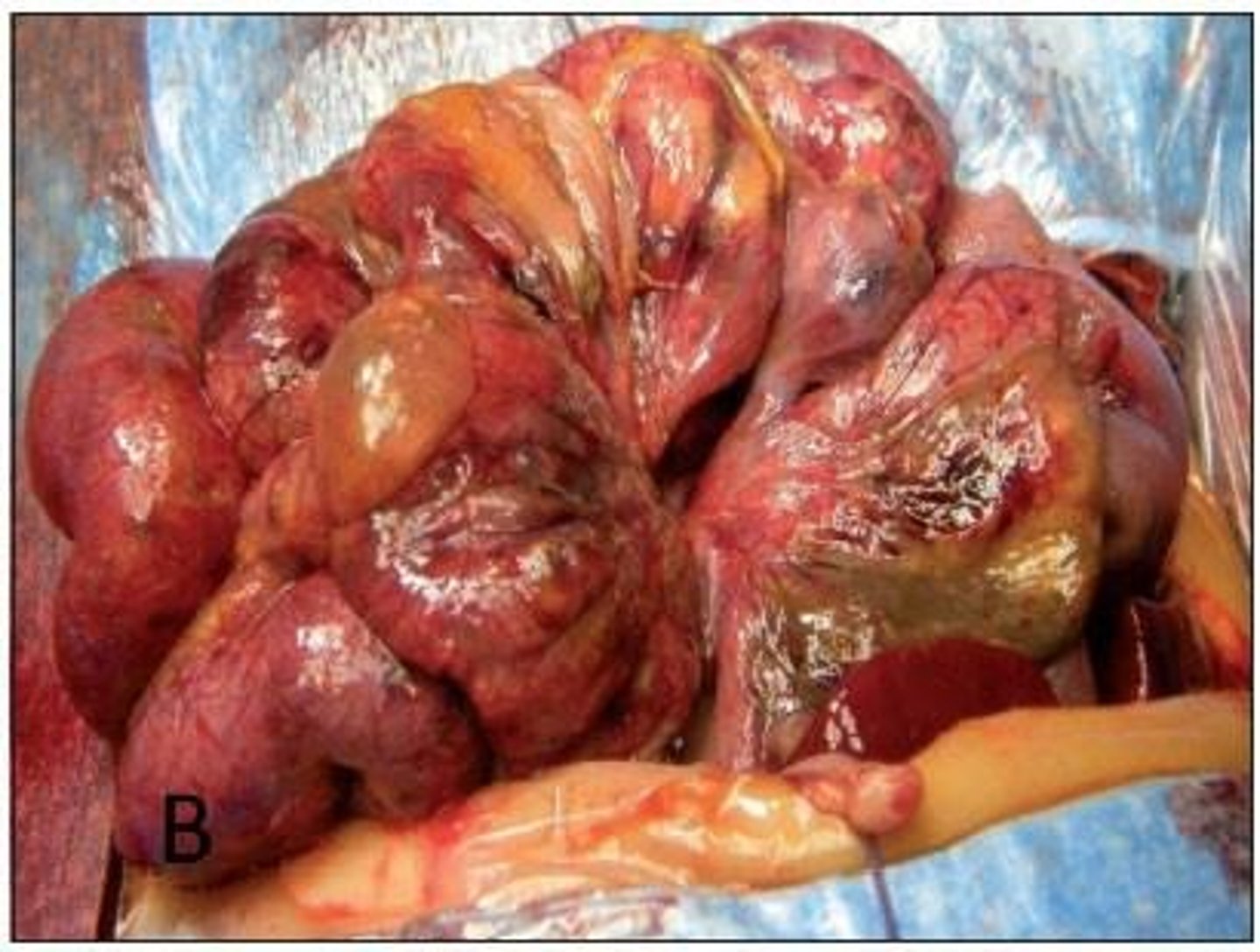
Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
A serious intestinal condition in preterm infants that can lead to bowel ischemia and septicemia.
Late Preterm Infant (LPI)
An infant born between 34 0/7 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation.
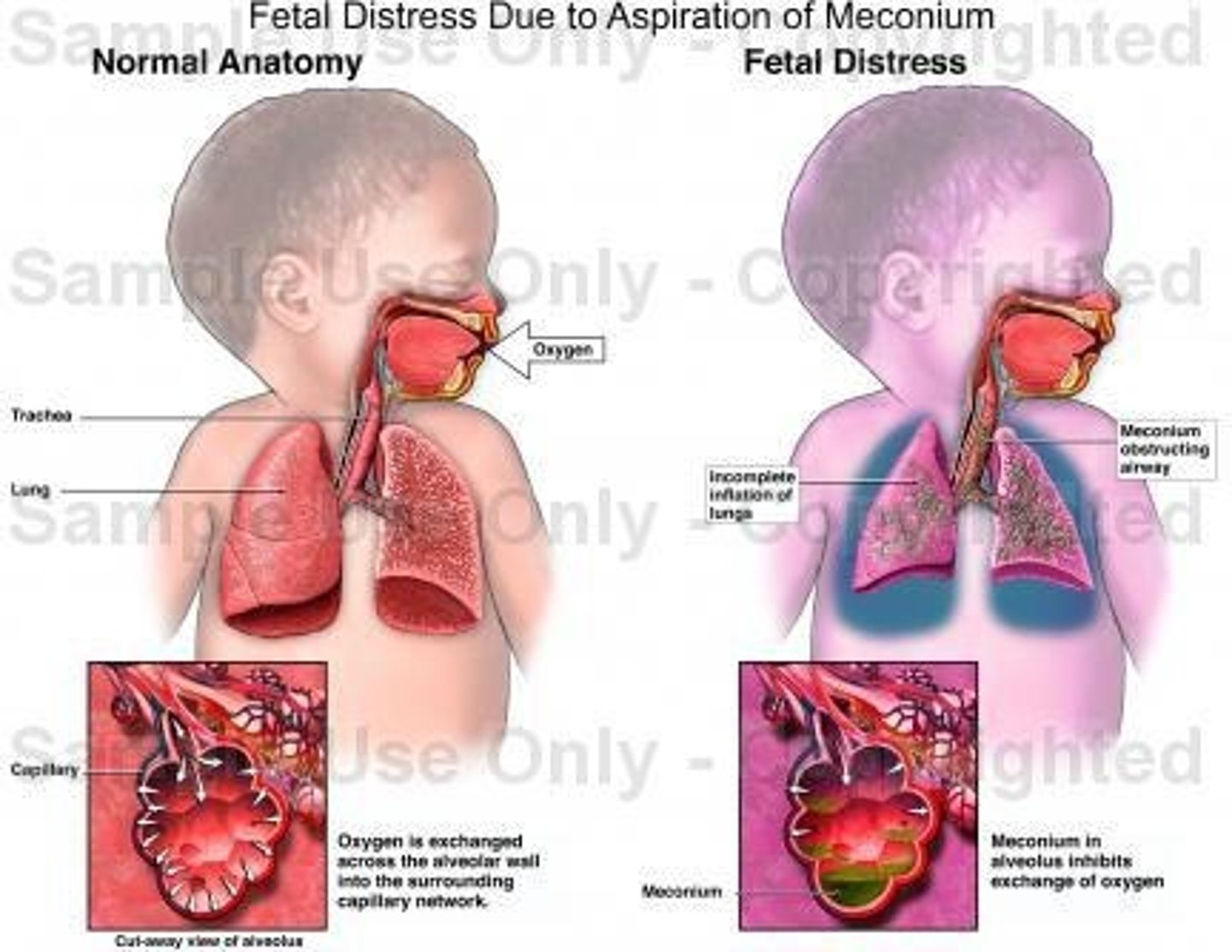
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS)
A condition occurring in newborns exposed to meconium, leading to respiratory distress.
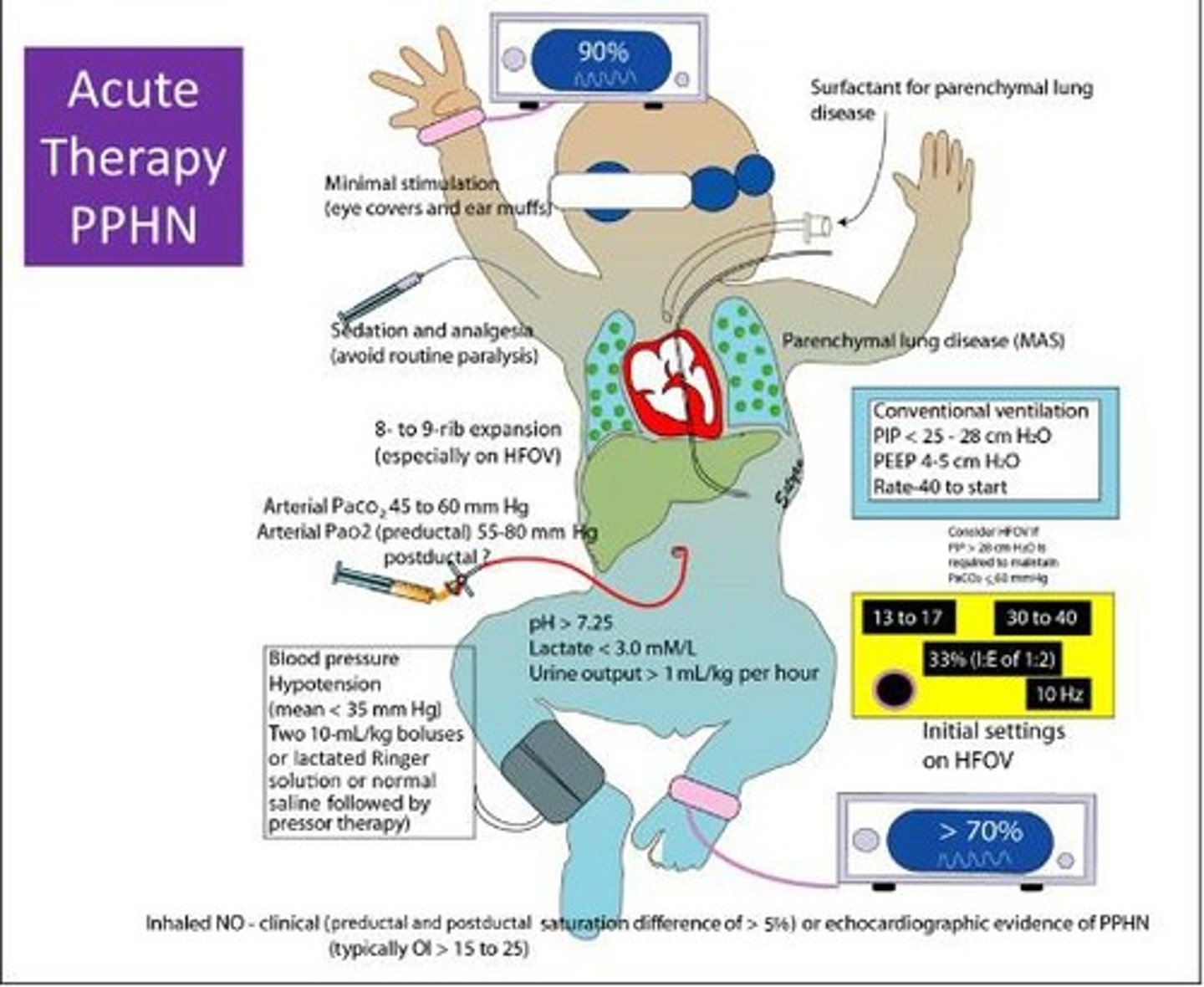
Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension
A condition in newborns characterized by high blood pressure in the lungs, often requiring treatment.
Growth Restricted Infants
Infants who are small for gestational age or have intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
Parental Adaptation to the Preterm Infant
The process by which parents adjust to the challenges of caring for a preterm infant.
Infant Pain Responses
The physiological and behavioral responses of infants to pain.
Complications of Post-term Newborn
Issues that arise in newborns who remain in utero beyond the optimal growth time of 42 weeks.
Perinatal Asphyxia
A condition occurring when an infant does not receive enough oxygen before, during, or right after birth.
Hypoglycemia
A medical condition characterized by an abnormally low level of glucose in the blood.
Polycythemia
Hyperviscosity of the blood, often resulting in increased red blood cell mass.
Heat Loss
The process by which an infant loses body heat, which can lead to hypothermia.
Large for Gestational Age (LGA) Infants
Infants weighing 4000 g or more at birth or whose weight is greater than the 90th percentile for their gestational age.
Level I NICU
Basic newborn care for healthy, full-term babies, stabilizing them for transfer to advanced care facilities.
Level II NICU
Advanced newborn care for babies born at greater than 32 weeks gestation or recovering from serious conditions.
Level III NICU
Subspecialty newborn care for babies born at less than 32 weeks gestation or with critical illness, offering a full range of pediatric medical subspecialties.
Level IV NICU
The highest level of neonatal care, providing acute care and surgical repair for complex conditions, with pediatric medical and surgical subspecialties on site.
Anticipatory Grief
Grief experienced when told of the impending death of an infant, preparing and protecting parents facing a loss.
Maladaptive Parent Behavior
Behaviors such as failure to visit or call, emotional withdraw, and resistance to caretaking.
Adaptive Parent Behavior
Behaviors such as frequent visits and calls, emotional involvement, and a growing sense of attachment.
Infant Care Management
The involvement of family in the infant's care, providing privacy, answering questions, and preparing for the inevitability of death.
Hospice and Palliative Care
An approach emphasizing care for infants with life-threatening conditions and support for their families.
Emotional Involvement
A parent's active engagement and connection with their infant during NICU care.
Emotional Withdrawal
A parent's detachment or lack of engagement with their infant during NICU care.
Interest in Caretaking
A parent's desire to participate in the care of their infant.
Resistance to Caretaking
A parent's reluctance or refusal to engage in the care of their infant.
Free Verbalization of Needs
A parent's ability to express their needs openly and freely.
Failure to Verbalize Needs
A parent's inability or unwillingness to communicate their needs.
Realistic Expectations of Staff
A parent's understanding and acceptance of the capabilities and limitations of the healthcare staff.
Hostility or Distrust of Staff
A parent's negative feelings or skepticism towards the healthcare staff.