Forensic Biology: Lecture 3 – Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid.
The structure of DNA was deciphered 60 years ago in 1953 by:
Francis Crick and James Watson
When combined with cellular machinery, the DNA molecule is capable of:
Self-replication and protein synthesis.
Nucleotides are composed of:
A phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
The four nitrogenous bases:
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
Base pairing rules:
A→T and C→G
A gene is:
The part of DNA molecule that codes for protein, or a unit of heredity.
The DNA sequence in a gene is arranged into a series of codons, or:
Groups of 3 nucleotides that code for amino acids.
Human beings have how many base pairs of DNA?
over 3 billion
Purines:
Bases with a double-ring structure; Adenine and Guanine.
Pyrimidines:
Bases with a single-ring structure; Cytosine and Thymine
DNA directionality:
5' to 3'
The two strands of DNA are:
complementary and antiparallel
DNA replication is:
semiconservative
Uncorrected replication errors are:
mutations
The leading strand is synthesized:
continuously in the 5' to 3' direction
The lagging strand is synthesized:
discontinuously, creating Okazaki fragments
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer using the parental DNA strand as a template.
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks.
Topoisomerase
An enzyme that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork.
DNA polymerase
An enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule.
Transcription
gene expression (DNA → RNA)
Translation
protein synthesis (RNA → protein)
DNA is subject to degradation, just like other biological evidence:
- Hydrolytic Attack
- Oxidative Damage
- Alkylation Damage
- Condensation Reactions
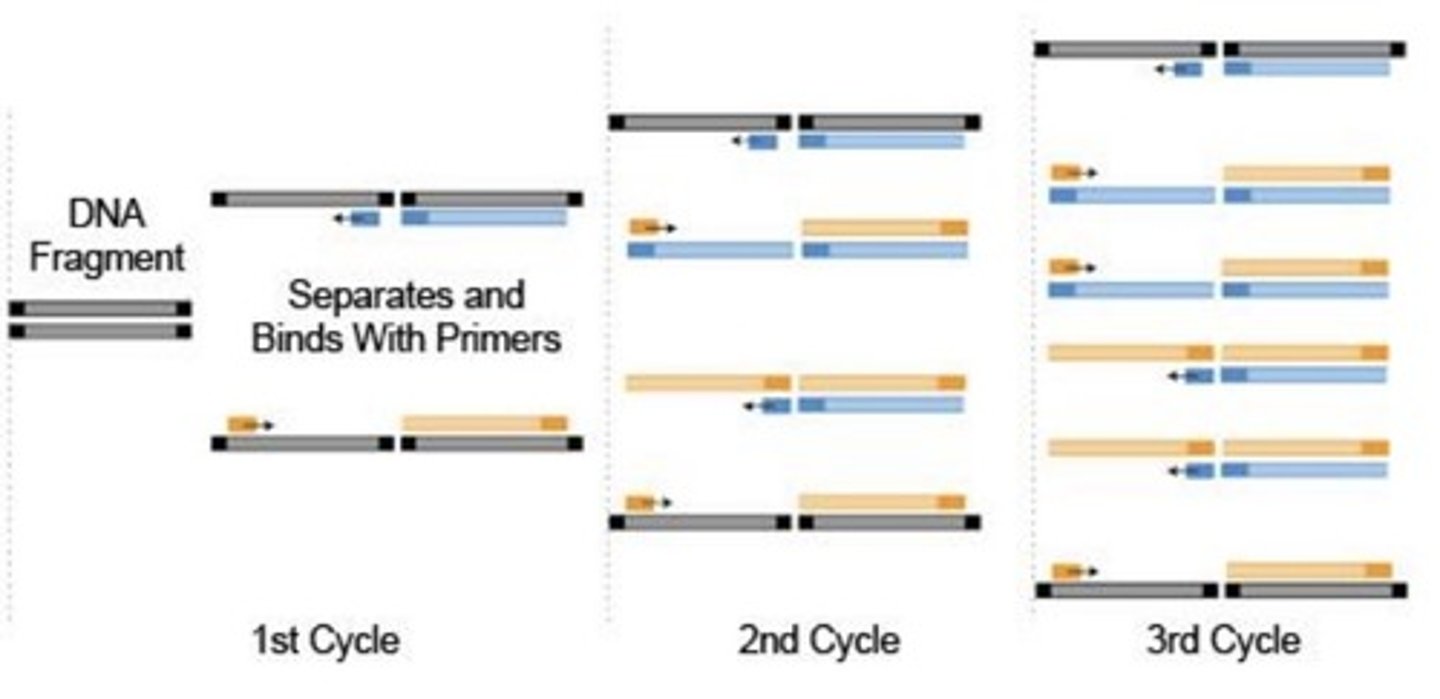
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A technique for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers, DNA polymerase molecules, and nucleotides.
PCR was invented by:
Kary Mullis in 1985
Multiplexing
More than one region can be copied in one reaction by adding more than one primer set.
Steps of PCR:
1. Denaturation
2. Annealing
3. Extension
Amplicon
A DNA sequence that has been amplified by PCR.
Denaturation
The reaction is heated to 94 centigrade which causes the double stranded DNA to melt and open to single strands. All enzymatic reactions stop.
Annealing
Temp is based on Primer. Brownian motion keeps primers constantly moving. Ionic bonds are formed and broken between the primer and the template. Primers that fit exactly will be more stable, allowing the polymerase to attach and start copying the template. Once a few bases are joined, the ionic bond between the template and the primer is very strong and resists breaking away.
Extension
The reaction is heated to 72 centigrade. Primers that are on positions with no exact match break away, allowing no extension of the fragment. For exact matches, bases are coupled to the primer on the 3' side. The polymerase adds dNTP's from 5' to 3', reading the template from 3' to 5' side.
Exponential
Because both strands are copied during PCR, there is a [blank] increase of the number of copies of the target.
Number of cycles of PCR based on number of target molecules:
3x10^5 → 25 to 30 1.5x10^4 → 30 to 35 1x10^3 → 35 to 40
50 → 40 to 45
Primer length:
18-30 bases
Oligonucleotides
A polynucleotide whose molecules contain a relatively small number of nucleotides.
PCR primers consist of:
Two oligonucleotides that hybridize to complementary stands of the DNA template identifying the region to be copied.
Chance of finding any given DNA sequence of the length (n):
1/(4^n)
Statistically, a seventeen-base sequence will be present only once in every:
4^17, or approximately 17 billion bases.
True/False: Primers longer than 30 bases do not demonstrate higher specificity?
True; long amplicons are more likely to cross-hybridize with other primers and sequences in the reaction mixture, which can terminate the DNA extension.
True
True/False: In forensics, loci are selected for their discriminating power?
Taq polymerase
A heat-stable form of DNA polymerase extracted from bacteria that live in hot environments, such as hot springs, that is used during PCR.
dNTPs
deoxy-nucleotide tri-phosphates; free deoxy-ribonucleotides needed for extension.
ddNTPs
di-deoxy-nucleotide tri-phosphates; DNA chain-terminating subunits.
Ingredients for PCR:
1. Taq polymerase
2. dNTPs/ddNTPs
3. primers
4. magnesium ions
5. template DNA
Primer dimers result from:
Hybridize to each other at the 3' ends, essentially competing with the with desired product for amplification.
Misincorporation:
When the wrong base is inserted in DNA synthesis (mutation). dNTPs should be used at equal concentrations to minimize errors.
Magnesium ion concentration may affect:
Primer annealing, strand dissociation of template or product, product specificity, formation of primer-dimers and enzyme activity and fidelity.
Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA)
Main soluble protein in the blood serum of the cattle that is often used as an enzymatically inert protein or a negative control in PCR. Included to help stabilize the enzyme and overcome inhibitors.
Plateau effect in PCR:
Attenuation in the exponential rate of product accumulation that occurs in later cycles. Initially low concentrations of nonspecific products resulting from mispriming events may continue to amplify preferentially—optimize number of cycles to avoid this.