The X-ray Tube (Cathode assembly)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What supplies the electrons?
the cathode
What attracts the electrons?
the anode
How are xrays emitted at the focal spot? hint: in all directions
isotropically
What is unusable that occurs in an x-ray tube?
the x-rays absorbed by tube shielding
List the 3 functions of the cathode assembly
to produce a thermionic cloud
conduct the high voltage between cathode and anode
focus the electron stream
What are the parts of the cathode?
filament (s)
focusing cup
associated wiring
What is the filament made of?
a small, thin coil of thoriated tungsten
How thick is the filament?
0.1-0.2 mm thick
What is the atomic number of Thorium (Th)?
z=90
Why is tungsten used for the filament?
because it has a high melting point (3370C) and it is hard to vaporize
What is the melting point of thoriated tungsten?
3420 C
List the two other types used for the filament with the atomic number and melting point
Rhenium (Re) z=75, melting point = 3170C
Molybdenum (Mo) z=42, melting point = 2620C
What does the filament provide to cause thermionic emission (electron cloud or space charge)?
enough resistance
What has a great effect on recorded detail (focal spot size)?
the length and width of the filament
(T/F) Most modern tubes have two filaments “dual focus tube”.
true
What does a “dual focus tube” refer to?
large and small focal spots
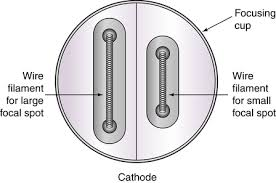
What is the length of the small focal spot?
0.3 to 1 mm
What is the length of the large focal spot?
1 to 3 mm
What is the shallow depression in which the filament sits?
the focusing cup
What is the charge of the focusing cup?
negative
What is it called when the focusing cup is not working properly, and the efficiency of the tube decreases?
focal bloom
What will too many electrons around the filament cause?
space charge effect